La insuficiencia renal aguda se refiere a la pérdida repentina y a menudo reversible de la función renal, la cual se desarrolla durante días o semanas. La azotemia Azotemia A biochemical abnormality referring to an elevation of blood urea nitrogen and creatinine. Azotemia can be produced by kidney diseases or other extrarenal disorders. When azotemia becomes associated with a constellation of clinical signs, it is termed uremia. Acute Kidney Injury se refiere a los LOS Neisseria niveles elevados de sustancias nitrogenadas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la sangre que acompañan a la IRA, como el BUN y la creatinina. La uremia Uremia A clinical syndrome associated with the retention of renal waste products or uremic toxins in the blood. It is usually the result of renal insufficiency. Most uremic toxins are end products of protein or nitrogen catabolism, such as urea or creatinine. Severe uremia can lead to multiple organ dysfunctions with a constellation of symptoms. Acute Kidney Injury se refiere específicamente a la constelación de síntomas que se producen con la disfunción renal grave. Las etiologías de la IRA se clasifican como prerrenales, renales intrínsecas o postrenales, y existe una presentación clínica variada según la gravedad de la disfunción renal. La insuficiencia renal aguda se diagnostica inicialmente por un cambio en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria niveles de creatinina sérica, y luego se determina la etiología mediante la historia clínica, las pruebas de laboratorio, la imagenología y, posiblemente, la biopsia renal. El tratamiento de la IRA depende de la etiología; sin embargo, siempre es importante prestar atención a la volemia del individuo y a los LOS Neisseria electrolitos séricos. Si el tratamiento no tiene éxito y la IRA evoluciona a ERC, es necesario un tratamiento de reemplazo renal con diálisis o trasplante renal.
Last updated: Jul 17, 2023
La insuficiencia renal aguda se refiere a una disminución brusca de la función renal, manifestada por un aumento del nivel de creatinina sérica, con o sin reducción de la diuresis.
Anteriormente, había más de 30 definiciones de “falla renal aguda” en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la literatura, y estas se han actualizado al AL Amyloidosis término de IRA.
Las causas de la IRA se suelen organizar en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum etiologías prerrenales, renales intrínsecas o postrenales. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las causas prerrenales y postrenales, los LOS Neisseria riñones tienen una anatomía normal y la lesión se debe a los LOS Neisseria efectos del factor incitante.
