La fiebre reumática aguda es un proceso inflamatorio autoinmune que generalmente sigue a la faringitis estreptocócica. La fiebre reumática aguda generalmente ocurre de 2–4 semanas después de una infección no tratada y afecta el corazón, piel, articulaciones y sistema nervioso. Esta condición comúnmente se presenta con fiebre, artritis de las grandes articulaciones, pancarditis y, a veces, erupción cutánea y manifestaciones neurológicas. El diagnóstico se hace HACE Altitude Sickness clínicamente con base en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria criterios de Jones y se confirma con pruebas serológicas. La prevención de la fiebre reumática aguda es la estrategia de tratamiento clave y se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el tratamiento antibiótico oportuno de la infección primaria, así como en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la profilaxis antibiótica de los LOS Neisseria episodios recurrentes. El tratamiento de los LOS Neisseria episodios agudos es primordialmente de soporte e incluye medicamentos antiinflamatorios. La complicación más grave de la fiebre reumática aguda es el desarrollo de cardiopatía reumática, que se manifiesta con mayor frecuencia como estenosis de la válvula mitral.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La fiebre reumática aguda es una afección autoinmune que se desarrolla como una complicación de una infección estreptocócica.
La patogenia no se comprende completamente.
La predisposición genética es probable, ya que la fiebre reumática tiende a ser familiar:
El principal mecanismo implícito es el mimetismo molecular:
Fase aguda
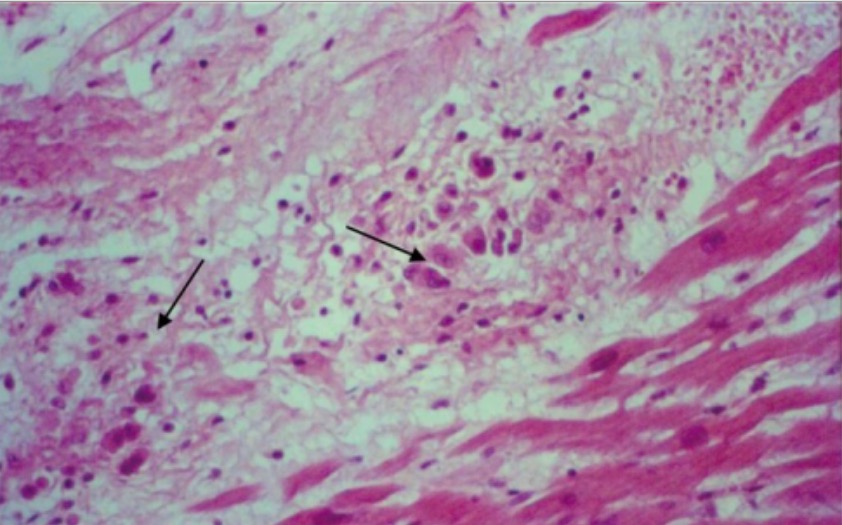
Cuerpos de Aschoff (flechas) en el músculo papilar de la válvula mitral
Imagen: “Histopathological findings” por Valvular Heart Disease Department, Heart Institute (InCor), University of São Paulo Medical School, São Paulo, Brazil. Licencia: CC BY 4.0Fase crónica
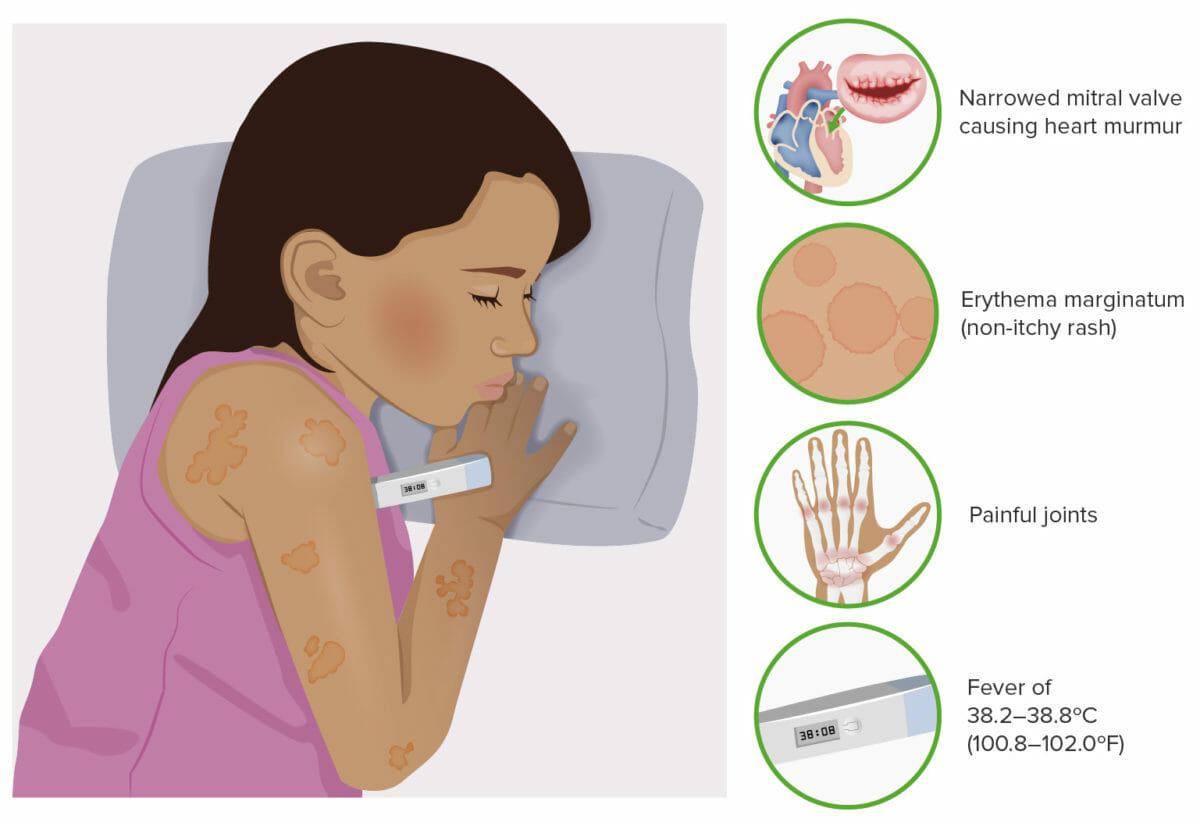
