Febrile Infant

Overview Definition of fever Etiology Systematic approach in determining the cause of fever When to admit to inpatient care Young Infants Overview Diagnosis and management Table: Criteria for the management of the febrile baby (28 days–56 days old) Rochester, NY Philadelphia, PA Boston, MA Ultrasonography, urine culture, CBC, blood culture Yes Yes Yes Spinal tap […]
Hepatitis C Virus
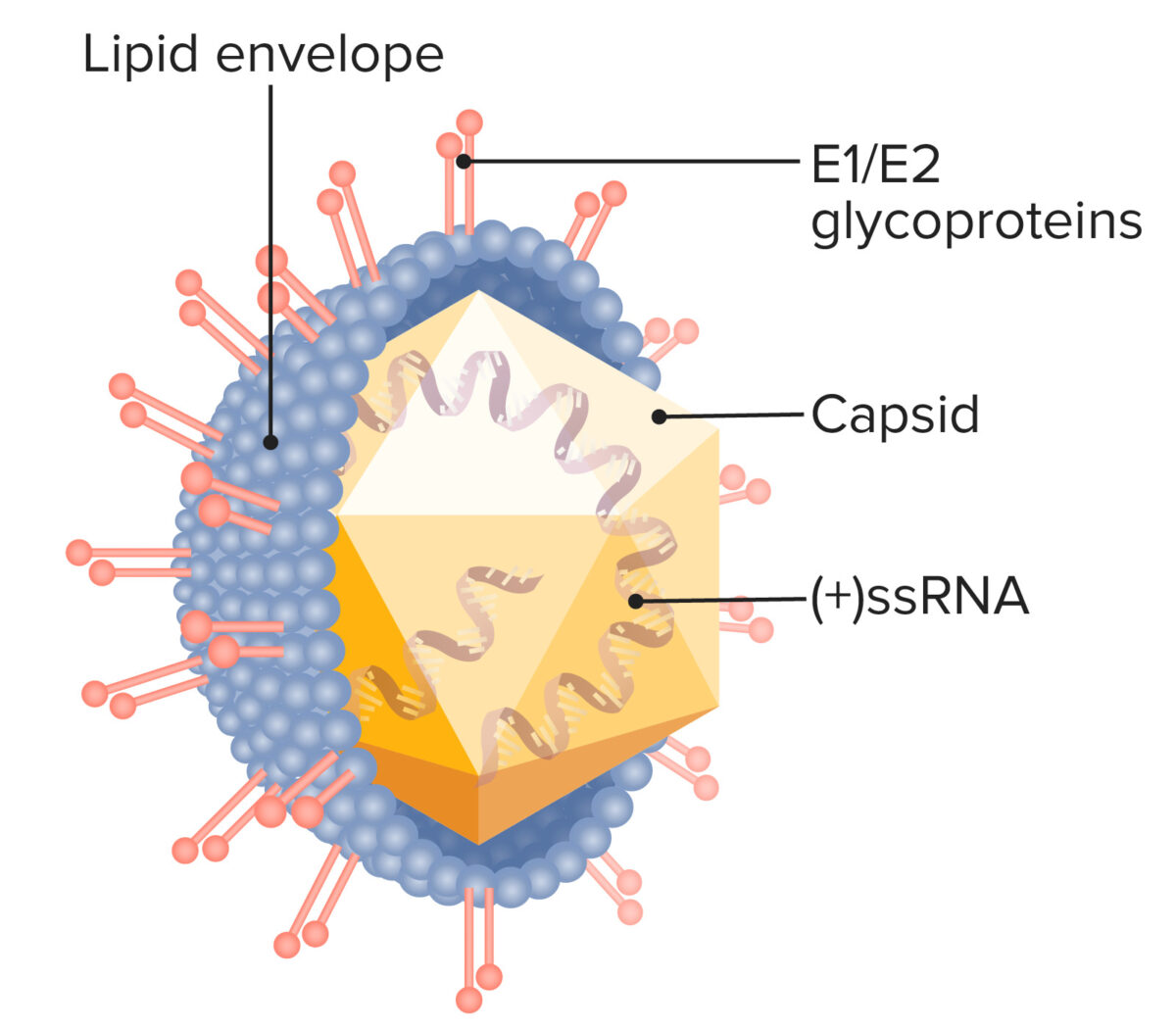
Classification General Characteristics Structure Features Epidemiology Pathogenesis Transmission Humans are the only reservoir for the virus. Modes of transmission include: Host risk factors Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation Acute infection Chronic infection Diagnosis Viral markers Further testing Management Pharmacotherapy Prevention Hepatitis Viruses Comparative Table Differential Diagnosis References
Hepatitis B Virus
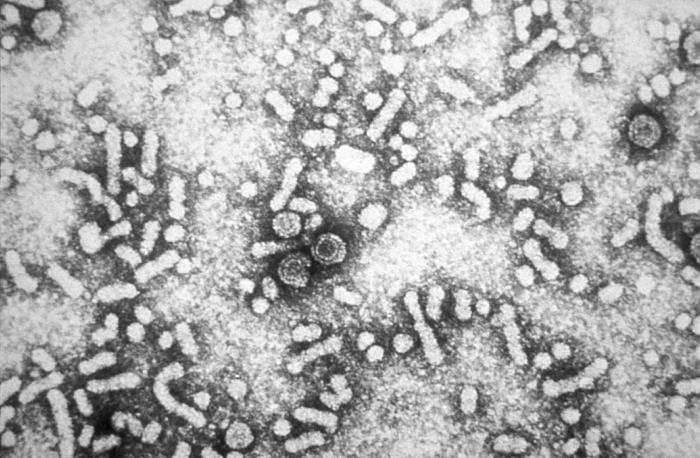
Classification General Characteristics Structure Features Epidemiology and Pathogenesis Epidemiology Transmission Host risk factors Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation Acute infection Chronic infection Diagnosis Viral markers Laboratory evaluation Screening for HBV infection: Acute hepatitis B: Past HBV infection (inactive): HBV-vaccinated individuals: Chronic hepatitis B: Table: Hepatitis B serologic panel HBsAg Anti-HBc-IgM Anti-HBc-IgG Anti-HBs Susceptible Negative Negative Negative Negative […]
Pyelonephritis and Perinephric Abscess
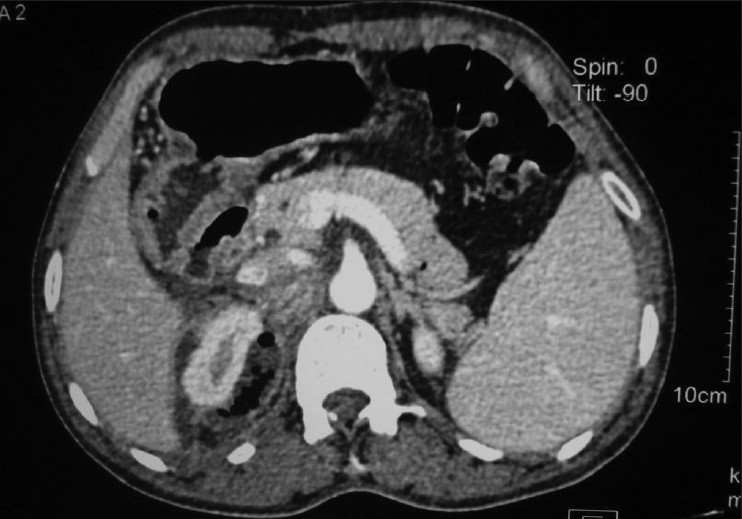
Overview Definitions Types of pyelonephritis Acute pyelonephritis is the sudden-onset infectious process and inflammation of the kidney(s) from ascending infection or hematogenous spread of systemic infections. Epidemiology Etiology Uropathogens Risk factors for urinary tract infections Associated with the development of pyelonephritis and perinephric abscess: Pathophysiology Acute pyelonephritis Chronic pyelonephritis Perinephric abscess Clinical Presentation Clinical features […]
Hepatitis D Virus
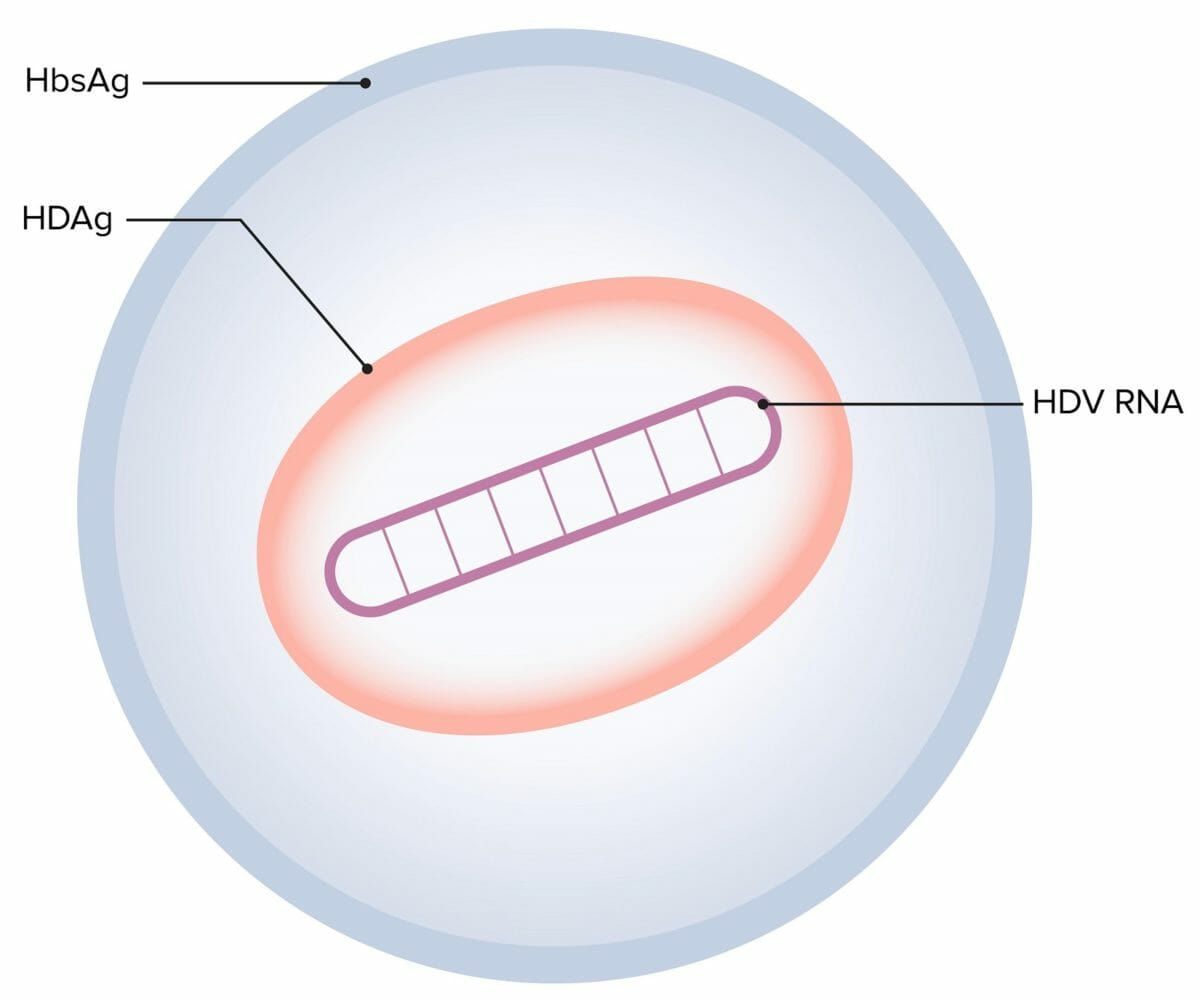
Classification General Characteristics Structure Features Epidemiology Pathogenesis Transmission Transmission of hepatitis D is similar to that of hepatitis B. Host risk factors Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation General Coinfection Superinfection Diagnosis and Management Diagnosis Table: Hepatitis D infection Serum markers Acute HBV/HDV coinfection Acute HDV superinfection Chronic HDV infection HBsAg Positive Positive Positive Anti-HBc IgM Positive Negative […]
Hepatitis A Virus
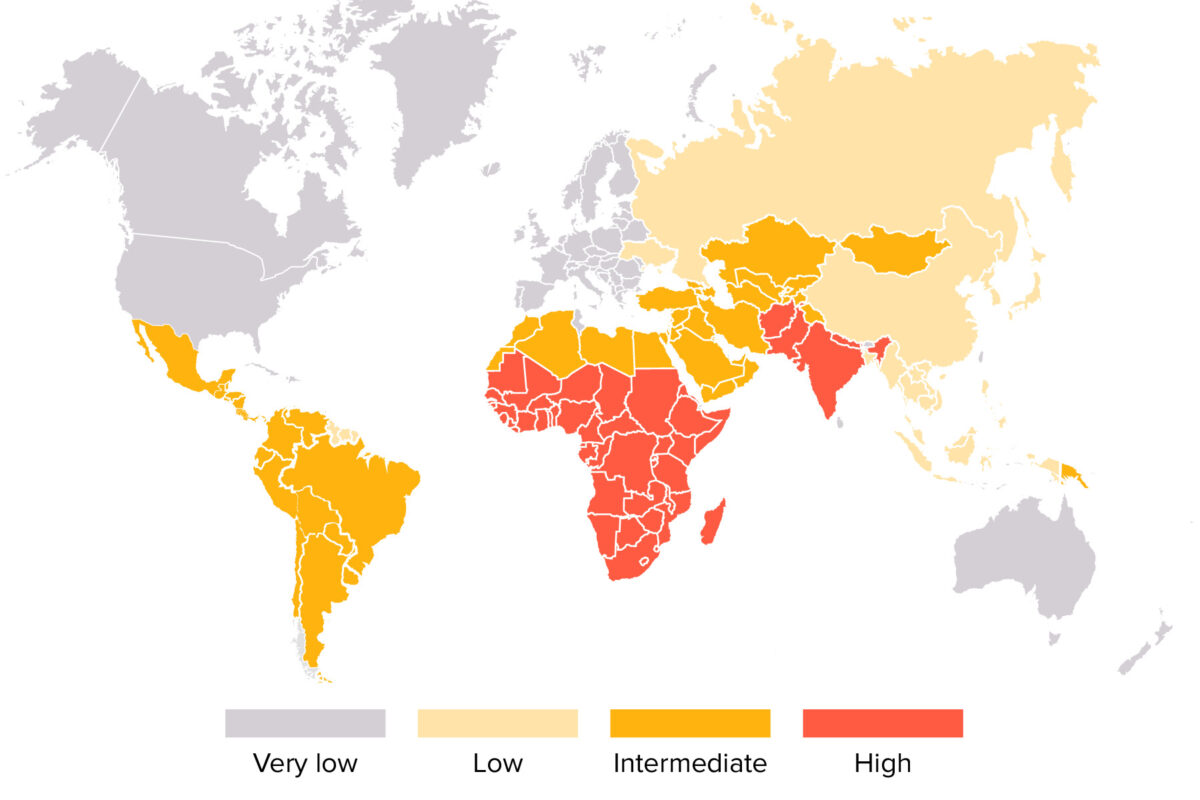
Classification General Characteristics Structure Basic features Epidemiology Pathogenesis Transmission Risk factors Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation General features Specific symptoms The presence of 1 of the following symptoms is a reason to suspect hepatitis A infection, especially in the presence of risk factors: Diagnosis and Management Diagnosis Management Prevention Comparison of Hepatitis Viruses Differential Diagnosis References
