Los LOS Neisseria virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology del Ébola y Marburgo son miembros de la familia Filoviridae Filoviridae A family of RNA viruses, of the order mononegavirales, containing filamentous virions. Although they resemble rhabdoviridae in possessing helical nucleocapsids, filoviridae differ in the length and degree of branching in their virions. There are two genera: ebolavirus and marburgvirus. Ebolavirus and Marburgvirus. Son virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de ARN monocatenarios de sentido negativo con una morfología pleomórfica filamentosa característica. La transmisión se produce principalmente a través del contacto con secreciones de un individuo infectado. Estos virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology causan enfermedades similares, con síntomas similares a los LOS Neisseria de la gripe, diarrea, hemorragia, disfunción multiorgánica y shock Shock Shock is a life-threatening condition associated with impaired circulation that results in tissue hypoxia. The different types of shock are based on the underlying cause: distributive (↑ cardiac output (CO), ↓ systemic vascular resistance (SVR)), cardiogenic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), hypovolemic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), obstructive (↓ CO), and mixed. Types of Shock. El diagnóstico se puede realizar mediante PCR PCR Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a technique that amplifies DNA fragments exponentially for analysis. The process is highly specific, allowing for the targeting of specific genomic sequences, even with minuscule sample amounts. The PCR cycles multiple times through 3 phases: denaturation of the template DNA, annealing of a specific primer to the individual DNA strands, and synthesis/elongation of new DNA molecules. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR), detección de antígenos y serología. El tratamiento es principalmente de soporte, aunque la terapia con anticuerpos monoclonales ha HA Hemolytic anemia (HA) is the term given to a large group of anemias that are caused by the premature destruction/hemolysis of circulating red blood cells (RBCs). Hemolysis can occur within (intravascular hemolysis) or outside the blood vessels (extravascular hemolysis). Hemolytic Anemia sido prometedora para tratar la enfermedad por el virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology del Ébola.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025

Identificación de los virus ARN:
Los virus pueden clasificarse de muchas maneras. Sin embargo, la mayoría de los virus tienen un genoma formado por ADN o ARN. Los virus con genoma ARN pueden caracterizarse además por tener ARN monocatenario o bicatenario. Los virus “envueltos” están cubiertos por una fina capa de membrana celular (normalmente tomada de la célula huésped). Si la envoltura está ausente, los virus se denominan “desnudos”. Los virus con genomas monocatenarios son virus de “sentido positivo” si el genoma se usa directamente como ARN mensajero (ARNm), que se traduce en proteínas. Los virus monocatenarios de “sentido negativo” utilizan la ARN polimerasa dependiente de ARN, una enzima viral, para transcribir su genoma en ARN mensajero.
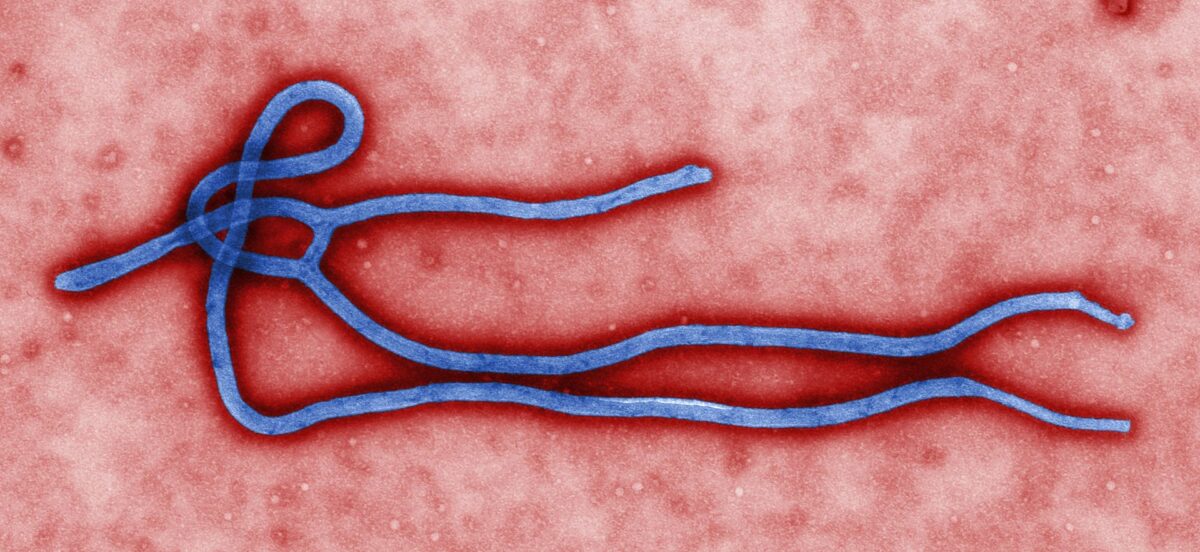
Micrografía electrónica de un virión del virus del Ébola:
Observe la estructura filamentosa.
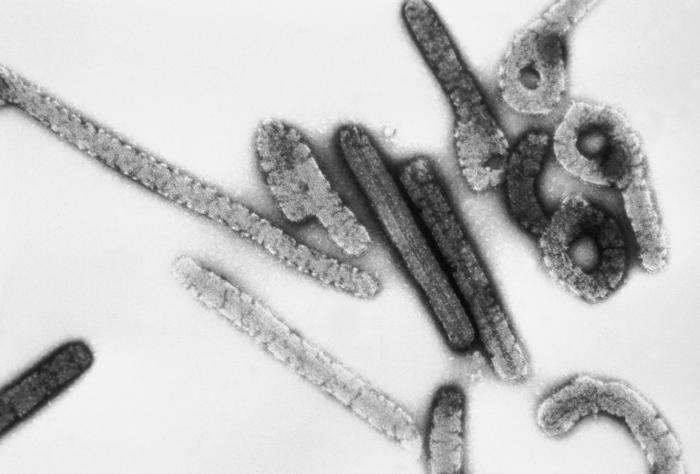
Micrografía electrónica de viriones del virus de Marburgo
Imagen: “Marburg virus” por Erskine Palmer, Russell Regnery. Licencia: Dominio Público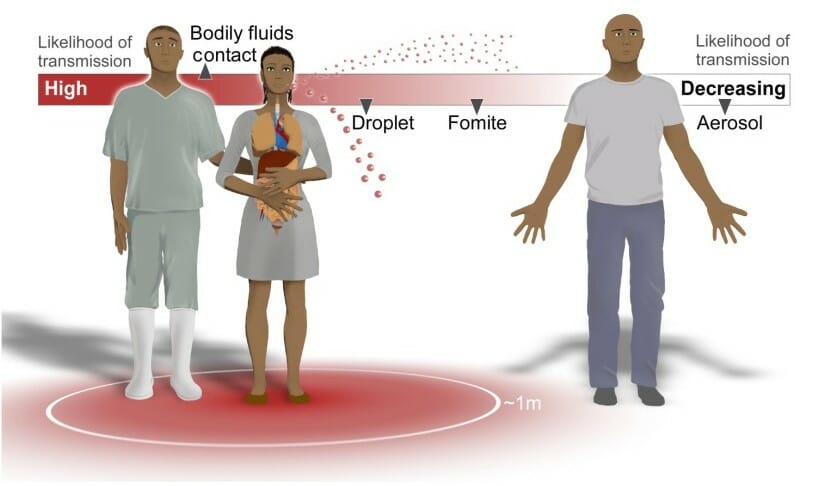
Rutas de la transmisión del virus del Ébola:
El contacto con fluidos corporales como la sangre, las heces, el semen, la leche materna y la saliva conlleva el mayor riesgo de transmisión. Los fluidos infecciosos también pueden formarse en gotas de aerosol, que conllevan un menor riesgo de transmisión.
La enfermedad por el virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology del Ébola y la enfermedad por el virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de Marburgo tienen presentaciones muy similares y pueden ser difíciles de distinguir.
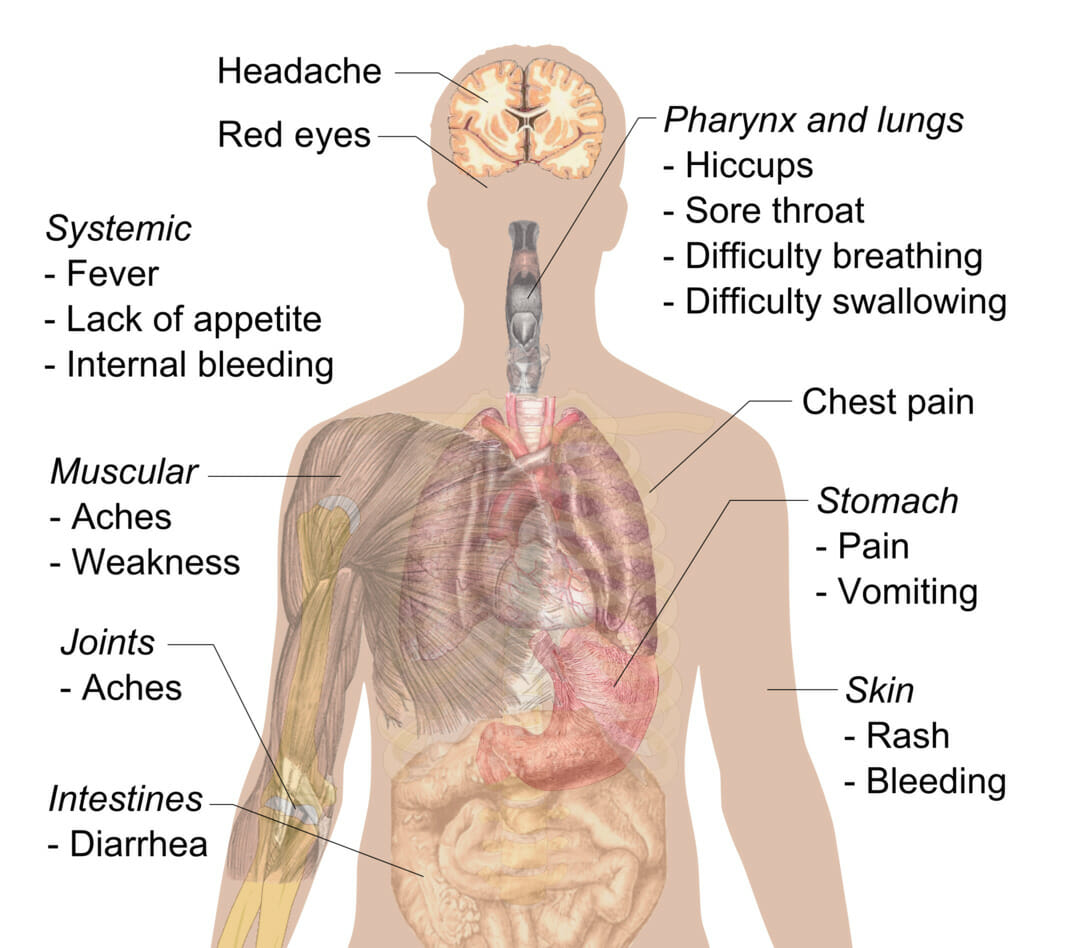
Signos y síntomas de la enfermedad por el virus del Ébola
Imagen: “Sympyoms of ebola” por Mikael Häggström. Licencia: CC0 1.0El diagnóstico de la enfermedad por el virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology del Ébola y enfermedad por el virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de Marburgo en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum una etapa temprana de la enfermedad puede ser difícil ( los LOS Neisseria primeros síntomas se asemejan a otras enfermedades más comunes). Se requiere un alto grado de sospecha, ya que el aislamiento temprano de los LOS Neisseria pacientes en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria que se sospecha de enfermedad por el virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology del Ébola o enfermedad por el virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de Marburgo es esencial para controlar un brote.
La siguiente tabla compara y contrasta varias causas virales de fiebre hemorrágica:
| Organismo | Virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology del Ébola | Virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de la fiebre amarilla | Hantavirus Hantavirus A genus of the family bunyaviridae causing hantavirus infections, first identified during the korean war. Infection is found primarily in rodents and humans. Transmission does not appear to involve arthropods. Hantaan virus is the type species. Bunyavirales | Virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de Lassa |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Familia | Filoviridae Filoviridae A family of RNA viruses, of the order mononegavirales, containing filamentous virions. Although they resemble rhabdoviridae in possessing helical nucleocapsids, filoviridae differ in the length and degree of branching in their virions. There are two genera: ebolavirus and marburgvirus. Ebolavirus and Marburgvirus | Flaviviridae Flaviviridae A family of RNA viruses, many of which cause disease in humans and domestic animals. There are three genera flavivirus; pestivirus; and hepacivirus, as well as several unassigned species. Hepatitis C Virus | Bunyaviridae Bunyaviridae A family of viruses, mainly arboviruses, consisting of a single strand of RNA. Virions are enveloped particles 90-120 nm diameter. The complete family contains over 300 members arranged in five genera: orthobunyavirus; hantavirus; nairovirus; phlebovirus; and tospovirus. Bunyavirales | Arenaviridae Arenaviridae A family of RNA viruses naturally infecting rodents and consisting of one genus (arenavirus) with two groups: old world arenaviruses and new world arenaviruses. Infection in rodents is persistent and silent. Vertical transmission is through milk-, saliva-, or urine-borne routes. Horizontal transmission to humans, monkeys, and other animals is important. Lassa Virus |
| Características |
|
|
|
|
| Transmisión |
|
Vector: mosquito |
|
|
| Presentación Clínica |
|
|
|
|
| Diagnóstico |
|
|
|
|
| Tratamiento |
|
De soporte | De soporte |
|