Eye: Anatomy
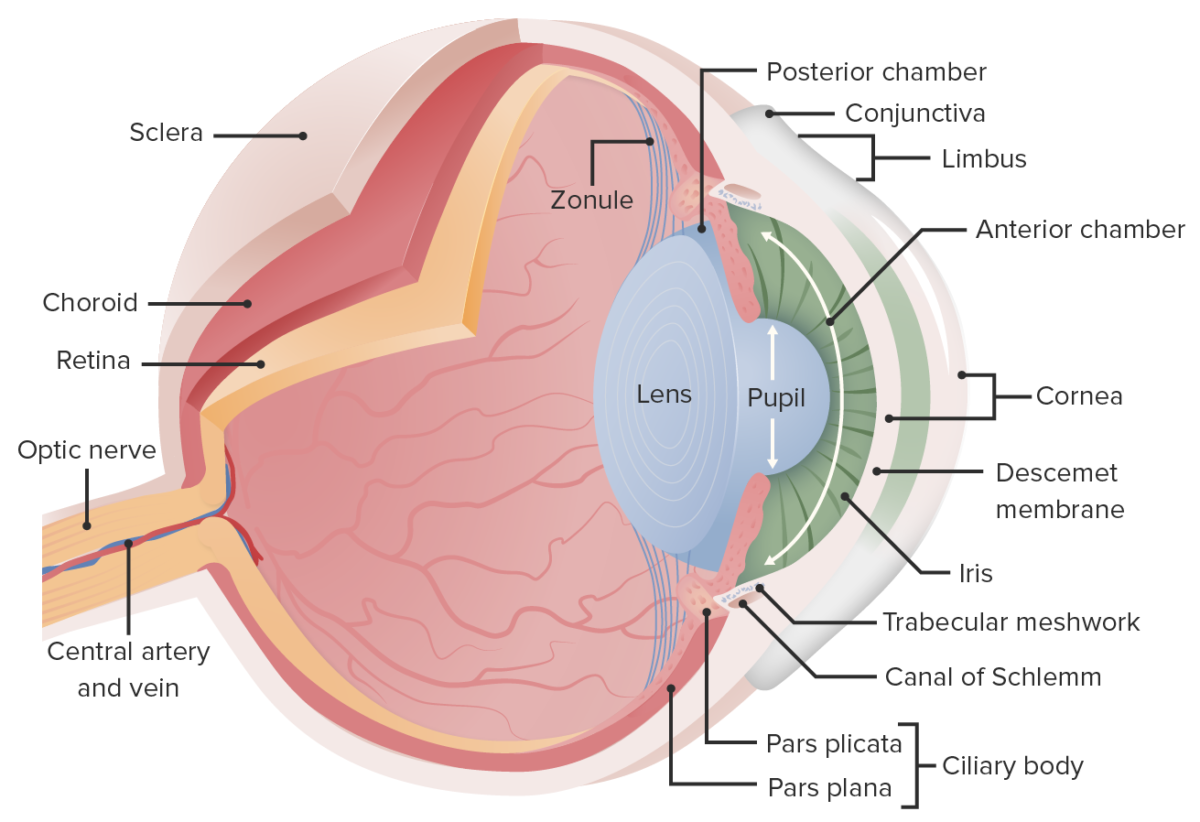
Development General Timeline Gross Anatomy General characteristics The adult eye is a complex organ contained within the orbital cavity (composed of 7 bones). Each eye has multiple layers and chambers and is surrounded by 6 extraocular muscles. Layers of the eye The eye is composed of 3 layers (fibrous, vascular, neural) and a transparent connective […]
Ophthalmic Exam
Introduction Overview Eye examination recommendations Recommended frequency of eye exams is not standard, but in general: A dilated exam helps diagnose: History Anatomy The eye and its appendages are situated in the orbit. The eyeball is spheroidal and attached to the extraocular muscles. Equipment for examination Vision Testing Visual acuity testing Snellen chart: Near-vision chart: […]