La insuficiencia renal aguda puede presentarse con una amplia gama de síntomas, desde ser asintomática con solo anormalidades de laboratorio hasta el coma Coma Coma is defined as a deep state of unarousable unresponsiveness, characterized by a score of 3 points on the GCS. A comatose state can be caused by a multitude of conditions, making the precise epidemiology and prognosis of coma difficult to determine. Coma debido a una uremia Uremia A clinical syndrome associated with the retention of renal waste products or uremic toxins in the blood. It is usually the result of renal insufficiency. Most uremic toxins are end products of protein or nitrogen catabolism, such as urea or creatinine. Severe uremia can lead to multiple organ dysfunctions with a constellation of symptoms. Acute Kidney Injury severa.
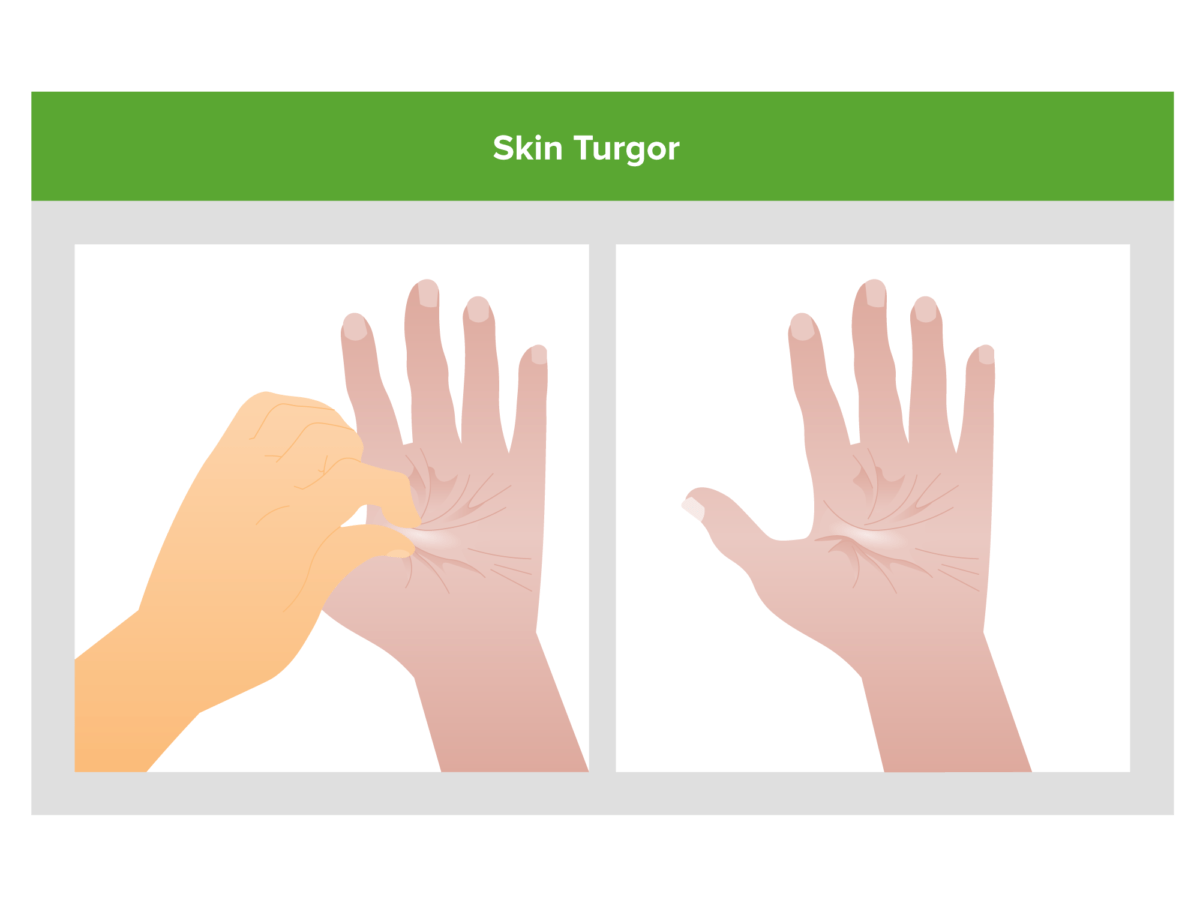
La pobre turgencia de la piel (la piel permanece tensa después de ser pellizcada) es un indicio potencial de que la depleción de volumen puede ser la causa de la lesión renal aguda de un individuo.
Imagen por Lecturio.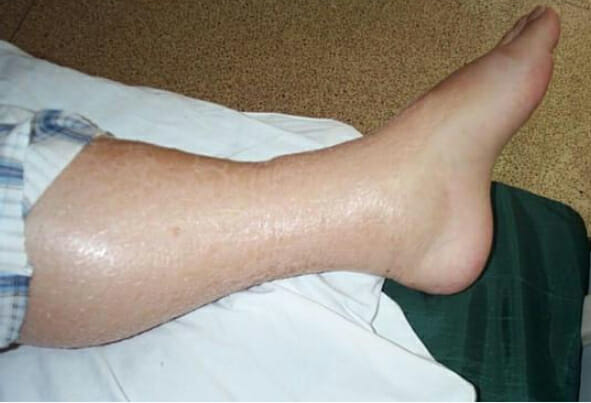
Edema de las extremidades inferiores: puede observarse en individuos que presentan hipervolemia como resultado de una lesión renal aguda
Imagen: “Leg Edema 01” por Wang Kai-feng, Pan Hong-ming, Lou Hai-zhou, Shen Li-rong, Zhu Xi-yan. Licencia: CC BY 2.0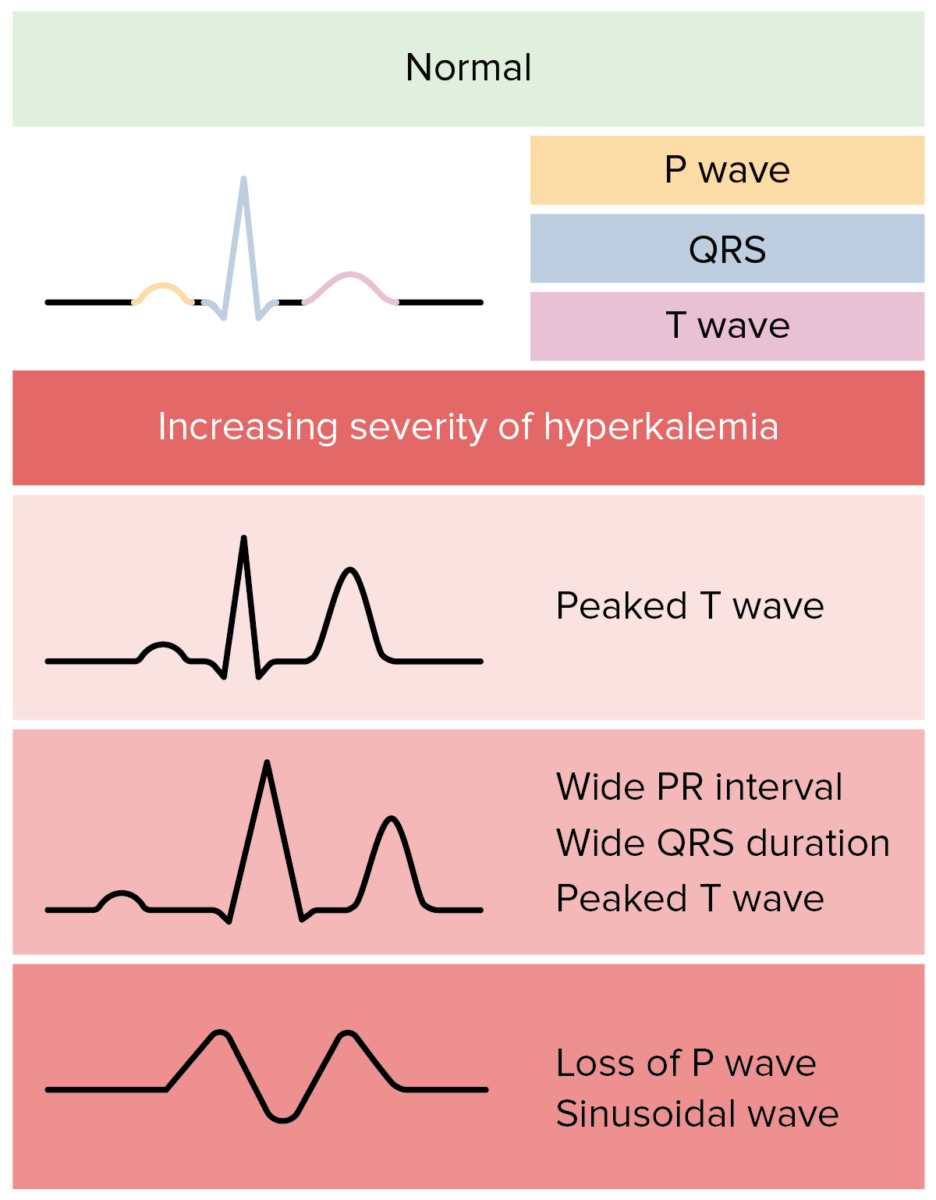
Posibles cambios en el ECG debidos a la hiperpotasemia en individuos con lesión renal aguda:
