La artritis reumatoide ( AR AR Aortic regurgitation (AR) is a cardiac condition characterized by the backflow of blood from the aorta to the left ventricle during diastole. Aortic regurgitation is associated with an abnormal aortic valve and/or aortic root stemming from multiple causes, commonly rheumatic heart disease as well as congenital and degenerative valvular disorders. Aortic Regurgitation) es una poliartritis inflamatoria simétrica y un trastorno autoinmune crónico y progresivo. La presentación ocurre con mayor frecuencia en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum mujeres de mediana edad con inflamación articular, dolor Dolor Inflammation y rigidez matutina (a menudo en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las manos). La inflamación sistémica puede conducir a manifestaciones extraarticulares como nódulos reumatoides, enfermedad pulmonar intersticial, síndrome de Felty y pericarditis Pericarditis Pericarditis is an inflammation of the pericardium, often with fluid accumulation. It can be caused by infection (often viral), myocardial infarction, drugs, malignancies, metabolic disorders, autoimmune disorders, or trauma. Acute, subacute, and chronic forms exist. Pericarditis. La enfermedad prolongada y grave puede conducir a deformidades articulares irreversibles. El diagnóstico se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum una fuerte sospecha clínica y se confirma por la presencia de factor reumatoideo, anticuerpos contra el péptido cíclico citrulinado e imagenología característica. El tratamiento incluye medicamentos antirreumáticos modificadores de la enfermedad a largo plazo, agentes biológicos y fisioterapia. Los LOS Neisseria glucocorticoides y los LOS Neisseria antiinflamatorios no esteroideos (AINE) son el tratamiento de elección para la exacerbación aguda.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Se desconoce la causa de la artritis reumatoide ( AR AR Aortic regurgitation (AR) is a cardiac condition characterized by the backflow of blood from the aorta to the left ventricle during