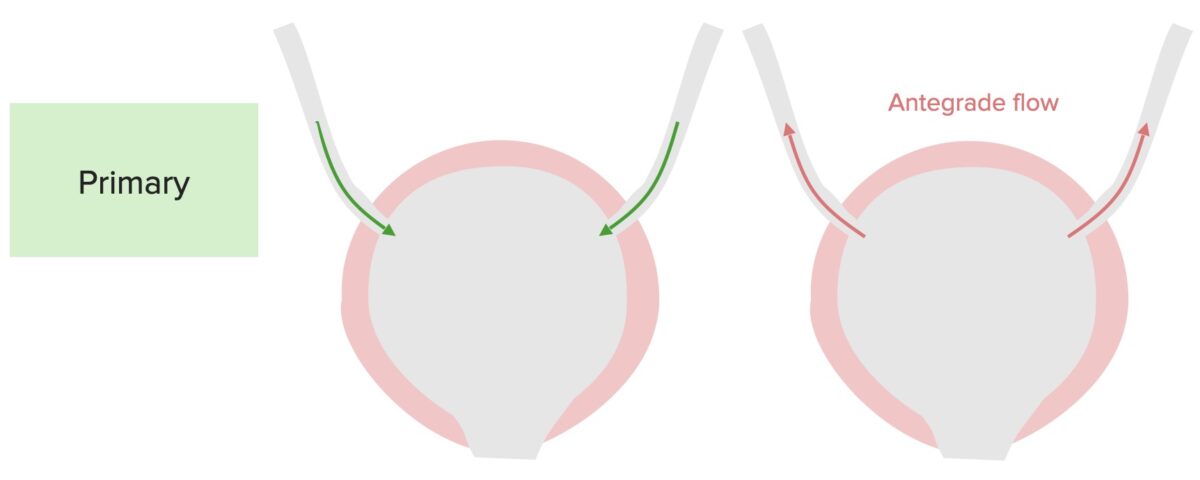
Vesicoureteral Reflux
Encephalitis
Methemoglobinemia

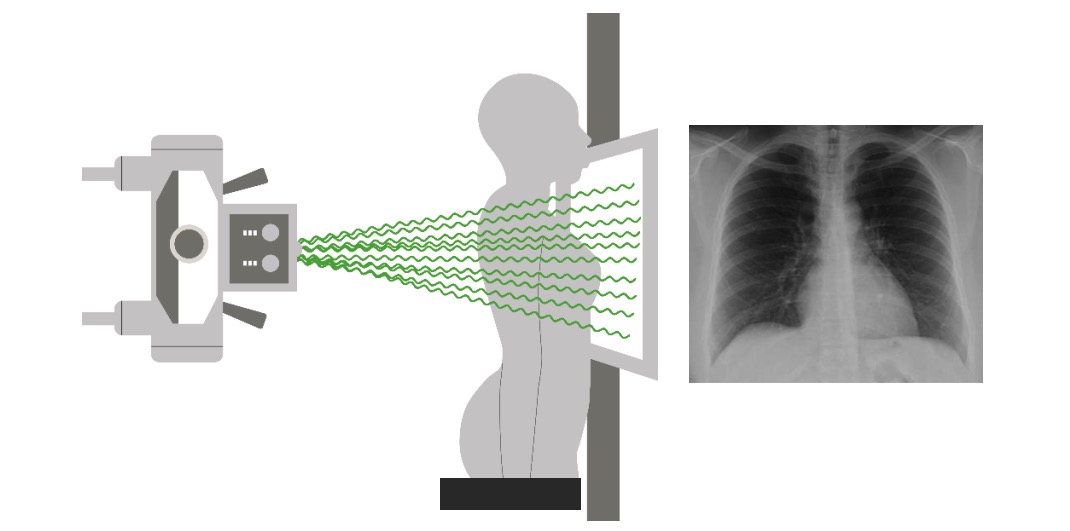
