La disfunción orgánica resultante de una respuesta sistémica desregulada del huésped a una infección separa la sepsis Sepsis Systemic inflammatory response syndrome with a proven or suspected infectious etiology. When sepsis is associated with organ dysfunction distant from the site of infection, it is called severe sepsis. When sepsis is accompanied by hypotension despite adequate fluid infusion, it is called septic shock. Sepsis and Septic Shock de una infección no complicada. La etiología es principalmente bacteriana y la neumonía es la fuente conocida más común. Los LOS Neisseria pacientes suelen presentar fiebre, taquicardia, taquipnea, hipotensión y/o alteraciones mentales. El shock Shock Shock is a life-threatening condition associated with impaired circulation that results in tissue hypoxia. The different types of shock are based on the underlying cause: distributive (↑ cardiac output (CO), ↓ systemic vascular resistance (SVR)), cardiogenic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), hypovolemic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), obstructive (↓ CO), and mixed. Types of Shock séptico se diagnostica durante el tratamiento, cuando los LOS Neisseria vasopresores son necesarios para controlar la hipotensión. La sepsis Sepsis Systemic inflammatory response syndrome with a proven or suspected infectious etiology. When sepsis is associated with organ dysfunction distant from the site of infection, it is called severe sepsis. When sepsis is accompanied by hypotension despite adequate fluid infusion, it is called septic shock. Sepsis and Septic Shock y el shock Shock Shock is a life-threatening condition associated with impaired circulation that results in tissue hypoxia. The different types of shock are based on the underlying cause: distributive (↑ cardiac output (CO), ↓ systemic vascular resistance (SVR)), cardiogenic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), hypovolemic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), obstructive (↓ CO), and mixed. Types of Shock séptico son emergencias médicas y los LOS Neisseria antibióticos se administran dentro de la hora siguiente al AL Amyloidosis diagnóstico.
Last updated: Jul 18, 2022
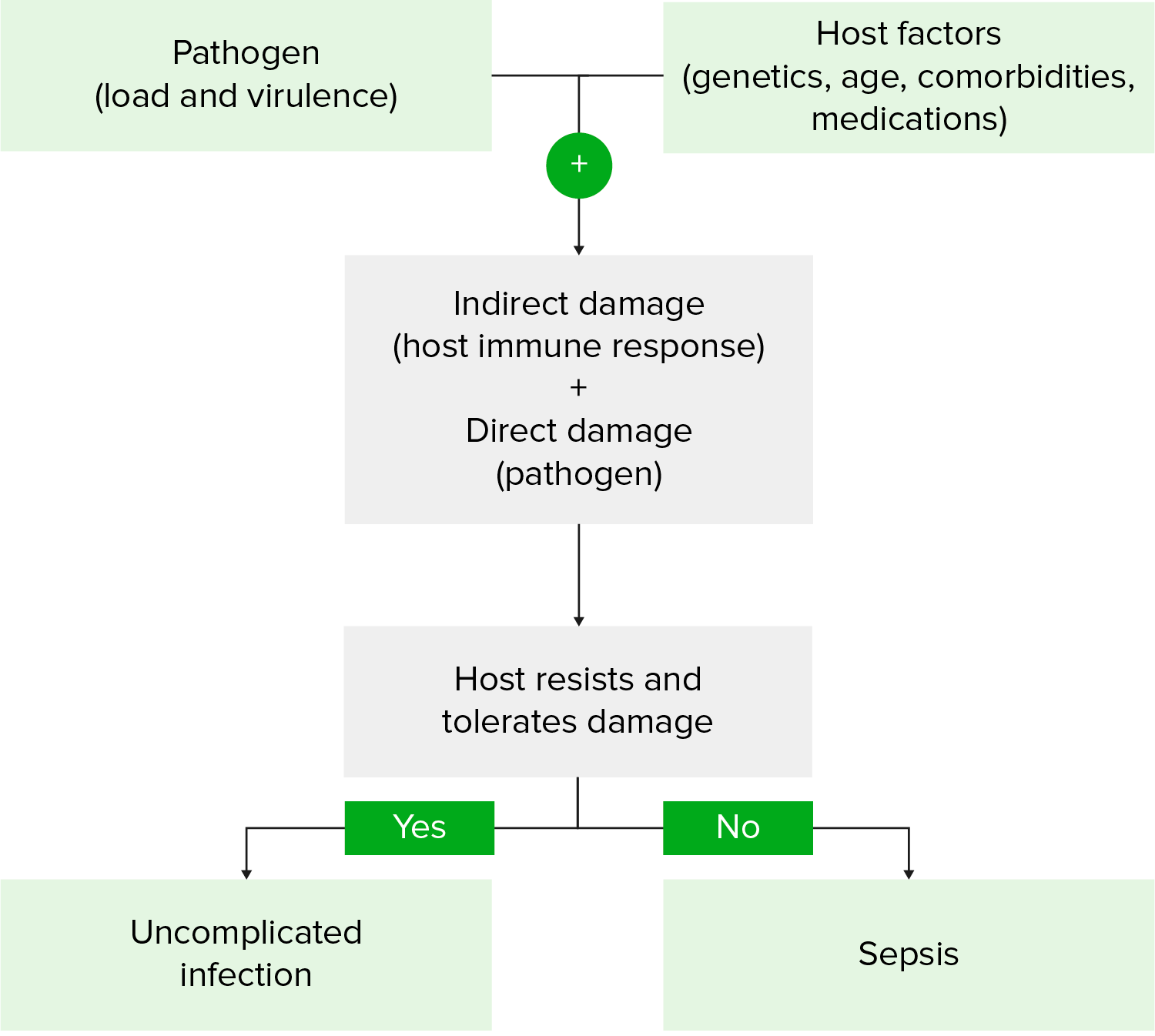
La carga y virulencia del patógeno + la composición genética y comorbilidades del huésped dan lugar a una respuesta compleja, exagerada y prolongada del huésped a la infección que evoluciona con el tiempo.
