La toxocariasis Toxocariasis Toxocariasis is caused by the nematodes Toxocara canis and T. cati. These species frequently infect dogs and cats and are most commonly transmitted to humans via accidental ingestion of eggs through the fecal-oral route. Toxocara are not able to complete their life cycle in humans, but they do migrate to organs (including the liver, lungs, heart, brain, and eyes), where they cause inflammation and tissue damage. Toxocariasis es causada por los LOS Neisseria nemátodos Toxocara canis Toxocara canis A species of parasitic nematode found in the intestine of dogs. Lesions in the brain, liver, eye, kidney, and lung are caused by migrating larvae. In humans, these larvae do not follow normal patterns and may produce visceral larva migrans (larva migrans, visceral). Toxocariasis y T. cati. Estas especies infectan con frecuencia a perros y gatos y se transmiten más comúnmente a los LOS Neisseria humanos a través de la ingestión accidental de huevos por la vía fecal-oral. Los LOS Neisseria Toxocara Toxocara A genus of ascarid nematodes commonly parasitic in the intestines of cats and dogs. Toxocariasis no son capaces de completar su ciclo de vida en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el humano, pero migran a los LOS Neisseria órganos (incluidos hígado, pulmones, corazón, cerebro y ojos), donde causan inflamación y daño tisular. Dependiendo de la zona afectada, los LOS Neisseria pacientes pueden desarrollar larva migrans visceral o larva migrans ocular. La larva migrans visceral puede presentarse con síntomas similares a los LOS Neisseria de la gripe, así como con manifestaciones hepáticas, pulmonares, neurológicas y cardíacas. La larva migrans ocular se presenta con alteración unilateral de la visión y en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la fundoscopia se puede observar un granuloma blanco y elevado. El diagnóstico se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la sospecha clínica y puede apoyarse en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la serología. El tratamiento para los LOS Neisseria casos con una enfermedad grave incluye una terapia antihelmíntica y esteroides.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
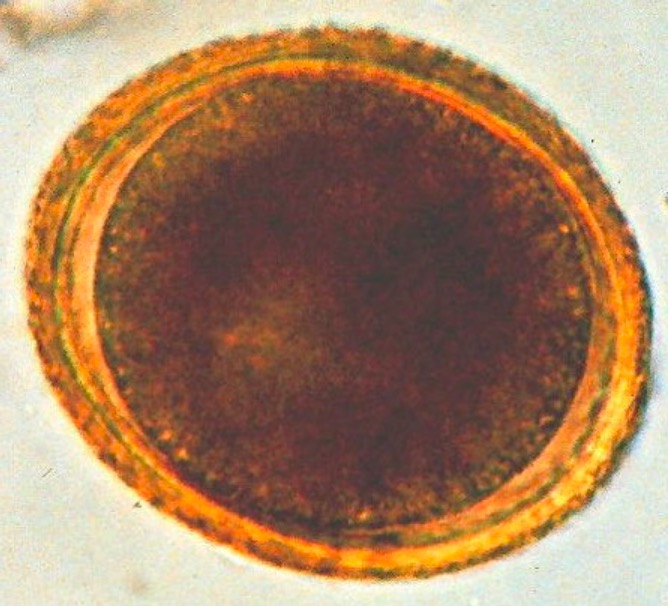
Huevo esférico de Toxocara con un aspecto marrón y granulado
Imagen: “Toxocara (roundworm)” por SuSanA Secretariat. Licencia: CC BY 2.0La toxocariasis Toxocariasis Toxocariasis is caused by the nematodes Toxocara canis and T. cati. These species frequently infect dogs and cats and are most commonly transmitted to humans via accidental ingestion of eggs through the fecal-oral route. Toxocara are not able to complete their life cycle in humans, but they do migrate to organs (including the liver, lungs, heart, brain, and eyes), where they cause inflammation and tissue damage. Toxocariasis es causada por las siguientes especies:
La transmisión se produce a través de:
En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria animales:
En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria humanos:
La mayoría de las infecciones por Toxocara Toxocara A genus of ascarid nematodes commonly parasitic in the intestines of cats and dogs. Toxocariasis son asintomáticas y tienen un curso benigno. Las 2 formas principales de toxocariasis Toxocariasis Toxocariasis is caused by the nematodes Toxocara canis and T. cati. These species frequently infect dogs and cats and are most commonly transmitted to humans via accidental ingestion of eggs through the fecal-oral route. Toxocara are not able to complete their life cycle in humans, but they do migrate to organs (including the liver, lungs, heart, brain, and eyes), where they cause inflammation and tissue damage. Toxocariasis son la larva migrans visceral y la larva migrans ocular.