Corneal Abrasions, Erosion, and Ulcers
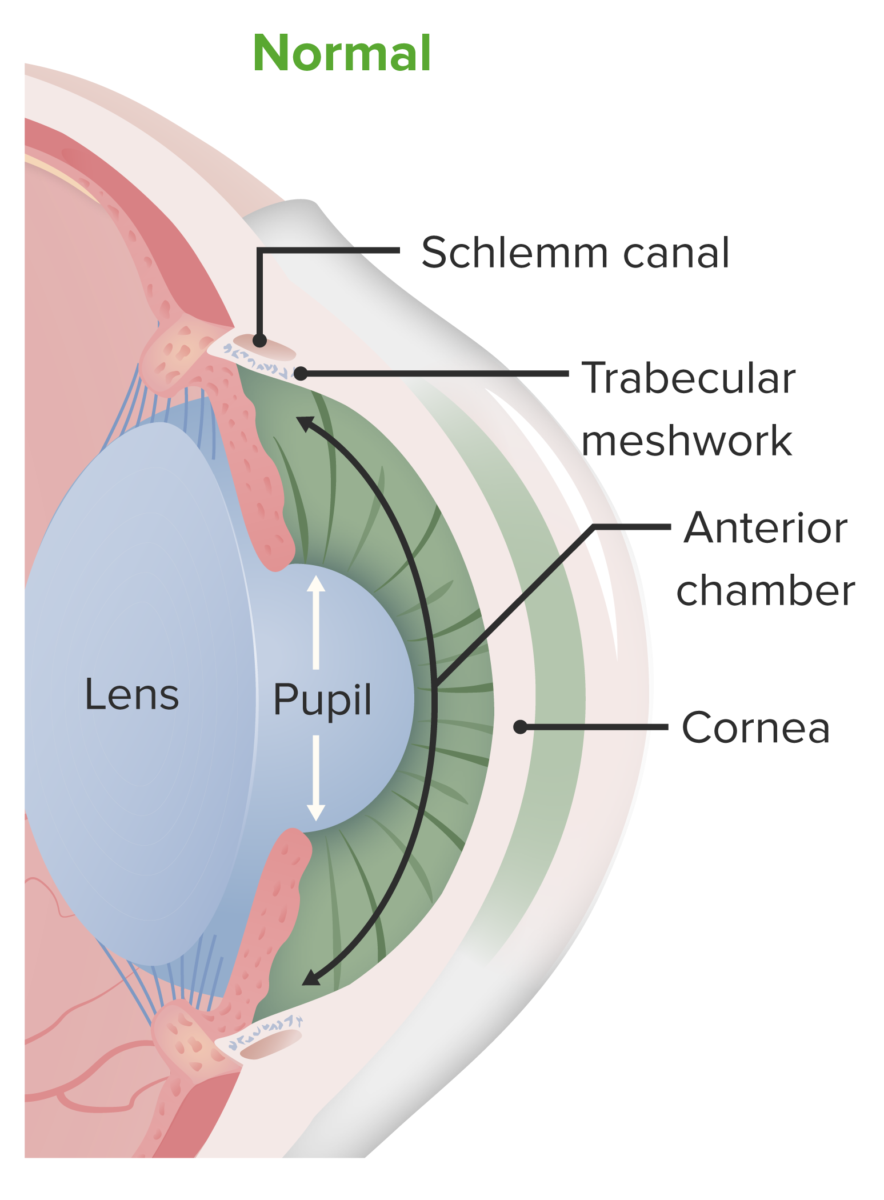
Overview Anatomy The cornea is a transparent, avascular part of the eye that covers the iris, anterior chamber, and pupil. The corneal layers include: Definition Corneal epithelial defects are conditions that disturb the structural integrity of the cornea. Corneal abrasions, erosions, and ulcers are defects in the corneal epithelium and are classified by the depth […]
Anomalies of the Cornea
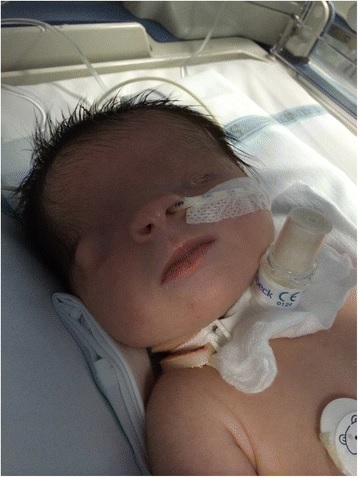
Overview Cornea The cornea is a transparent, avascular, watch glass-like structure that covers the iris, anterior chamber, and pupil. Classification of corneal abnormalities Cryptophthalmos Cryptophthalmos is an autosomal recessive