diastole. Aortic regurgitation is associated with an abnormal aortic valve and/or aortic root stemming from multiple causes, commonly rheumatic heart disease as well as congenital and degenerative valvular disorders. Aortic Regurgitation), pero varios factores de riesgo juegan un papel.
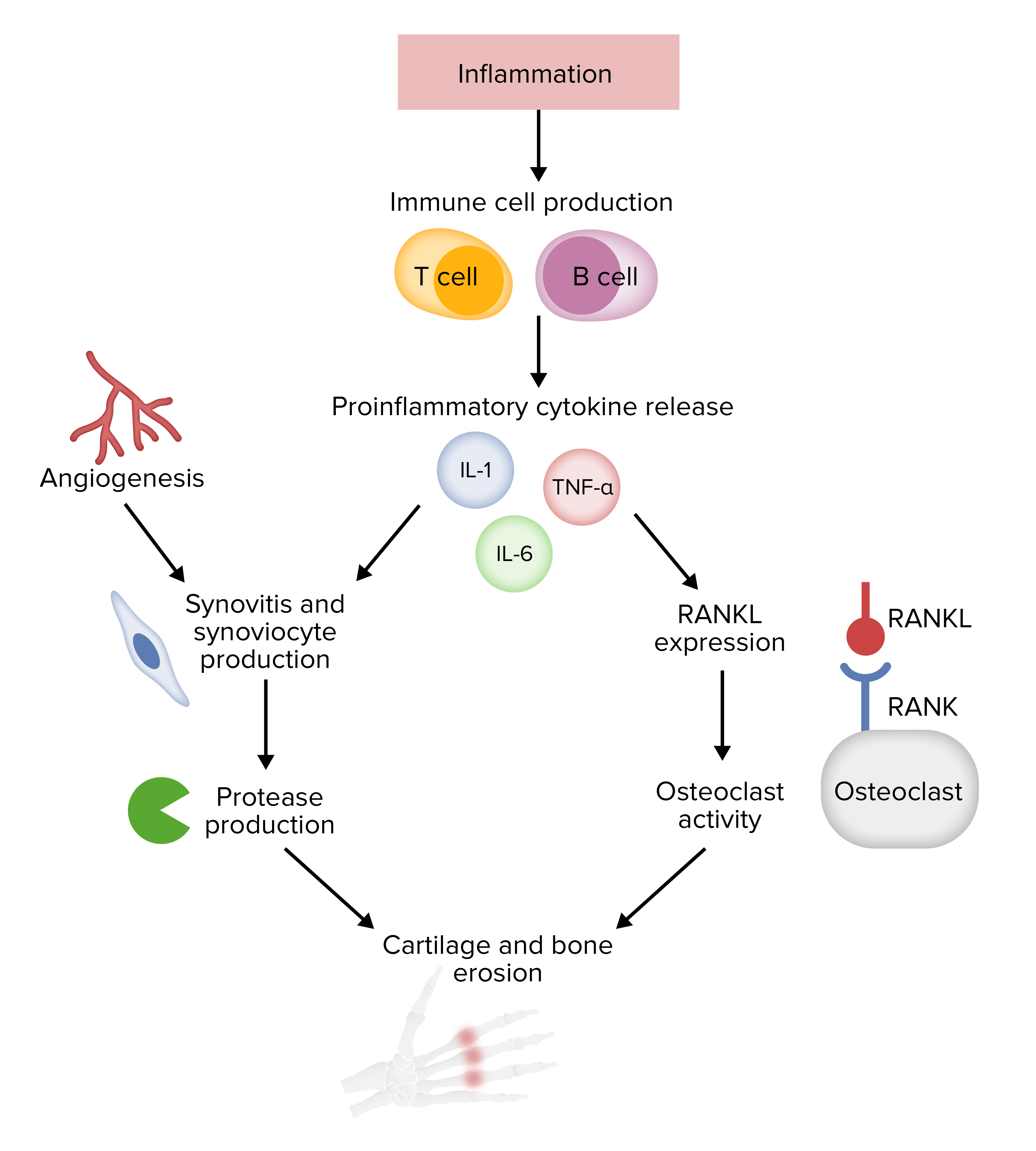
Fisiopatología de la artritis reumatoide
RANK: receptor activador del factor nuclear kappa-Β
RANKL: receptor activador del factor nuclear kappa-Β ligando Imagen de Lecturio.
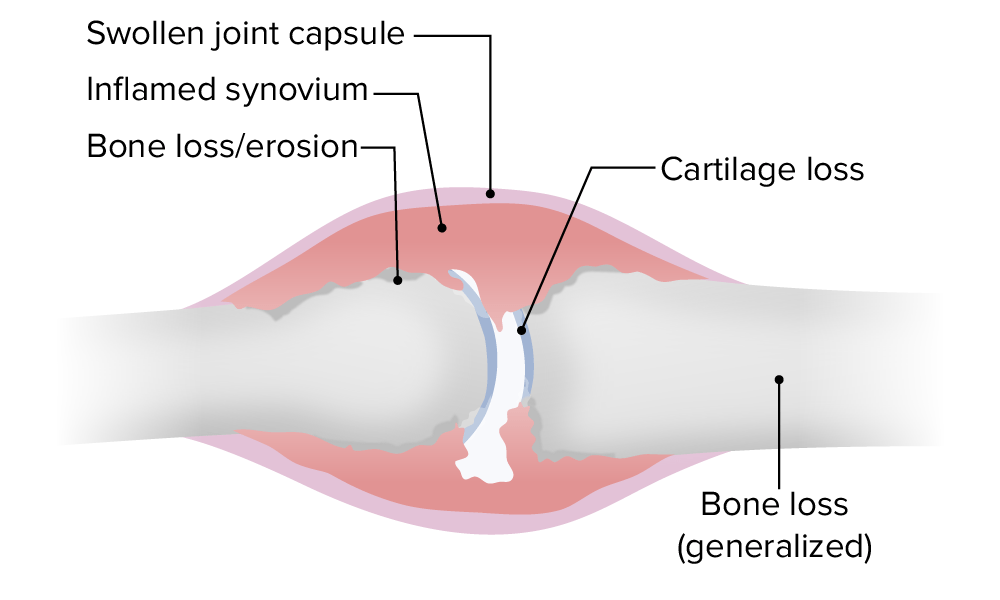
Cambios articulares patológicos en la AR
Imagen por Lecturio.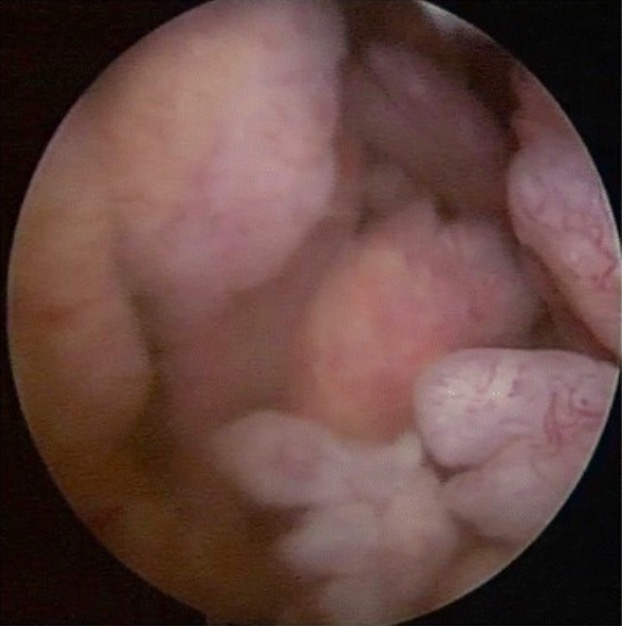
Imagenología artroscópica en AR: Crecimiento sinovial exuberante con proliferación tipo vellosidades
Imagen: “Arthroscopic image of synovial growth” por Department of Orthopaedics, Grant Government Medical College & Sir J.J. Group of Hospitals, Byculla, Mumbai, India. Licencia: CC BY 4.0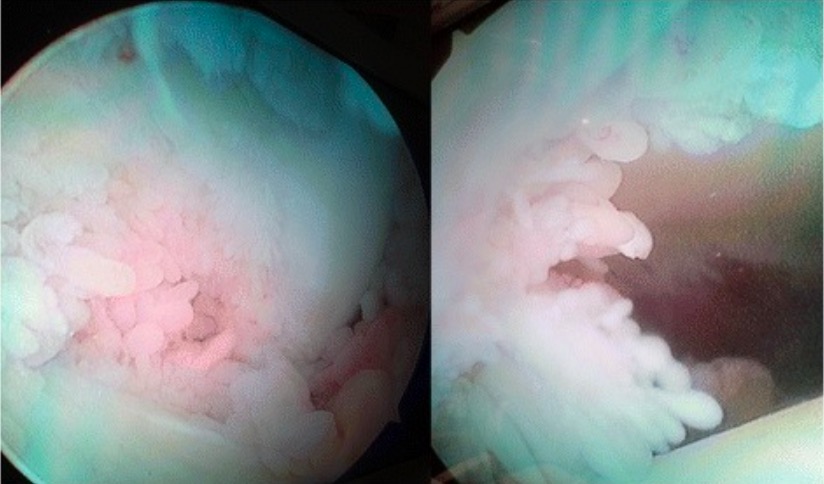
Imagenología artroscópica de proliferación sinovial de rodilla en paciente con AR
