Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia

Overview Definition Multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN) syndromes are genetic disorders characterized by the presence of ≥ 2 endocrine tumors. Types General descriptions Table: Multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN) syndromes MEN1 MEN2A and MEN2B MEN4 Pattern Autosomal dominant Autosomal dominant Autosomal dominant Genetic mutation MEN1 gene on chromosome 11 (11q13) RET proto-oncogene on chromosome 10 (10q11.2) CDKN1B […]
Hyperaldosteronism
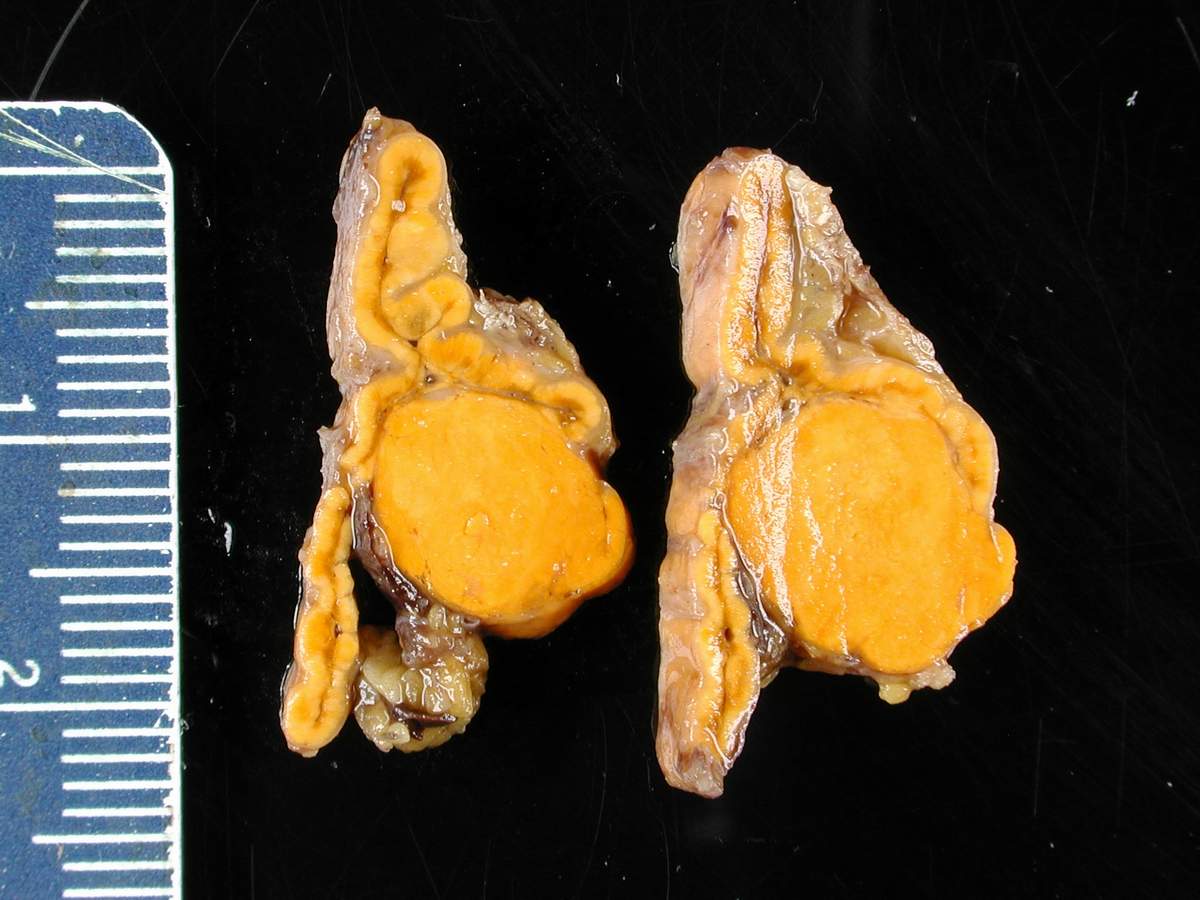
Overview Definition Hyperaldosteronism is defined as an increased secretion of aldosterone from the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal cortex. Primary hyperaldosteronism: autonomous (renin-independent) secretion of aldosterone Secondary hyperaldosteronism: physiological oversecretion of aldosterone that occurs in response to overstimulation of the RAAS, triggered by decreases in renal blood flow. Epidemiology Prevalence of primary hyperaldosteronism: 0.5%‒2% in […]
Adrenal Insufficiency and Addison Disease

