La uveítis es la inflamación de la úvea, la capa media pigmentada del ojo, que comprende el iris, el cuerpo ciliar y la coroides. La condición se clasifica en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum función de la localización de la enfermedad; la uveítis anterior es la más común. La uveítis puede ser causada por una infección o una enfermedad sistémica, pero en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum algunos casos la causa es idiopática. Los LOS Neisseria pacientes presentan visión borrosa, enrojecimiento del ojo y dolor Dolor Inflammation (frecuentemente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum uveítis anterior), o visión reducida y miodesopsias ( en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la uveítis intermedia y posterior). El diagnóstico se realiza mediante una fundoscopia dilatada y un examen con lámpara de hendidura. El tratamiento para la uveítis anterior consiste en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum esteroides tópicos, mientras que la uveítis en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum zonas más profundas requiere terapia periocular o sistémica. La uveítis por infecciones y trastornos sistémicos requiere un tratamiento dirigido a la etiología.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La uveítis es una inflamación de la úvea, la capa media del ojo, que comprende el iris, el cuerpo ciliar y la coroides.
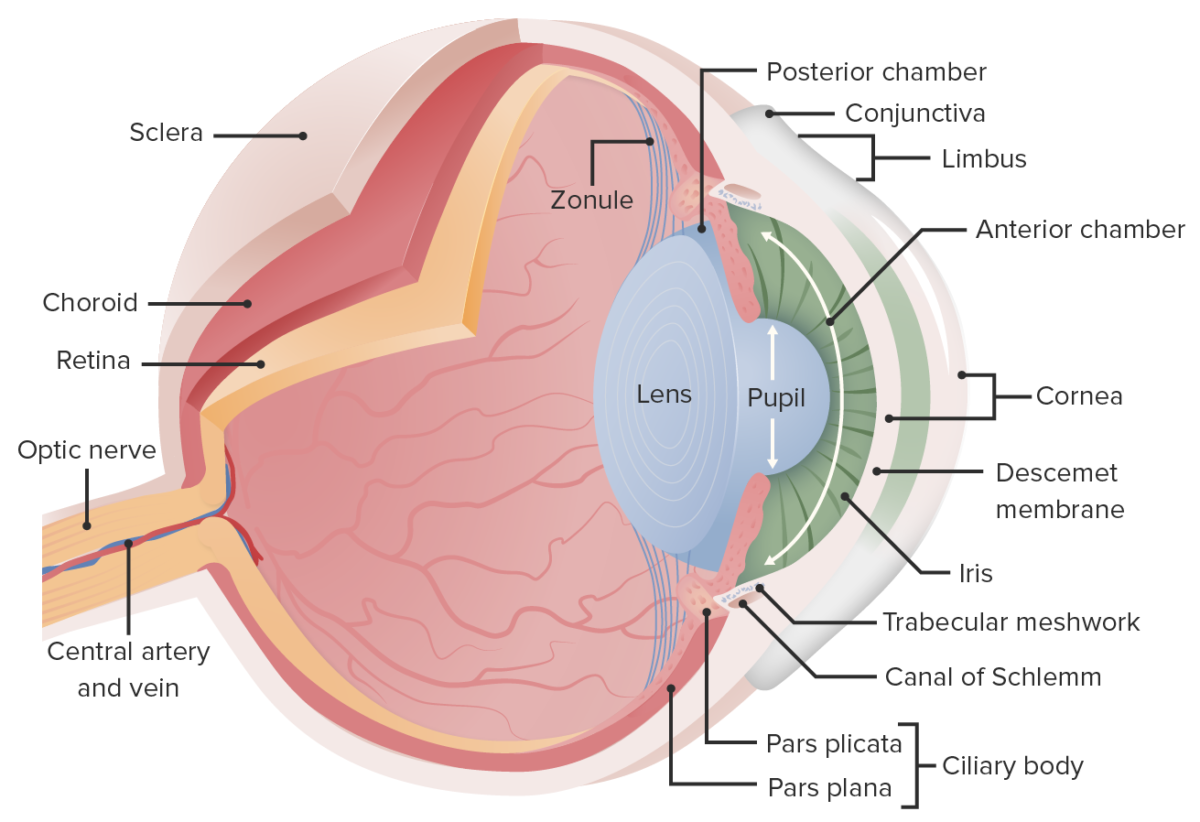
Esta imagen muestra la anatomía del ojo. En las cataratas, se produce un enturbiamiento del cristalino, que opacifica la luz cuando se proyecta en la retina; esto provoca una reducción de la visión, sobre todo por la noche, cuando los niveles de luz son bajos.
Imagen por Lecturio.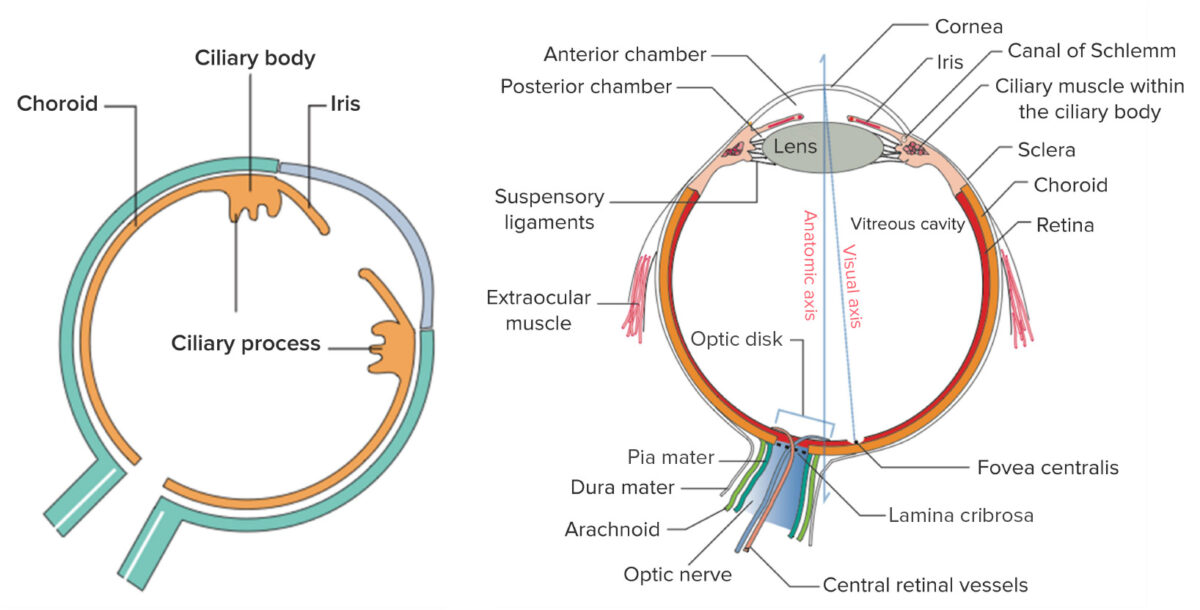
Izquierda: los componentes de la úvea, la capa vascular media del ojo
Derecha: estructura general del ojo
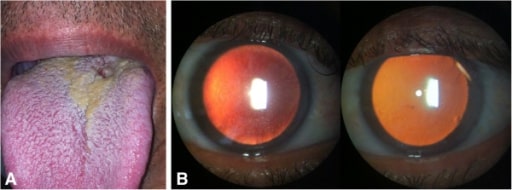
Uveítis anterior bilateral no granulomatosa asociada a la sífilis. (A): Lesión consistente con chancro sifilítico en la base de la lengua; (B): Examen con lámpara de hendidura: pequeños precipitados queráticos (derecha) y depósitos de fibrina sobre el endotelio corneal (izquierda) en retroiluminación.
Imagen: “initial presentation of syphilis” por Hospital de Olhos Santa Luzia, Estrada do Encanamento 909, CEP 52070-000, Recife-Pernambuco, Brazil. Licencia: CC BY 2.0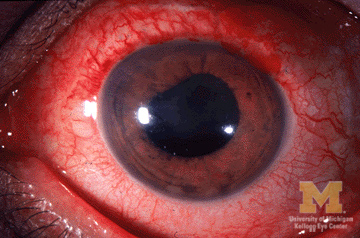
Imagen que muestra el enrojecimiento del ojo y la pupila irregular de la uveítis anterior
Imagen: “Anterior-uveitis” por Jonathan Trobe, M.D. Licencia: CC BY 3.0El diagnóstico se realiza mediante un examen de fondo de ojo dilatado y un examen con lámpara de hendidura. La depresión escleral es una maniobra adicional para visualizar las estructuras posteriores al AL Amyloidosis cristalino.
Hallazgos
Las pruebas de laboratorio y los LOS Neisseria estudios imagenológicos adicionales están indicados cuando los LOS Neisseria signos y síntomas extraoculares son atribuibles a una enfermedad causal (e.g., sarcoidosis Sarcoidosis Sarcoidosis is a multisystem inflammatory disease that causes noncaseating granulomas. The exact etiology is unknown. Sarcoidosis usually affects the lungs and thoracic lymph nodes, but it can also affect almost every system in the body, including the skin, heart, and eyes, most commonly. Sarcoidosis, sífilis).
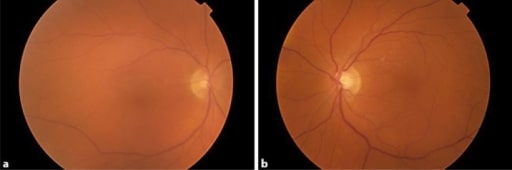
Fotografías del fondo de ojo que muestra la neblina vítrea en ambos ojos. El paciente fue tratado con dabrafenib y trametinib, y desarrolló una uveítis bilateral.
Imagen: “Uveitis as a Result of MAP Kinase Pathway Inhibition” por Royal Surrey County Hospital NHS Foundation Trust, Guildford, Surrey, London, UK. Licencia: CC BY 3.0
Mujer embarazada de 27 años con panuveítis por enfermedad de Behçet con rubor ciliar e hipopión (estratificación de leucocitos en la parte inferior de la cámara anterior)
Imagen: “Behçet’s Uveitis” por Department of Ophthalmology, Istanbul University, Istanbul Faculty of Medicine, Istanbul, Turkey. Licencia: CC BY 2.0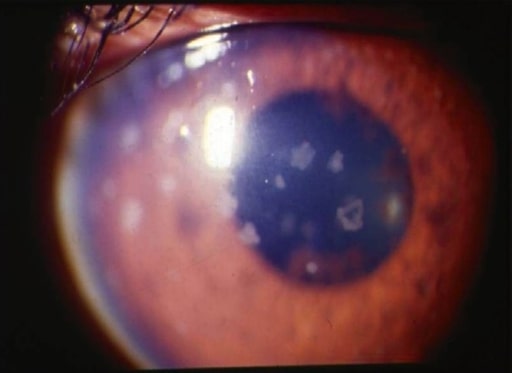
Uveítis anterior: fotografía con lámpara de hendidura que muestra grandes precipitados queráticos antiguos
Imagen: “anterior uveitis” por L. V. Prasad Eye Institute, Kallam Anji Reddy Campus, Hyderabad, India. Licencia: CC BY 2.0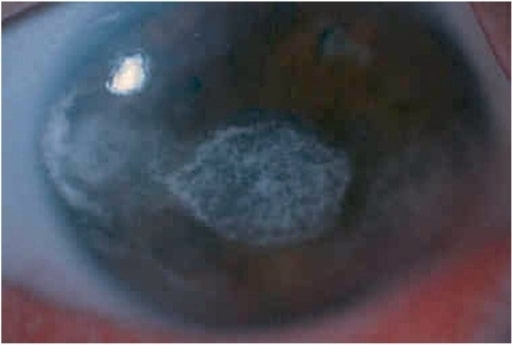
La iluminación difusa en la lámpara de hendidura muestra una queratopatía en banda grave en el ojo izquierdo de un niño con uveítis anterior (asociada a artritis idiopática juvenil).
Imagen: “keratopathy” por Department of Ophthalmology, Faculty of Medicine, Istanbul University, Istanbul, Turkey. Licencia: CC BY 2.5