La enfermedad de Crohn es una condición crónica y recurrente que provoca una inflamación transmural irregular que puede afectar a cualquier parte del tracto gastrointestinal. Es un tipo de enfermedad inflamatoria intestinal junto con la colitis Colitis Inflammation of the colon section of the large intestine, usually with symptoms such as diarrhea (often with blood and mucus), abdominal pain, and fever. Pseudomembranous Colitis ulcerosa. Suelen estar afectados el íleon terminal y el colon Colon The large intestines constitute the last portion of the digestive system. The large intestine consists of the cecum, appendix, colon (with ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid segments), rectum, and anal canal. The primary function of the colon is to remove water and compact the stool prior to expulsion from the body via the rectum and anal canal. Colon, Cecum, and Appendix: Anatomy proximal. La enfermedad de Crohn suele presentarse con diarrea intermitente, sin sangre, y dolor Dolor Inflammation abdominal tipo cólico. Las manifestaciones extraintestinales pueden incluir cálculos renales de oxalato de calcio, cálculos biliares, eritema nodoso y artritis. El diagnóstico se establece a través de una endoscopia con biopsia que muestra una inflamación transmural, una mucosa característica en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum forma de adoquín y granulomas Granulomas A relatively small nodular inflammatory lesion containing grouped mononuclear phagocytes, caused by infectious and noninfectious agents. Sarcoidosis no caseificantes. El tratamiento es con corticosteroides, azatioprina, antibióticos y agentes anti factor de necrosis Necrosis The death of cells in an organ or tissue due to disease, injury or failure of the blood supply. Ischemic Cell Damage tumoral (anti-TNF, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés) ( infliximab Infliximab A chimeric monoclonal antibody to tnf-alpha that is used in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis; ankylosing spondylitis; psoriatic arthritis and Crohn's disease. Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs) y adalimumab Adalimumab A humanized monoclonal antibody that binds specifically to tnf-alpha and blocks its interaction with endogenous tnf receptors to modulate inflammation. It is used in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis; psoriatic arthritis; Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs)). Las complicaciones son malabsorción, desnutrición, obstrucción intestinal o fístulas, y un mayor riesgo de cáncer de colon Colon The large intestines constitute the last portion of the digestive system. The large intestine consists of the cecum, appendix, colon (with ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid segments), rectum, and anal canal. The primary function of the colon is to remove water and compact the stool prior to expulsion from the body via the rectum and anal canal. Colon, Cecum, and Appendix: Anatomy.
Last updated: Sep 22, 2025
Se desconoce la fisiopatología exacta, pero es probable que esté asociada a una combinación de desregulación del epitelio intestinal y del sistema inmunitario.
Localización y patrón de inflamación:
La presentación típica de la enfermedad de Crohn es un trastorno recidivante que incluye:
La reactivación de la enfermedad de Crohn en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum un período asintomático puede ser desencadenada por el estrés físico o psicológico, los LOS Neisseria cambios bruscos o drásticos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la dieta y el tabaquismo.
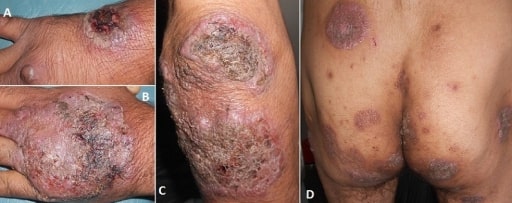
Pioderma gangrenoso
Imagen: “Vegetating idiopathic pyoderma gangrenosum” por Service de Dermatologie, CHU Ibn Sina, Rabat, Maroc. Licencia: CC BY 2.0El diagnóstico de la enfermedad de Crohn debe sospecharse si un paciente presenta los LOS Neisseria síntomas antes mencionados de dolor Dolor Inflammation abdominal, diarrea crónica intermitente, fatiga y pérdida de peso. El examen inicial incluye lo siguiente:
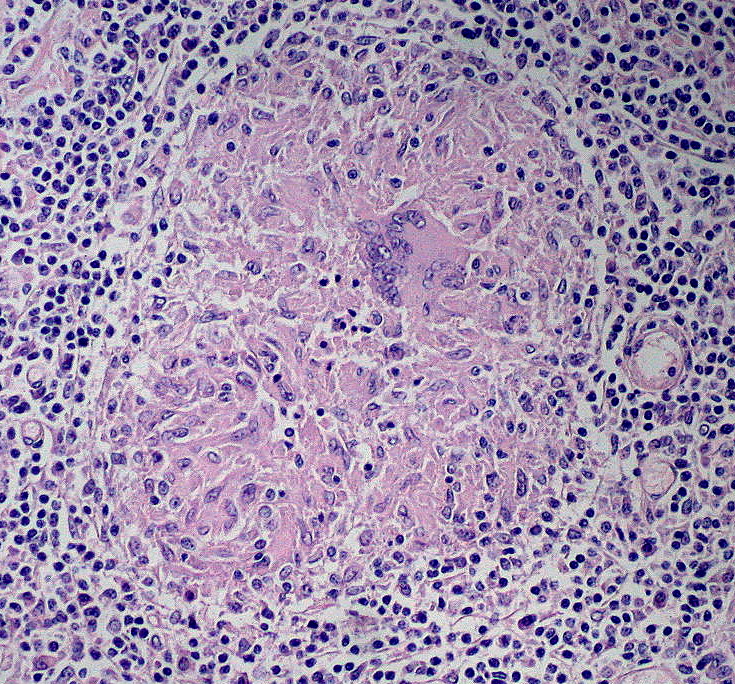
Granuloma no caseificante
Imagen: “Noncaseating Granuloma” por Ed Uthman. Licencia: CC BY 2.0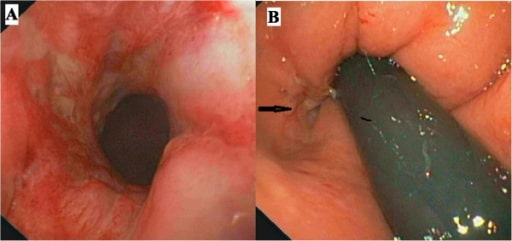
Colonoscopia. El panel A muestra la mucosa rectal inflamada y el panel B (flecha) la apertura de una fístula anal.
Imagen: “Colonoscopy” por Gastroenterology Unit, Department of Medicine and Surgery, University of Salerno, Baronissi Campus, via S, Allende, 84081 Baronissi, Salerno, Italy. Licencia: CC BY 4.0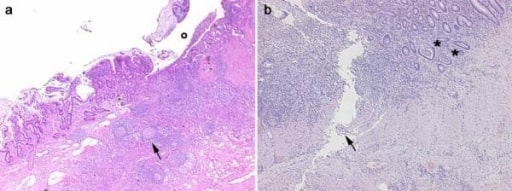
Imágenes histológicas obtenidas de 2 pacientes con enfermedad inflamatoria intestinal. Panel A, enfermedad de Crohn: en la sección transmural es claramente evidente una ulceración (o) en la mucosa y submucosa con infiltrados inflamatorios difusos, nódulos pseudofoliculares (flecha) y fibrosis de la pared intestinal. Panel B, colitis ulcerosa: la infiltración inflamatoria es más evidente en la mucosa y submucosa con abscesos de criptas (asteriscos). Es evidente una úlcera lineal serpiginosa (flecha).
Imagen: “Histological images obtained from two IBD patients enrolled in the study affected by CD” por Department of Surgery, Ospedale Maggiore di Milano, IRCCS, University of Milan, V. F. Sforza, 35 – 20122, Milan, Italy. Licencia: CC BY 2.0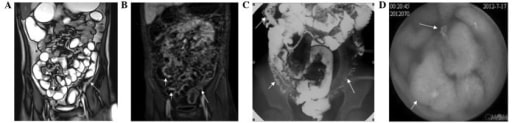
(A) La elastografía por resonancia magnética (RM) muestra un engrosamiento irregular de la pared, separación de las asas ileales (flecha blanca corta), engrosamiento de la pared del colon y estenosis luminal (flecha blanca larga);
(B) La RM muestra un engrosamiento de la pared del íleon distal (flechas blancas cortas) y del colon descendente (flechas blancas largas) con un realce significativo;
(C) La radiografía gastrointestinal convencional muestra estenosis del íleon distal (flechas blancas cortas) y del colon descendente (flechas blancas largas), edema y ensanchamiento del espacio graso alrededor del intestino;
(D) La videocápsula endoscópica muestra ulceraciones (flecha blanca corta) y lesiones polipoides (flecha blanca larga) en el íleon.
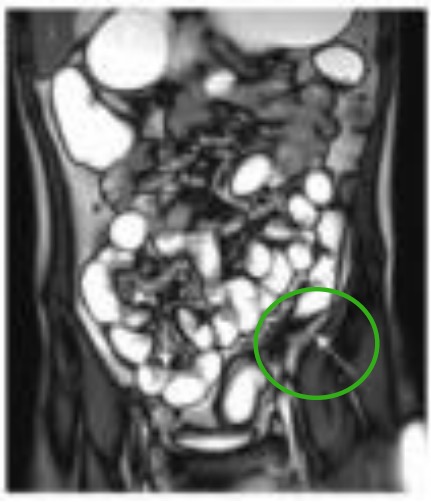
Asa ileal dilatada con engrosamiento irregular de la pared (flecha blanca en el cuadrante inferior derecho) y engrosamiento de la pared del colon descendente y estenosis luminal (flecha blanca en círculo verde en el cuadrante inferior izquierdo).
Imagen: “MRE, CGR and VCE correlation” por Departments of Radiology, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou, Zhejiang 310000, P.R. China. Licencia: CC BY 3.0, editada por Lecturio.Las terapias médicas para la enfermedad de Crohn dependen de la gravedad de la enfermedad. Los LOS Neisseria 2 objetivos terapéuticos principales son poner fin a un ataque agudo y sintomático y prevenir los LOS Neisseria ataques recurrentes.
En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum general, el tratamiento consiste en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum lo siguiente:
Las siguientes condiciones son diagnósticos diferenciales de la enfermedad de Crohn:
| Enfermedad de Crohn | Colitis Colitis Inflammation of the colon section of the large intestine, usually with symptoms such as diarrhea (often with blood and mucus), abdominal pain, and fever. Pseudomembranous Colitis ulcerosa | |
|---|---|---|
| Patrón de compromiso | Lesiones
en
EN
Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins.
Erythema Nodosum parches
en
EN
Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins.
Erythema Nodosum cualquier parte del tracto gastrointestinal:
|
Lesiones continuas:
|
| Síntomas gastrointestinales | Generalmente diarrea no sanguinolenta, a veces puede ser sanguinolenta | Diarrea con sangre
|
| Manifestaciones extraintestinales | Colelitiasis y nefrolitiasis con cálculos de oxalato de calcio | Colangitis esclerosante primaria |
|
||
| Complicaciones |
|
|
|
||
| Hallazgos macroscópicos | Inflamación transmural
|
Inflamación de la mucosa y submucosa
|
| Hallazgos microscópicos |
|
|
| Tratamiento |
|
|