Imagen: “Arthroscopic image of synovial growth” por Department of Orthopaedics, Grant Government Medical College & Sir J.J. Group of Hospitals, Byculla, Mumbai, India. Licencia: CC BY 4.0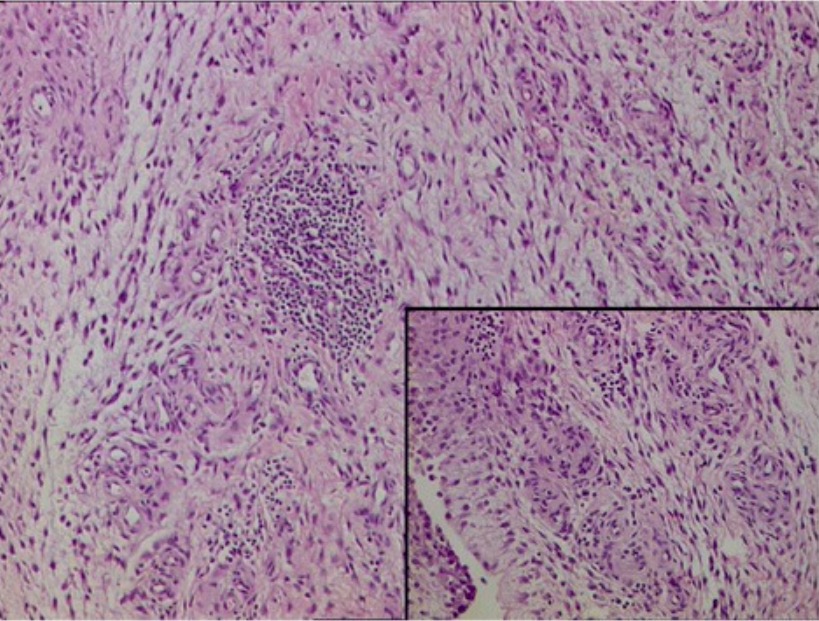
Histopatología de la membrana sinovial en la AR: tejido fibrocolágeno con infiltrado inflamatorio mixto denso compuesto por linfocitos, células plasmáticas, neutrófilos y vasos sanguíneos proliferativos
Imagen: “Histopathology” por Department of Orthopaedics, Grant Government Medical College & Sir J.J. Group of Hospitals, Byculla, Mumbai, India. Licencia: CC BY 4.0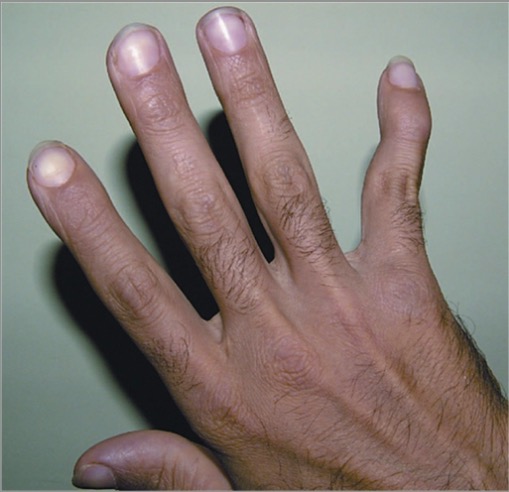
Deformidad en cuello de cisne del quinto dedo en un paciente con AR
Imagen: “Swan-neck deformity” por Khatam-al-Anbia Eye Research Center, Mashhad University of Medical Sciences, Mashhad, Iran. Licencia: CC BY 2.5
Sinovitis en AR:
La presentación incluye inflamación simétrica y sensibilidad de las articulaciones metacarpofalángicas, articulaciones interfalángicas proximales y muñecas.