Overview Definition Adrenal insufficiency (AI) is the deficiency in adrenal production of glucocorticoids, adrenal androgens, and mineralocorticoids. Forms of adrenal insufficiency Epidemiology Etiology Etiology of primary adrenal insufficiency Etiology of secondary and tertiary adrenal insufficiency Consequence of dysfunction of the hypothalamus and pituitary gland: Pathophysiology Hormonal regulation Adrenal insufficiency Primary AI: Secondary AI: Tertiary AI: […]
Hypoaldosteronism

Overview Definition Hypoaldosteronism is defined as decreased secretion of aldosterone from the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal cortex, which may be primary or secondary in nature. Epidemiology Exact incidence is unknown. Age at diagnosis: Generally occurs in older adults (> 50 years of age) May occur in children with underlying disorders (e.g., diabetes mellitus, sickle […]
Goiter
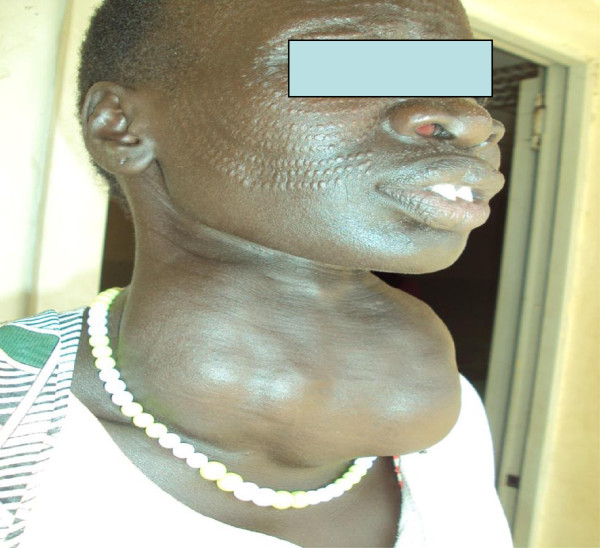
Overview Definition Abnormal nonneoplastic enlargement of the thyroid, a highly vascular gland in the anterior neck region Types according to morphology: Uninodular or multinodular goiter: associated with 1 or more thyroid nodules, causing thyroid enlargement Diffuse goiter: smooth and symmetrically enlarged thyroid gland Types according to thyroid function: Toxic goiter: associated with hyperthyroidism (↑ thyroid […]
Hypothyroidism
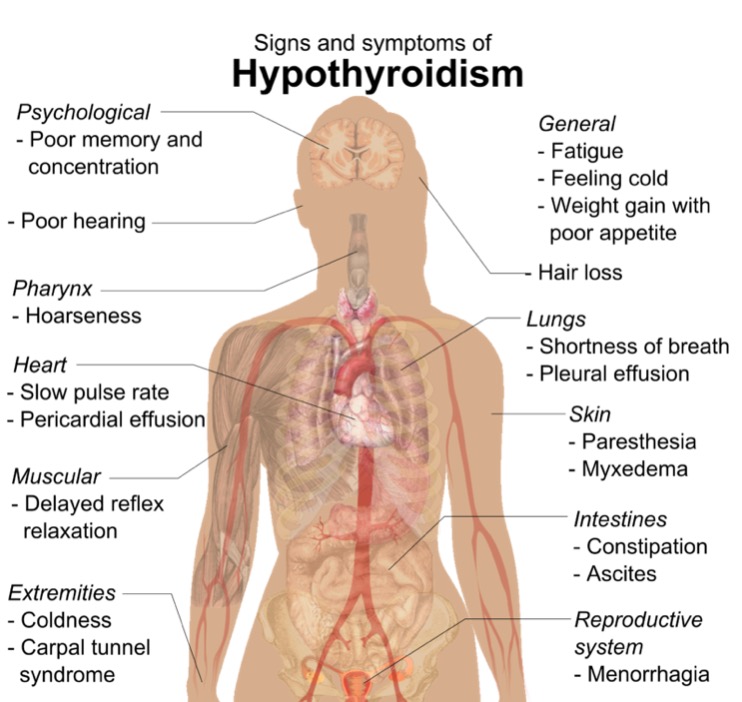
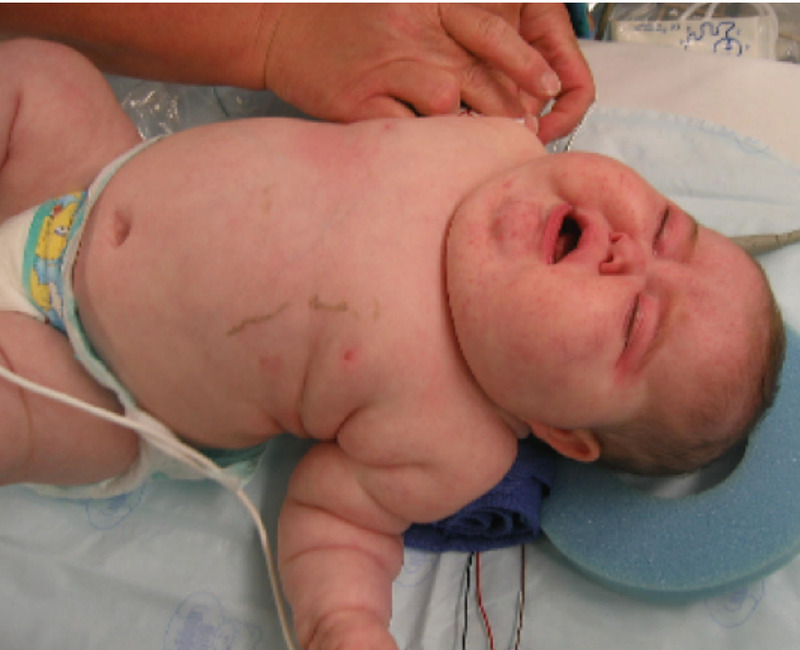