Glycopeptides
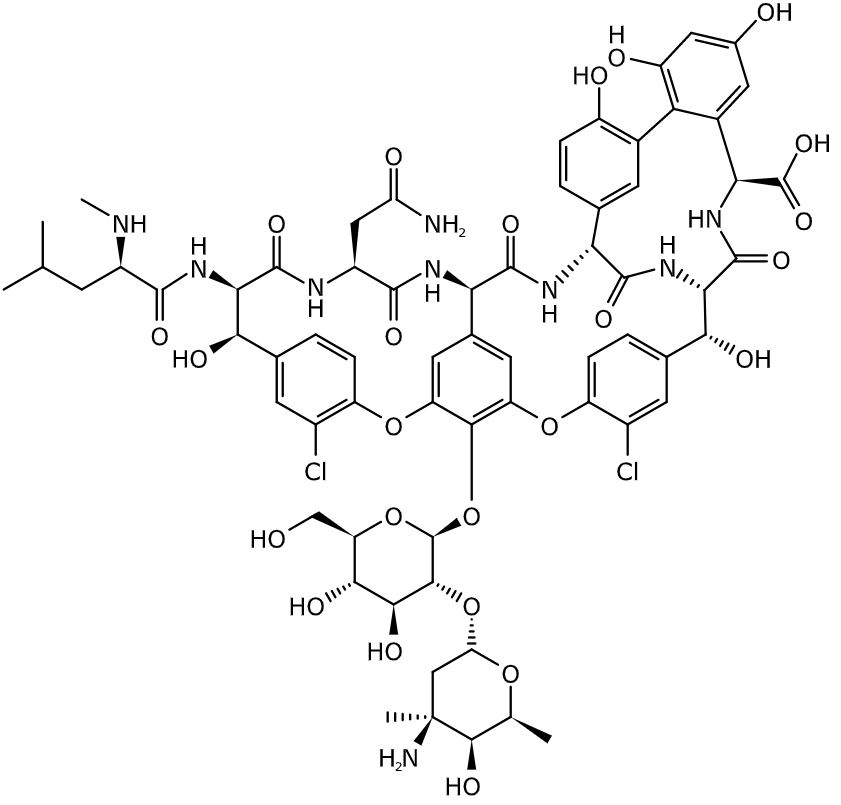
Chemistry and Pharmacodynamics Definition Glycopeptide antibiotics (GPAs) are actinomycete-derived, glycosylated, nonribosomal peptides, which target gram-positive bacteria by inhibition of cell wall synthesis: Vancomycin Teicoplanin (not available in the United States) Chemical structure Both vancomycin and teicoplanin are heptapeptides, but the carbohydrate groups of each drug differ. Mechanism of action Glycopeptides are bactericidal through inhibition of […]
Hepatitis E Virus

Classification General Characteristics Structure Basic features Epidemiology Pathogenesis Transmission Host risk factors Pathophysiology Primary replication: Clinical Presentation Diagnosis and Management Diagnosis Management Prevention Comparison of Hepatitis Viruses Table: Comparison of hepatitis viruses A–E Differential Diagnosis References
Herpes Simplex Virus 1 and 2
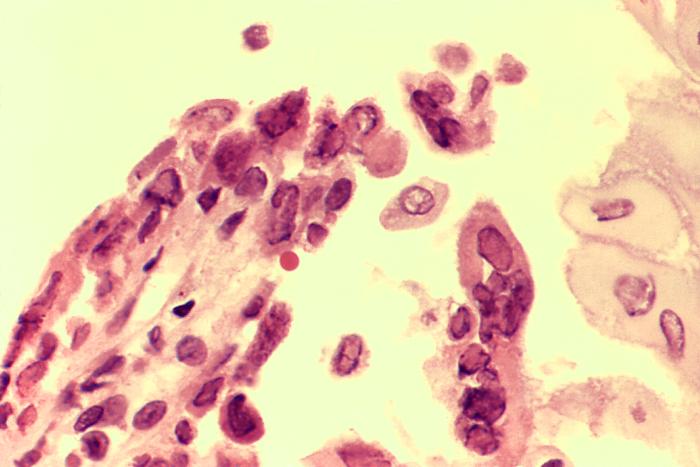
Classification General Characteristics and Epidemiology Basic features of herpes simplex virus Clinically relevant species Two types have been recognized to cause infections: Epidemiology HSV-1: HSV-2: Neonatal herpes infection: Pathogenesis Reservoir Humans are the main reservoir. Transmission HSV-1: HSV-2: Pathophysiology Primary infection: Lifetime latency: Reactivation: Pathology Herpes simplex viruses cause cytolytic infections that form the basis […]
Acute Otitis Media
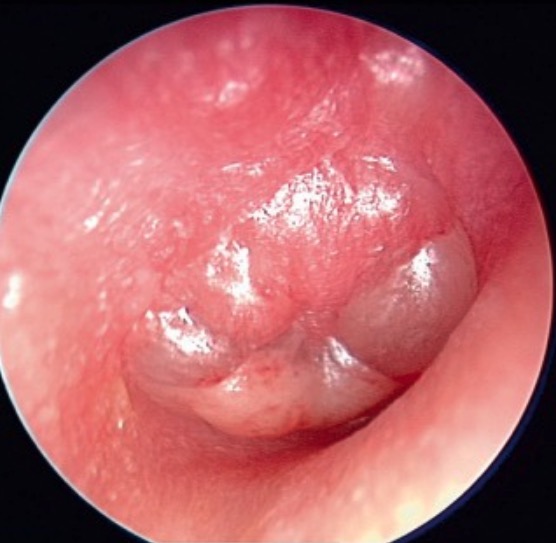
Overview Definition Acute otitis media is an infection characterized by the accumulation of fluid and inflammation within the middle ear. Epidemiology Etiology Acute otitis media is an inflammatory condition of the middle ear with an infectious etiology that may be bacterial (most common) or viral. Causes include: Bacterial: Viral: Risk factors Pathophysiology and Clinical Presentation […]