La gonorrea es una infección de transmisión sexual (ITS) causada por la bacteria Bacteria Bacteria are prokaryotic single-celled microorganisms that are metabolically active and divide by binary fission. Some of these organisms play a significant role in the pathogenesis of diseases. Bacteriology gram-negativa Neisseria gonorrhoeae Neisseria gonorrhoeae A species of gram-negative, aerobic bacteria primarily found in purulent venereal discharges. It is the causative agent of gonorrhea. Neisseria ( N. gonorrhoeae N. gonorrhoeae A species of gram-negative, aerobic bacteria primarily found in purulent venereal discharges. It is the causative agent of gonorrhea. Neisseria). La gonorrea puede ser asintomática, pero comúnmente se manifiesta como cervicitis Cervicitis Inflammation of the uterine cervix. Gonorrhea o uretritis, con presentaciones menos comunes como proctitis Proctitis Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the rectum, the distal end of the large intestine. Chronic Granulomatous Disease, conjuntivitis o faringitis. Sin tratamiento antibiótico, pueden presentarse complicaciones. Las complicaciones para los LOS Neisseria hombres pueden incluir epididimitis, prostatitis Prostatitis Prostatitis is inflammation or an irritative condition of the prostate that presents as different syndromes: acute bacterial, chronic bacterial, chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain, and asymptomatic. Bacterial prostatitis is easier to identify clinically and the management (antibiotics) is better established. Prostatitis, balanitis Balanitis Inflammation of the head of the penis, glans penis. Penile Anomalies and Conditions y absceso periuretral. Las mujeres pueden desarrollar una enfermedad inflamatoria pélvica, que puede causar perihepatitis y problemas de fertilidad. La infección gonocócica diseminada se asocia con fiebre, dermatitis Dermatitis Any inflammation of the skin. Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema), tenosinovitis, artritis séptica y (raramente) endocarditis Endocarditis Endocarditis is an inflammatory disease involving the inner lining (endometrium) of the heart, most commonly affecting the cardiac valves. Both infectious and noninfectious etiologies lead to vegetations on the valve leaflets. Patients may present with nonspecific symptoms such as fever and fatigue. Endocarditis o meningitis Meningitis Meningitis is inflammation of the meninges, the protective membranes of the brain, and spinal cord. The causes of meningitis are varied, with the most common being bacterial or viral infection. The classic presentation of meningitis is a triad of fever, altered mental status, and nuchal rigidity. Meningitis. El diagnóstico de la gonorrea se realiza mediante microscopía, cultivo o pruebas de amplificación de ácidos nucleicos. El tratamiento suele consistir en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum ceftriaxona, pero debe seguirse un tratamiento con doxiciclina si no se excluye una coinfección con Chlamydia Chlamydia Chlamydiae are obligate intracellular gram-negative bacteria. They lack a peptidoglycan layer and are best visualized using Giemsa stain. The family of Chlamydiaceae comprises 3 pathogens that can infect humans: Chlamydia trachomatis, Chlamydia psittaci, and Chlamydia pneumoniae. Chlamydia trachomatis (C. trachomatis).
Last updated: Jun 27, 2022
La gonorrea está causada por el patógeno Neisseria gonorrhoeae Neisseria gonorrhoeae A species of gram-negative, aerobic bacteria primarily found in purulent venereal discharges. It is the causative agent of gonorrhea. Neisseria ( N. gonorrhoeae N. gonorrhoeae A species of gram-negative, aerobic bacteria primarily found in purulent venereal discharges. It is the causative agent of gonorrhea. Neisseria):
Factores de riesgo:
Imagen tridimensional (3D) generada por computador de la bacteria N. gonorrhoeae:
Diplococos típicos y múltiples pili
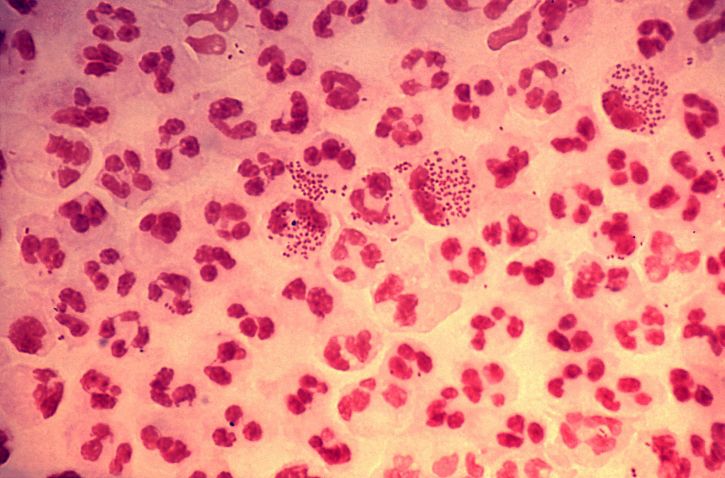
Tinción de Gram de un exudado purulento que contiene N. gonorrhoeae:
N. gonorrhoeae se ve como diplococos gram-negativos. Como se ve aquí, las bacterias suelen provocar una marcada respuesta neutrofílica con varios neutrófilos que contienen muchas bacterias fagocitadas. Aunque no está presente en la imagen, la tinción de Gram también revelaría las bacterias dentro de las células epiteliales infectadas.
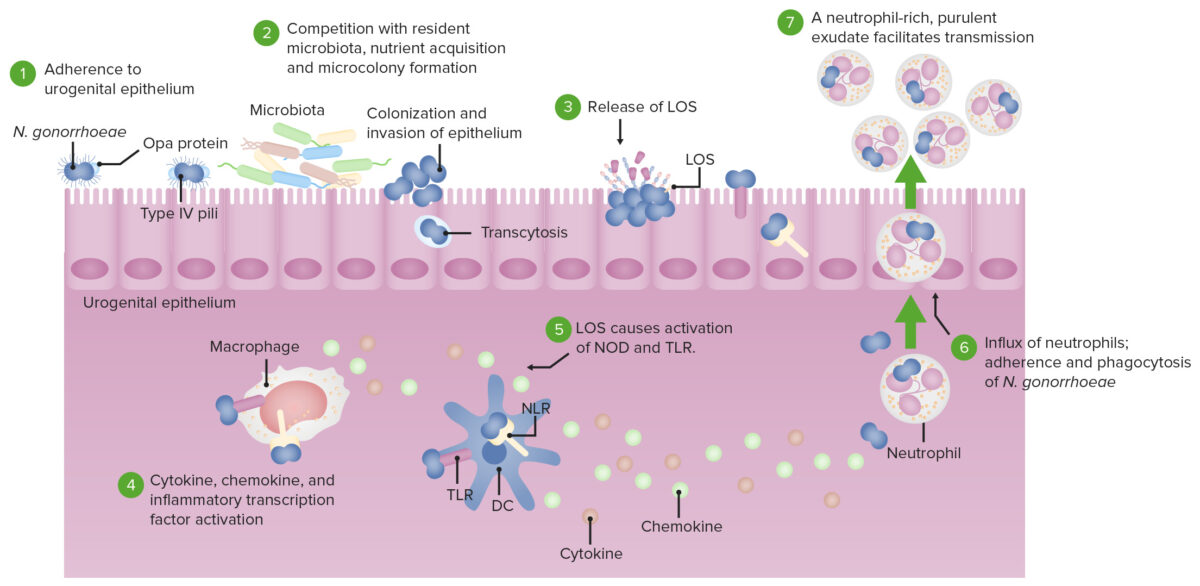
Patogénesis de N. gonorrhoeae:
DC: célula dendrítica
LOS: lipooligosacárido
TLR: receptor tipo Toll
NOD: proteína con dominio de oligomerización de unión a nucleótidos
NLR: Receptor tipo NOD
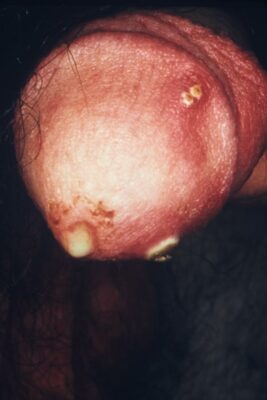
Secreción del pene purulenta por infección de gonorrea urogenital
Imagen: “4065” de CDC. Licencia: Public Domain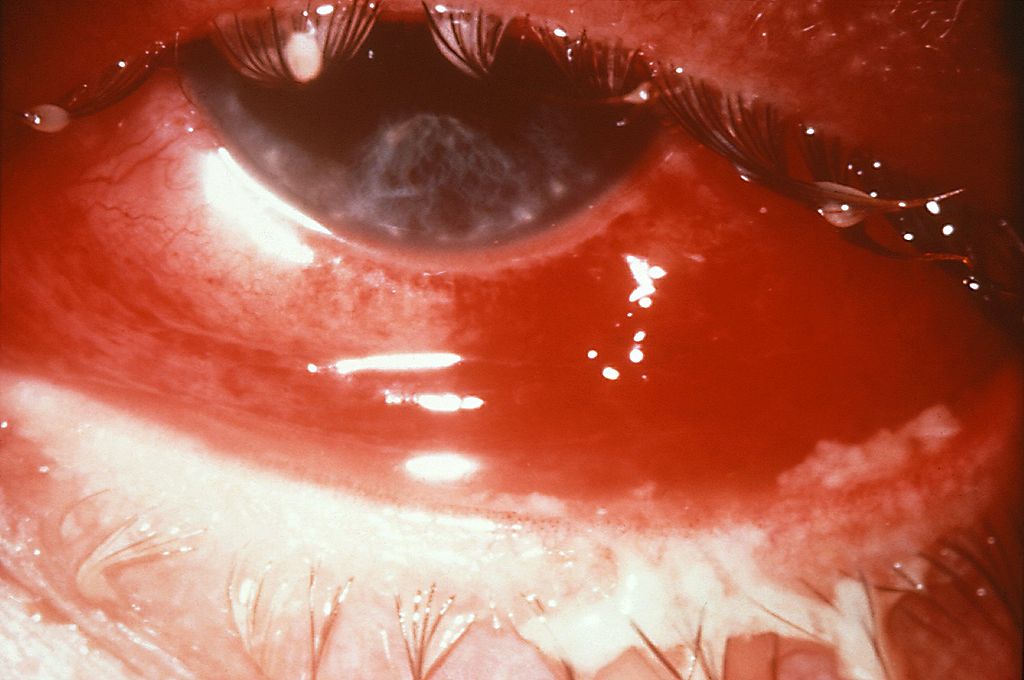
Hiperemia, quemosis y secreción purulenta por conjuntivitis gonocócica:
El paciente desarrolló una ceguera parcial como resultado de la infección.
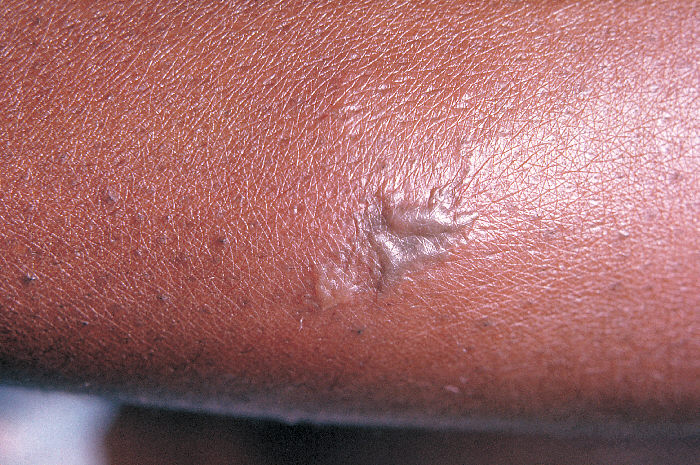
Primer plano de una lesión gonocócica en la piel del brazo de un paciente:
una pústula gris asociada a una infección gonocócica diseminada
Infecciones en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria recién nacidos:

Un recién nacido que presenta una oftalmia neonatal gonocócica, causada por una infección gonocócica de transmisión materna.
Imagen: “Gonococcal ophthalmia neonatorum” por CDC/J. Pledger. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoDespués del periodo neonatal:
Además de las evaluaciones de laboratorio mencionadas anteriormente, en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria pacientes en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria que se sospecha una infección gonocócica diseminada se pueden realizar las siguientes pruebas:
Tratamiento con antibióticos:
Medidas adicionales: