El síndrome nefrótico se caracteriza por proteinuria Proteinuria The presence of proteins in the urine, an indicator of kidney diseases. Nephrotic Syndrome in Children grave, hipoalbuminemia y edema Edema Edema is a condition in which excess serous fluid accumulates in the body cavity or interstitial space of connective tissues. Edema is a symptom observed in several medical conditions. It can be categorized into 2 types, namely, peripheral (in the extremities) and internal (in an organ or body cavity). Edema periférico. Por el contrario, los LOS Neisseria síndromes nefríticos se presentan con hematuria Hematuria Presence of blood in the urine. Renal Cell Carcinoma, pérdida variable Variable Variables represent information about something that can change. The design of the measurement scales, or of the methods for obtaining information, will determine the data gathered and the characteristics of that data. As a result, a variable can be qualitative or quantitative, and may be further classified into subgroups. Types of Variables de función renal e hipertensión, aunque a veces hay superposición de > 1 enfermedad glomerular en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el mismo individuo. Las etiologías principales del síndrome nefrótico son la enfermedad por cambios mínimos, la nefropatía membranosa y la glomeruloesclerosis focal y segmentaria. La presentación clínica del síndrome nefrótico incluye proteinuria Proteinuria The presence of proteins in the urine, an indicator of kidney diseases. Nephrotic Syndrome in Children (> 3,5 g/día), hipoalbuminemia (< 3 g/dL) y edema Edema Edema is a condition in which excess serous fluid accumulates in the body cavity or interstitial space of connective tissues. Edema is a symptom observed in several medical conditions. It can be categorized into 2 types, namely, peripheral (in the extremities) and internal (in an organ or body cavity). Edema periférico. Otros hallazgos clínicos que se observan con frecuencia son hiperlipidemia y enfermedad trombótica. Los LOS Neisseria hallazgos clínicos sugieren el diagnóstico y en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la mayoría de los LOS Neisseria casos es necesaria una biopsia renal. El tratamiento varía con la etiología y por lo general incluye glucocorticoides u otros medicamentos inmunosupresores.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
El síndrome nefrótico se caracteriza por proteinuria Proteinuria The presence of proteins in the urine, an indicator of kidney diseases. Nephrotic Syndrome in Children intensa (> 3,5 g/día), albúmina sérica baja (< 3 g/dL) y edema Edema Edema is a condition in which excess serous fluid accumulates in the body cavity or interstitial space of connective tissues. Edema is a symptom observed in several medical conditions. It can be categorized into 2 types, namely, peripheral (in the extremities) and internal (in an organ or body cavity). Edema periférico.
El principal lugar de la lesión en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las enfermedades que causan el síndrome nefrótico primario es el podocito. El aumento de la filtración a través de la pared capilar glomerular produce proteinuria Proteinuria The presence of proteins in the urine, an indicator of kidney diseases. Nephrotic Syndrome in Children.
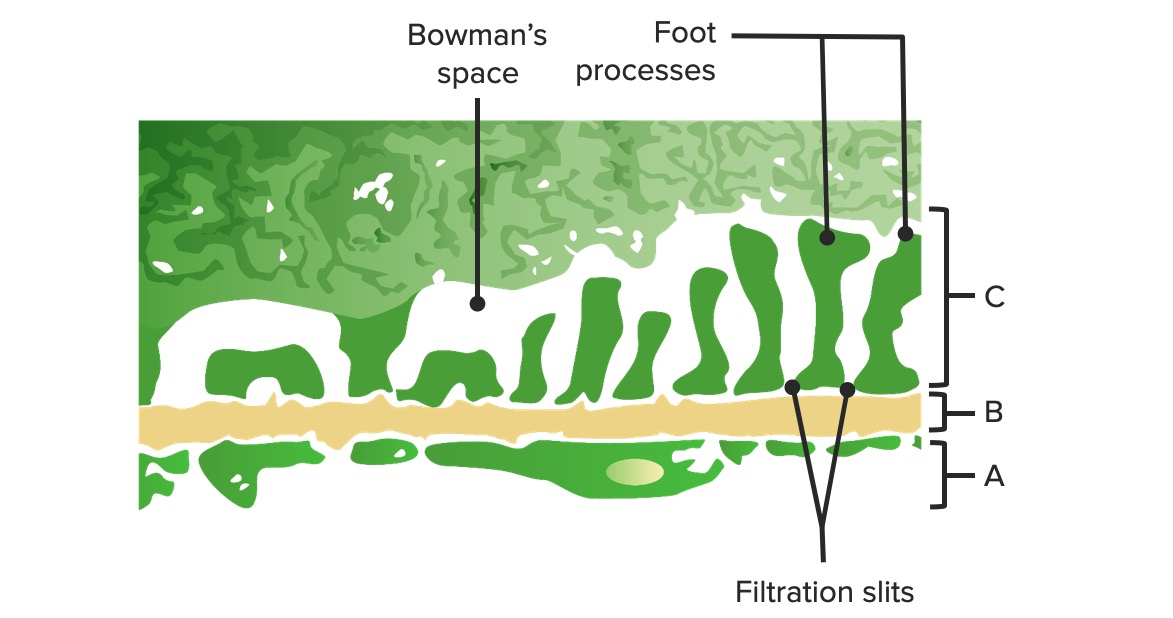
Diagrama de la barrera glomerular:
A: Endotelio fenestrado de los capilares glomerulares
B: Membrana basal
C: Capa epitelial que muestra los procesos podocitarios de los podocitos y las proteínas estructurales que crean el diafragma de hendidura
Es más probable que las etiologías primarias se presenten con los LOS Neisseria hallazgos clásicos del síndrome nefrótico ( proteinuria Proteinuria The presence of proteins in the urine, an indicator of kidney diseases. Nephrotic Syndrome in Children, edema Edema Edema is a condition in which excess serous fluid accumulates in the body cavity or interstitial space of connective tissues. Edema is a symptom observed in several medical conditions. It can be categorized into 2 types, namely, peripheral (in the extremities) and internal (in an organ or body cavity). Edema, hipoalbuminemia), mientras que las causas secundarias tienen más probabilidades de presentarse solo con proteinuria Proteinuria The presence of proteins in the urine, an indicator of kidney diseases. Nephrotic Syndrome in Children en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum rango nefrótico. El diagnóstico se establece mediante la historia clínica y la presentación, el grado de proteinuria Proteinuria The presence of proteins in the urine, an indicator of kidney diseases. Nephrotic Syndrome in Children y los LOS Neisseria hallazgos de la biopsia.
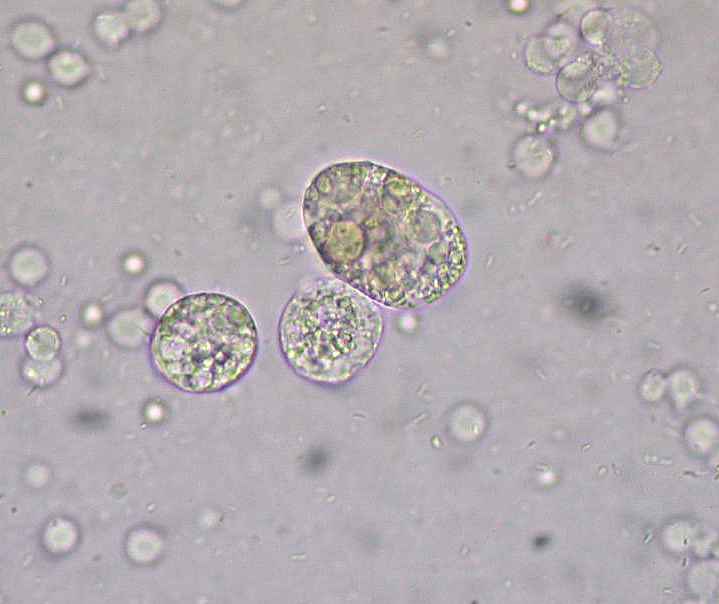
Síndrome nefrótico: cuerpos grasos ovalados en la microscopía de orina
Imagen: “Unidentified structures in urine” por Ed Uthman. Licencia: CC BY 2.0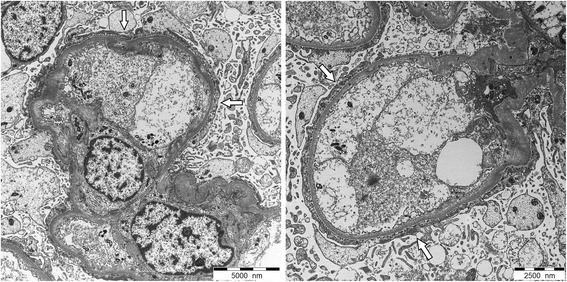
Microscopía electrónica que muestra asas capilares glomerulares con hallazgos de enfermedad de cambios mínimos:
Podocitos con borramiento extenso y difuso de los procesos podocitarios (flechas blancas) y transformación de microvellosidades
Sin depósitos electro-densos
Espesor normal de la membrana basal glomerular.
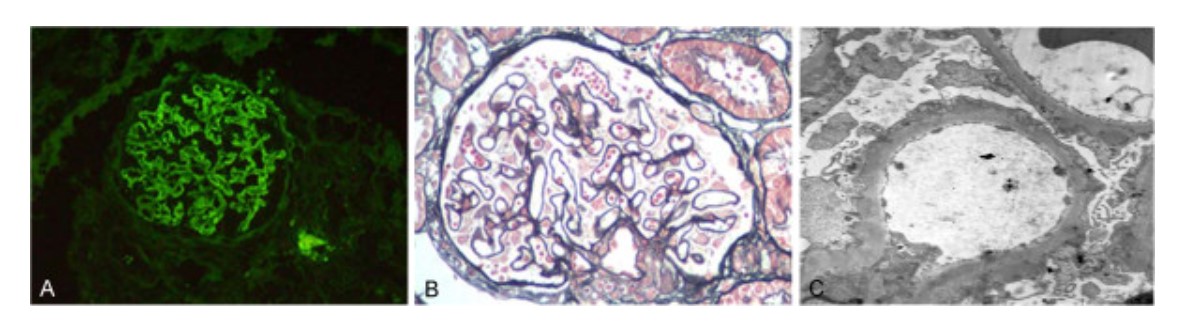
Individuo con nefropatía membranosa y nefropatía diabética:
A: Los depósitos de IgG en la membrana basal aparecen como un patrón granular difuso como se muestra en la inmunofluorescencia (200x).
B: El microscopio óptico muestra glomerulonefritis membranosa con asas capilares engrosadas y prominentes. Se localizaron numerosos depósitos granulares densos en áreas subepiteliales (tinción de ácido peryódico-Schiff (PAS), 200x).
C: Micrografía electrónica de la membrana basal glomerular engrosada con numerosos depósitos granulares densos localizados en áreas subepiteliales (5 000x).
Es menos probable que las siguientes etiologías se presenten con el síndrome nefrótico clásico, pero aún se pueden encontrar en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum biopsias renales realizadas por proteinuria Proteinuria The presence of proteins in the urine, an indicator of kidney diseases. Nephrotic Syndrome in Children en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum rango nefrótico.