congenital anomaly associated with systemic anomalies and is characterized by an uninterrupted continuity of the skin extending from the forehead to the malar region. Epidemiology Clinical […]
Orbital Fractures
Overview Definition An orbital fracture is a broken bone involving the eye socket, either in the orbital rim, the orbital floor, or both. Epidemiology Etiology Anatomy and Pathophysiology To understand the pathophysiology of orbital fractures, it is important to understand the anatomy of the orbit, the clinical presentation, and the potential consequences of fractures. Anatomy […]
Endophthalmitis
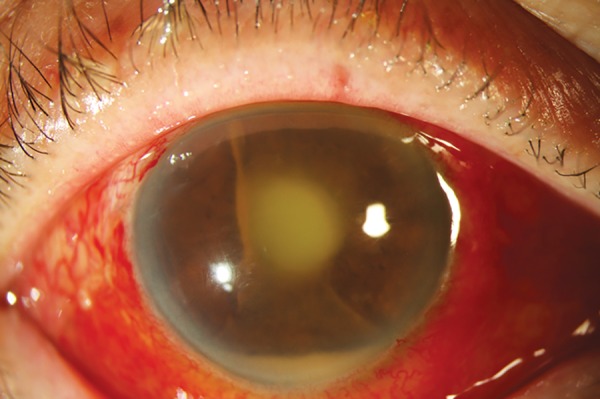
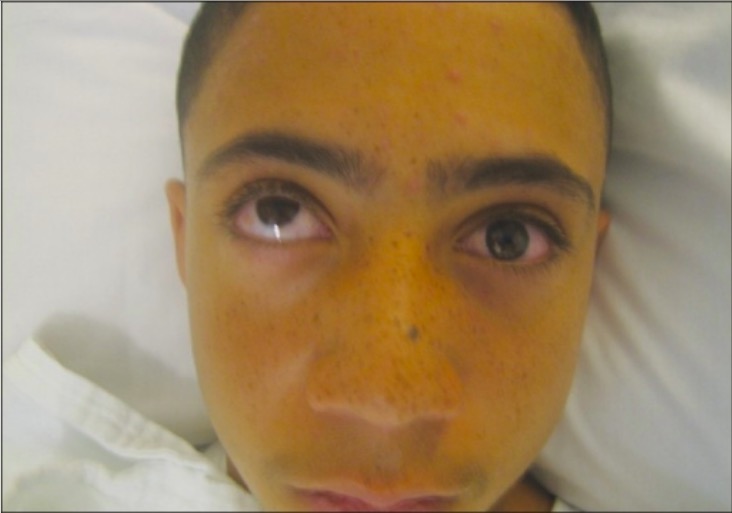
Definition and Epidemiology Definition Endophthalmitis is an inflammatory process of the intraocular cavities (e.g., aqueous and/or vitreous humor) usually caused by bacteria or fungi. Epidemiology Etiology Sterile endophthalmitis Infectious endophthalmitis Exogenous: Endogenous: Pathogenesis Normally, the ocular-blood barrier naturally resists invasive organisms. Exogenous endophthalmitis Pathophysiology: Risk factors: Endogenous endophthalmitis Pathophysiology: In unilateral cases, the right eye […]
The Visual Pathway and Related Disorders
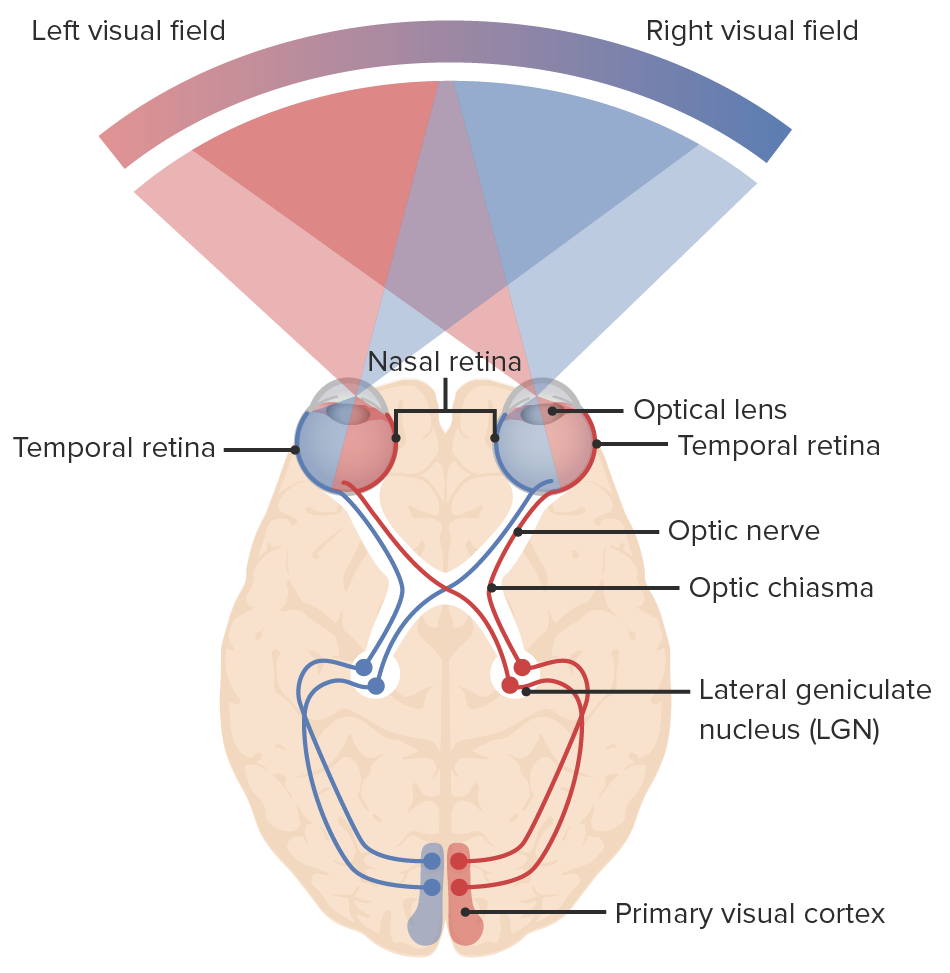
Visual Pathway Visual Fields Anterior to the OC Posterior to the OC Visual Field Defects Unilateral visual field defect Bilateral visual field defects Synopsis Table: Overview of visual field defects Site of lesion Visual field defect Description Possible cause Macula (central retina) Central scotoma Ipsilateral central vision loss Optic neuritis, retrobulbar neuritis Optic nerve Ipsilateral […]
Pupil: Physiology and Abnormalities
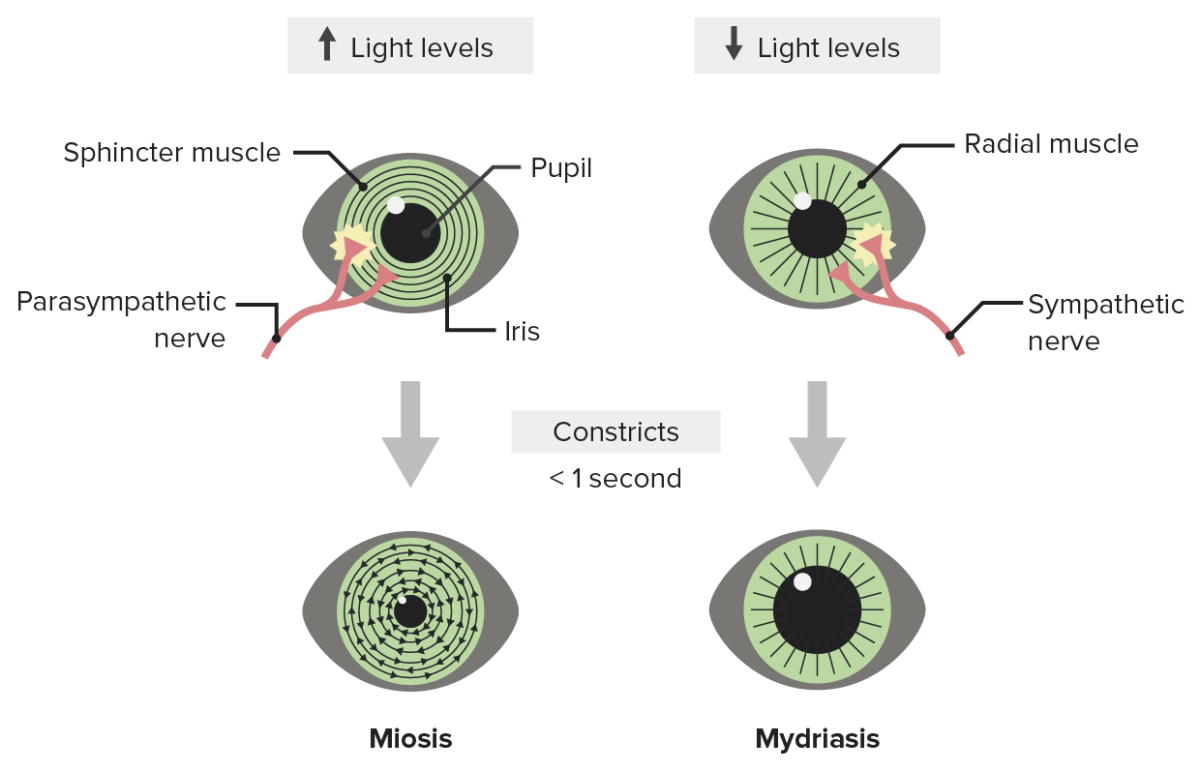
Overview Pupil Adjacent structures Physiology of the Pupil Visual pathway Afferent pathway From stimuli to the primary visual cortex: Parasympathetic innervation pathway (pupillary light reflex) Sympathetic innervation pathway Near response Consists of 3 responses: Examination of the Pupil Light and near response Pupil size Swinging-flashlight test Slit-lamp examination Pharmacologic tests Disorders of the Afferent Pathway […]
Hypertensive Retinopathy
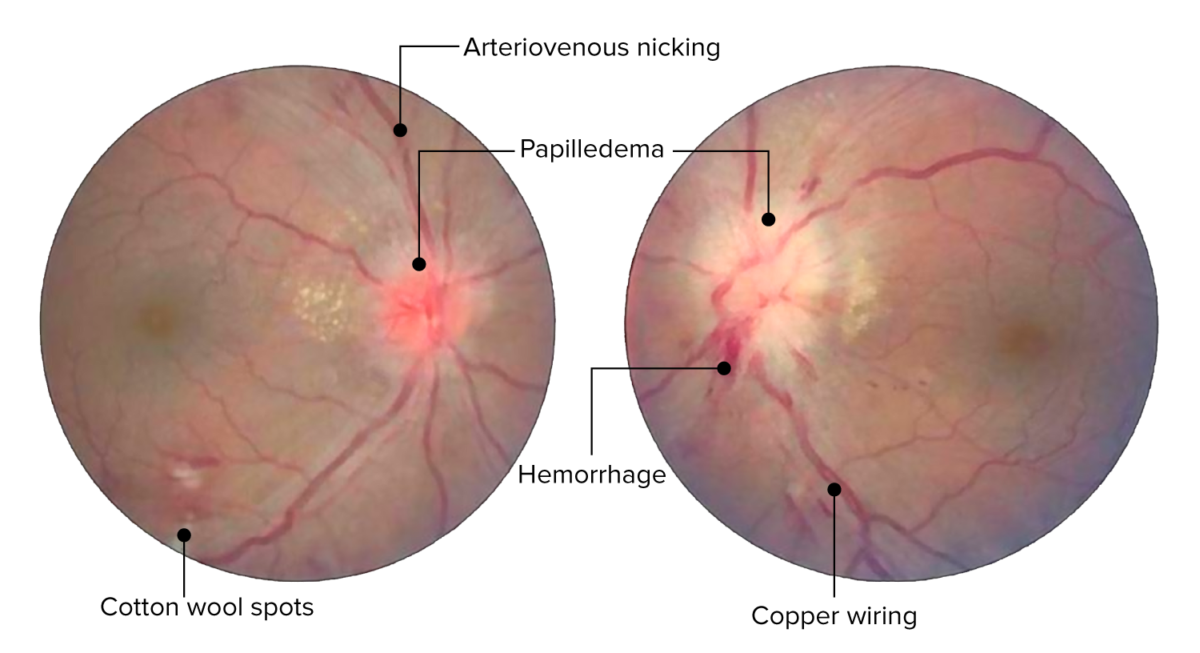
