Las proteínas tienen una amplia gama de funciones en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el cuerpo. Las proteínas estructurales ayudan a mantener la integridad física de las células y permiten el movimiento de sustancias dentro de las células. Las proteínas catalíticas son enzimas, que son críticas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum casi todas las funciones biológicas (e.g., metabolismo, coagulación, digestión). Las proteínas de comunicación, señalización y regulación son fundamentales para coordinar las respuestas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum todo el organismo e incluyen receptores, hormonas, neurotransmisores, moléculas de señalización intracelular (como quinasas y proteínas G) y factores de transcripción. Además, las proteínas participan en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el transporte de sustancias a través del torrente sanguíneo, así como a través de las membranas celulares. Las proteínas también juegan un papel crítico en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el sistema inmunológico.
Last updated: Apr 25, 2025
Las proteínas son 1 de los LOS Neisseria 3 principales macronutrientes utilizados en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el cuerpo. Las proteínas están compuestas de aminoácidos y tienen una amplia gama de funciones en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el cuerpo, que incluyen:
Las proteínas estructurales son importantes para mantener la forma celular y la integridad física.
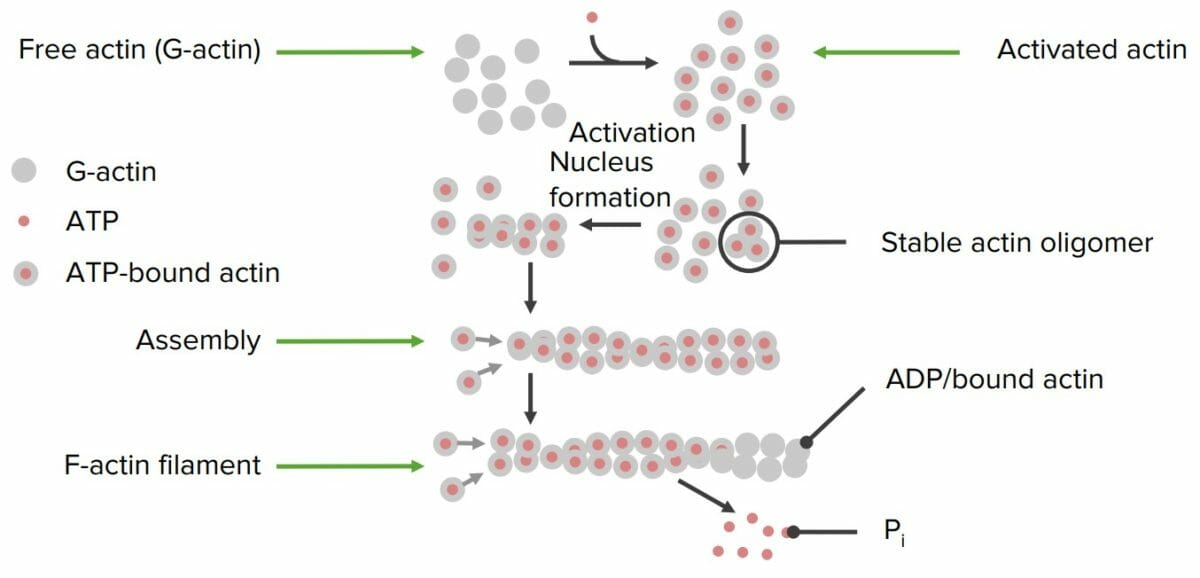
Formación de filamentos de actina a partir de proteínas individuales de actina:
La actina libre se activa con adenosin trifosfato (ATP, por sus siglas en inglés). Se forma un núcleo de activación y comienza la polimerización. Una vez ensamblado el filamento, se libera un fosfato individual (Pi) de las proteínas individuales de actina, que lo “desactiva”, dando como resultado un filamento final estable. Un adenosin difosfato (ADP, por sus siglas en inglés) permanece unido a cada actina.