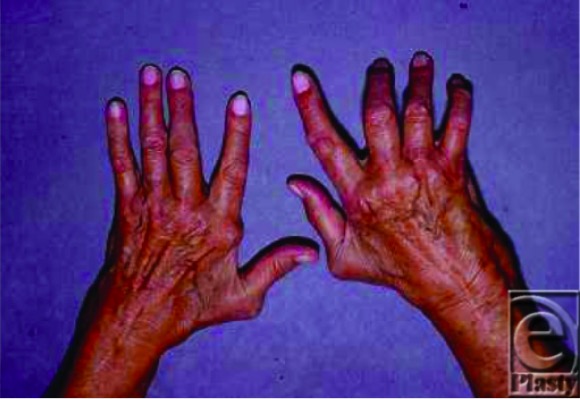
Hallazgos del examen físico en la AR:
Paciente con AR con varias deformidades clásicas: desviación cubital (mano izquierda) y deformidad en ojal (tercer, cuarto y quinto dedos de la mano derecha)
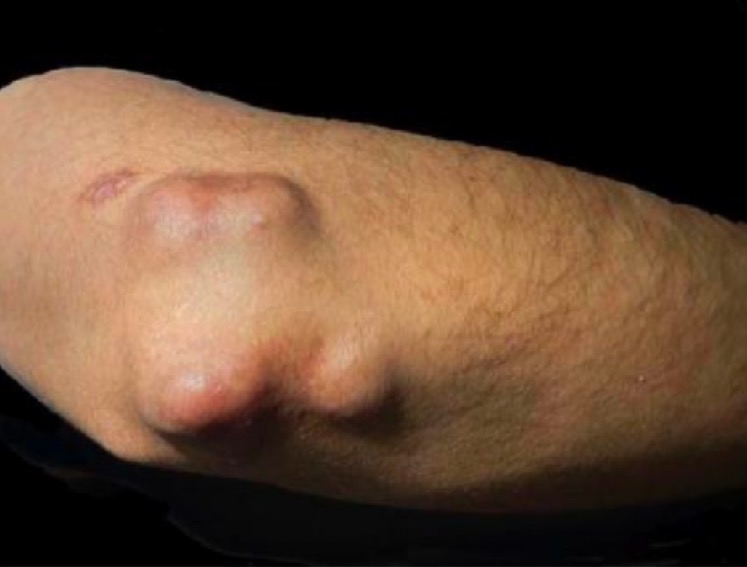
Nódulos reumatoides en AR:
Tumefacción subcutánea firme, no dolorosa, en la superficie extensora del codo en un paciente con AR
El diagnóstico de artritis reumatoide ( AR AR Aortic regurgitation (AR) is a cardiac condition characterized by the backflow of blood from the aorta to the left ventricle during diastole. Aortic regurgitation is associated with an abnormal aortic valve and/or aortic root stemming from multiple causes, commonly rheumatic heart disease as well as congenital and degenerative valvular disorders. Aortic Regurgitation) se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum una alta sospecha clínica y se confirma mediante serología e imagenología.
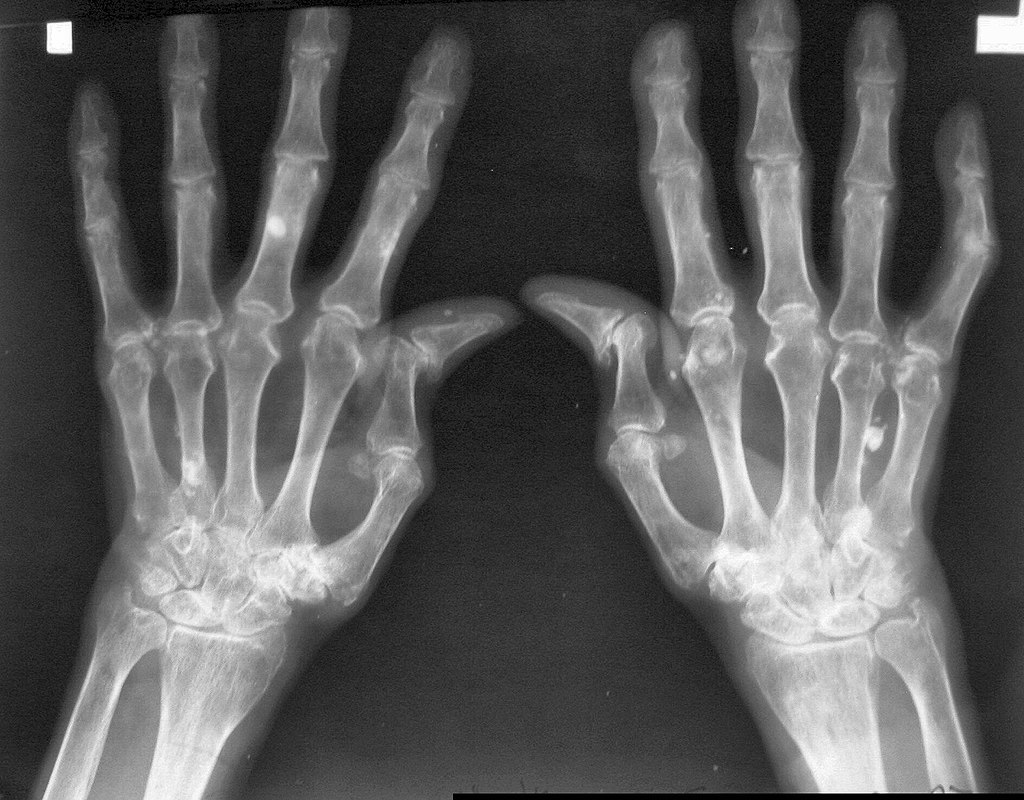
Radiografía de las manos en un paciente con AR:
Deformidad en “Z” mostrada en ambos pulgares y estrechamiento del espacio articular/erosión ósea observada en las articulaciones carpometacarpianos, metacarpofalángicas y interfalángicas proximales
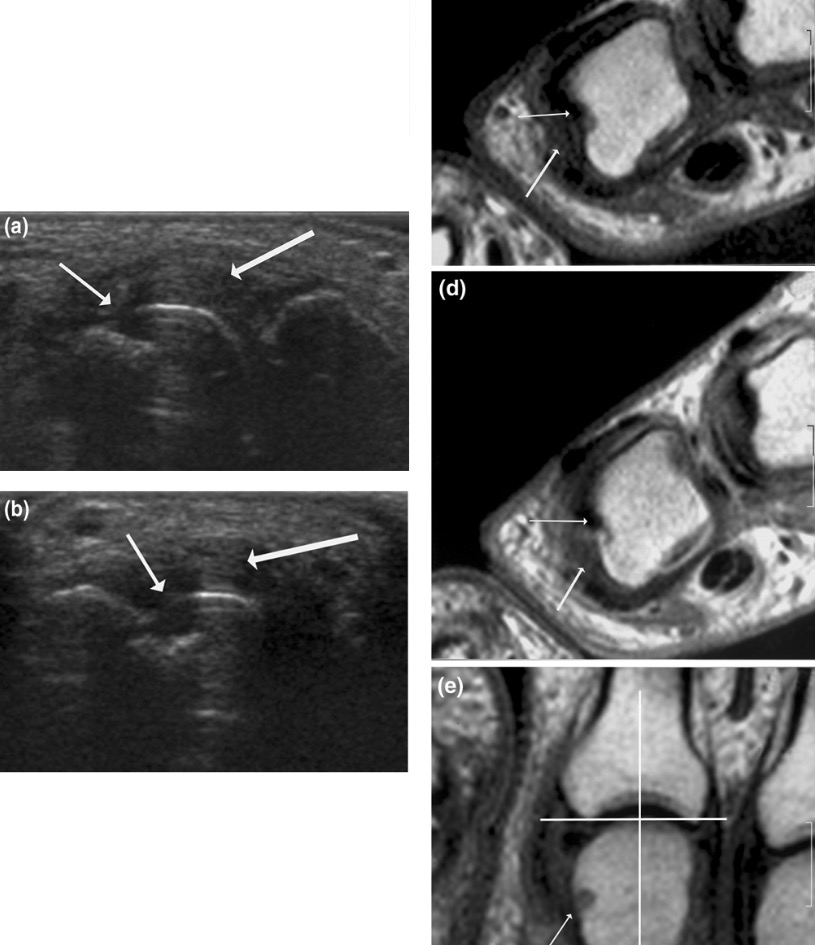
Hallazgos de ultrasonido y resonancia magnética en la AR:
(a) (b): signos de destrucción e inflamación en el ultrasonido
(C) (D) (e): resonancia magnética que muestra la segunda articulación metacarpofalángica en un paciente con AR establecida.
(las flechas finas indican cambio erosivo; las flechas gruesas indican sinovitis)
El objetivo es prevenir la deformidad y el daño permanente. Los LOS Neisseria pacientes deben ser derivados a un reumatólogo.
Terapias no medicamentosas
Tratamiento de exacerbaciones agudas:
Terapia con medicamentos a largo plazo:
Cirugía:
Consideraciones adicionales: