La hemoptisis se define como la expectoración de sangre originada en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el tracto respiratorio inferior. La hemoptisis es una consecuencia de un proceso de otra enfermedad y se puede clasificar como amenazante o no amenazante. Solo 5%–15% de los LOS Neisseria pacientes con hemoptisis presentan una hemorragia potencialmente mortal. Sin embargo, la hemoptisis puede dar lugar a morbilidad y mortalidad significativas debido a ahogamiento (intercambio reducido de gases, porque los LOS Neisseria pulmones se llenan de sangre) y a shock Shock Shock is a life-threatening condition associated with impaired circulation that results in tissue hypoxia. The different types of shock are based on the underlying cause: distributive (↑ cardiac output (CO), ↓ systemic vascular resistance (SVR)), cardiogenic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), hypovolemic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), obstructive (↓ CO), and mixed. Types of Shock hemorrágico. Las causas más comunes de hemoptisis incluyen bronquiectasia, cáncer de pulmón, tuberculosis Tuberculosis Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex bacteria. The bacteria usually attack the lungs but can also damage other parts of the body. Approximately 30% of people around the world are infected with this pathogen, with the majority harboring a latent infection. Tuberculosis spreads through the air when a person with active pulmonary infection coughs or sneezes. Tuberculosis y aspergilosis. El diagnóstico implica imagenología de tórax y broncoscopia. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum casos de sangrado potencialmente mortal, el tratamiento se dirige inicialmente a estabilizar al AL Amyloidosis paciente y, si el sangrado está en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum curso, la hemostasia a menudo se puede lograr con técnicas mínimamente invasivas (e.g., embolización arterial).
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La hemoptisis se define como la expectoración de sangre originada en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las vías respiratorias inferiores. La hemoptisis es una consecuencia del proceso de otra enfermedad y se puede clasificar como amenazante o no amenazante.
| Enfermedad de las vías respiratorias |
|
|---|---|
| Neoplasias |
|
| Infecciones |
|
| Otra enfermedad del parénquima pulmonar |
|
| Enfermedad vascular pulmonar |
|
| Trastornos hemorrágicos |
|
| Trauma |
|
| Otros |
|
El suministro de sangre a los LOS Neisseria pulmones implica la circulación pulmonar y sistémica.
La hemoptisis no amenazante generalmente surge del sangrado en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la circulación pulmonar.
Arteria pulmonar:
La hemoptisis amenazante se presenta generalmente por sangrado en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la circulación de la arteria bronquial.
Arterias bronquiales:
Fisiopatología de la hemoptisis amenazante:
La presentación clínica depende de la etiología subyacente.
Hallazgos comunes:
Hallazgos sugestivos de etiologías infecciosas:
Hallazgos con sangrado amenazante:
Hallazgos sugestivos de pseudohemoptisis:
Otros signos y síntomas específicos de la etiología subyacente pueden estar presentes (e.g., el edema Edema Edema is a condition in which excess serous fluid accumulates in the body cavity or interstitial space of connective tissues. Edema is a symptom observed in several medical conditions. It can be categorized into 2 types, namely, peripheral (in the extremities) and internal (in an organ or body cavity). Edema unilateral de las extremidades inferiores puede sugerir trombosis venosa profunda (TVP) indicativa de EP EP Ectopic pregnancy refers to the implantation of a fertilized egg (embryo) outside the uterine cavity. The main cause is disruption of the normal anatomy of the fallopian tube. Ectopic Pregnancy).
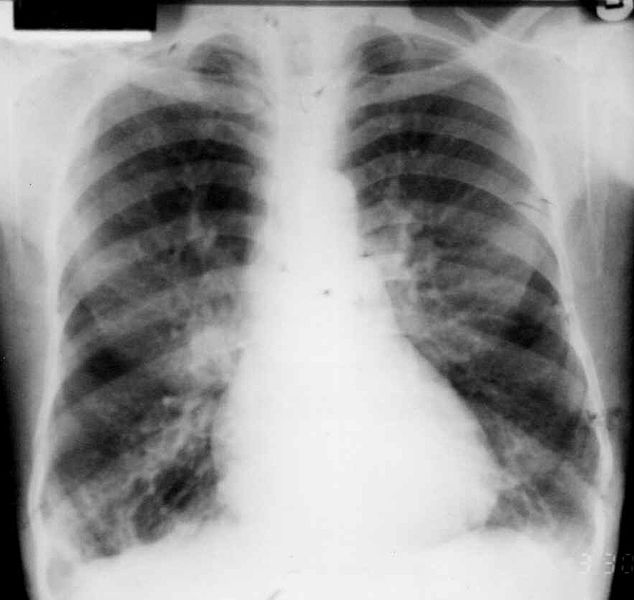
Una radiografía de tórax que demuestra bronquiectasia
Imagen: “Bronchiectasis imaging” por Arinna’l. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoEl 1er paso en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la hemoptisis amenazante es estabilizar al AL Amyloidosis paciente.
El tratamiento se enfoca en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum tratar la causa subyacente.
Cuando un paciente se presenta con hemoptisis, las siguientes etiologías deben ser las primeras en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el diagnóstico diferencial: