La mastitis Mastitis Mastitis is inflammation of the breast tissue with or without infection. The most common form of mastitis is associated with lactation in the first few weeks after birth. Non-lactational mastitis includes periductal mastitis and idiopathic granulomatous mastitis (IGM). Mastitis es la inflamación del tejido mamario con o sin infección. La forma más común de mastitis Mastitis Mastitis is inflammation of the breast tissue with or without infection. The most common form of mastitis is associated with lactation in the first few weeks after birth. Non-lactational mastitis includes periductal mastitis and idiopathic granulomatous mastitis (IGM). Mastitis está asociada a la lactancia en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las primeras semanas después del parto. La mastitis Mastitis Mastitis is inflammation of the breast tissue with or without infection. The most common form of mastitis is associated with lactation in the first few weeks after birth. Non-lactational mastitis includes periductal mastitis and idiopathic granulomatous mastitis (IGM). Mastitis no asociada a la lactancia incluye la mastitis Mastitis Mastitis is inflammation of the breast tissue with or without infection. The most common form of mastitis is associated with lactation in the first few weeks after birth. Non-lactational mastitis includes periductal mastitis and idiopathic granulomatous mastitis (IGM). Mastitis periductal y la mastitis Mastitis Mastitis is inflammation of the breast tissue with or without infection. The most common form of mastitis is associated with lactation in the first few weeks after birth. Non-lactational mastitis includes periductal mastitis and idiopathic granulomatous mastitis (IGM). Mastitis granulomatosa idiopática. La mastitis Mastitis Mastitis is inflammation of the breast tissue with or without infection. The most common form of mastitis is associated with lactation in the first few weeks after birth. Non-lactational mastitis includes periductal mastitis and idiopathic granulomatous mastitis (IGM). Mastitis asociada a la lactancia suele ser causada por Staphylococcus aureus Staphylococcus aureus Potentially pathogenic bacteria found in nasal membranes, skin, hair follicles, and perineum of warm-blooded animals. They may cause a wide range of infections and intoxications. Brain Abscess, que se introduce en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la leche materna durante el amamantamiento. La etiología de la mastitis Mastitis Mastitis is inflammation of the breast tissue with or without infection. The most common form of mastitis is associated with lactation in the first few weeks after birth. Non-lactational mastitis includes periductal mastitis and idiopathic granulomatous mastitis (IGM). Mastitis no asociada a la lactancia es poco conocida, pero la mastitis Mastitis Mastitis is inflammation of the breast tissue with or without infection. The most common form of mastitis is associated with lactation in the first few weeks after birth. Non-lactational mastitis includes periductal mastitis and idiopathic granulomatous mastitis (IGM). Mastitis periductal se asocia comúnmente con el tabaquismo, y la mastitis Mastitis Mastitis is inflammation of the breast tissue with or without infection. The most common form of mastitis is associated with lactation in the first few weeks after birth. Non-lactational mastitis includes periductal mastitis and idiopathic granulomatous mastitis (IGM). Mastitis granulomatosa idiopática se asocia frecuentemente con Corynebacterium Corynebacterium Corynebacteria are gram-positive, club-shaped bacilli. Corynebacteria are commonly isolated on tellurite or Loeffler's media and have characteristic metachromatic granules. The major pathogenic species is Corynebacterium diphtheriae, which causes a severe respiratory infection called diphtheria. Corynebacterium. Las pacientes presentan edema Edema Edema is a condition in which excess serous fluid accumulates in the body cavity or interstitial space of connective tissues. Edema is a symptom observed in several medical conditions. It can be categorized into 2 types, namely, peripheral (in the extremities) and internal (in an organ or body cavity). Edema, eritema, sensibilidad y, posiblemente, una masa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la mama. Generalmente, el diagnóstico es clínico, aunque en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum algunos casos puede ser necesario realizar ultrasonidos, cultivos y biopsias. El tratamiento incluye antibióticos, analgésicos, drenaje de cualquier absceso y escisión quirúrgica del conducto para la mastitis Mastitis Mastitis is inflammation of the breast tissue with or without infection. The most common form of mastitis is associated with lactation in the first few weeks after birth. Non-lactational mastitis includes periductal mastitis and idiopathic granulomatous mastitis (IGM). Mastitis periductal.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La mastitis Mastitis Mastitis is inflammation of the breast tissue with or without infection. The most common form of mastitis is associated with lactation in the first few weeks after birth. Non-lactational mastitis includes periductal mastitis and idiopathic granulomatous mastitis (IGM). Mastitis se refiere a la inflamación de la mama que puede o no estar asociada a una infección.
Mastitis Mastitis Mastitis is inflammation of the breast tissue with or without infection. The most common form of mastitis is associated with lactation in the first few weeks after birth. Non-lactational mastitis includes periductal mastitis and idiopathic granulomatous mastitis (IGM). Mastitis periductal:
Mastitis Mastitis Mastitis is inflammation of the breast tissue with or without infection. The most common form of mastitis is associated with lactation in the first few weeks after birth. Non-lactational mastitis includes periductal mastitis and idiopathic granulomatous mastitis (IGM). Mastitis granulomatosa idiopática:
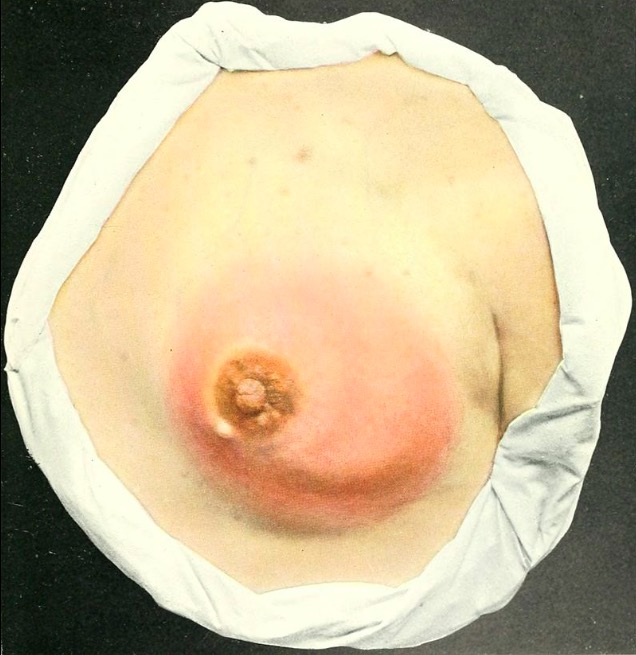
La mastitis asociada a la lactancia se presenta como una mama edematosa y eritematosa.
Imagen: “atlasofclinicals00bock” por Internet Archive Book Images. Licencia: Dominio Público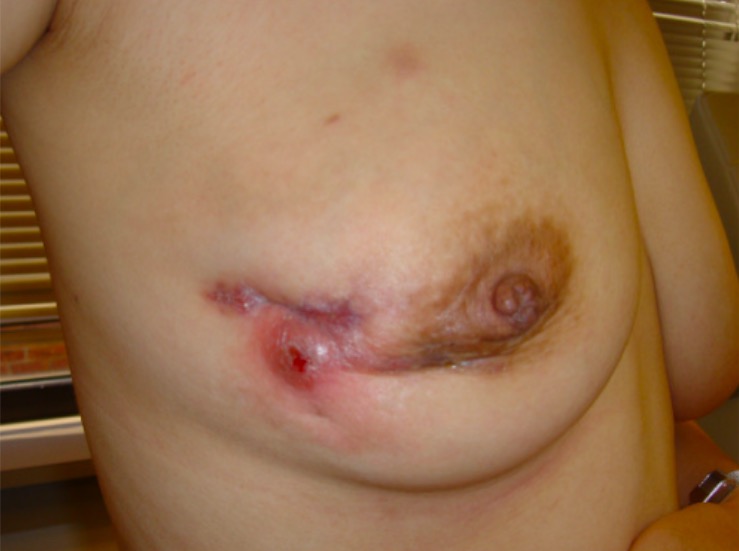
Mastitis granulomatosa idiopática (estado posterior a la biopsia de mama por incisión)
Imagen: “IGM of the right breast” por Dept. of Radiation Oncology, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD 21231, USA. Licencia: CC BY 2.0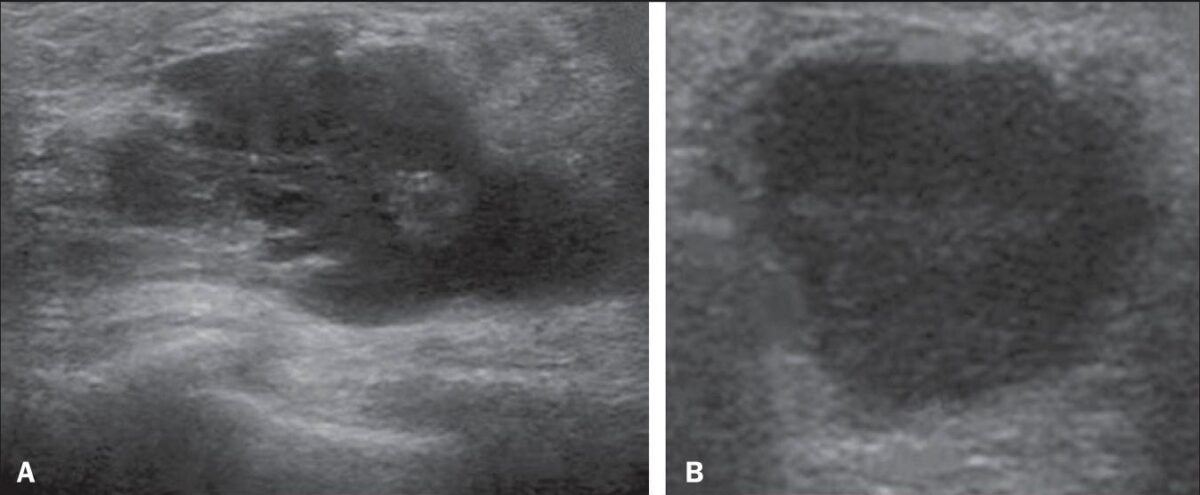
Imagen por ultrasonido de un absceso mamario:
A: compleja, con límites mal definidos
B: aspecto homogéneo con bordes bien definidos
Mastitis Mastitis Mastitis is inflammation of the breast tissue with or without infection. The most common form of mastitis is associated with lactation in the first few weeks after birth. Non-lactational mastitis includes periductal mastitis and idiopathic granulomatous mastitis (IGM). Mastitis periductal:
Mastitis Mastitis Mastitis is inflammation of the breast tissue with or without infection. The most common form of mastitis is associated with lactation in the first few weeks after birth. Non-lactational mastitis includes periductal mastitis and idiopathic granulomatous mastitis (IGM). Mastitis granulomatosa idiopática:
Mastitis Mastitis Mastitis is inflammation of the breast tissue with or without infection. The most common form of mastitis is associated with lactation in the first few weeks after birth. Non-lactational mastitis includes periductal mastitis and idiopathic granulomatous mastitis (IGM). Mastitis periductal:
Mastitis Mastitis Mastitis is inflammation of the breast tissue with or without infection. The most common form of mastitis is associated with lactation in the first few weeks after birth. Non-lactational mastitis includes periductal mastitis and idiopathic granulomatous mastitis (IGM). Mastitis granulomatosa idiopática: