El embarazo es el periodo de tiempo que transcurre entre la fecundación de un ovocito y el parto de un feto, aproximadamente 9 meses después. El 1er signo de embarazo suele ser la ausencia de la menstruación, tras lo cual, el embarazo debe confirmarse clínicamente mediante una prueba positiva de β-hCG (normalmente una prueba cualitativa de orina) y un ultrasonido pélvico. Existen numerosas adaptaciones maternas al AL Amyloidosis embarazo, tanto anatómicas como fisiológicas, que se producen para ayudar a mantener al AL Amyloidosis feto en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum desarrollo y preparar el cuerpo de la madre para el parto. El embarazo no es una condición patológica, pero un buen cuidado prenatal de rutina puede ayudar a lograr los LOS Neisseria mejores resultados tanto para la madre como para el bebé. La atención prenatal incluye la realización de pruebas de laboratorio y de ultrasonido adecuadas, la orientación anticipatoria y el ofrecimiento de soluciones o consejos para las molestias comunes del embarazo.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
El embarazo se define como el periodo de tiempo entre la fecundación de un ovocito y el parto de un feto, aproximadamente 9 meses después.
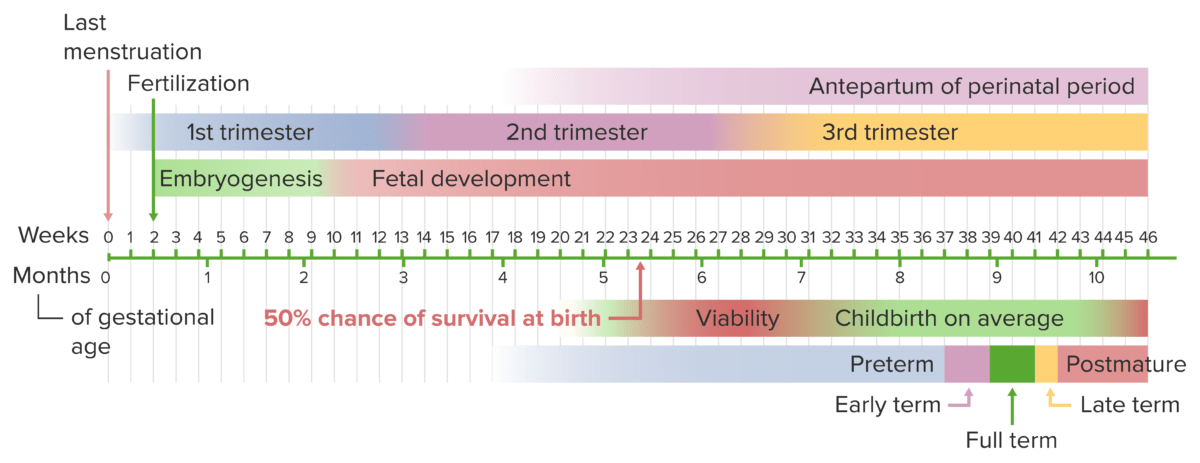
Cronología del embarazo desde el día de la última menstruación hasta el parto
Imagen por Lecturio.Las personas que intentan quedar embarazadas suelen presentar una prueba de embarazo casera positiva. Muchas otras pueden no saber que están embarazadas y presentarán síntomas de embarazo temprano, que pueden incluir:
El embarazo se confirma mediante pruebas de laboratorio y ultrasonidos obstétricos.
El principal análisis utilizado para establecer el embarazo es la β-hCG.
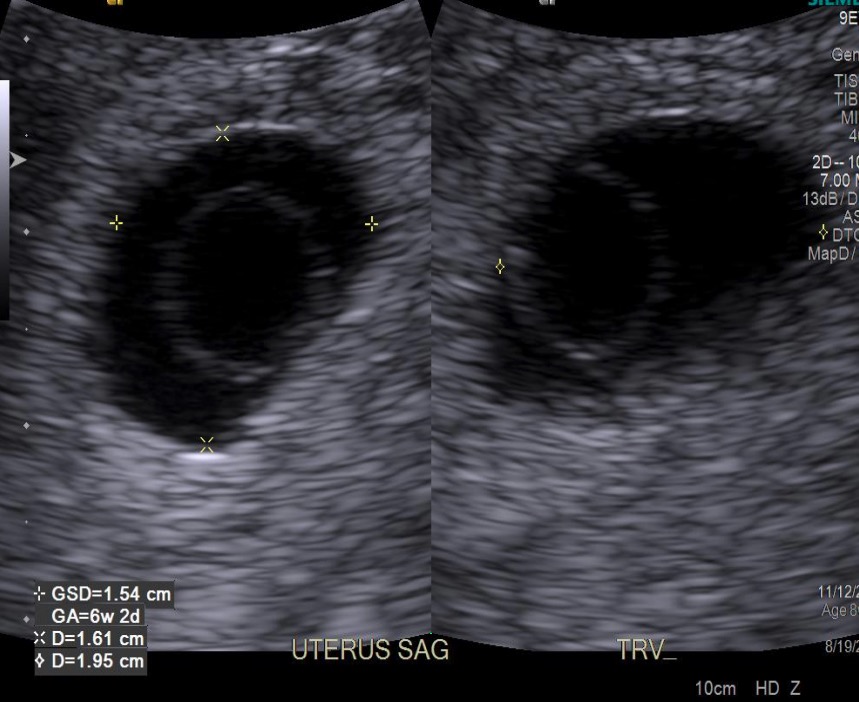
Saco vitelino dentro de un saco gestacional:
El saco vitelino es el “círculo blanco”, que está dentro del saco gestacional (el “círculo negro”).
GSD: diámetro del saco gestacional
GA: edad gestacional (basada en la medición de la GSD)
D: diámetro
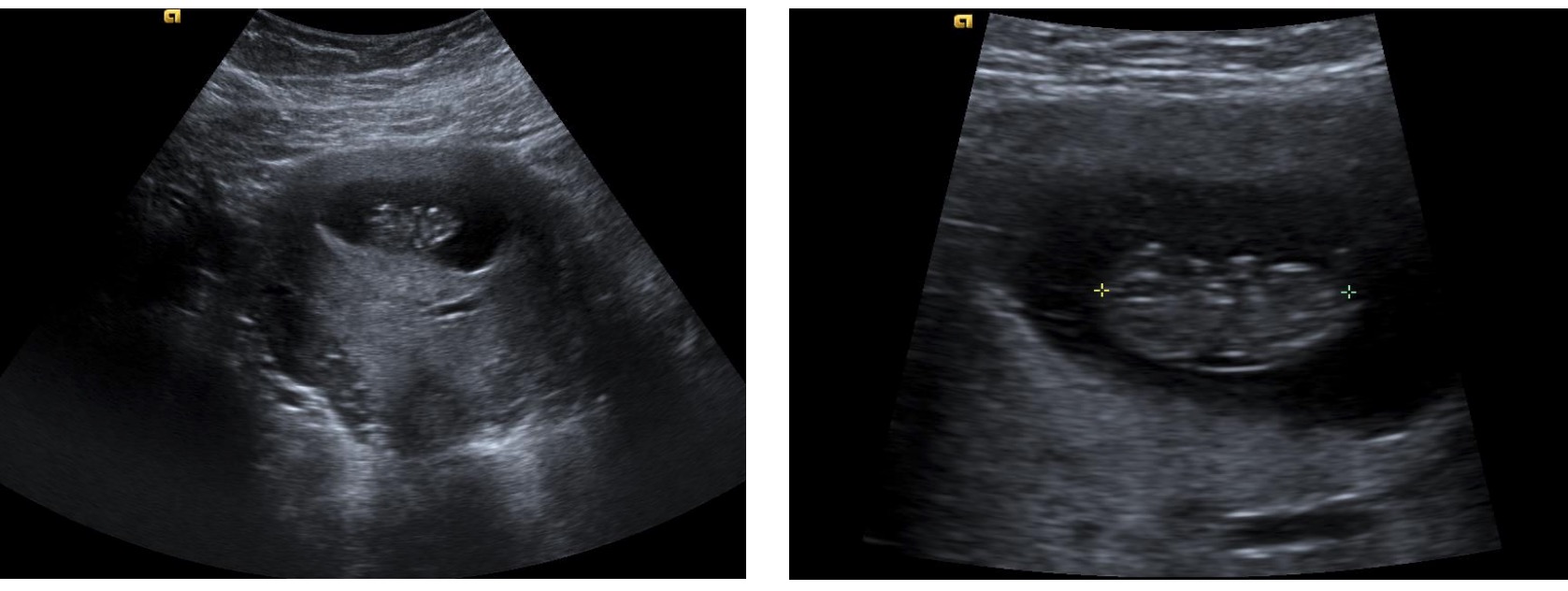
Embarazo intrauterino dentro de un saco gestacional:
La imagen de la derecha muestra la medición de la longitud cráneo-caudal. La cabeza del feto está a la izquierda y el extremo caudal a la derecha. También hay brotes tempranos de las extremidades. La placenta se encuentra en la parte inferior del saco gestacional en estas imágenes.