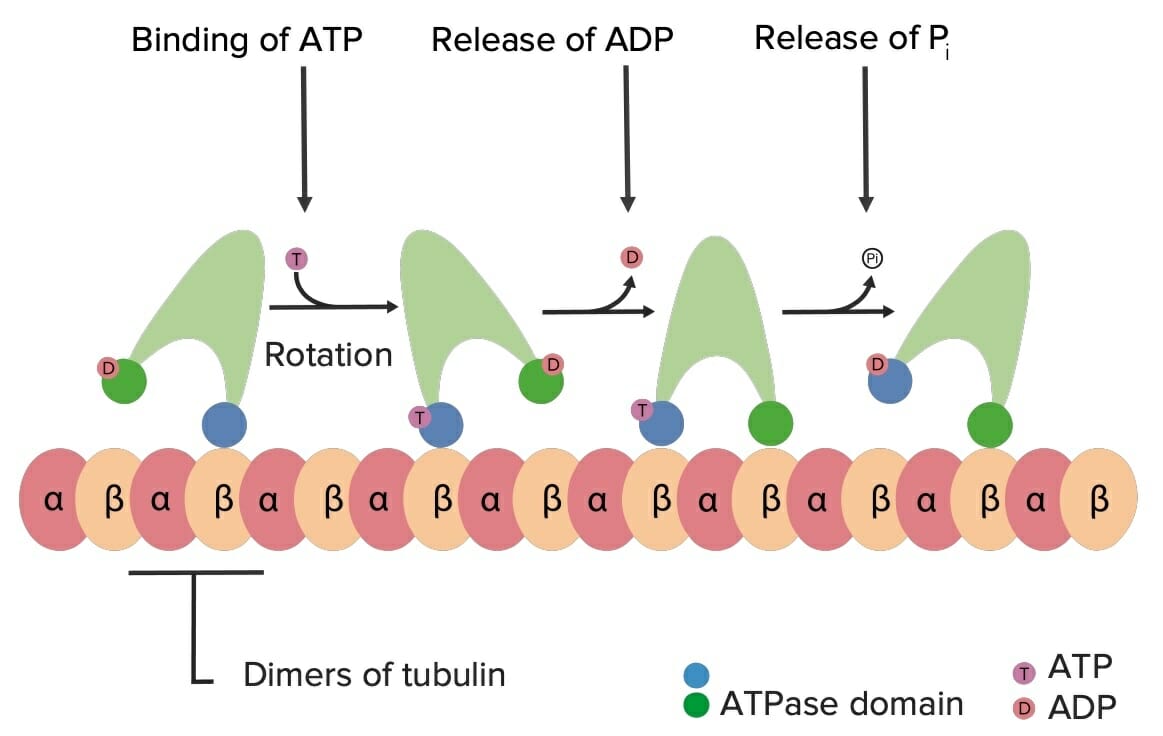
Ejemplo de cómo la quinesina se mueve por los microtúbulos utilizando energía ATP:
Cuando el ATP se une a la quinesina, da como resultado un cambio conformacional en la molécula, lo que hace que “gire” sobre la tubulina. Esto conduce a un movimiento de “marcha” de la quinesina (y su carga) por las “carreteras” de los microtúbulos dentro de la célula.
Pi: fosfato
Estas proteínas son responsables de:
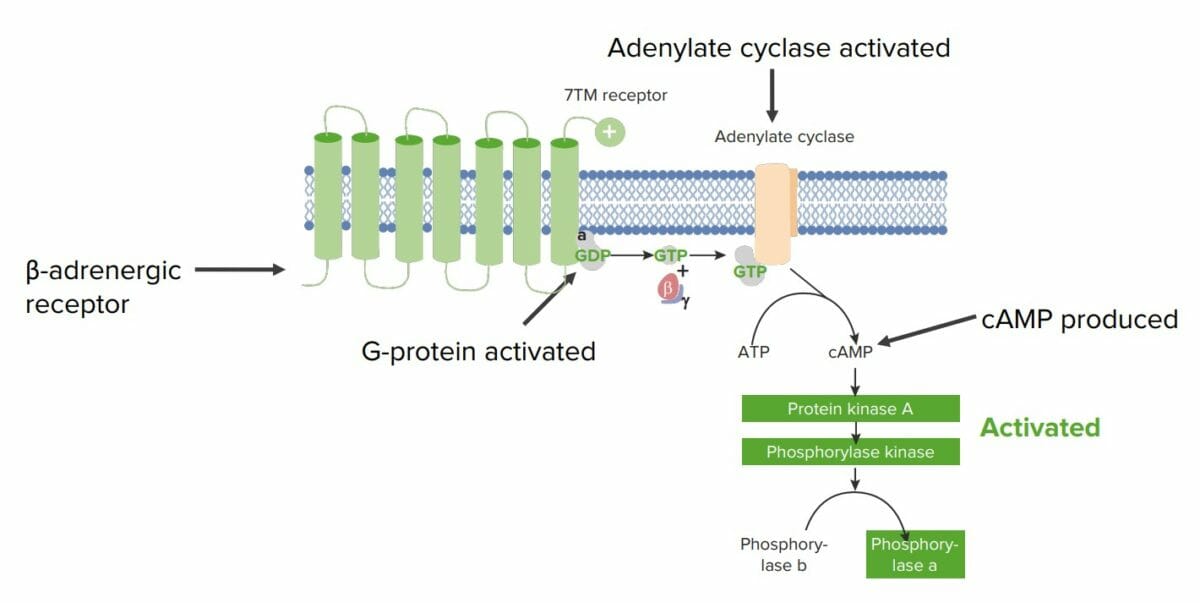
Ejemplo de cómo las proteínas están involucradas en la señalización celular en un hepatocito:
Los receptores adrenérgicos β son receptores 7TM unidos a la membrana (receptor con 7 dominios transmembranales) que se une a una proteína G en el lado citosólico y responden a las catecolaminas circulantes (e.g., epinefrina, una monoamina derivada de los aminoácidos).
La epinefrina induce un cambio conformacional en el receptor, que activa a la proteína G unida.
La proteína G se une a guanosin trifosfato (GTP, por sus siglas en inglés) y libera 2 de sus subunidades (β y 𝝲). La unidad α restante unida a GTP luego activa otra proteína unida a la membrana llamada adenilato ciclasa.
La adenilato ciclasa convierte el ATP en AMPc, que es un 2do mensajero intracelular común. Aquí, el AMPc activa la proteína quinasa A (PKA), que fosforila la fosforilasa quinasa, activándola.
La fosforilasa quinasa luego fosforila la glucógeno fosforilasa B, creando glucógeno fosforilasa A, que es capaz de descomponer el glucógeno para producir moléculas de glucosa.
En este ejemplo, la molécula de señalización (epinefrina) desencadenó la formación de un 2do mensajero intracelular y luego una cascada de fosforilación, lo que resultó en la liberación de glucosa del hepatocito.
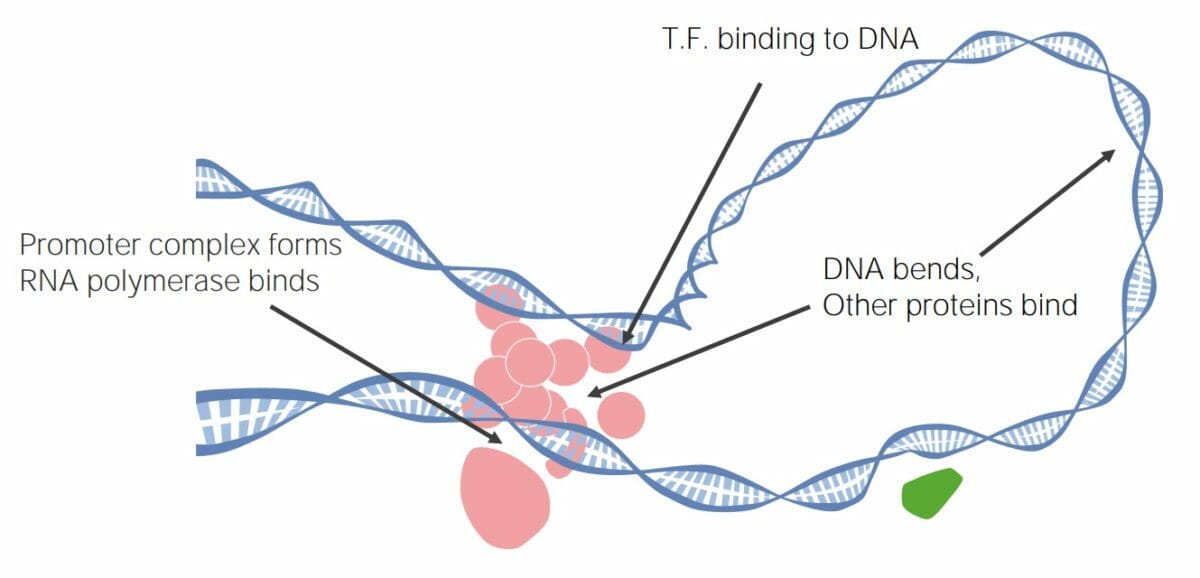
Los factores de transcripción (TFs) pueden unirse al ADN, creando grandes complejos de transcripción que promueven o inhiben la transcripción y, en última instancia, regulan la expresión génica.
Imagen por Lecturio.Existen 2 modelos principales que ayudan a explicar cómo funcionan las enzimas:
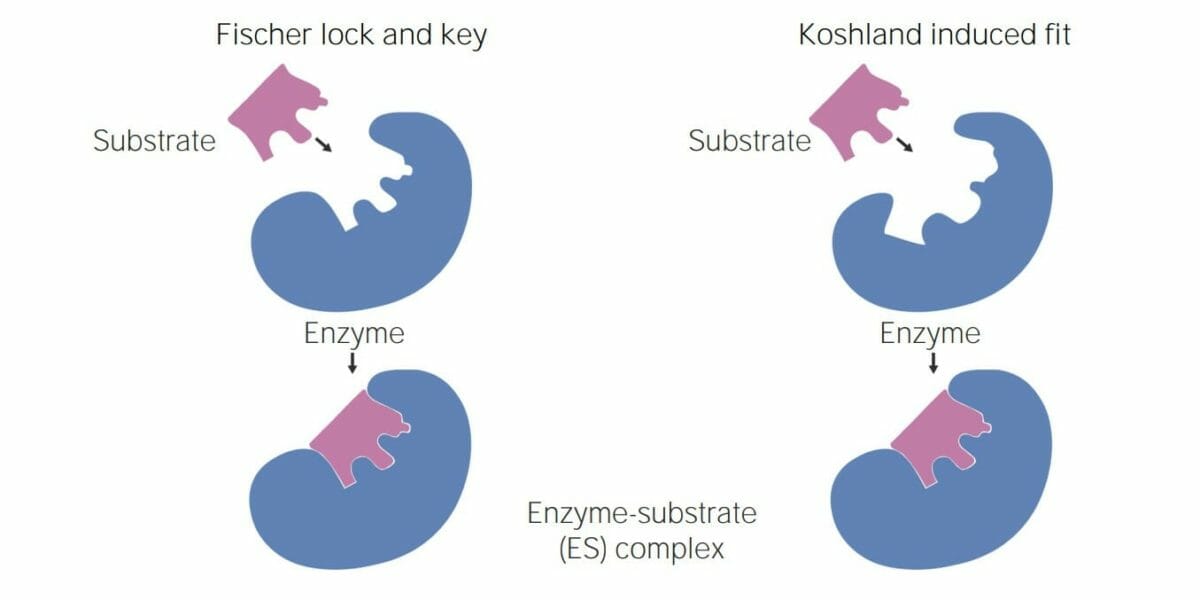
Imagen que muestra las 2 teorías de la interacción enzima–sustrato
Imagen por Lecturio.Otra función importante de las proteínas es transportar y/o almacenar biomoléculas, incluidas sustancias como oxígeno, vitaminas y minerales, hormonas y más.