Síntomas típicos de la fiebre reumática
Imagen por Lecturio.Para recordar las principales manifestaciones clínicas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la fiebre reumática aguda, recuerde los LOS Neisseria criterios de Jones (escritos como J❤NES, en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés):
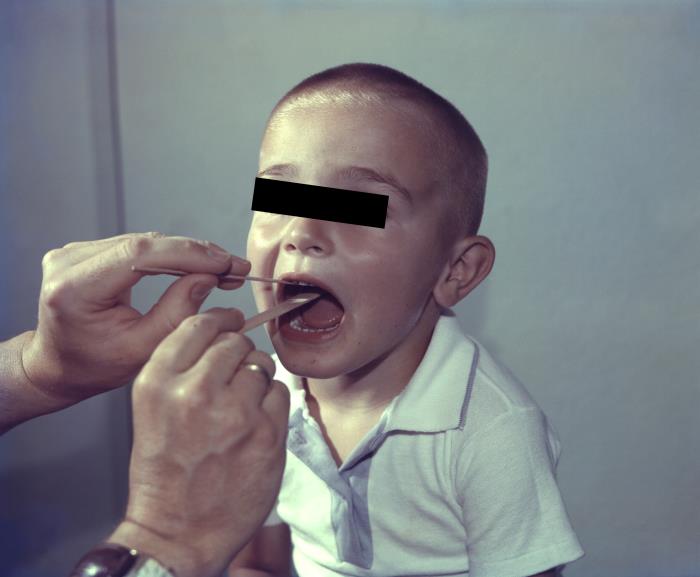
Es necesario obtener una muestra de frotis de garganta por sospecha de faringitis estreptocócica.
Imagen: “10190” por CDC/ Dr. M. Moody. Licencia: Dominio Público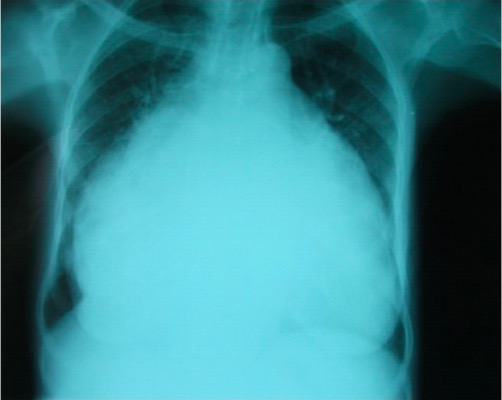
Radiografía de tórax que muestra cardiomegalia marcada asociada con estenosis reumática de la válvula mitral
Imagen: “Chest radiography” por Institut de Cardiologie d’Abidjan, BP V 206 Abidjan, Cote d’Ivoire ; Thorax and Vessels Department, Université de Cocody, 01 BP 166 Abidjan, Cote d’Ivoire. Licencia: CC BY 3.0
Cuadros ecocardiográficos en el eje largo paraesternal (A) y apical de 4 cámaras (B) vistas de una niña de 13 años con estenosis mitral grave e insuficiencia leve, que muestra una aurícula izquierda gigante
MV: válvula mitral
LV: ventrículo izquierdo
RV: ventrículo derecho
RA: aurícula derecha
Objetivos:
Erradicación de la infección estreptocócica:
Artritis:
Carditis Carditis Rheumatic Fever severa:
La corea de Sydenham suele ser autolimitada y no requiere tratamiento específico.
| Presentación de fiebre reumática | Duración de la profilaxis |
|---|---|
| Fiebre reumática con carditis Carditis Rheumatic Fever y cardiopatía residual (enfermedad valvular persistente) | 10 años o hasta los LOS Neisseria 40 años (lo que sea mayor); puede ser necesaria la profilaxis de por vida |
| Fiebre reumática con carditis Carditis Rheumatic Fever pero sin cardiopatía residual (sin enfermedad valvular) | 10 años o hasta los LOS Neisseria 21 años (lo que sea mayor) |
| Fiebre reumática sin carditis Carditis Rheumatic Fever | 5 años o hasta los LOS Neisseria 21 años (lo que sea mayor) |