En realidad, los cambios del ECG en la hiperpotasemia son más variables y menos predecibles.
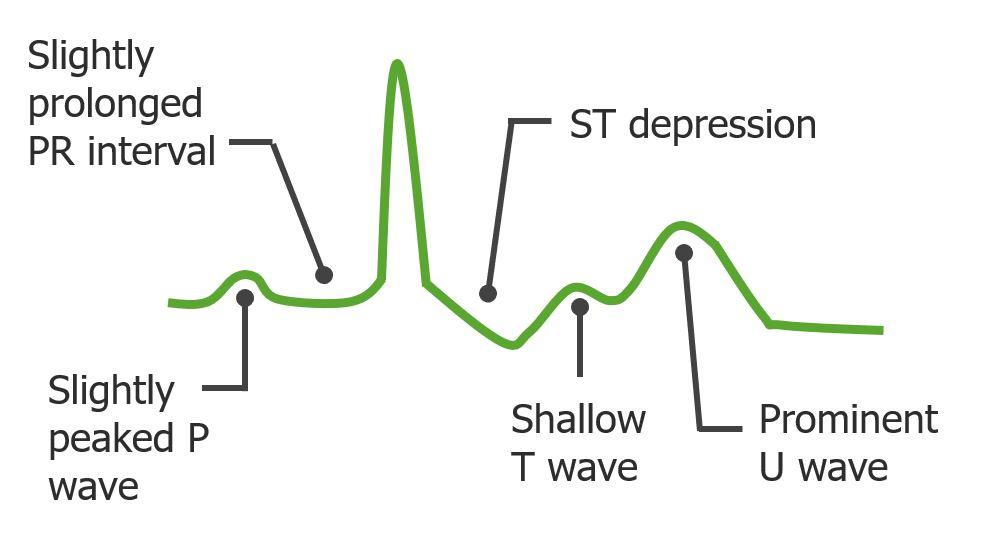
Posibles cambios en el ECG de personas con lesión renal aguda que presentan hipopotasemia
Imagen por Lecturio. Licencia: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0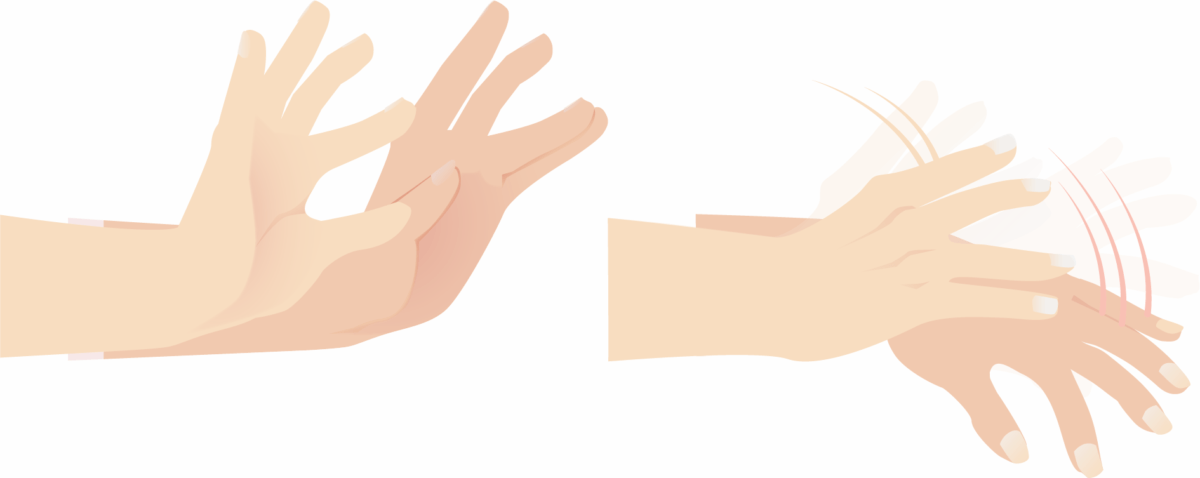
Asterixis: un posible hallazgo de examen en un individuo con uremia por lesión renal aguda
Imagen por Lecturio.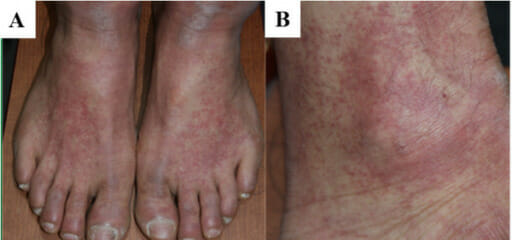
Máculas de tamaño variable y parches eritematosos en un individuo con nefritis intersticial aguda
Imagen: “F1: Gross and microscopic exam of the skin.” por Ha Yeon Kim, Sung Sun Kim, Soo Hyeon Bae, Eun Hui Bae, Seong Kwon Ma & Soo Wan Kim. Licencia: CC BY 4.0, cortada por Lecturio.La necrosis Necrosis The death of cells in an organ or tissue due to disease, injury or failure of the blood supply. Ischemic Cell Damage tubular aguda sigue un curso clínico característico que incluye 3 fases.
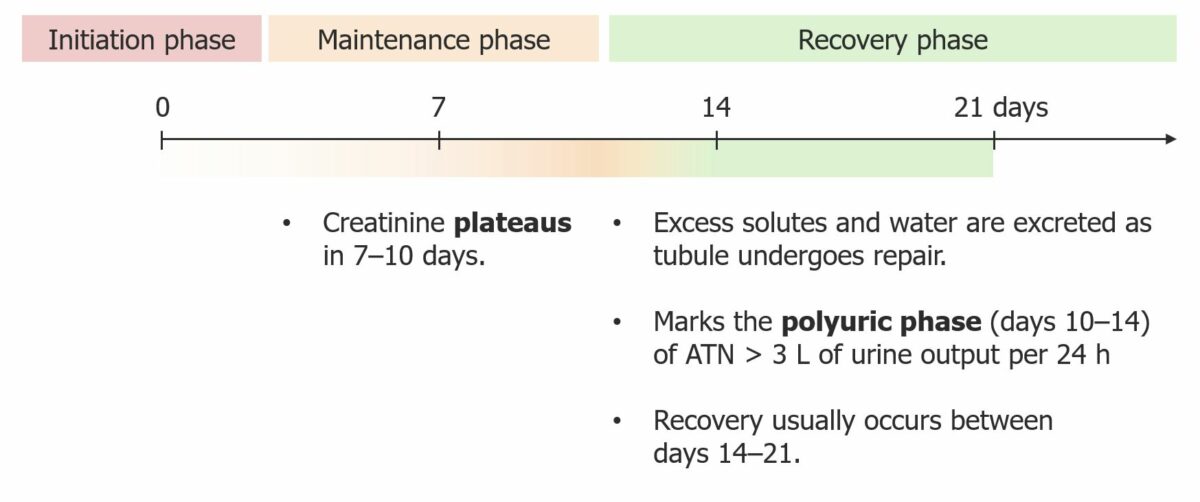
Evolución clínica de la necrosis tubular aguda (NTA)
Imagen por Lecturio. Licencia CC BY-NC-SA 4.0El diagnóstico de la IRA incluye la identificación de los LOS Neisseria factores desencadenantes y determinar si la etiología es prerrenal, intrarrenal o postrenal, con el fin de planificar el tratamiento adecuado.
