La epiglotitis (o "supraglotitis") es una inflamación de la epiglotis y de las estructuras supraglóticas adyacentes. La mayoría de los LOS Neisseria casos están causados por una infección bacteriana; sin embargo, se han identificado varios patógenos virales y fúngicos, en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum función del estado inmunitario y la edad del paciente. Los LOS Neisseria síntomas son de rápida aparición y graves. Si no se trata, la epiglotitis puede causar una obstrucción de las vías respiratorias potencialmente mortal que se presenta con dificultad para respirar, estridor y cianosis. El diagnóstico es principalmente clínico, pero puede confirmarse mediante laringoscopia. El tratamiento se centra en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el manejo de las vías respiratorias y la administración de antibióticos.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
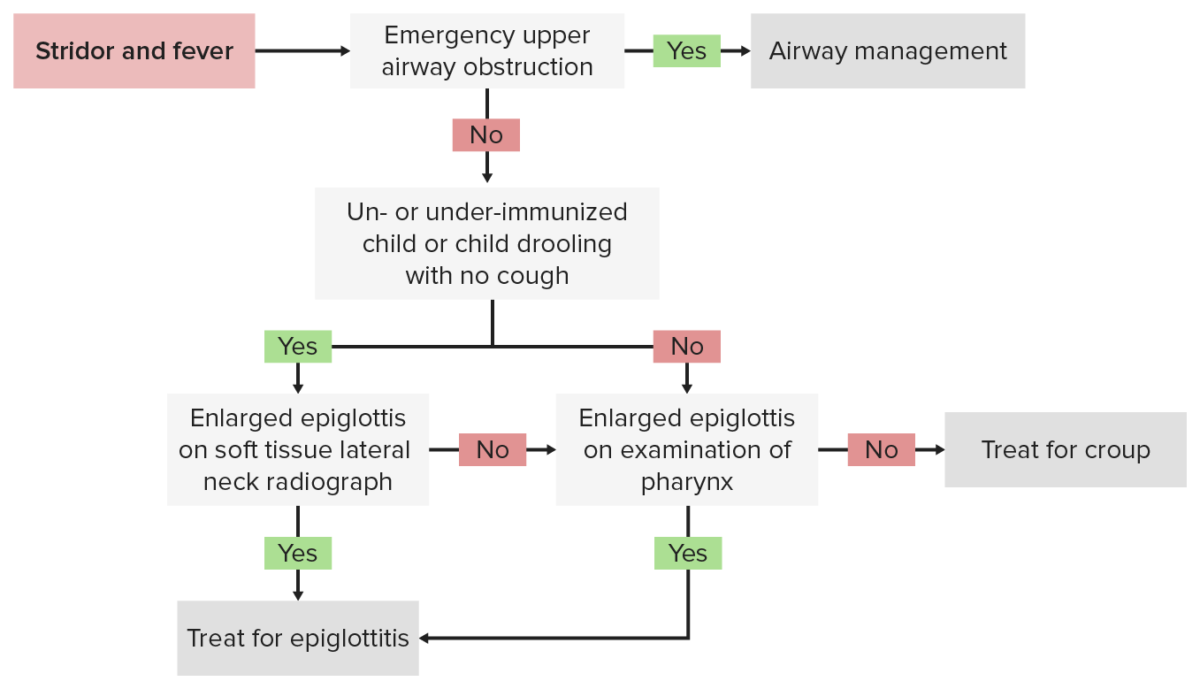
Algoritmo diagnóstico de la epiglotitis
Imagen por Lecturio.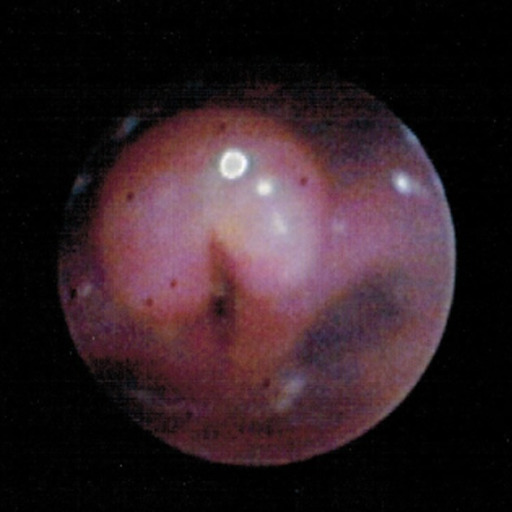
La imagen de la broncoscopia muestra una epiglotis y aritenoides hinchados e inflados junto con pliegues ariepiglóticos consistentes con una epiglotitis aguda (supraglotitis).
Image: “Bronchoscopy” por Department of Pediatrics, University of Toledo Toledo, Ohio, United States of America. Licencia: CC BY 3.0
Epiglotitis aguda que se presenta con el “signo del pulgar” en una radiografía lateral del cuello
Image: “Acute epiglottitis; Lateral view in X-ray imaging.” por Med Chaos – Obra propia. Licencia: CC0El pronóstico es bueno si se diagnostica y se trata inmediatamente, pero la enfermedad puede conducir a la muerte si hay una obstrucción aguda y no tratada de las vías respiratorias.
Complicaciones de la epiglotitis