El término vulvovaginitis Vulvovaginitis The term vulvovaginitis is used to describe an acute inflammation of the vulva and vagina. Vulvovaginitis can be caused by several infectious and non-infectious etiologies, and results from disruption of the normal vaginal environment. Common signs and symptoms include pain, pruritus, erythema, edema, vaginal discharge and dyspareunia. Vulvovaginitis se utiliza para describir una inflamación aguda de la vulva Vulva The vulva is the external genitalia of the female and includes the mons pubis, labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, vestibule, vestibular bulb, and greater vestibular glands. Vagina, Vulva, and Pelvic Floor: Anatomy y la vagina Vagina The vagina is the female genital canal, extending from the vulva externally to the cervix uteri internally. The structures have sexual, reproductive, and urinary functions and a rich blood supply, mainly arising from the internal iliac artery. Vagina, Vulva, and Pelvic Floor: Anatomy. La vulvovaginitis Vulvovaginitis The term vulvovaginitis is used to describe an acute inflammation of the vulva and vagina. Vulvovaginitis can be caused by several infectious and non-infectious etiologies, and results from disruption of the normal vaginal environment. Common signs and symptoms include pain, pruritus, erythema, edema, vaginal discharge and dyspareunia. Vulvovaginitis puede estar causada por varias etiologías infecciosas y no infecciosas y es el resultado de la alteración del entorno vaginal normal. Los LOS Neisseria signos y síntomas más comunes son dolor Dolor Inflammation, prurito, eritema y edema Edema Edema is a condition in which excess serous fluid accumulates in the body cavity or interstitial space of connective tissues. Edema is a symptom observed in several medical conditions. It can be categorized into 2 types, namely, peripheral (in the extremities) and internal (in an organ or body cavity). Edema de la región afectada, así como flujo vaginal y dispareunia. El diagnóstico se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la presentación clínica, los LOS Neisseria hallazgos del examen físico y la inspección de las secreciones vaginales. El tratamiento depende de la etiología, incluyendo los LOS Neisseria antimicrobianos para las causas infecciosas.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La vaginosis bacteriana (VB) es una disbiosis polimicrobiana de la microbiota vaginal, frecuentemente asociada con Gardnerella vaginalis Gardnerella vaginalis Polymicrobial, nonspecific vaginitis associated with positive cultures of gardnerella vaginalis and other anaerobic organisms and a decrease in lactobacilli. It remains unclear whether the initial pathogenic event is caused by the growth of anaerobes or a primary decrease in lactobacilli. Vulvovaginitis.
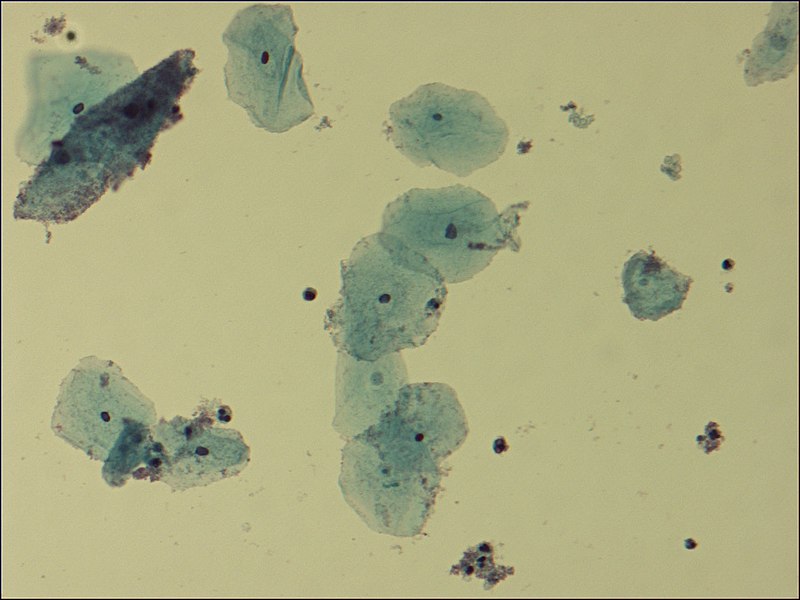
Vista microscópica de las células claves en la VB:
Pequeñas bacterias se adhieren a la periferia de las células epiteliales (la célula más oscura en la esquina superior izquierda).
