Los LOS Neisseria síndromes paraneoplásicos son un grupo heterogéneo de trastornos causados por una respuesta inmune anormal a una neoplasia. Las sustancias producidas no se deben al AL Amyloidosis efecto directo del tumor Tumor Inflammation, como metástasis, efecto de masa o invasión. Se generan anticuerpos, hormonas, citoquinas y otras sustancias que afectan múltiples sistemas de órganos. Alrededor del 10% de los LOS Neisseria casos de cáncer se ven afectados por síndromes paraneoplásicos. Los LOS Neisseria cánceres comunes que se presentan con síndromes paraneoplásicos incluyen cáncer de pulmón, seno, ovarios, riñón, hígado y estómago, y linfomas.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Los LOS Neisseria síndromes paraneoplásicos son síndromes clínicos que surgen de una respuesta inmune a una neoplasia, produciendo sustancias que no son un efecto directo del tumor Tumor Inflammation, como metástasis, efecto de masa o invasión del tumor Tumor Inflammation.
Hay 2 mecanismos principales:
| Síndrome clínico | Neoplasia asociada | Patogénesis |
|---|---|---|
| Síndrome de Cushing |
|
Producción de ACTH o sustancias similares a ACTH |
| Síndrome de secreción inadecuada de hormona antidiurética |
|
Producción de hormona antidiurética (ADH) o vasopresina |
| Hipercalcemia |
|
Hormona relacionada con la hormona paratiroidea ( PTHrP PTHrP Hypercalcemia) |
| Hipoglucemia |
|
Insulina o sustancia similar a la insulina |
| Síndrome clínico | Neoplasia asociada | Patogénesis |
|---|---|---|