Nefropatía diabética:
Glomerulonefritis membranoproliferativa:
Amiloidosis:
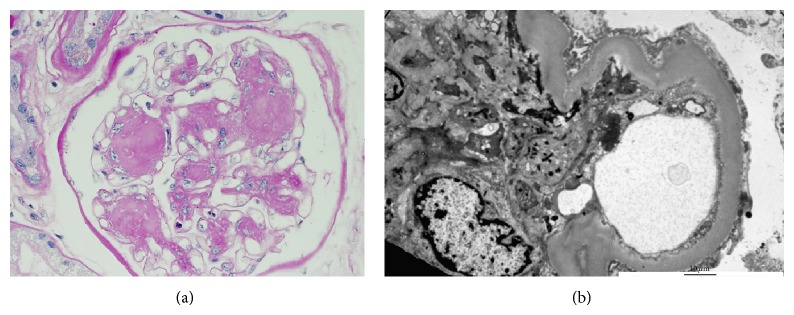
Nefropatía diabética:
(a): La microscopía óptica con tinción hematoxilina y eosina revela una expansión mesangial extensa sin un aumento marcado de la celularidad. Aquí se muestra una lesión de Kimmelstiel-Wilson y se refiere a la glomeruloesclerosis nodular que se puede observar en la enfermedad tardía, pero no es tan común como la glomeruloesclerosis diabética difusa. Las lesiones de Kimmelstiel-Wilson suelen ser esféricas y eosinofílicas y tienen un área central hipocelular o acelular. La expansión mesangial y las lesiones de Kimmelstiel-Wilson se deben a una mayor producción de matriz extracelular.
(b): La microscopía electrónica revela una membrana basal engrosada y un borramiento del proceso podocitario.
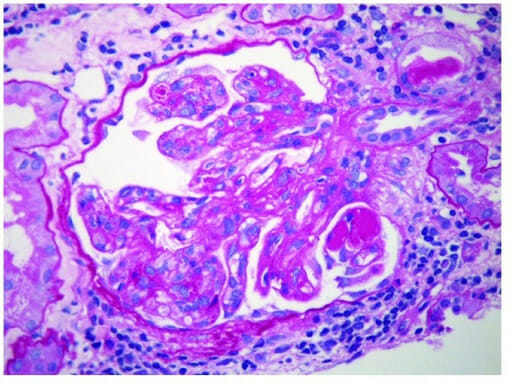
Glomerulonefritis membranoproliferativa:
Se observan “trombos hialinos” positivos al PAS dentro de los lúmenes capilares (aumento original del PAS × 400)
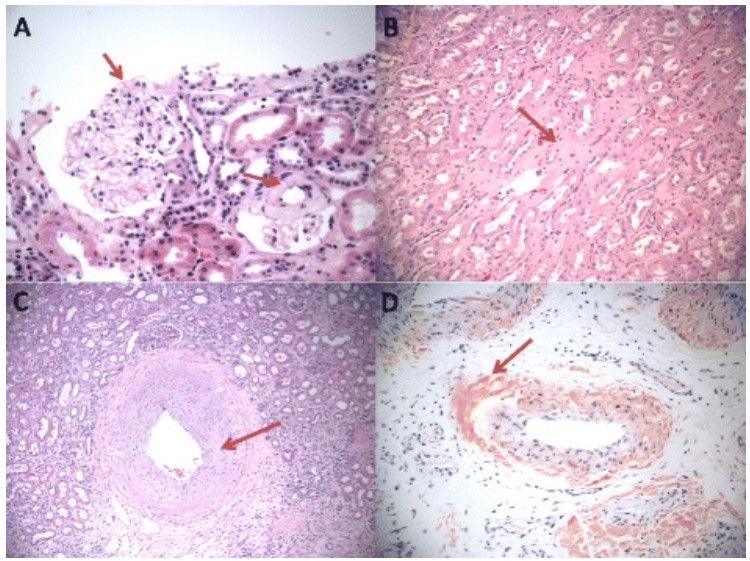
Depósitos de amiloide en los 3 compartimentos principales del riñón:
A: Depósitos de amiloide glomerular predominantemente en los espacios mesangiales (hematoxilina y eosina, 400x, flecha).
B: Amiloidosis intersticial (hematoxilina y eosina, 200x).
C: Amiloidosis vascular (hematoxilina y eosina, 100x).
D: Tinción con rojo congo de depósitos vasculares de amiloide (100x).
Todas las etiologías del síndrome nefrótico comparten medidas de tratamiento similares; en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las etiologías secundarias también se deben abordar las causas subyacentes.