Respiratory Acidosis
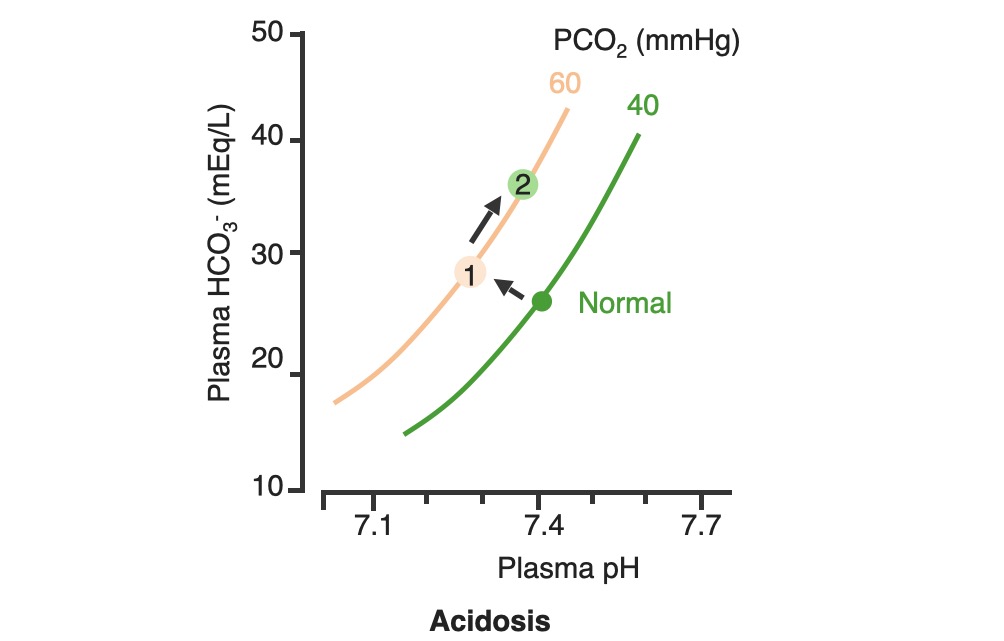
Overview Definition Respiratory acidosis is the process that results in an accumulation of carbon dioxide (CO2) due to abnormal gas exchange in the lungs. In primary respiratory acidosis, the arterial blood gas will show: Epidemiology Acid–Base Review Acid–base disorders are classified according to the primary disturbance (respiratory or metabolic) and the presence or absence of […]
Bronchiectasis
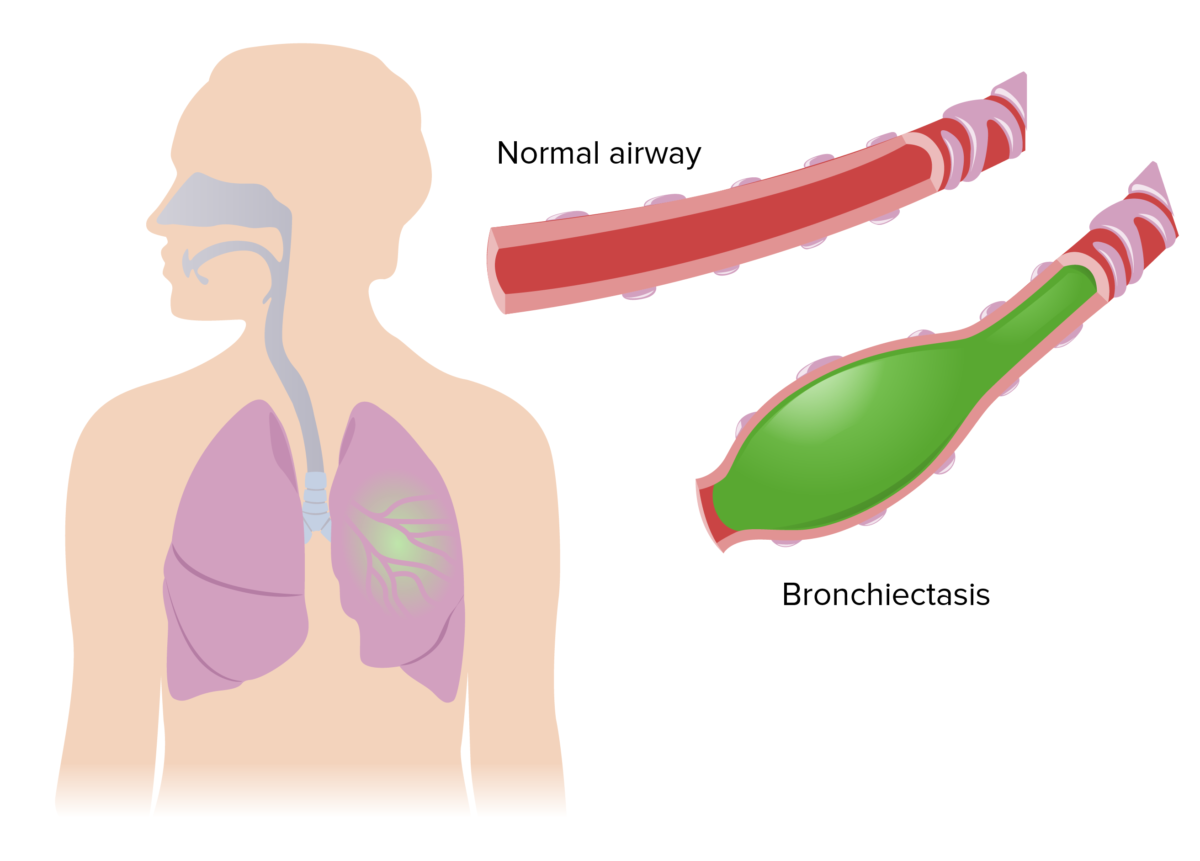
Epidemiology and Etiology Definition Bronchiectasis is a chronic disease in which there is permanent damage to the airways, causing abnormal bronchial dilation and mucosal inflammation. Epidemiology Prevalence is estimated to be approximately 350,000–500,000 cases in the United States. Age: Occurs at any age Increased incidence with older age More common in women Etiology Idiopathic (most […]
Respiratory Failure
Definition and Classification Definition Respiratory failure is a syndrome that develops when the respiratory system is unable to maintain oxygenation and/or ventilation. Classification Respiratory failure may be classified based on: The time course: The underlying issue: Etiology Etiology of hypoxemic respiratory failure Etiology of hypercapnic respiratory failure Pathophysiology Right-to-left shunt Ventilation-to-perfusion inequality A mismatch between […]
Acute Bronchitis
Overview Definition Acute bronchitis is an acute inflammation of the large airways of the lower respiratory tract wherein the pulmonary parenchyma is not affected. Epidemiology Acute bronchitis is a very common disease. Etiology Acute bronchitis is most commonly caused by a viral infection, although bacterial causes are possible. Pathophysiology Acute bronchitis is characterized by infection […]
Pulmonary Examination

Introduction Positioning: Environment: Initial steps: Inspection The 1st part of the pulmonary exam begins with an inspection of the patient noting pertinent positive and negative findings. Inspection overview General appearance/distress level of patient: Level of consciousness: Respiratory rate (RR): Table: Normal respiratory rate ranges in children Age group Age Normal respiratory rate range Infant 0–12 […]
Pleural Effusion
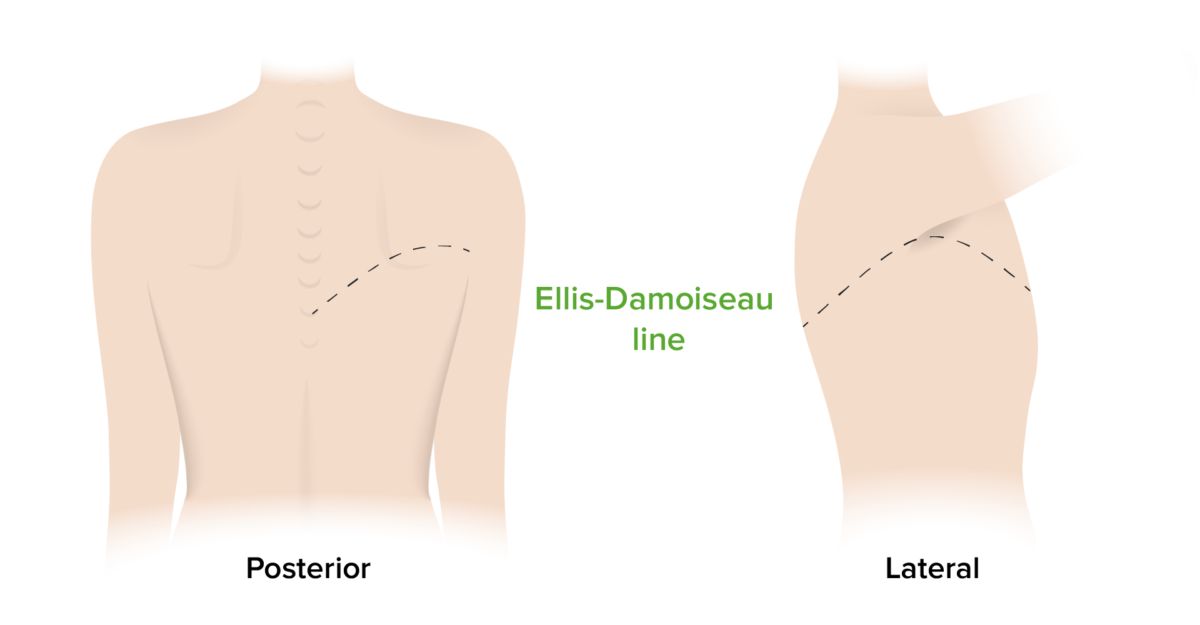