Imaging of the Lungs and Pleura
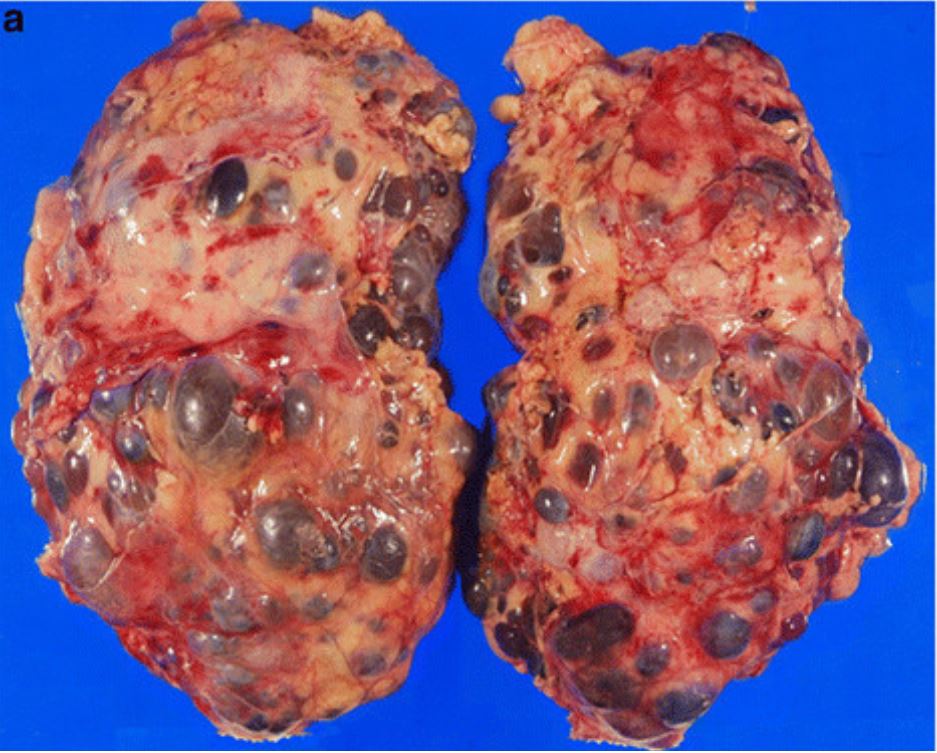
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD)