Síntomas generales:
Síntomas hepáticos:
Síntomas pulmonares:
Manifestaciones menos comunes:
Síntomas unilaterales:
Hallazgos:
Complicaciones:
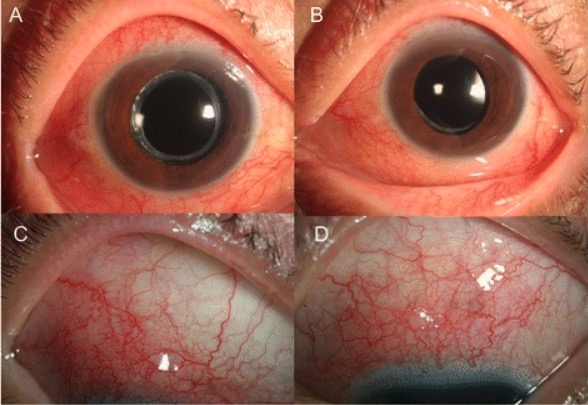
Imágenes de la derecha (A y C) y la izquierda (B y D) que muestran unos ojos con enrojecimiento difuso y congestión de los vasos esclerales, consistente con una escleritis, debido a una infección por Toxocara
Imagen: “Ocular toxocariasis” por Kang Yeun Pak et al. Licencia: CC BY 4.0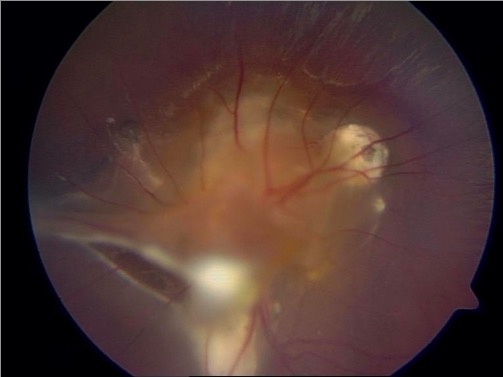
Fundoscopia que muestra granulomas subretinianos con dos bandas de tracción fibrosa que proliferan en la periferia en un paciente con larva migrans ocular debido a una infección por Toxocara
Imagen: “Central and peripheric subretinal granulomas” por Department and Clinic of Tropical and Parasitic Diseases, University of Medical Sciences, Przybyszewskiego 49, 60-355 Poznań, Poland. Licencia: CC BY 3.0El diagnóstico de la toxocariasis Toxocariasis Toxocariasis is caused by the nematodes Toxocara canis and T. cati. These species frequently infect dogs and cats and are most commonly transmitted to humans via accidental ingestion of eggs through the fecal-oral route. Toxocara are not able to complete their life cycle in humans, but they do migrate to organs (including the liver, lungs, heart, brain, and eyes), where they cause inflammation and tissue damage. Toxocariasis requiere un alto índice de sospecha.
Pruebas serológicas:
Estudios adicionales:
Generalmente, la imagenología es guiada por la presentación clínica del paciente.
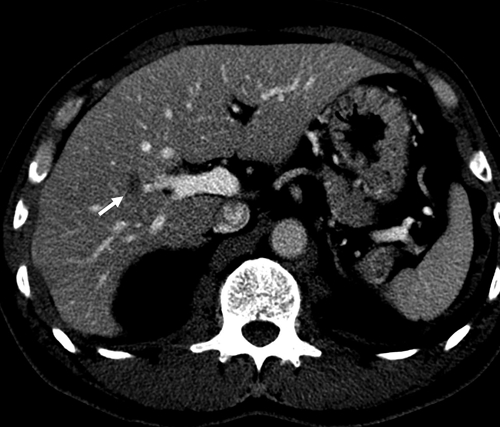
Imagen de una TC que muestra un pequeño nódulo ovalado de baja atenuación en el lóbulo derecho del hígado (flecha) debido a la larva migrans visceral hepática de Toxocara canis
Imagen: “Contrast-enhanced CT” por Lim JH. Licencia: CC BY 2.5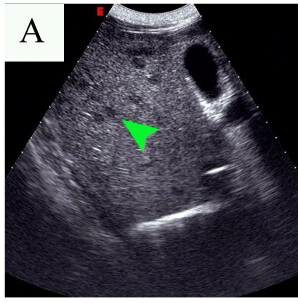
Ultrasonido abdominal que muestra múltiples lesiones pequeñas e hipoecoicas (punto de flecha) en el hígado debido a la larva migrans visceral hepática de Toxocara
Imagen: “Abdominal ultrasound results before and after the first therapy” por Tao Yu et al. Licencia: CC BY 2.0Los LOS Neisseria pacientes con síntomas leves no requieren terapia, ya que la enfermedad es autolimitada. A los LOS Neisseria pacientes con una enfermedad moderada o grave se les puede proporcionar tratamiento:
| Organismo | Enterobius vermicularis Enterobius Vermicularis Enterobius/Enterobiasis | Toxocara canis Toxocara canis A species of parasitic nematode found in the intestine of dogs. Lesions in the brain, liver, eye, kidney, and lung are caused by migrating larvae. In humans, these larvae do not follow normal patterns and may produce visceral larva migrans (larva migrans, visceral). Toxocariasis | Ascaris Ascaris Ascaris is a genus of parasitic nematodes. The infection, ascariasis, is most often caused by A. lumbricoides. Transmission occurs primarily via ingestion of water or food contaminated with Ascaris eggs. Most patients with ascariasis are asymptomatic. Ascaris/Ascariasis lumbricoides | Strongyloides stercoralis Strongyloides stercoralis A species of parasitic nematode widely distributed in tropical and subtropical countries. The females and their larvae inhabit the mucosa of the intestinal tract, where they cause ulceration and diarrhea. Strongyloidiasis | Schistosoma Schistosoma Schistosomiasis is an infection caused by Schistosoma, a trematode. Schistosomiasis occurs in developing countries with poor sanitation. Freshwater snails are the intermediate host and are transmitted to humans through skin contact with contaminated fresh water. The clinical presentation occurs as a result of the host’s immune response to antigens from the eggs. Schistosoma/Schistosomiasis mansoni |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Características | Nemátodo | Nemátodo | Nemátodo | Nemátodo | Trematodos |
| Reservorio | Humanos | Perros | Humanos |
|
Humanos |
| Transmisión | Fecal-oral | Fecal-oral | Fecal-oral | Contacto de la piel con suelo contaminado | Contacto de la piel con agua contaminada |
| Cuadro clínico |
|
|
|
|
|
| Diagnóstico |
|
|
Análisis de heces |
|
|
| Tratamiento |
|
|
|
|
Praziquantel Praziquantel An anthelmintic used in most schistosome and many cestode infestations. Anthelmintic Drugs |
| Prevención | Buena higiene |
|
|
|
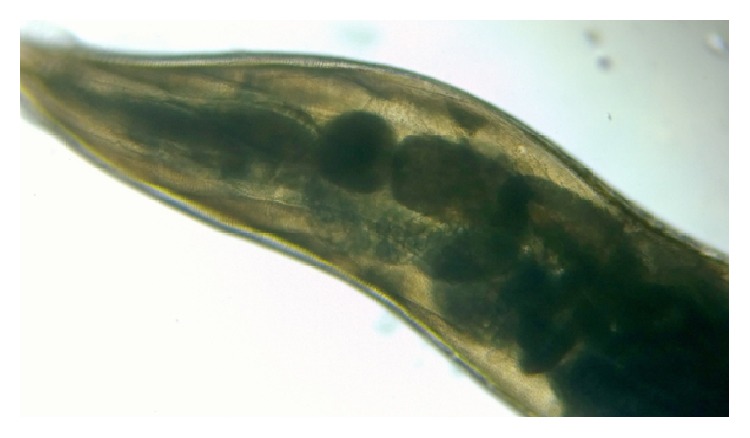
Vista microscópica de bajo poder de Enterobius vermicularis
Imagen: “Double bulb oesophagus of Enterobius vermicularis, under low power” por Kaniyarakkal V et al. Licencia: CC BY 4.0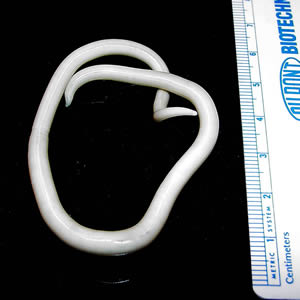
Verme adulto de Ascaris lumbricoides
Imagen: “An adult Ascaris lumbricoides worm” por CDC Division of Parasitic Diseases. Licencia: Dominio Público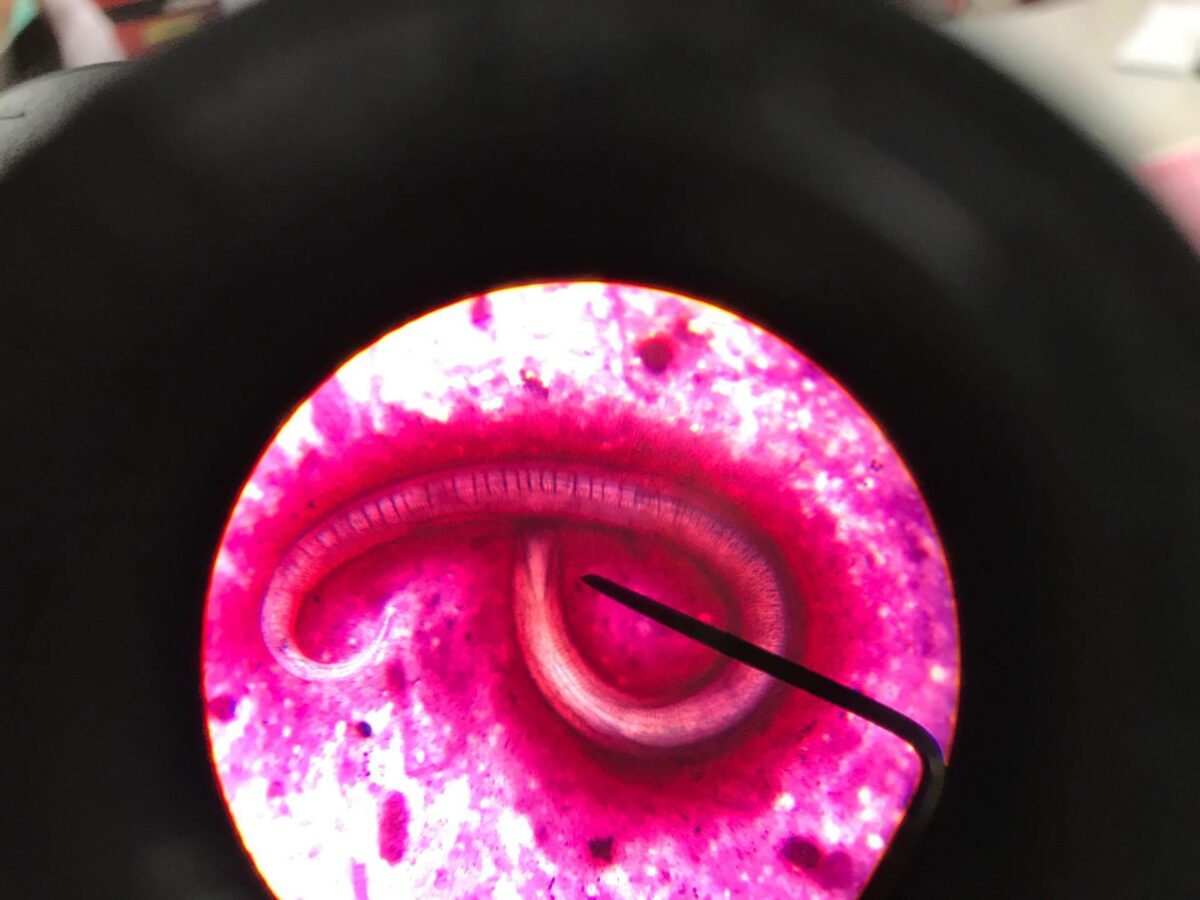
Parásito Strongyloides stercoralis
Imagen: “Strongyloides Stercoralis in sputum” por CDC Division of Parasitic Diseases. Licencia: CC BY 4.0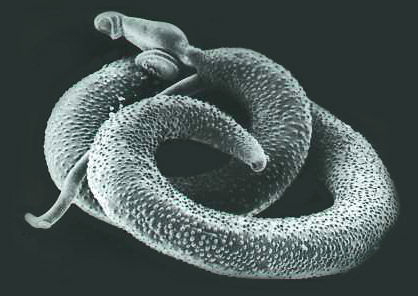
Schistosoma mansoni adulto visto bajo microscopía electrónica
Imagen: “Schistosoma mansoni, adult. SEM [Scanning electron microscopy] of worm, unstained” por Otis Historical Archives of “National Museum of Health & Medicine”. Licencia: CC BY 2.0