Considerar otras pruebas específicas para etiologías menos comunes:
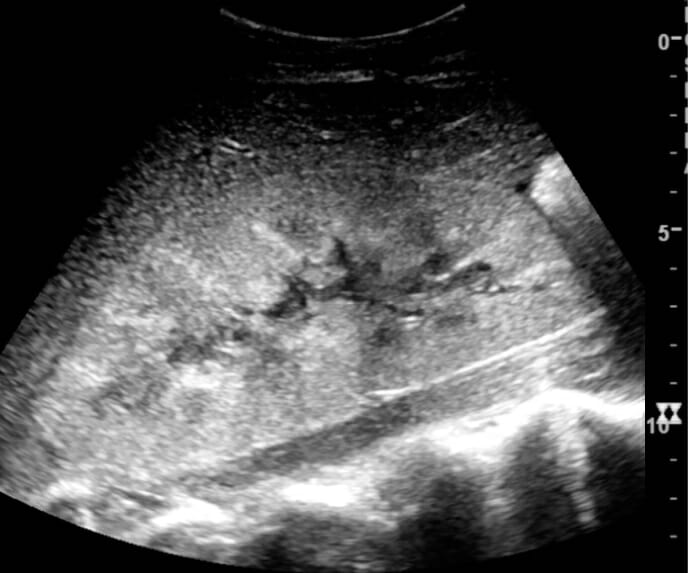
Imagen por ultrasonido que muestra un aumento de la ecogenicidad cortical y un riñón agrandado:
La biopsia posterior mostró una necrosis tubular aguda.
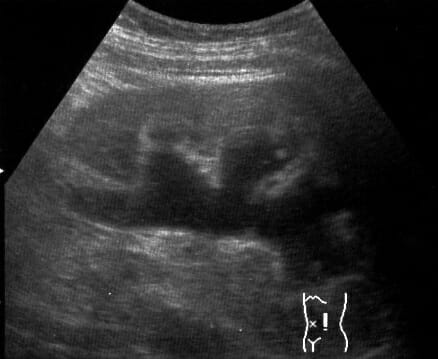
Imagen por ultrasonido que muestra la hidronefrosis del riñón izquierdo debido a un cálculo ureteral
Imagen: “Hydro” por morning2k. Licencia: CC BY 2.5| Prerrenal | Renal (NTA) | |
|---|---|---|
| Densidad urinaria | ≥ 1,020 | ≤ 1,010 |
| Osmolalidad urinaria (mOsm/kg) | > 500 | < 350 |
| Sodio urinario (mEq/L) | < 20 | > 20 |
| FENa | < 1% | > 1% |
| Proteína en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum orina | Mínima | De mínima a grave, según la etiología |
| Hallazgo | Significado |
|---|---|
| Células tubulares renales | Lesión tubular aguda |
| Eritrocitos | Hemorragia no glomerular/ en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum cualquier parte del tracto urinario |
| Eritrocitos dismórficos | Enfermedad glomerular |
| Cilindros eritrocitarios | Diagnóstico para la enfermedad glomerular |
| Leucocitos | Infección del tracto urinario |
| Cilindros leucocitarios | Infección renal |
| Cilindros hialinos | Cualquier tipo de enfermedad renal |
| Cilindros granulares | Enfermedad renal más significativa |
| “Cilindros marrón fangoso” | Células tubulares necróticas/lesión tubular aguda |
La etiología de la IRA orienta el tratamiento; la evaluación adicional con una biopsia puede estar indicada después de haber completado el estudio y el tratamiento adecuados para la hipovolemia o la sobrecarga de líquidos.