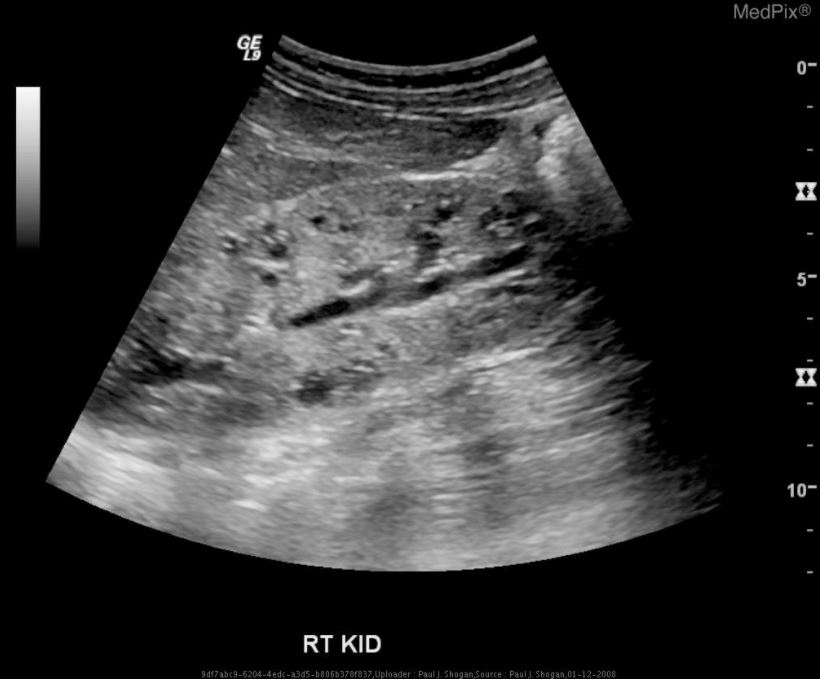
Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease (ARPKD)