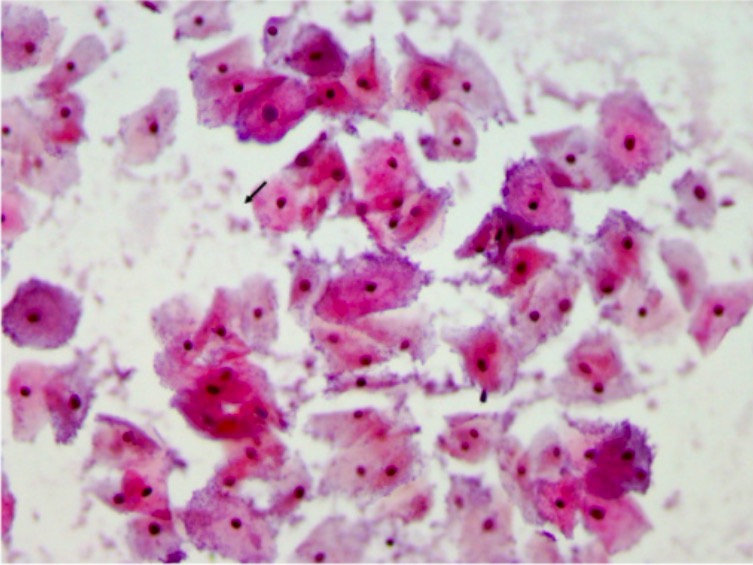
Frotis de Papanicolaou que muestra células claves, lo que indica VB
Imagen: “Pap smear” por el Department of Pathology, Muhimbili University of Health and Allied Sciences (MUHAS), P,O, Box 65001, Dar es Salaam, Tanzania. Licencia: CC BY 2.0.La vaginosis bacteriana se asocia con un mayor riesgo de:
La vaginitis candidiásica es una vaginitis por hongos causada por:
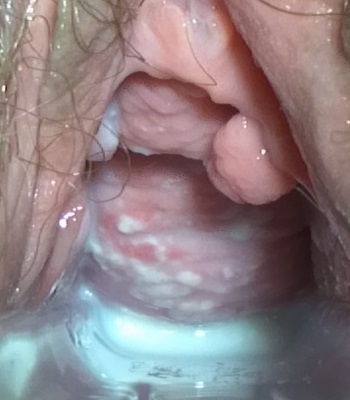
Hallazgos del examen con espéculo en la vulvovaginitis candidiásica:
Flujo vaginal espeso, similar a queso cottage, sobre una pared vaginal ligeramente eritematosa
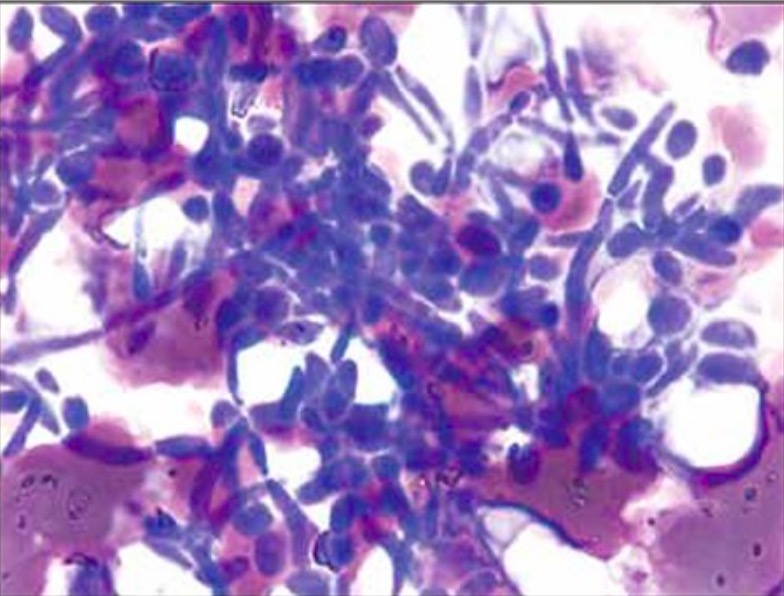
Montaje húmedo que demuestra las pseudohífas de Candida albicans
Imagen: “Extra-leukocytic yeast and hyphal forms of candida” por Medanta The Medicity, Haematology, Gurgaon, India. Licencia: CC BY 2.5Las opciones de tratamiento incluyen antifúngicos orales o tópicos.
La tricomoniasis es la ITS no viral más común.
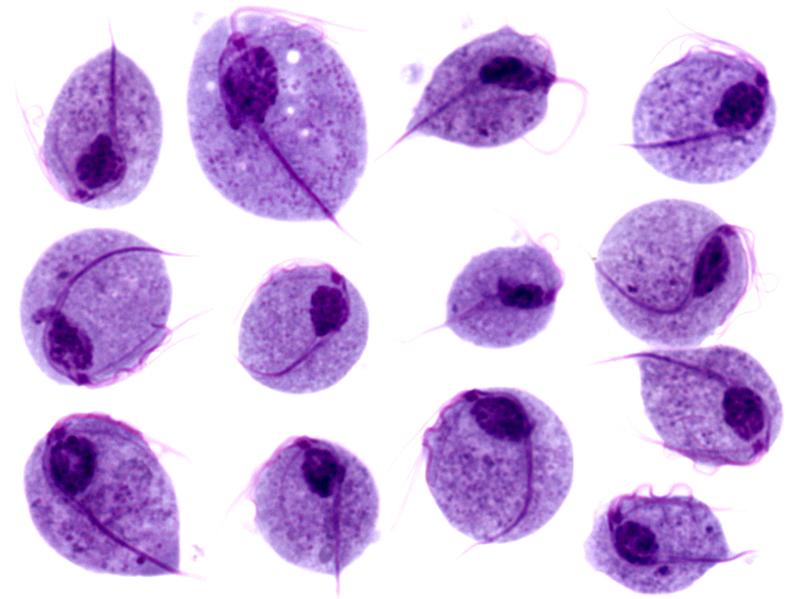
Imágenes microscópicas de trofozoítos de Trichomonas vaginalis
Imagen: “Trichomonas protozoa” por isis325. Licencia: CC BY 2.0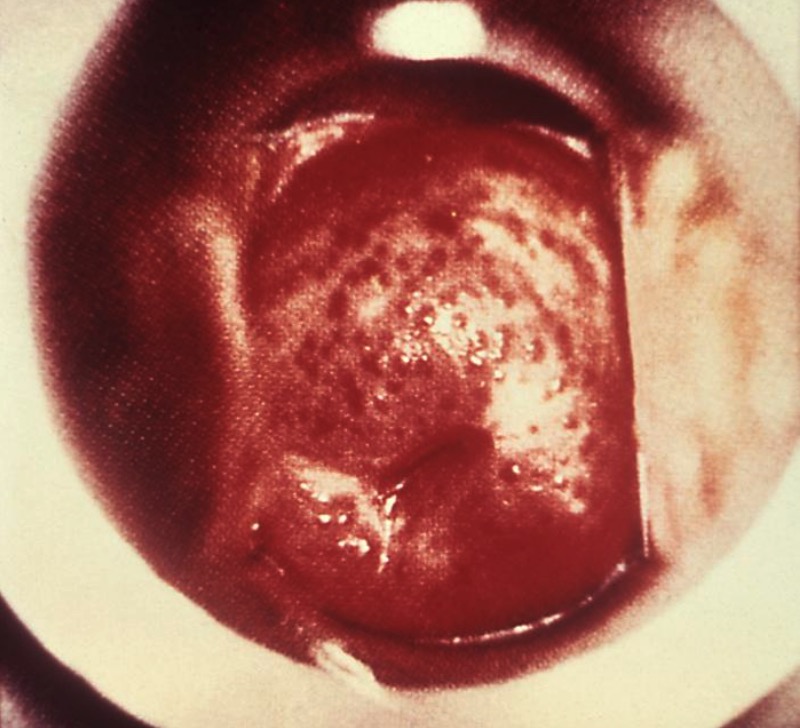
Aspecto “fresa” del cuello uterino en la tricomoniasis
Imagen: “5240” por CDC. Licencia: Public Domain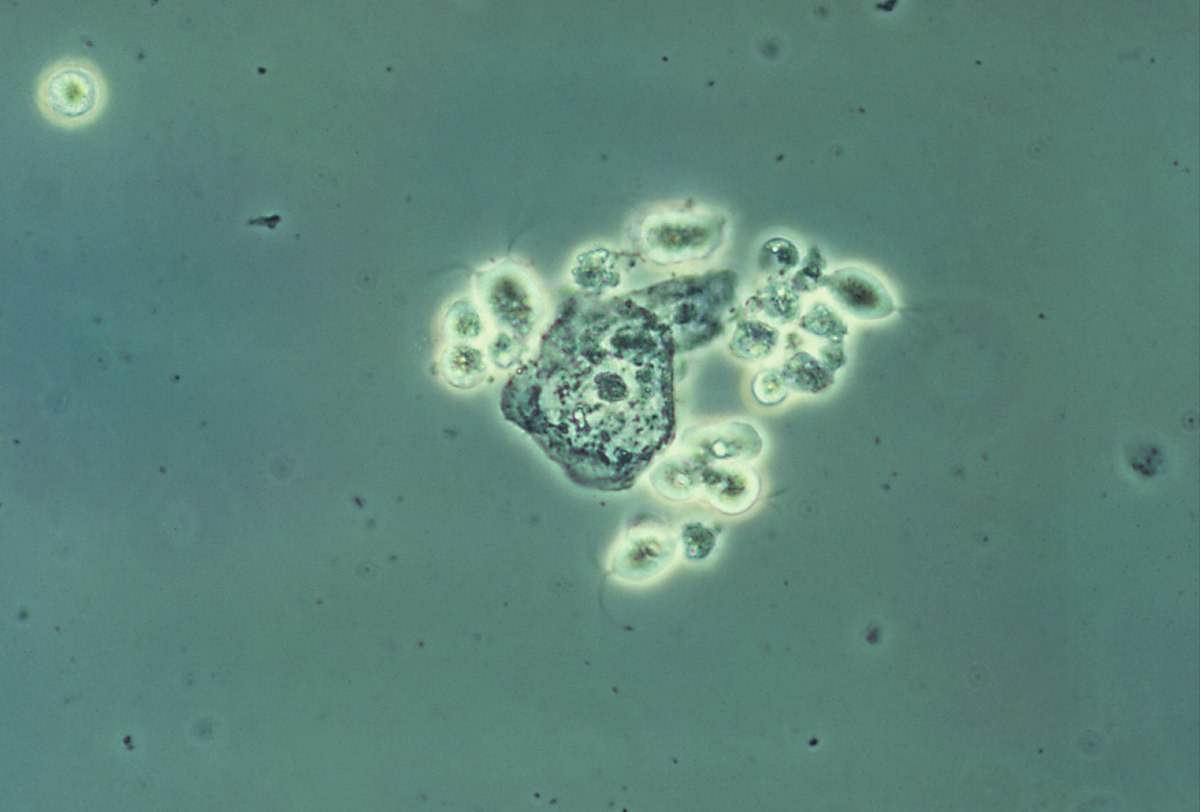
