La dermatomiositis es una miopatía autoinmune e inflamatoria. Aunque la etiología de la dermatomiositis no está clara, tiene varias asociaciones genéticas y ambientales. La dermatomiositis es común en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum mujeres alrededor de los LOS Neisseria 50 años. Los LOS Neisseria pacientes presentan debilidad proximal simétrica, manifestaciones cutáneas características y síntomas sistémicos. El diagnóstico se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la presentación clínica y los LOS Neisseria estudios de laboratorio y se confirma con una biopsia muscular. Los LOS Neisseria anticuerpos específicos de miositis, incluido el anti-Mi-2, son marcadores específicos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la dermatomiositis. El tratamiento es con glucocorticoides sistémicos, inmunosupresores y fisioterapia. Como existe una fuerte asociación de dermatomiositis con malignidad, todos los LOS Neisseria pacientes deben someterse a un tamizaje de cáncer.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La dermatomiositis es una miopatía inflamatoria idiopática autoinmune que causa debilidad muscular proximal progresiva y simétrica y manifestaciones cutáneas características.
El síndrome antisintetasa es un subtipo de dermatomiositis caracterizado por la presencia de anticuerpos antisintetasa y acompañado de ciertas manifestaciones extramusculares.
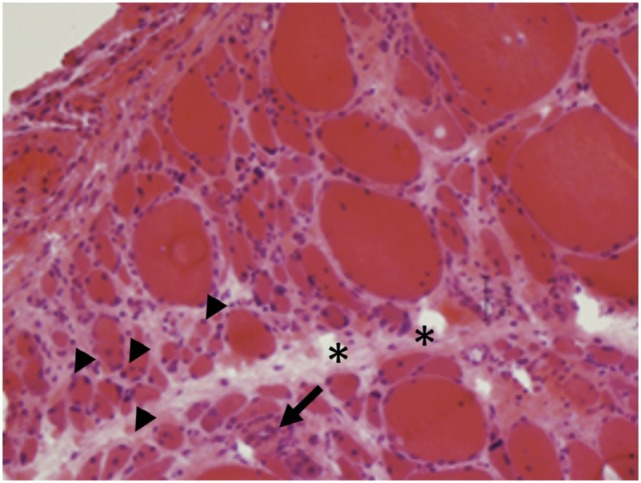
Hallazgos histológicos de dermatomiositis:
La atrofia perifascicular (puntas de flecha) y los infiltrados inflamatorios (flechas) son características de la dermatomiositis.
Hallazgos histológicos de dermatomiositis:
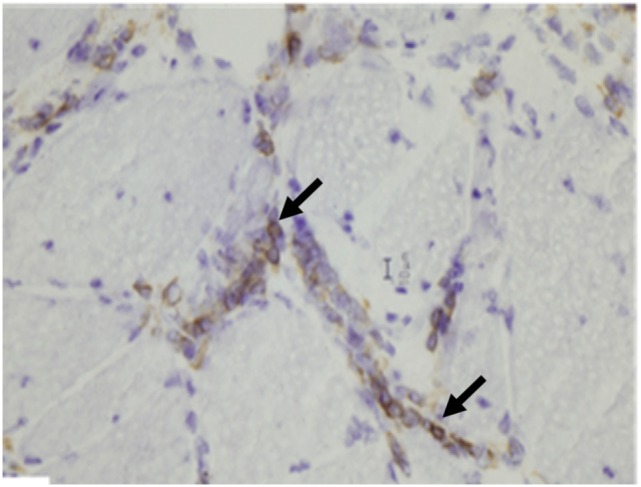
En la dermatomiositis se encuentran agregados de linfocitos B (flechas) positivos para la tinción inmunohistoquímica de CD20.
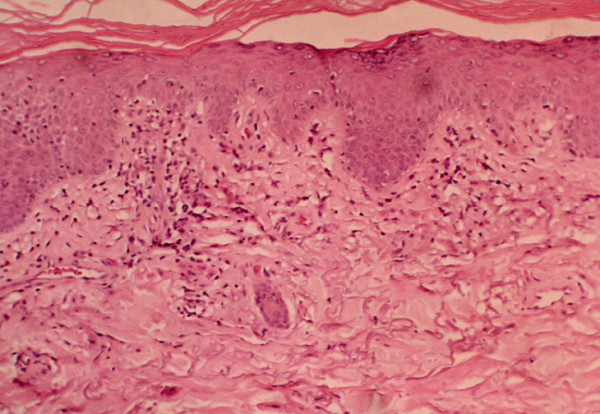
Hallazgos histológicos de dermatomiositis:
En la dermatomiositis se encuentran cambios vacuolares del epitelio cilíndrico e infiltrado inflamatorio linfocitario en la interfase dermoepidérmica.
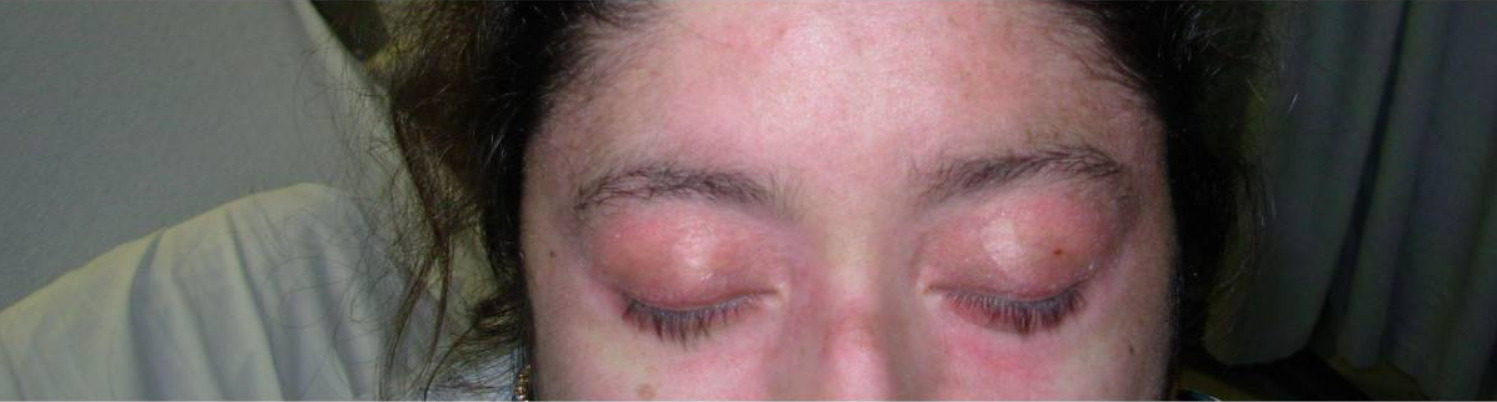
Erupción en heliotropo en dermatomiositis:
Se puede ver una erupción eritematosa alrededor de los párpados superiores con edema periorbitario.
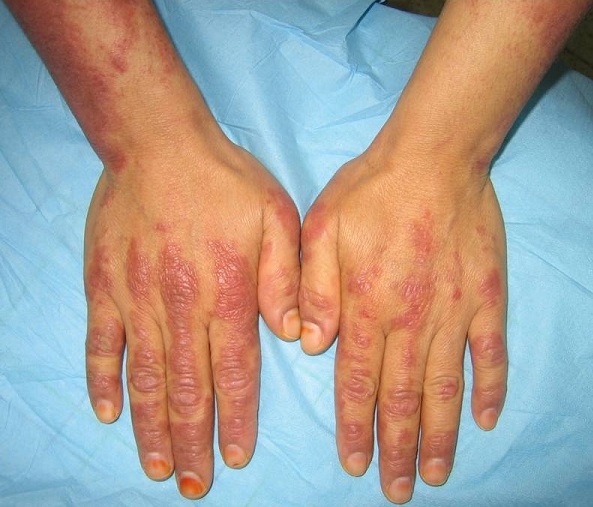
Pápulas de Gottron en dermatomiositis:
Se observa una manifestación cutánea en las articulaciones metacarpofalángicas e interfalángicas dorsales.
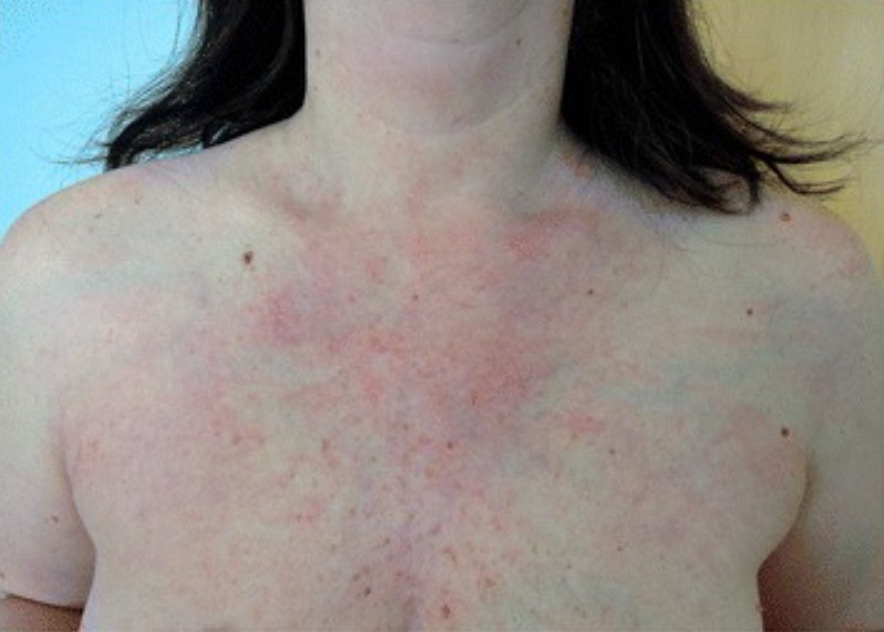
Signo V visto en dermatomiositis: una erupción macular, fotodistribuida y eritematosa que se asemeja a la letra V en la cara anterior del tórax
Imagen: “Dermatomyositis with anti-TIF-1γ antibodies as a presenting symptom of underlying triple-negative breast cancer: A case report” por BMC Cancer. Licencia: CC BY 4.0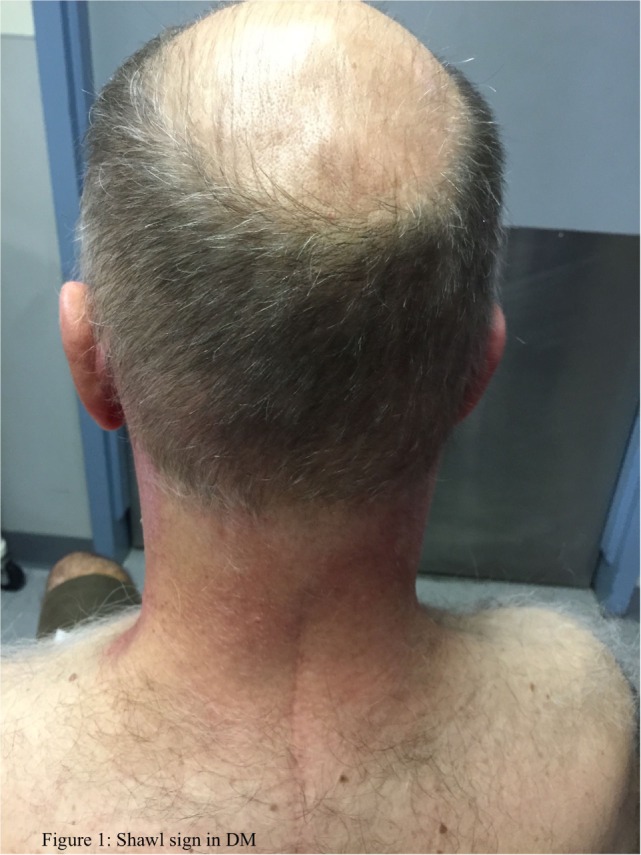
Signo de chal en dermatomiositis
Imagen: “Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies: Clinical approach and management” por Malik A, Hayat G, Kalia JS, Guzman MA. C BY 4.0El tratamiento de la dermatomiositis se dirige hacia la restauración de la fuerza muscular y la minimización de la inflamación.