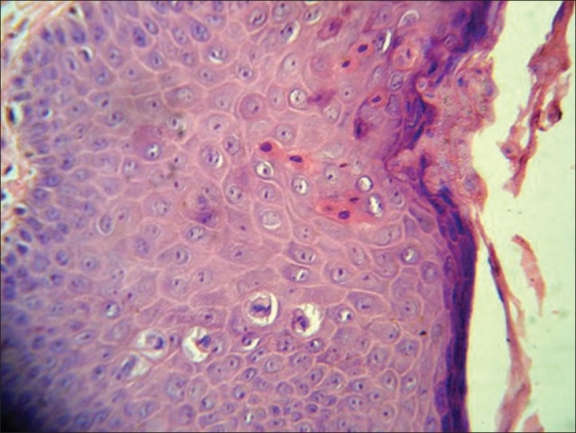
Bowenoid Papulosis
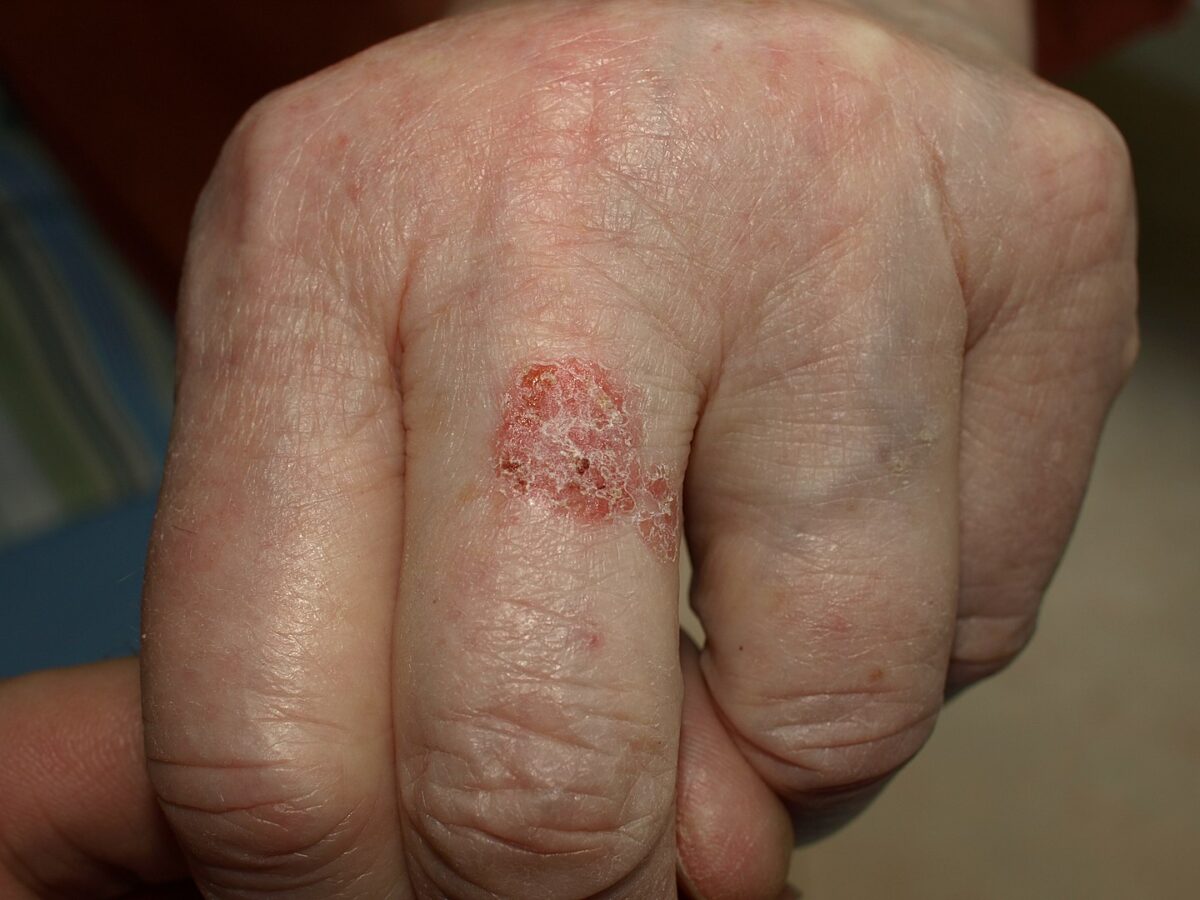
Bowen Disease and Erythroplasia of Queyrat