| Síndrome miasténico de Lambert-Eaton | Cáncer de pulmón de células pequeñas | Autoanticuerpos contra los LOS Neisseria canales presinápticos de Ca CA Condylomata acuminata are a clinical manifestation of genital HPV infection. Condylomata acuminata are described as raised, pearly, flesh-colored, papular, cauliflower-like lesions seen in the anogenital region that may cause itching, pain, or bleeding. Condylomata Acuminata (Genital Warts)2+ (canal de calcio dependiente de anti-voltaje) |
| Miastenia gravis |
|
Anticuerpo anti-receptores de acetilcolina |
| Degeneración cerebelosa paraneoplásica |
|
Anticuerpos contra antígenos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum células de Purkinje del cerebelo (anticuerpo anticélulas de Purkinje) |
| Encefalitis/encefalomielitis paraneoplásica (e.g., encefalitis límbica) |
|
Anti-Hu o anticuerpo nuclear antineuronal-1 |
| Síndrome clínico | Neoplasia asociada | Patogénesis |
|---|---|---|
| Estado de hipercoagulabilidad o trombosis venosa (síndrome de Trousseau) |
|
Liberación de mucina que activa los LOS Neisseria factores de coagulación. |
| Endocarditis Endocarditis Endocarditis is an inflammatory disease involving the inner lining (endometrium) of the heart, most commonly affecting the cardiac valves. Both infectious and noninfectious etiologies lead to vegetations on the valve leaflets. Patients may present with nonspecific symptoms such as fever and fatigue. Endocarditis trombótica no bacteriana (trombos estériles) | Adenocarcinoma secretor de mucina | Sustancia similar a la tromboplastina (estado hipercoagulable) |
| Policitemia |
|
Producción de eritropoyetina |
| CID |
|
Productos tumorales que activan la coagulación |
| Síndrome clínico | Neoplasia asociada | Patogénesis |
|---|---|---|
| Acantosis nigricans |
|
Secreción del factor de crecimiento epidérmico |
| Signo de Leser-Trélat | Adenocarcinomas gastrointestinales | Hipersensibilidad al AL Amyloidosis factor de crecimiento |
| Dermatomiositis |
|
Respuesta inmunológica a las proteínas expresadas por el tumor Tumor Inflammation; depósito de anticuerpos donde se encuentran los LOS Neisseria antígenos de la piel y del músculo |
| Eritema necrolítico migratorio | Glucagonoma Glucagonoma A glucagonoma is a glucagon-secreting neuroendocrine tumor that originates from the β-cells in the pancreatic islets. Most glucagonomas are malignant, and many of them are part of the autosomal dominant condition known as multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome type 1 (MEN 1). Elevated levels of glucagon lead to increased gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis. Glucagonoma | Desconocida |
| Síndrome de Sweet |
|
Reacción inmunitaria a tumor Tumor Inflammation(es) y otros antígenos |
| Síndrome clínico | Neoplasia asociada | Patogénesis |
|---|---|---|
| Síndrome nefrótico (nefropatía membranosa) |
|
Antígeno tumoral, depósito de inmunocomplejos |
| Osteoartropatía hipertrófica y dedos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum palillo de tambor | Cáncer de pulmón | Proliferación fibrovascular |
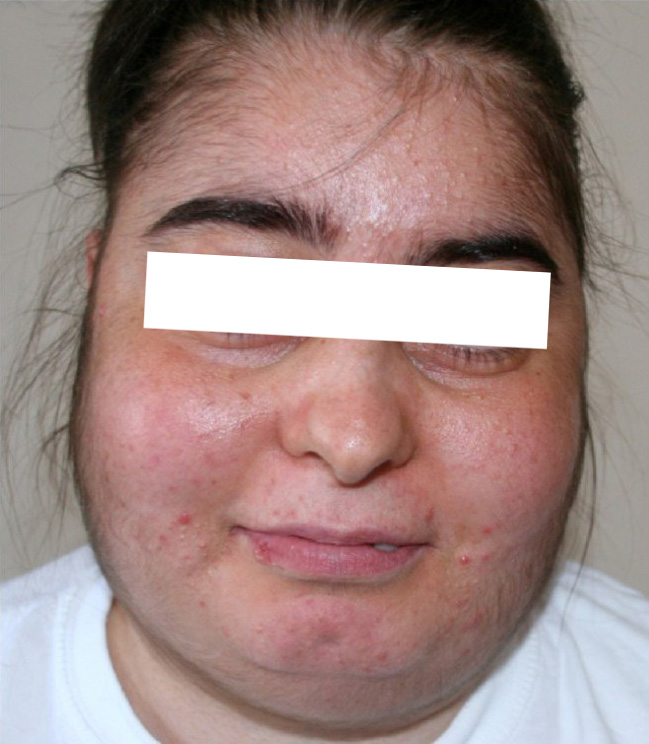
Características del síndrome de Cushing:
Mujer que presenta hirsutismo, acné y facies de luna
Facies de luna en el síndrome de Cushing:
Hallazgo clásico causado por hipercortisolismo
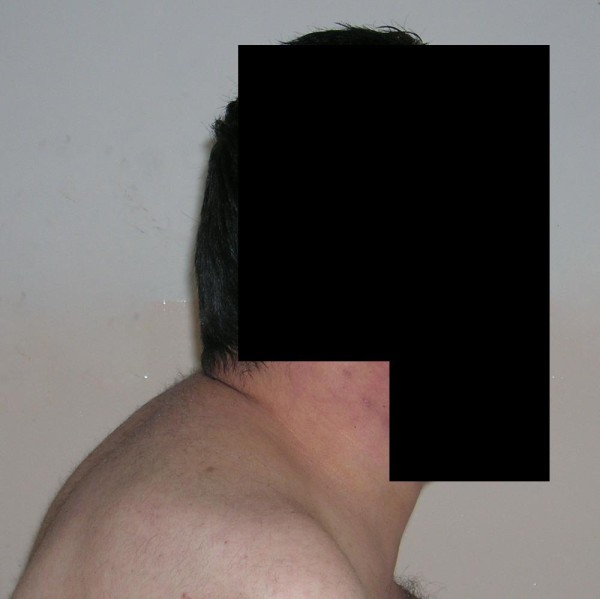
Joroba de búfalo en el síndrome de Cushing:
Hallazgo clásico causado por hipercortisolismo
Hiperpigmentación causada por el síndrome de Cushing paraneoplásico
Imagen: “Fig1: Detail of the patient’s anonymized face showing moon face, hyperpigmentation, and hirsutism” por V. B. Weeda et al. Licencia: CC BY 4.0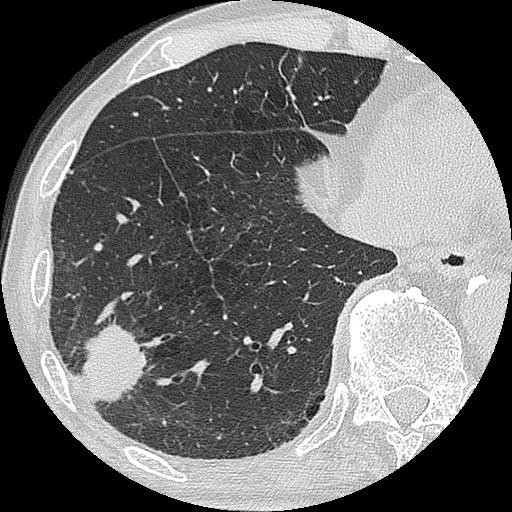
Síndrome miasténico de Lambert-Eaton causado por cáncer de pulmón:
TC de tórax que muestra una masa sólida con espiculación
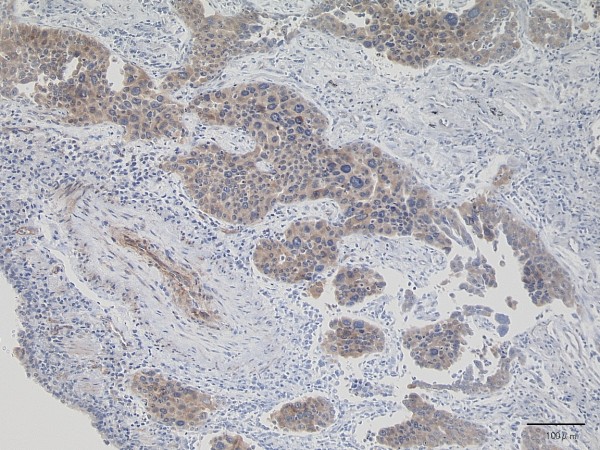
Síndrome miasténico de Lambert-Eaton causado por cáncer de pulmón:
La histología de la muestra células cancerosas, que resultaron positivas para el canal de calcio dependiente de voltaje tipo P/Q en inmunohistoquímica
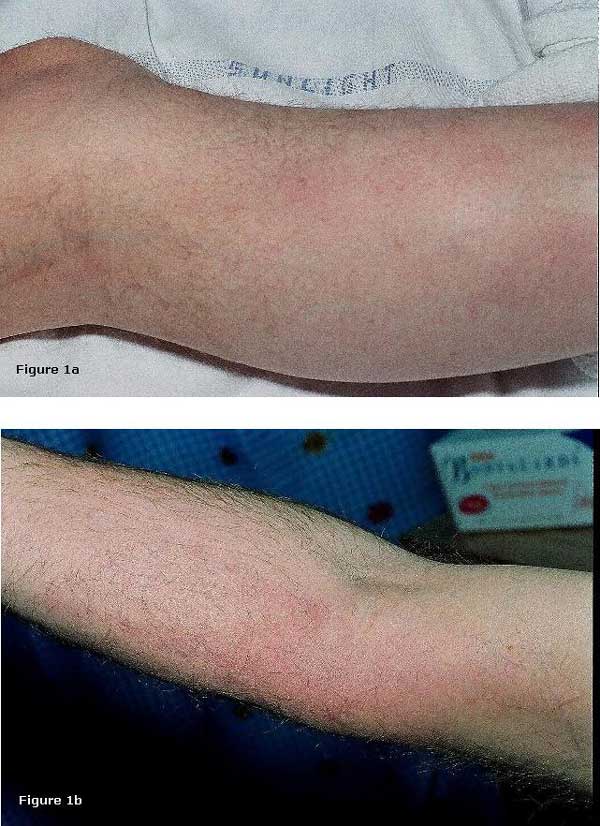
Síndrome de Trousseau:
Tromboflebitis migratoria en un hombre con adenocarcinoma de páncreas
Erupción eritematosa dolorosa en la cara medial del antebrazo derecho y miembro inferior izquierdo
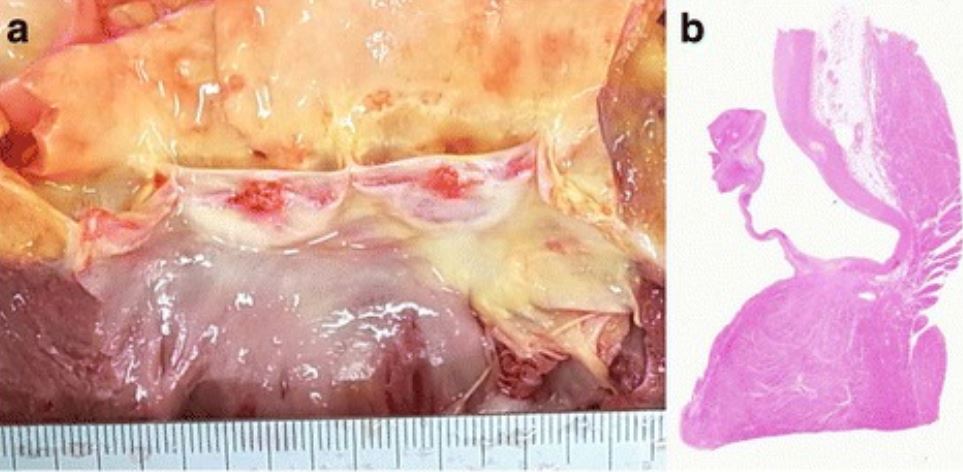
Vegetaciones de la válvula aórtica en la autopsia:
a: El aspecto macroscópico de la válvula aórtica muestra 2 vegetaciones de 4 mm y 5 mm de diámetro.
b: La evaluación histológica muestra que las vegetaciones consisten en fibrina sin colonias bacterianas, compatibles con endocarditis no infecciosa.
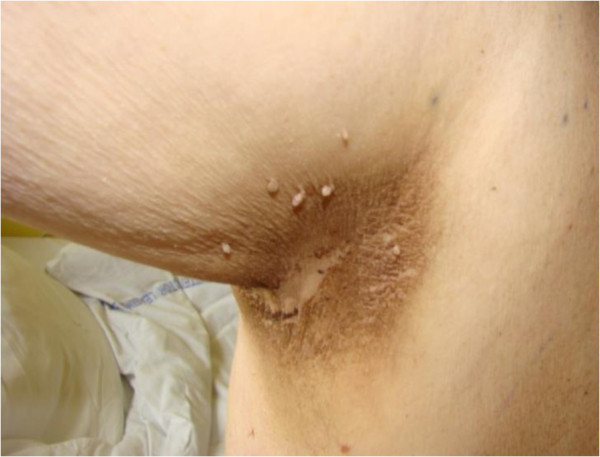
Acantosis nigricans:
Decoloración oscura que generalmente se desarrolla en los pliegues o pliegues del cuerpo, afectando aquí la axila derecha. La piel se vuelve gruesa debido a la hiperqueratosis y puede parecer aterciopelada.
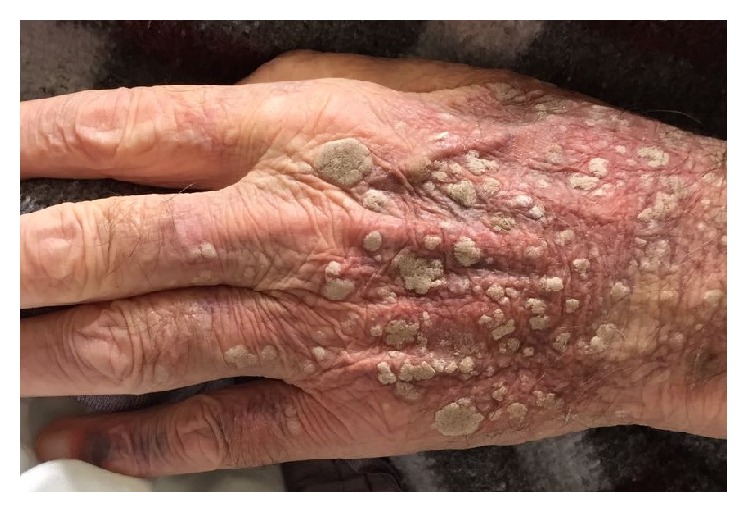
Signo de Leser-Trélat:
Queratosis seborreicas en el dorso de la mano que aparecieron y aumentaron de tamaño en un período corto
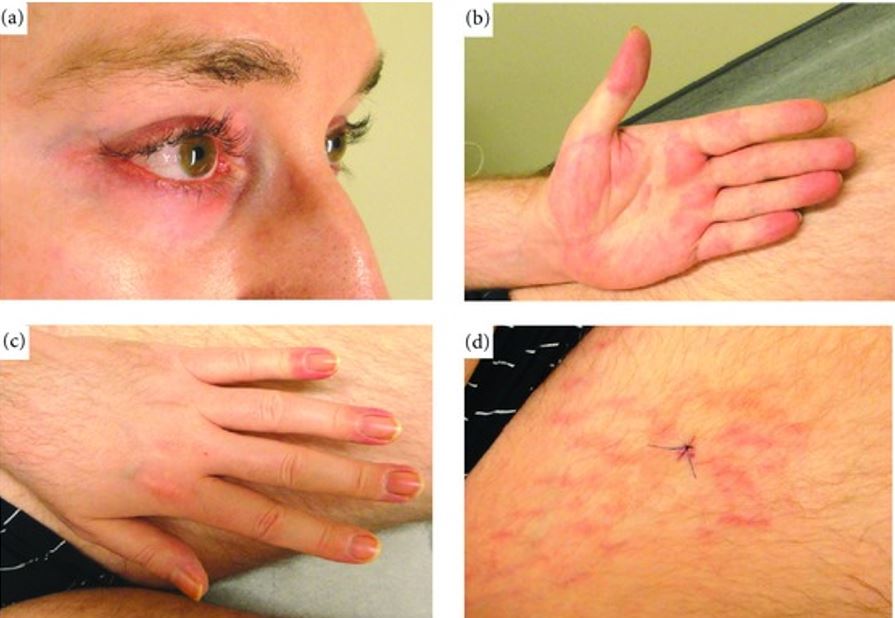
Dermatomiositis:
Las características clínicas de la dermatomiositis incluyen:
(a): eritema heliotropo
(b): eritema palmar
(c): eritema periungueal
(d): eritema flagelado
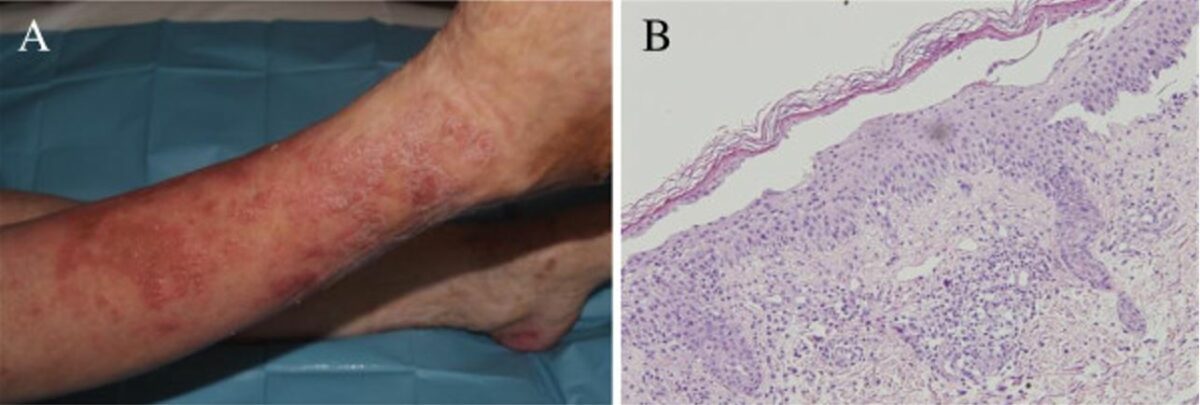
Eritema necrolítico migratorio:
A: erupciones cutáneas extremadamente eritematosas en el área pretibial
B: biopsia que muestra una zona de necrólisis y queratinocitos vacuolados
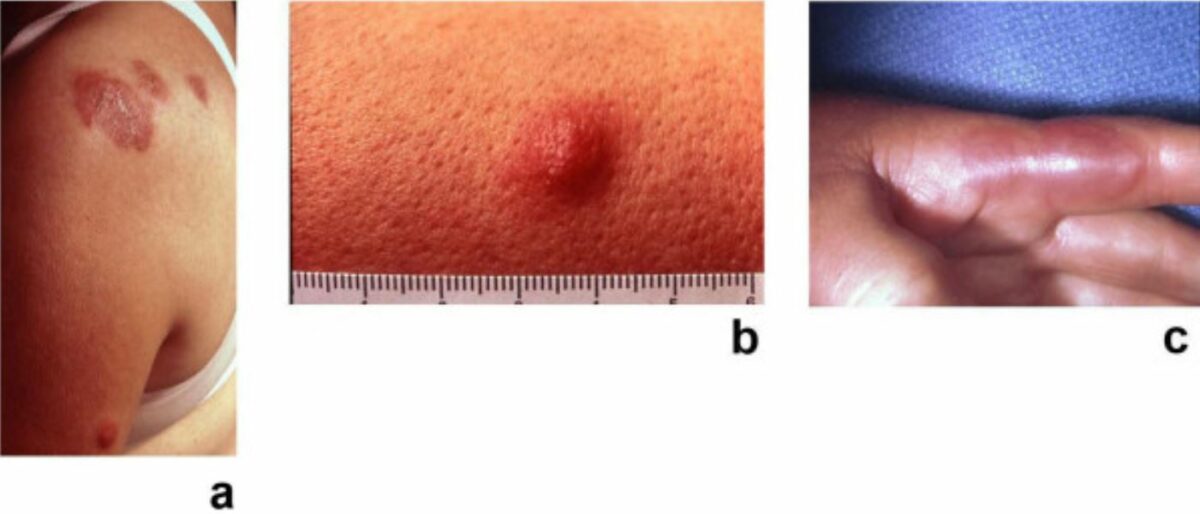
Síndrome de Sweet: placas dolorosas, eritematosas, seudovasculares de dermatosis neutrofílica febril aguda
a: Placa eritematosa en el hombro izquierdo
b: Lesión nodular en el brazo
c: Placa eritematosa en un dedo
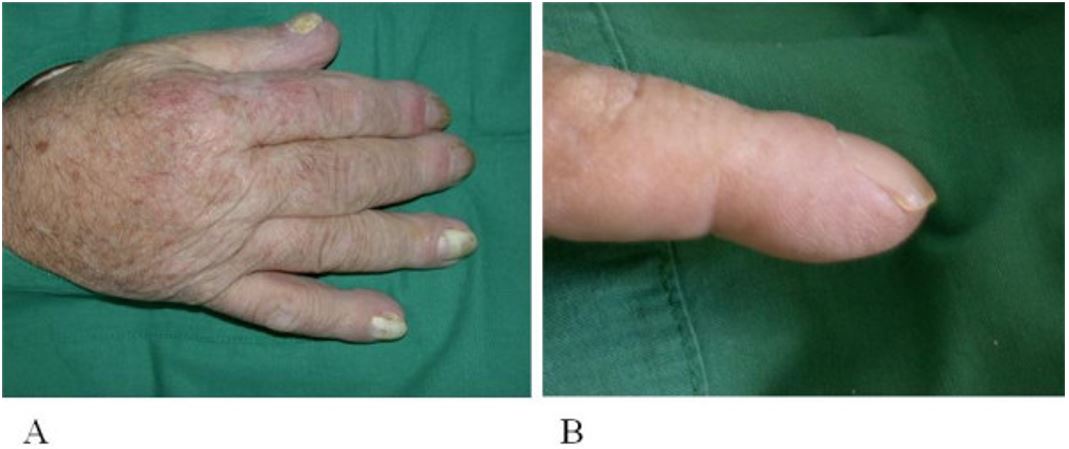
Osteoartropatía hipertrófica:
A: Mano derecha grande con hinchazón edematosa
B: Eritema periungueal y acropaquias