Las proteínas circulantes transportan sustancias a través de la sangre y/o los LOS Neisseria espacios intersticiales; Ejemplos incluyen:
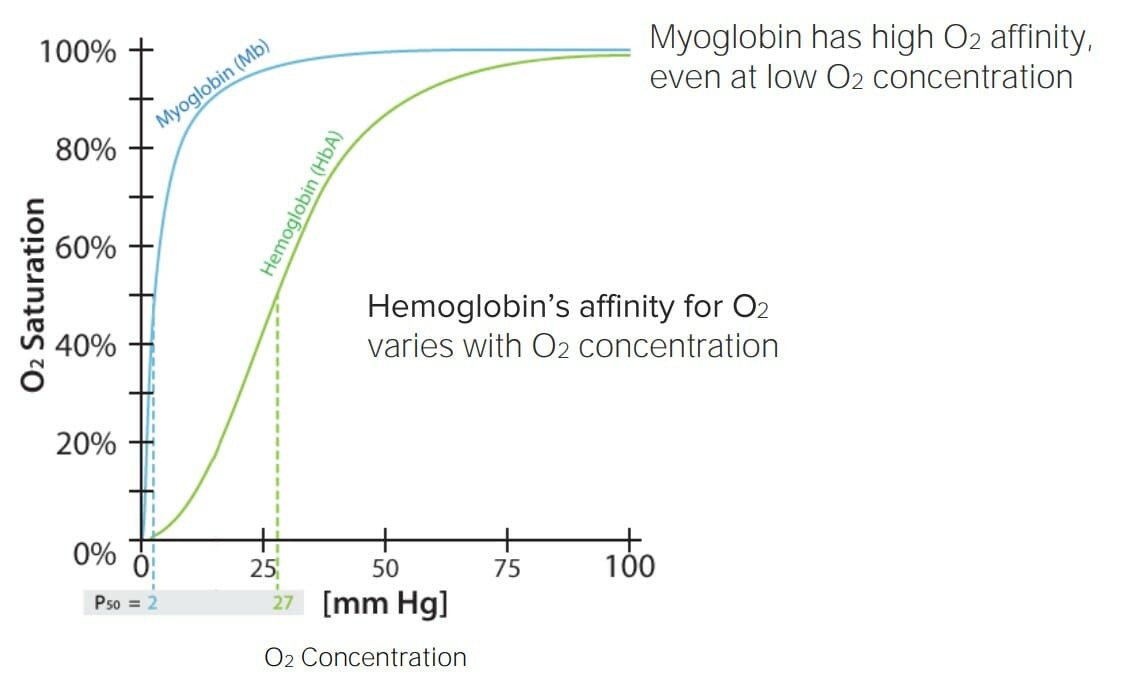
Afinidad de la hemoglobina y la mioglobina por el oxígeno (O2) en función de la saturación de O2:
Obsérvese las variaciones en la afinidad de la hemoglobina en función de la saturación de O2 circundante. Esto significa que la hemoglobina se unirá fácilmente al O2 cuando él O2 sea abundante (e.g., durante la inhalación en los pulmones), pero lo liberará fácilmente cuando la saturación de O2 sea baja (e.g., en los tejidos).
Esto hace que la hemoglobina sea una excelente molécula de transporte de O2. Por otro lado, la mioglobina tiene una alta afinidad por él O2 independientemente de la saturación de O2 circundante, lo que significa que se unirá fácilmente al O2 y no lo liberará hasta que la saturación de O2 circundante sea casi 0. Esto hace que la mioglobina sea una excelente molécula de almacenamiento de O2.
P50: presión a la que el 50% de las moléculas (hemoglobina o mioglobina) están saturadas de O2/p>
Imagen por Lecturio.
Las proteínas unidas a la membrana mueven sustancias a través de la membrana celular. Ejemplos incluyen:
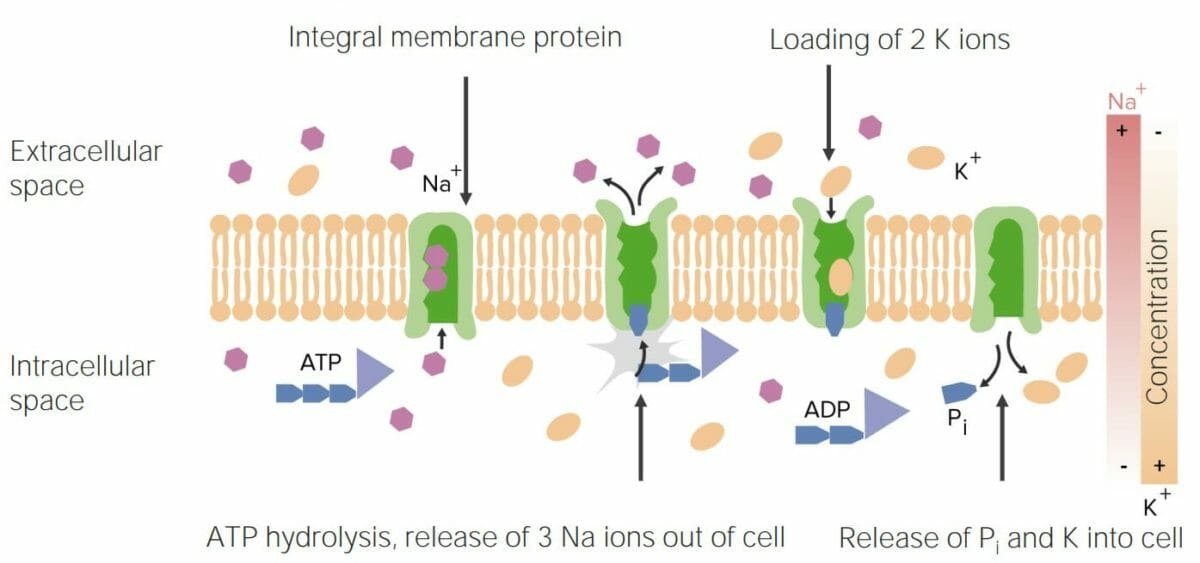
Imagen que muestra el funcionamiento del transportador Na/K-ATPasa, que es una función importante de las proteínas
Pi: fosfato
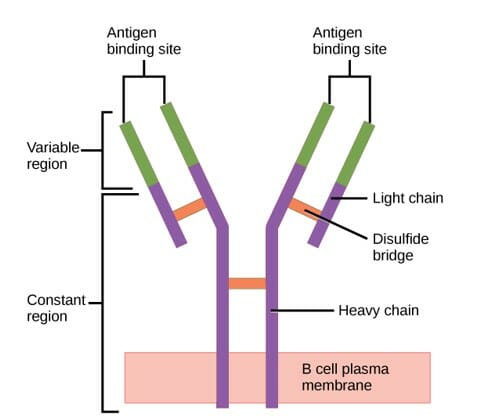
Estructura del anticuerpo (regiones):
El anticuerpo tiene una región variable única (formada por cadenas pesadas y ligeras) capaz de unirse a un antígeno diferente y una región constante (formada por cadenas pesadas).