Imagen de montaje húmedo de secreciones vaginales que muestra varios protozoos de T. vaginalis (imagen con contraste)
Imagen: “Trichomonas vaginalis” por CDC. Licencia: Public Domain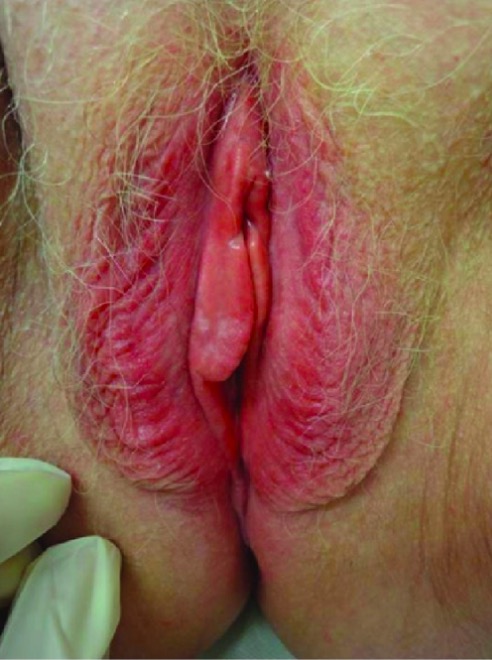
Hallazgos del examen físico en la dermatitis de contacto:
Este paciente tuvo una reacción alérgica a los productos de higiene, lo que provocó una piel roja y edematosa.