Overview Definition Hypertensive retinopathy: Hypertension: Blood pressure category Systolic blood pressure Diastolic blood pressure Elevated blood pressure 120–129 mm Hg AND < 80 mm Hg Hypertension stage 1 130–139 mm Hg OR 80–89 mm Hg Hypertension stage 2 ≥ 140 mm Hg OR ≥ 90 mm Hg Epidemiology Pathophysiology Vasoconstrictive phase Sclerotic phase Exudative phase […]
Hordeolum (Stye)
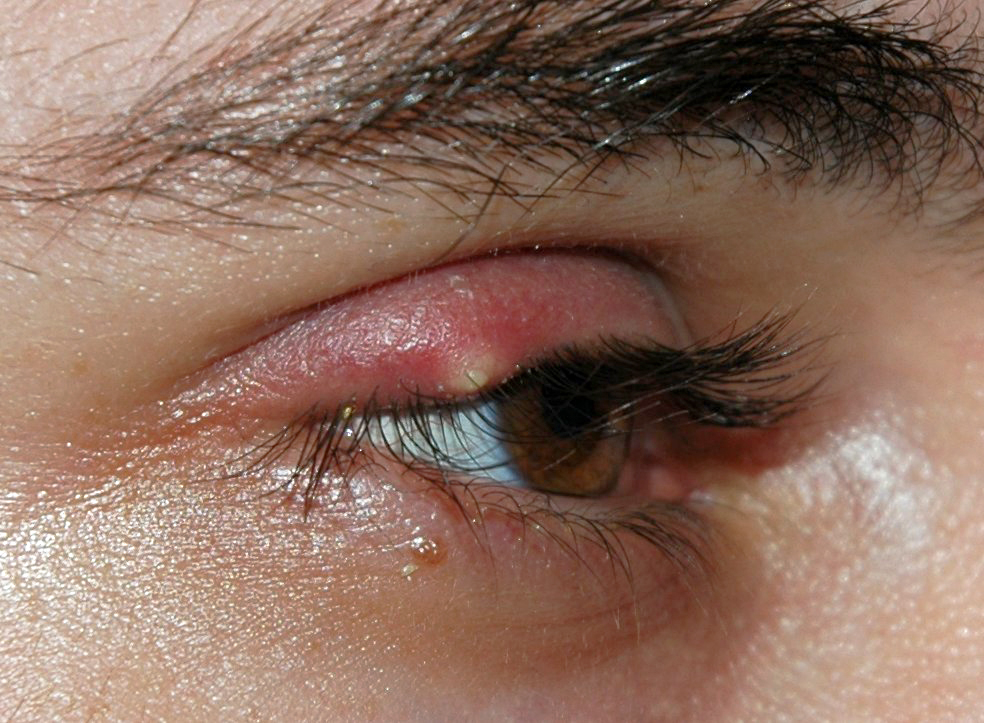
Overview Anatomy Hordeolum Table: Eyelid glands Name Type Opening location Infection Gland of Zeis Sebaceous gland Directly into the eyelash follicle External hordeolum Gland of Moll Modified sweat glands Between adjacent lashes External hordeolum Meibomian gland Modified sebaceous gland Behind eyelashes Internal hordeolum Etiology Clinical Presentation Complications Management Most hordeola resolve spontaneously, lasting up to […]