Fisiopatología del shock séptico
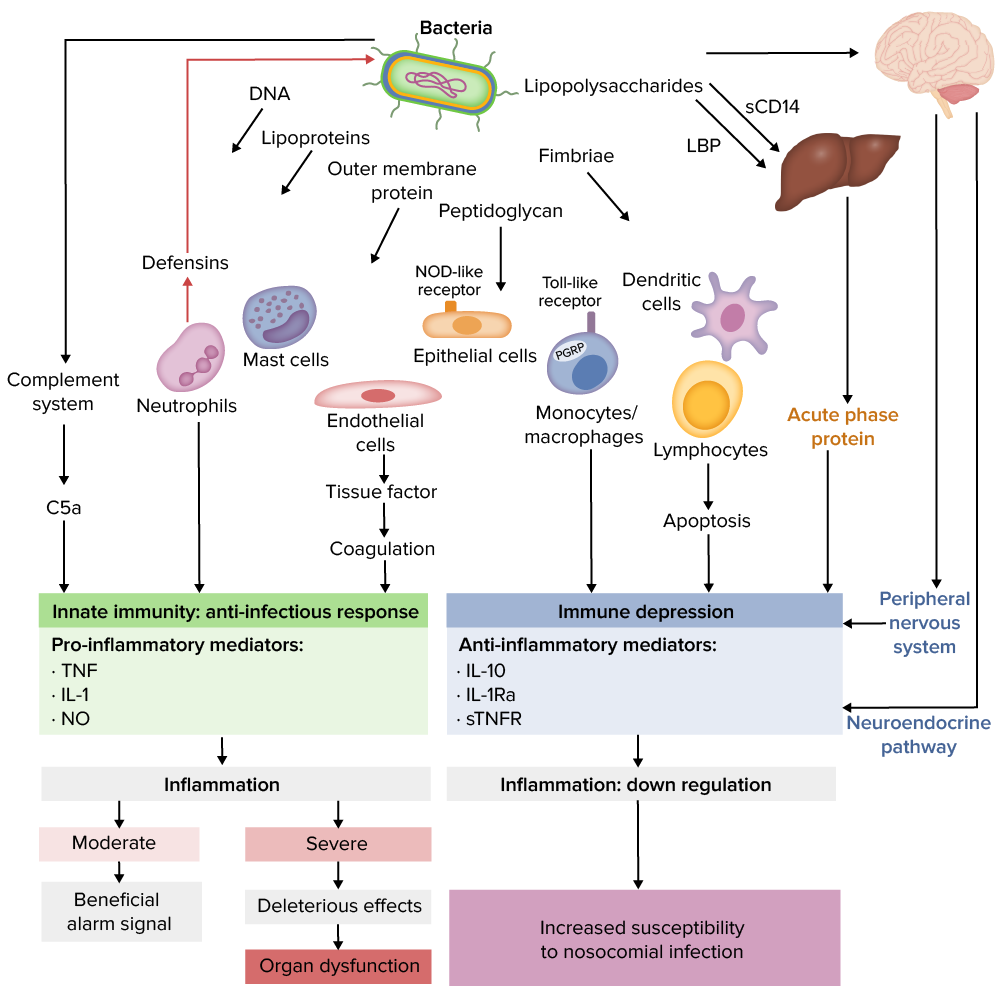
sTNFR: receptor soluble del factor de necrosis tumoral
LBP: proteína de unión a lipopolisacáridos
Patogénesis de la sepsis
Imagen por Lecturio.| Órgano/sistema | Puntuación SOFA SOFA Sepsis and Septic Shock | Indicación |
|---|---|---|
| Sistema respiratorio: PaO2/FiO2 (mm Hg) | 0 | ≥ 400 |
| + 1 | 300–399 | |
| + 2 | 200–299 | |
| + 3 | 100–199 + ventilación mecánica | |
| + 4 | < 100 + ventilación mecánica | |
| Sistema nervioso: Glasgow Coma Coma Coma is defined as a deep state of unarousable unresponsiveness, characterized by a score of 3 points on the GCS. A comatose state can be caused by a multitude of conditions, making the precise epidemiology and prognosis of coma difficult to determine. Coma Scale Scale Dermatologic Examination | 0 | 15 |
| + 1 | 13–14 | |
| + 2 | 10–12 | |
| +3 | 6–9 | |
| + 4 | < 6 | |
| Sistema cardiovascular: Presión arterial media (PAM) O necesidad de vasopresores | 0 | PAM ≥ 70 mm Hg |
| + 1 | PAM < 70 mm Hg | |
| + 2 | Dopamina ≤ 5 μg/kg/min o dobutamina (cualquier dosis) | |
| + 3 | Dopamina > 5 μg/kg/min O epinefrina ≤ 0,1 μg/kg/min O norepinefrina ≤ 0,1 μg/kg/min | |
| + 4 | Dopamina > 15 μg/kg/min O epinepfrina > 0,1 μg/kg/min O norepinefrina > 0,1 μg/kg/min | |
| Hígado: bilirrubina (mg/dL) | 0 | < 1,2 |
| + 1 | 1,2–1,9 | |
| + 2 | 2–5,9 | |
| + 3 | 6–11,9 | |
| + 4 | ≥ 12 | |
| Coagulación: plaquetas × 1 000/μL | 0 | ≥ 150 |
| + 1 | 100–149 | |
| + 2 | 50–99 | |
| + 3 | 20–49 | |
| + 4 | < 20 | |
| Riñones: creatinina (mg/dL) o diuresis | 0 | < 1,2 |
| + 1 | 1,2–1,9 | |
| + 2 | 2–3,4 | |
| + 3 | 3,4–4,9 o < 500 mL/día | |
| + 4 | > 5,0 o < 200 mL/día |
¡La sepsis Sepsis Systemic inflammatory response syndrome with a proven or suspected infectious etiology. When sepsis is associated with organ dysfunction distant from the site of infection, it is called severe sepsis. When sepsis is accompanied by hypotension despite adequate fluid infusion, it is called septic shock. Sepsis and Septic Shock y el shock Shock Shock is a life-threatening condition associated with impaired circulation that results in tissue hypoxia. The different types of shock are based on the underlying cause: distributive (↑ cardiac output (CO), ↓ systemic vascular resistance (SVR)), cardiogenic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), hypovolemic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), obstructive (↓ CO), and mixed. Types of Shock séptico son emergencias médicas!
El paquete de medidas de la hora 1 incita a los LOS Neisseria médicos a actuar lo más rápidamente posible. Idealmente, los LOS Neisseria siguientes pasos se inician en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la 1ra hora tras el diagnóstico de sepsis Sepsis Systemic inflammatory response syndrome with a proven or suspected infectious etiology. When sepsis is associated with organ dysfunction distant from the site of infection, it is called severe sepsis. When sepsis is accompanied by hypotension despite adequate fluid infusion, it is called septic shock. Sepsis and Septic Shock.
| Estado inmunitario del paciente | Elección del antibiótico |
|---|---|
| Inmunocompetente | Cualquiera de
los
LOS
Neisseria siguientes:
Vancomicina (o linezolid Linezolid An oxazolidinone and acetamide derived anti-bacterial agent and protein synthesis inhibitor that is used in the treatment of gram-positive bacterial infections of the skin and respiratory tract. Oxazolidinones) si el riesgo de S. aureus S. aureus Potentially pathogenic bacteria found in nasal membranes, skin, hair follicles, and perineum of warm-blooded animals. They may cause a wide range of infections and intoxications. Staphylococcus resistente a la meticilina ( MRSA MRSA A strain of Staphylococcus aureus that is non-susceptible to the action of methicillin. The mechanism of resistance usually involves modification of normal or the presence of acquired penicillin binding proteins. Staphylococcus, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés) es alto o si está en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum shock Shock Shock is a life-threatening condition associated with impaired circulation that results in tissue hypoxia. The different types of shock are based on the underlying cause: distributive (↑ cardiac output (CO), ↓ systemic vascular resistance (SVR)), cardiogenic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), hypovolemic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), obstructive (↓ CO), and mixed. Types of Shock séptico |
| Neutropénico (< 500 neutrófilos/μL) | Cualquiera de
los
LOS
Neisseria siguientes:
Vancomicina (o linezolid Linezolid An oxazolidinone and acetamide derived anti-bacterial agent and protein synthesis inhibitor that is used in the treatment of gram-positive bacterial infections of the skin and respiratory tract. Oxazolidinones), tobramicina y caspofungina |
| Esplenectomía | Cualquiera de
los
LOS
Neisseria siguientes:MÁS: Vancomicina (o linezolid Linezolid An oxazolidinone and acetamide derived anti-bacterial agent and protein synthesis inhibitor that is used in the treatment of gram-positive bacterial infections of the skin and respiratory tract. Oxazolidinones) |
| Asociación con neumonía | Referirse al AL Amyloidosis tratamiento de la neumonía adquirida en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la comunidad y asociada a la ventilación. |
| Asociado a infecciones intraabdominales graves | Cualquiera de
los
LOS
Neisseria siguientes:
Metronidazol |