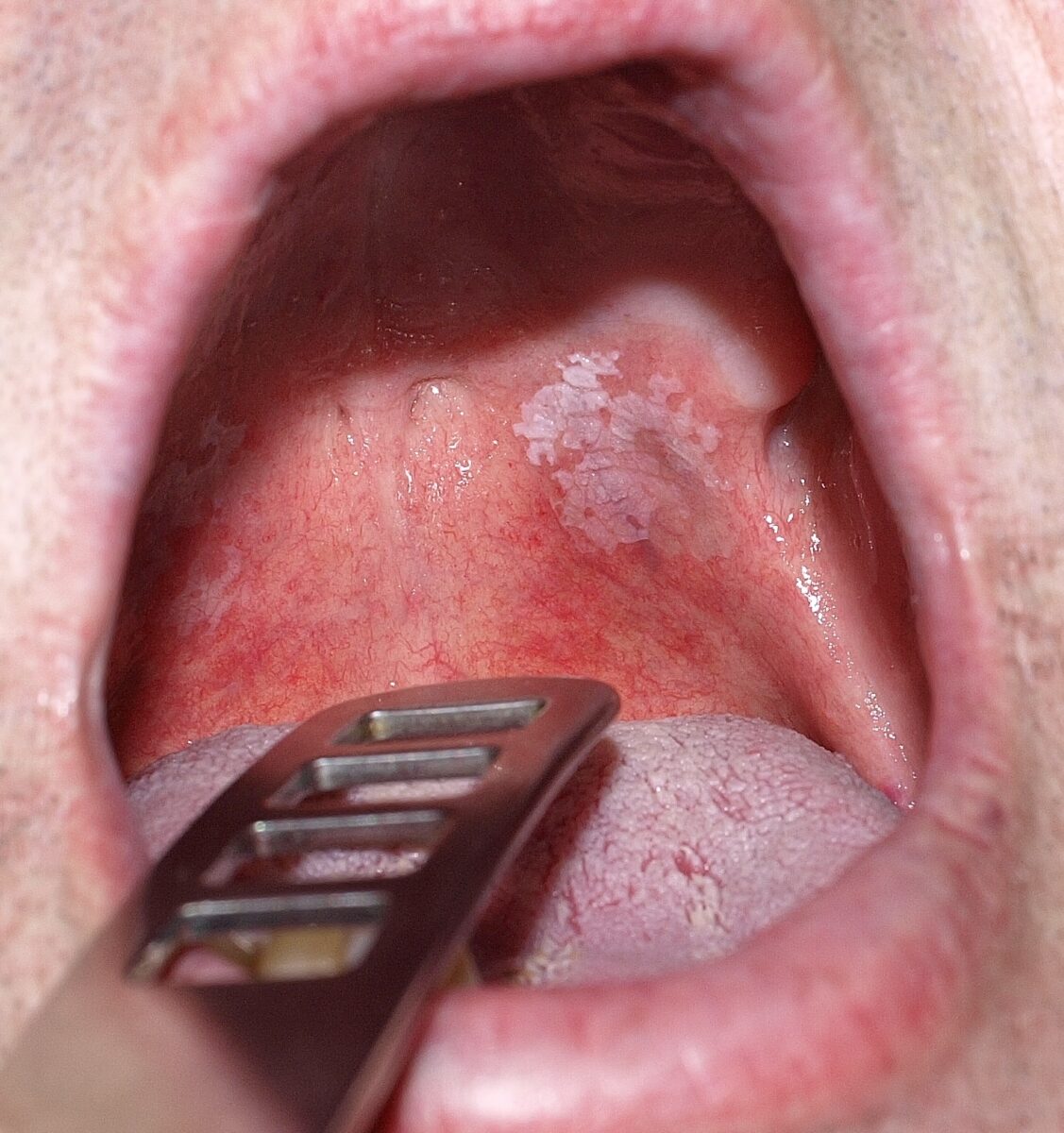
Leukoplakia
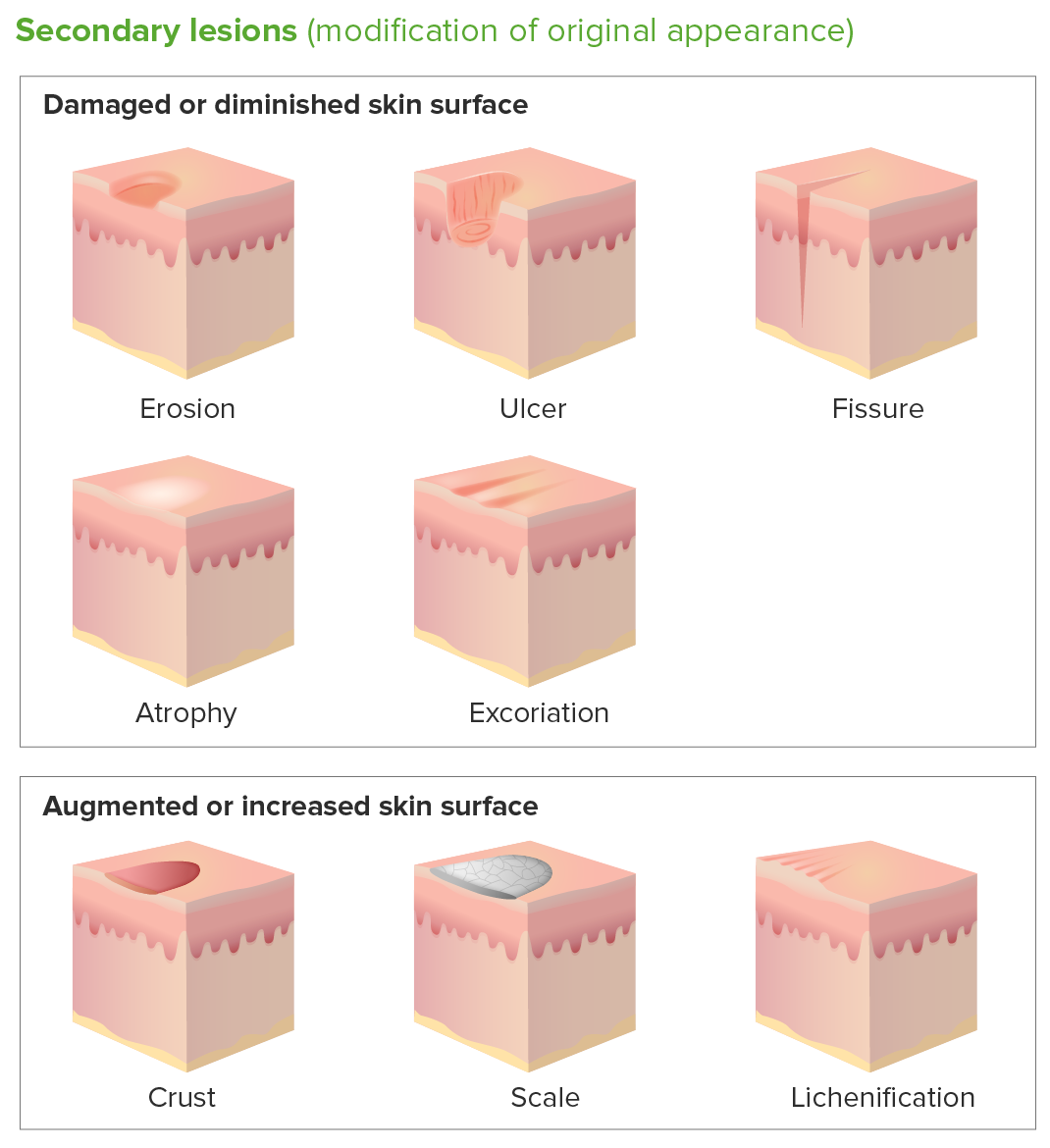
Secondary Skin Lesions