Las vasculitis Vasculitis Inflammation of any one of the blood vessels, including the arteries; veins; and rest of the vasculature system in the body. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus son un grupo de enfermedades caracterizadas por vasculitis Vasculitis Inflammation of any one of the blood vessels, including the arteries; veins; and rest of the vasculature system in the body. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, isquemia y daño a los LOS Neisseria órganos irrigados por los LOS Neisseria vasos afectados. Las arterias afectadas son de diferentes tamaños y ubicaciones y varían según el tipo de vasculitis Vasculitis Inflammation of any one of the blood vessels, including the arteries; veins; and rest of the vasculature system in the body. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Las vasculitis Vasculitis Inflammation of any one of the blood vessels, including the arteries; veins; and rest of the vasculature system in the body. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus pueden ser una condición primaria o secundaria a otra enfermedad subyacente. No existe una fisiopatología claramente conocida. El diagnóstico debe considerarse en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum cualquier individuo con púrpura palpable, infiltrados pulmonares, eventos isquémicos y enfermedad multisistémica. Es imprescindible reconocer y tratar con prontitud las vasculitis Vasculitis Inflammation of any one of the blood vessels, including the arteries; veins; and rest of the vasculature system in the body. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, ya que suelen ser enfermedades graves y a veces mortales. El tratamiento incluye agentes inmunosupresores, antivirales y/o antiinflamatorios.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Las vasculitis Vasculitis Inflammation of any one of the blood vessels, including the arteries; veins; and rest of the vasculature system in the body. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus son enfermedades de los LOS Neisseria vasos sanguíneos, con una inflamación de las paredes de los LOS Neisseria vasos que provoca hemorragias, isquemia y necrosis Necrosis The death of cells in an organ or tissue due to disease, injury or failure of the blood supply. Ischemic Cell Damage de los LOS Neisseria tejidos y órganos distales.
La siguiente clasificación es una adaptación de la Nomenclatura de Vasculitis Vasculitis Inflammation of any one of the blood vessels, including the arteries; veins; and rest of the vasculature system in the body. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus de la International Chapel Hill Consensus Conference en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum 2012:
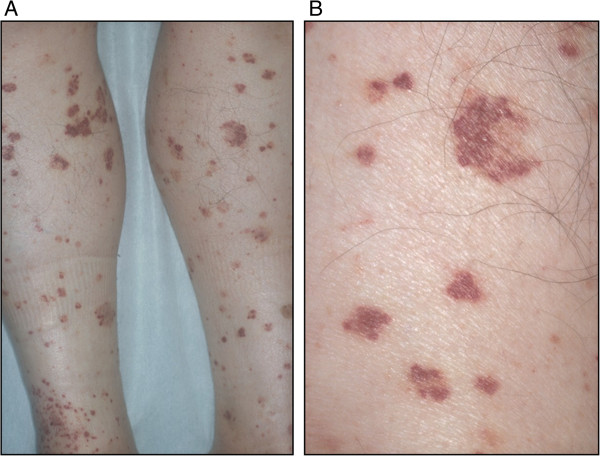
Púrpura:
A: Púrpura difusa palpable pequeña en las extremidades inferiores
B: Vista ampliada
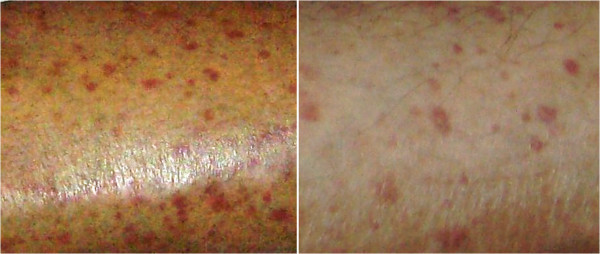
Erupción cutánea purpúrica en un individuo con vasculitis crioglobulinémica secundaria a una enfermedad del tejido conectivo.
Imagen: “Purpuric skin rash” por Gheita TA et al. Licencia: CC BY 4.0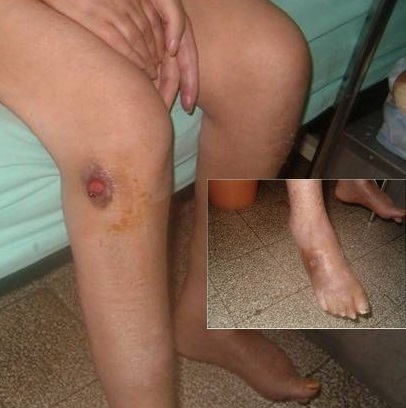
Múltiples ulceraciones en un individuo con poliangeítis microscópica
Imagen: “Multiple ulcerations in a patient with microscopic polyangiitis” por Khammassi N et al. Licencia: CC BY 2.0La evaluación de laboratorio inicial en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la sospecha de vasculitis Vasculitis Inflammation of any one of the blood vessels, including the arteries; veins; and rest of the vasculature system in the body. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus incluye:
Las pruebas adicionales pueden incluir:
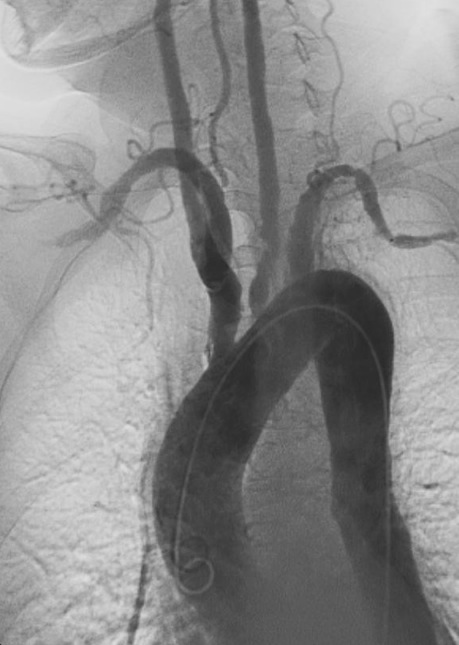
Angiografía de la arteritis de Takayasu:
Obsérvese la estenosis y las dilataciones postestenóticas en las ramas principales del arco aórtico.
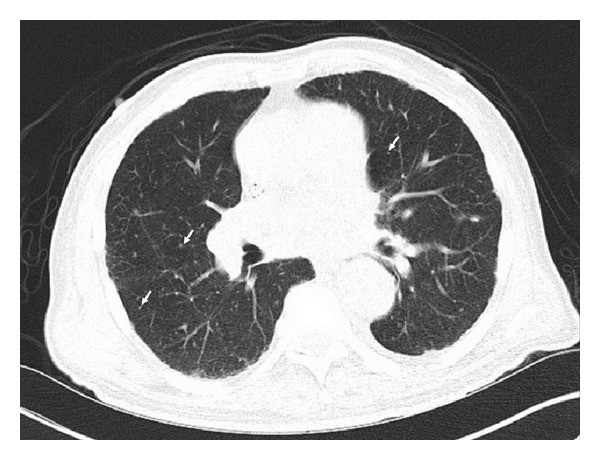
TC con nódulos pulmonares bilaterales diminutos y difusos (flechas) secundarios a enfermedad granulomatosa, especialmente con grandes granulomas calcificados con linfadenopatía mediastínica e hiliar.
Este paciente fue positivo para ANCA y se le diagnosticó poliangeítis microscópica. Imagen: “CT scan with diffuse tiny bilateral pulmonary nodules” por Iruku P et al. License: CC BY 3.0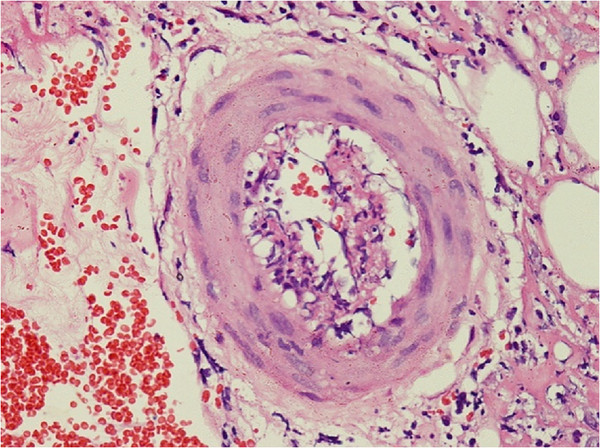
La biopsia de piel muestra una infiltración perivascular linfocítica y neutrofílica con necrosis fibrinoide de la pared del vaso y extravasaciones leucocitoclásticas y de eritrocitos en un individuo con poliarteritis nodosa.
Imagen: “Skin biopsy shows perivascular lymphocytic and neutrophilic infiltration” por Rodrigo D et al. Licencia: CC BY 2.0