Overview Definition Pleural effusion is an excessive accumulation of fluid within the pleural cavity (between the parietal and visceral pleura). Classification Light’s criteria are used to categorize effusions and to guide further workup. An effusion is classified as exudative if any of these 3 criteria are met: If these 3 criteria are not met, the […]
Sarcoidosis
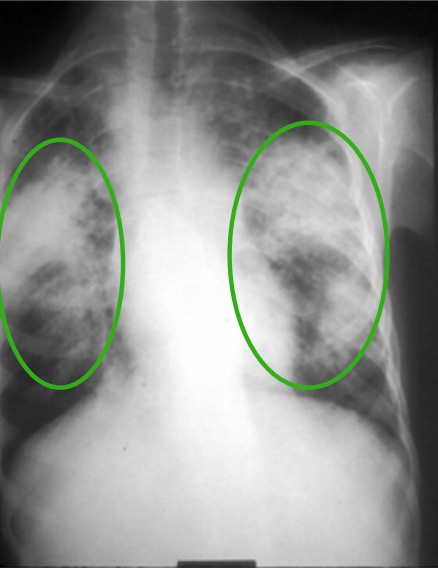
Overview Definition Sarcoidosis is a multisystem inflammatory disease characterized by the formation of noncaseating granulomas that are most likely caused by a cell-mediated immune reaction of unknown etiology. Pulmonary sarcoidosis is a restrictive interstitial lung disease with granuloma formation in the: Extrapulmonary sarcoidosis is characterized by granuloma formation in: Sarcoidosis may be acute or chronic: […]
Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis
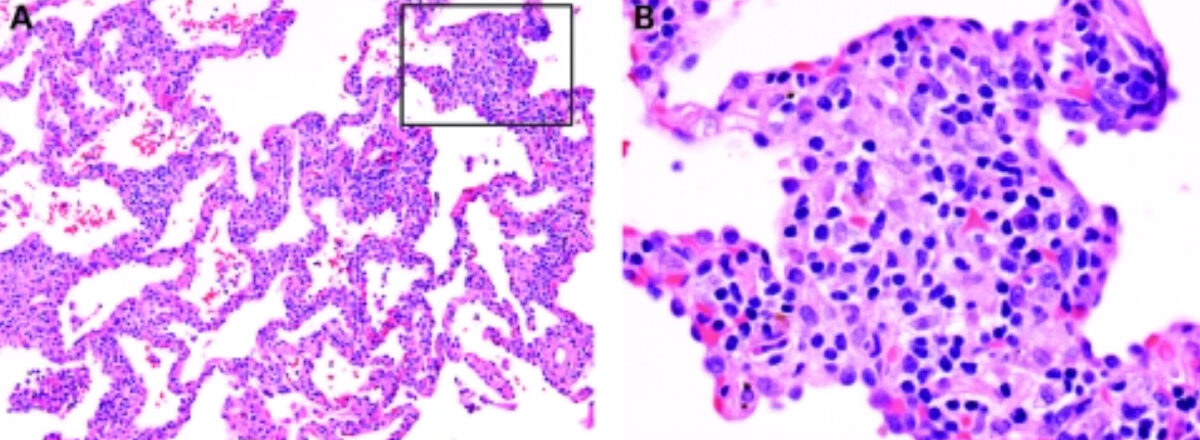
Overview Definition Hypersensitivity pneumonitis (HP), also called extrinsic allergic alveolitis, is an immunologically induced inflammatory disease affecting the lung parenchyma, alveoli, and bronchioles. This disorder is caused by repeated inhalation of inciting agents in a susceptible host. Interstitial lung disease caused by hypersensitivity reactions: Classification Classification is based on duration of illness and frequency, duration, […]
Pulmonary Embolism
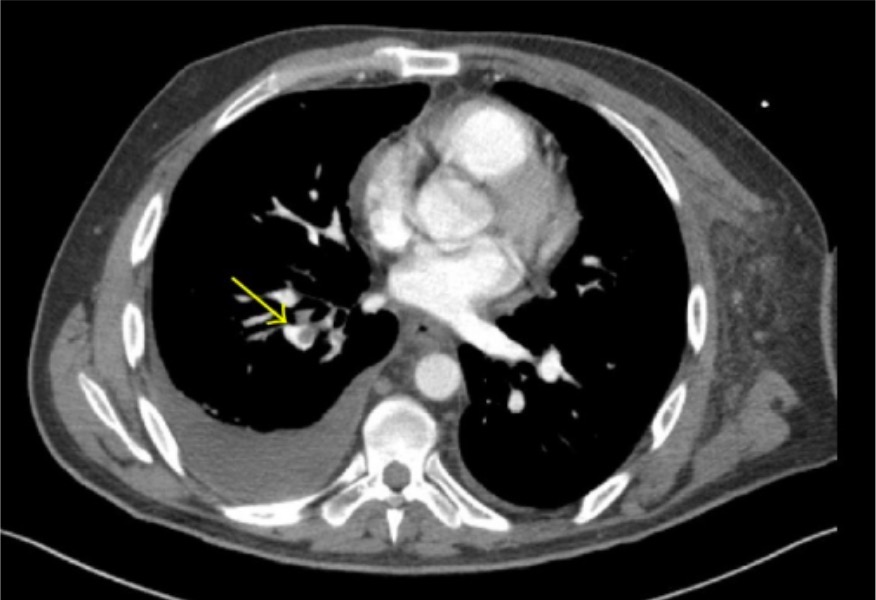
Overview Definition Pulmonary embolism (PE) is the intraluminal obstruction of a main pulmonary artery or any of its branches by a thrombus, air, amniotic fluid, or fat. When thrombotic PE is considered together with DVT, the condition is known as venous thromboembolic (VTE) disease. Epidemiology Etiology and risk factors The 3 primary factors that contribute […]
Lung Cancer
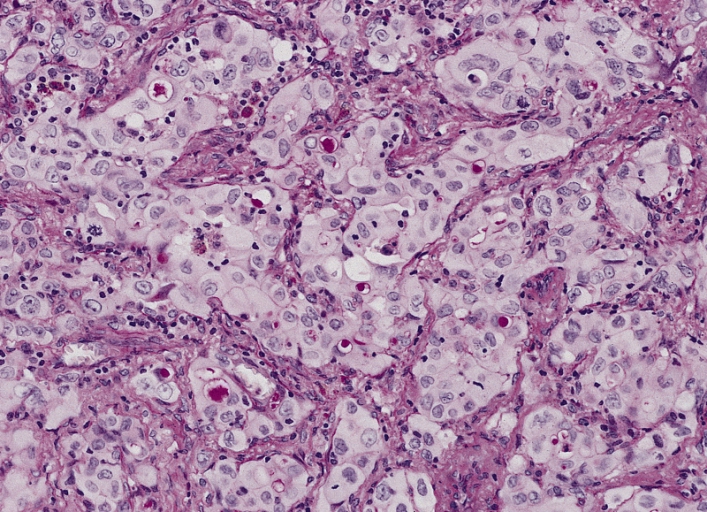
Overview Epidemiology Risk factors Pathophysiology and Classification Pathophysiology Classification scheme 2015 classification Pathology Adenocarcinoma Subtypes: Squamous cell carcinoma Subtypes: Large cell carcinoma Small cell lung carcinoma Large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma Carcinoids Clinical Presentation General symptoms Regional spread Metastasis Paraneoplastic syndrome Diagnosis Chest radiography Computed tomography Follow-up imaging In addition to CT, the following modalities are […]