Existen 5 clases diferentes de inmunoglobulinas:
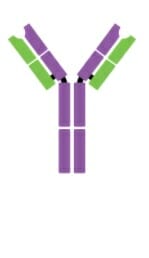
Monómero IgD
Imagen: “Five classes of antibodies” por OpenStax. Licencia: CC BY 4.0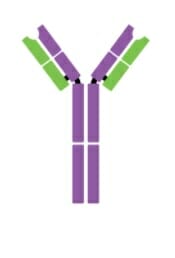
Monómero de IgE
Imagen: “Five classes of antibodies” por OpenStax. Licencia: CC BY 4.0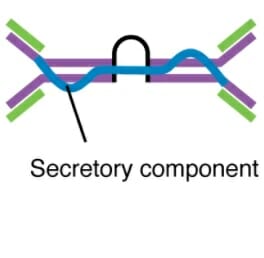
Dímero secretor de IgA
Imagen: “Five classes of antibodies” por OpenStax. Licencia: CC BY 4.0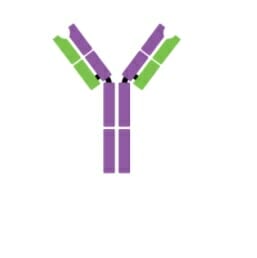
Monómero de IgM
Imagen: “Five classes of antibodies” por OpenStax. Licencia: CC BY 4.0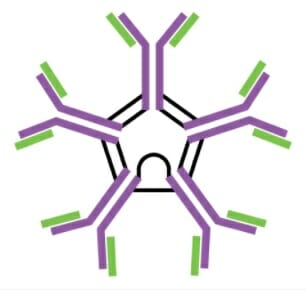
Pentámero de IgM
Imagen: “Five classes of antibodies” por OpenStax. Licencia: CC BY 4.0| Pentámero de IgM IgM A class of immunoglobulin bearing mu chains (immunoglobulin mu-chains). Igm can fix complement. The name comes from its high molecular weight and originally being called a macroglobulin. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions | Monómero de IgG IgG The major immunoglobulin isotype class in normal human serum. There are several isotype subclasses of igg, for example, igg1, igg2a, and igg2b. Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis | Dímero secretor de IgA IgA Represents 15-20% of the human serum immunoglobulins, mostly as the 4-chain polymer in humans or dimer in other mammals. Secretory iga is the main immunoglobulin in secretions. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions | Monómero de IgE IgE An immunoglobulin associated with mast cells. Overexpression has been associated with allergic hypersensitivity. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions | Monómero de IgD IgD An immunoglobulin which accounts for less than 1% of plasma immunoglobulin. It is found on the membrane of many circulating B lymphocytes. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cadenas pesadas | μ | γ | α | ε | δ |
| Número de sitios de unión a antígenos | 10 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 2 |
| Peso molecular (daltons) | 900 000 | 150 000 | 385 000 | 200 000 | 180 000 |
| Porcentaje de anticuerpos totales en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum suero | 6% | 80% | 13% | 0,002% | 1% |
| Atraviesa la placenta Placenta A highly vascularized mammalian fetal-maternal organ and major site of transport of oxygen, nutrients, and fetal waste products. It includes a fetal portion (chorionic villi) derived from trophoblasts and a maternal portion (decidua) derived from the uterine endometrium. The placenta produces an array of steroid, protein and peptide hormones (placental hormones). Placenta, Umbilical Cord, and Amniotic Cavity | No | Si | No | No | No |
| Fija el complemento | Si | Si | No | No | No |
| Fc Fc Crystallizable fragments composed of the carboxy-terminal halves of both immunoglobulin heavy chains linked to each other by disulfide bonds. Fc fragments contain the carboxy-terminal parts of the heavy chain constant regions that are responsible for the effector functions of an immunoglobulin (complement fixation, binding to the cell membrane via fc receptors, and placental transport). This fragment can be obtained by digestion of immunoglobulins with the proteolytic enzyme papain. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions se une a | Fagocitos | Mastocitos y basófilos | |||
| Función | Anticuerpo principal de las respuestas primarias, es el mejor en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la fijación del complemento; la forma monomérica de IgM IgM A class of immunoglobulin bearing mu chains (immunoglobulin mu-chains). Igm can fix complement. The name comes from its high molecular weight and originally being called a macroglobulin. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions sirve como receptor Receptor Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors de células B | Anticuerpo sanguíneo principal de las respuestas secundarias, neutraliza toxinas, opsonización | Se secreta hacia el moco, lágrimas, saliva Saliva The clear, viscous fluid secreted by the salivary glands and mucous glands of the mouth. It contains mucins, water, organic salts, and ptyalin. Salivary Glands: Anatomy, calostro | Anticuerpo de actividad alérgica y antiparasitaria | Receptor Receptor Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors de células B |
Un sinnúmero de trastornos clínicos son causados por anormalidades o deficiencias de proteínas y/o metabolismo proteico anormal. A continuación se enumeran algunos ejemplos.