Overview Definition Hypothyroidism is an endocrine disorder resulting from thyroid hormone deficiency. Epidemiology Prevalence: 0.1%–2% More common in women than in men: range, 5–8 times higher Congenital hypothyroidism: Annual incidence: 1 in 4000 births in the United States High incidence in Down syndrome (trisomy 21) Secondary hypothyroidism: 1 in 20,000–80,000 in the general population Classification […]
Cushing Syndrome
Overview Definition Cushing’s syndrome or hypercortisolism is a disorder characterized by features resulting from chronic exposure to excess glucocorticoids. Types of Cushing’s syndrome Epidemiology Etiology Pathophysiology Hormonal regulation Hypercortisolism Clinical Presentation Table: Signs and symptoms of Cushing’s syndrome Skin Acne, facial plethora, violaceous striae/stretch marks, easy bruising, hirsutism Secondary hypercortisolism: hyperpigmentation (both ACTH and ɑ-melanin-stimulating […]
Hypopituitarism
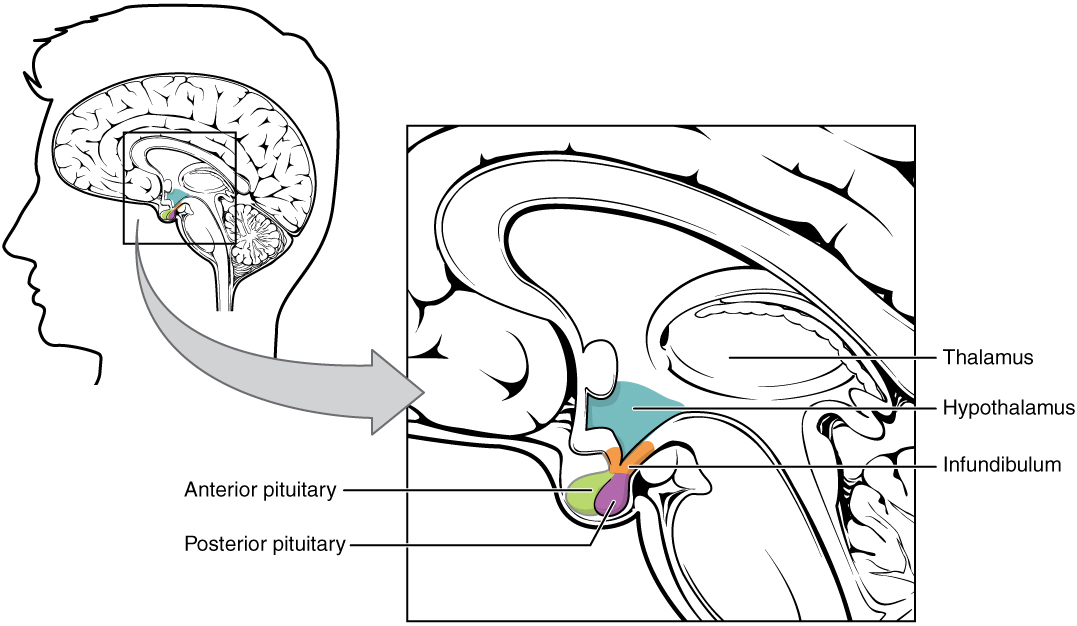
Overview Definition Hypopituitarism is the condition resulting from inadequate production of pituitary hormones: Epidemiology Etiology Pathophysiology Pituitary gland Loss of pituitary gland function Hormones of anterior pituitary: target organs, function, and effects Hormone Pituitary cell type Target organ Function Decreased production ACTH Corticotroph Adrenal cortex Stimulates: Cortisol Androgen Aldosterone Secondary adrenal insufficiency GH Somatotroph Liver […]
Graves’ Disease
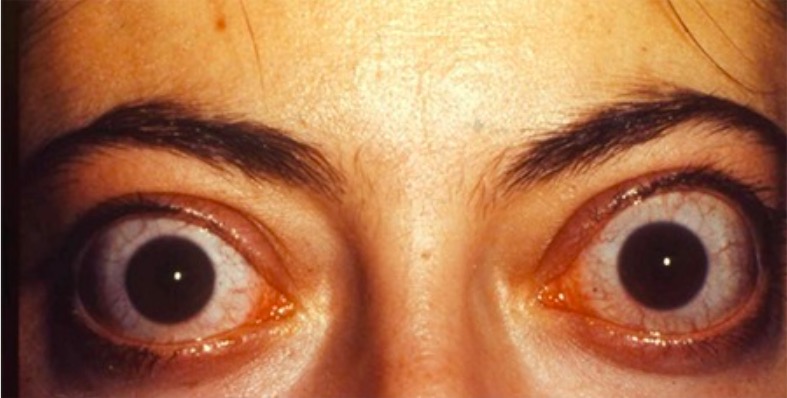
Overview Definition Graves’ disease is an autoimmune disorder in which antibodies against the thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) receptors cause the thyroid gland to hyperfunction. The syndrome may have the following features: Epidemiology Etiology Susceptibility to Graves’ disease is considered to be a combination of multiple factors. Risk factors: Pathophysiology Hyperthyroidism and goiter Orbitopathy and myxedema Clinical […]
Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis
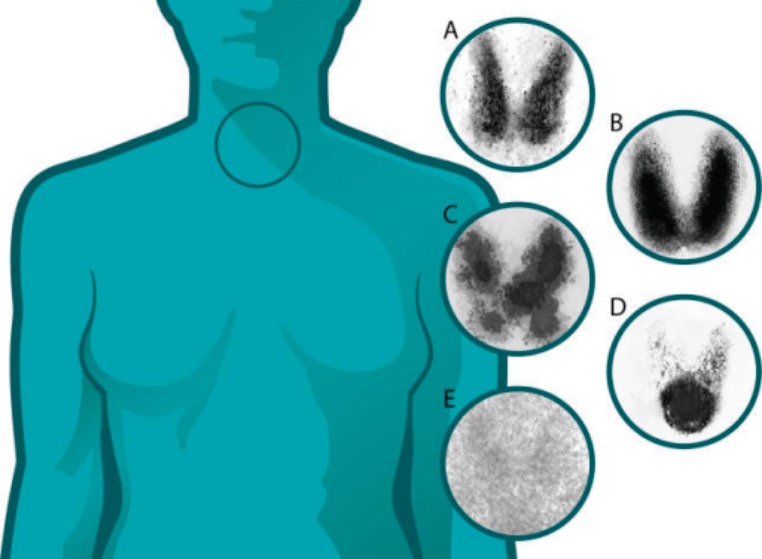
Overview Definition Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is an autoimmune thyroid disease resulting in the destruction and failure of the thyroid gland. Epidemiology Etiology Exact cause unknown, although genetic and environmental factors play a role: Pathophysiology Immunology When thyroid autoimmunity is induced, progressive depletion of thyroid epithelial cells ensues. Thyroid cell destruction mediated by: Lymphocytic infiltration and fibrosis […]