Establecer la FEP es uno de los LOS Neisseria factores más importantes que hay que cumplir después de diagnosticar un embarazo. La datación de un embarazo se suele hacer calculando la FEP a partir de la FUM y comparando esa fecha con la FEP obtenida a partir de las primeras mediciones ecográficas.
Para favorecer el crecimiento y el desarrollo del feto y preparar el cuerpo de la madre para un eventual parto, se producen numerosos cambios anatómicos y fisiológicos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el cuerpo de la mujer durante el embarazo.
Útero:
Cérvix:
Ovarios:
| Sistema | Parámetros que ↑ en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el embarazo | Parámetros que ↓ en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el embarazo | Síntomas y cambios anatómicos |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sistema cardiovascular |
|
|
|
| Sistema hematológico |
|
|
|
| Sistema respiratorio |
|
|
|
| Sistema gastrointestinal | Presión intraabdominal |
|
|
| Sistema renal |
|
|
|
| Sistemas endocrino y metabólico |
|
|
|
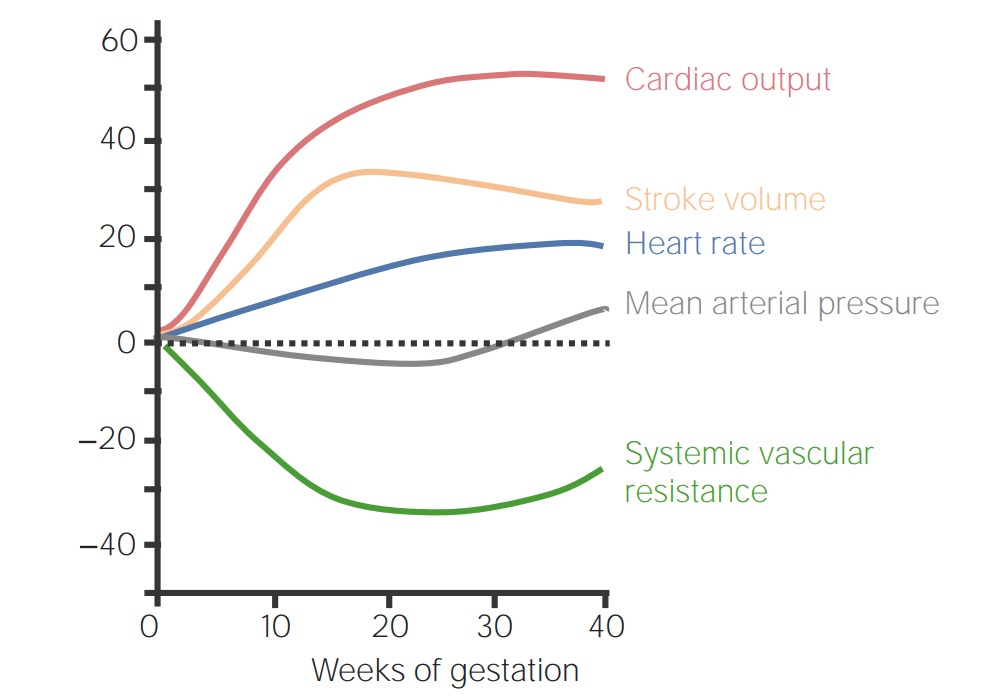
Cambios fisiológicos maternos en el sistema cardiovascular durante el embarazo: cambio porcentual sobre los valores sin embarazo
Imagen por Lecturio. Licencia: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0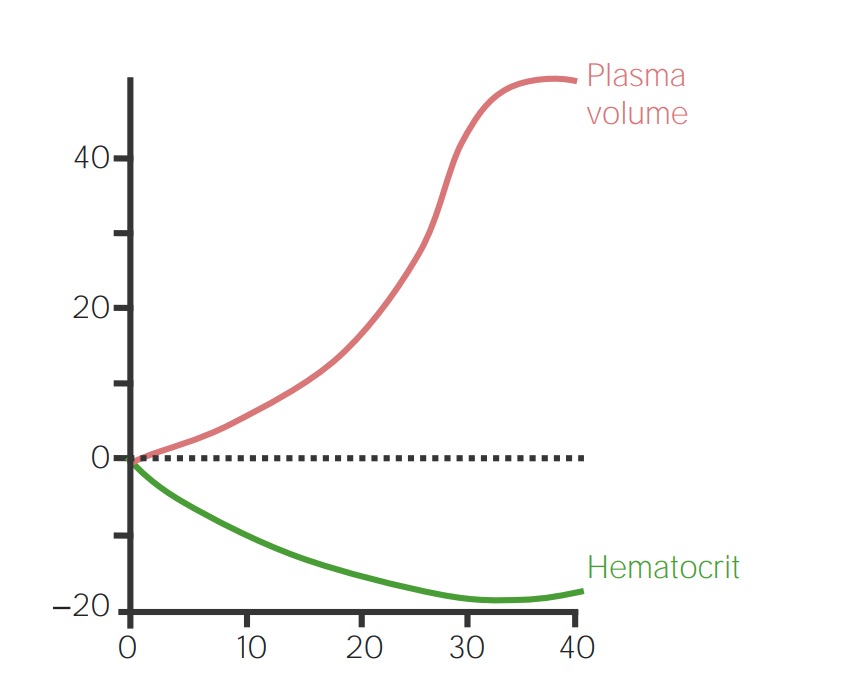
Cambios fisiológicos maternos en el sistema cardiovascular durante el embarazo: cambio porcentual sobre los valores sin embarazo
Imagen por Lecturio. Licencia: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0
Linea nigra e hiperpigmentación del ombligo en el embarazo
Imagen: “Linea nigra” by Daniel Lobo. License: CC BY 2.0El cronograma típico de controles prenatales para personas de bajo riesgo:
Parámetros a medir/monitorear individuos sanos y sin complicaciones en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las visitas prenatales de rutina:
Todas las personas embarazadas deben hacerse ciertos análisis en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum diferentes momentos del embarazo. Entre ellos se encuentran:
| Seguras | Inseguras |
|---|---|
|
|
Aumento de peso:
El aumento de peso recomendado durante el embarazo se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el IMC previo a la gestación. Recomendaciones para el aumento de peso normal:
Ejercicio:
El principal síntoma de embarazo es la “ausencia” del ciclo menstrual. Se debe descartar siempre el embarazo mediante una sencilla prueba de embarazo de orina en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las mujeres en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum edad reproductiva que presenten una hemorragia anormal. Otras causas comunes de hemorragia uterina anormal son:
Algunas personas pueden presentar dolor Dolor Inflammation pélvico y/o hemorragia, que son síntomas más preocupantes de un embarazo anormal. Una vez más, en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum estas personas siempre se debe realizar una prueba de embarazo con un test de orina. Si la prueba es positiva, el diagnóstico diferencial incluye: