Lipopeptides and Lipoglycopeptides
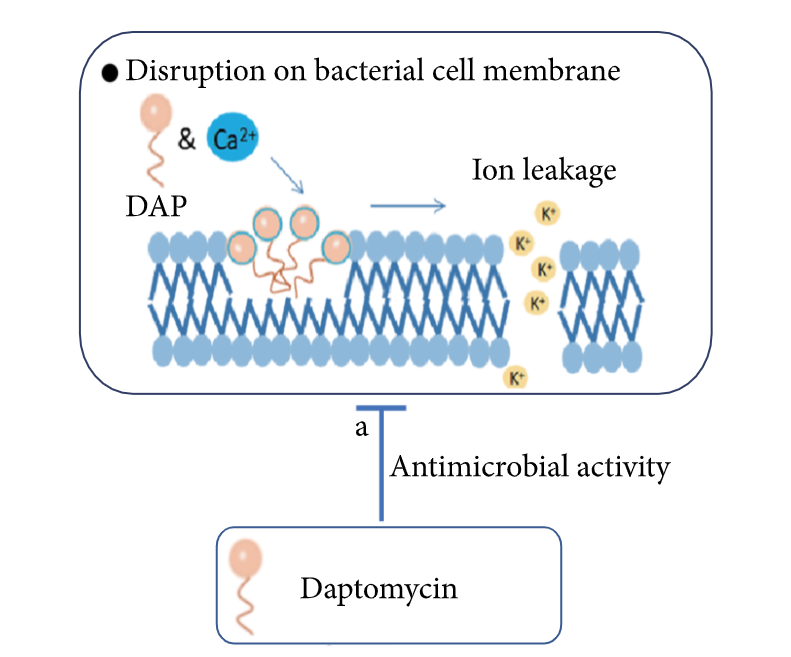
Chemistry and Pharmacodynamics Lipopeptides Mechanism of action of lipopeptides Lipoglycopeptides Mechanism of action of lipoglycopeptides Pharmacokinetics Lipopeptides: daptomycin Lipoglycopeptides Indications Lipopeptides and lipoglycopeptides are agents active against gram-positive bacteria. Lipopeptides: daptomycin (IV) Lipoglycopeptides Adverse Effects and Contraindications Lipopeptides: daptomycin Lipoglycopeptides Comparison of Antibiotics The following antibiotics are agents with activity against gram-positive bacteria. All act […]
Cephalosporins
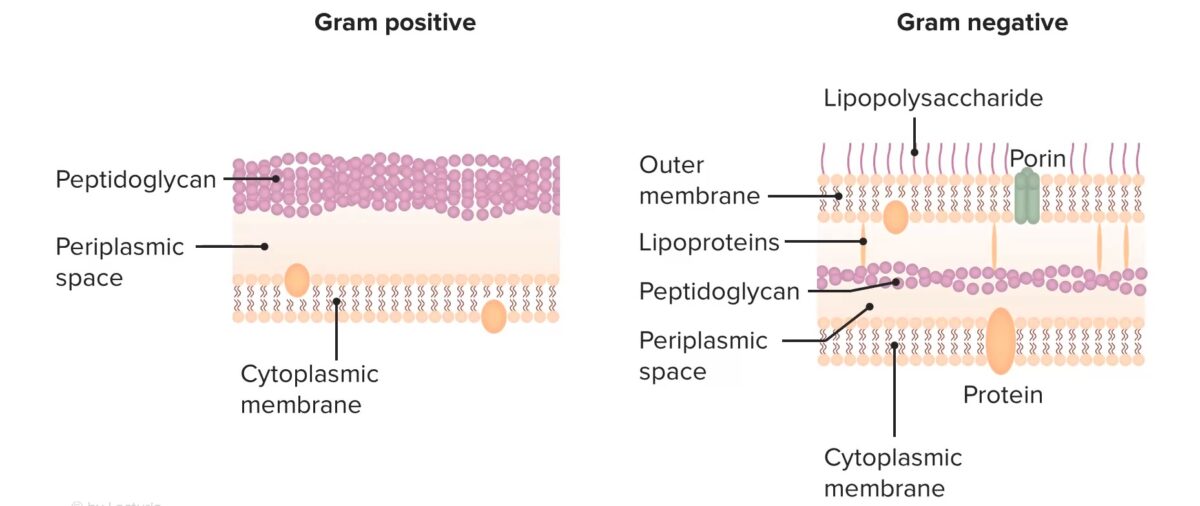
Chemistry Cephalosporin structure Cephalosporins are members of the beta-lactam drug family and consist of: Mechanisms of Action and Resistance All beta-lactams, including cephalosporins, exert their effects by inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis. Background: understanding cell walls Mechanism of action All beta-lactams work by irreversibly binding to and inhibiting the PBPs → beta-lactam antibiotics inhibit cell […]
Penicillins
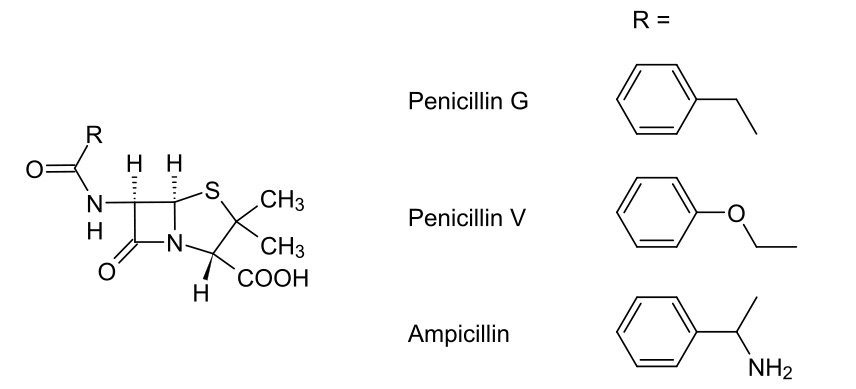
Chemistry Penicillins are members of the beta-lactam family of drugs and consist of: Mechanism of Action and Resistance All beta-lactams, including penicillins, exert their effects by inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis. Background: understanding cell walls Mechanism of action All beta-lactams work by irreversibly inhibiting PBPs → beta-lactam antibiotics inhibit cell wall synthesis Bactericidal activity Beta-lactams, […]
Antispasmodics

Overview Definition Antispasmodics are a group of medications used to reduce excessive GI smooth muscle contractility and spasm. Classification Antispasmodic agents are classified based on their action: Indications This group of medications is used in individuals with abdominal discomfort from bowel spasm, such as that due to irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Anticholinergics Mechanism of action […]
Nonsteroidal Antiinflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
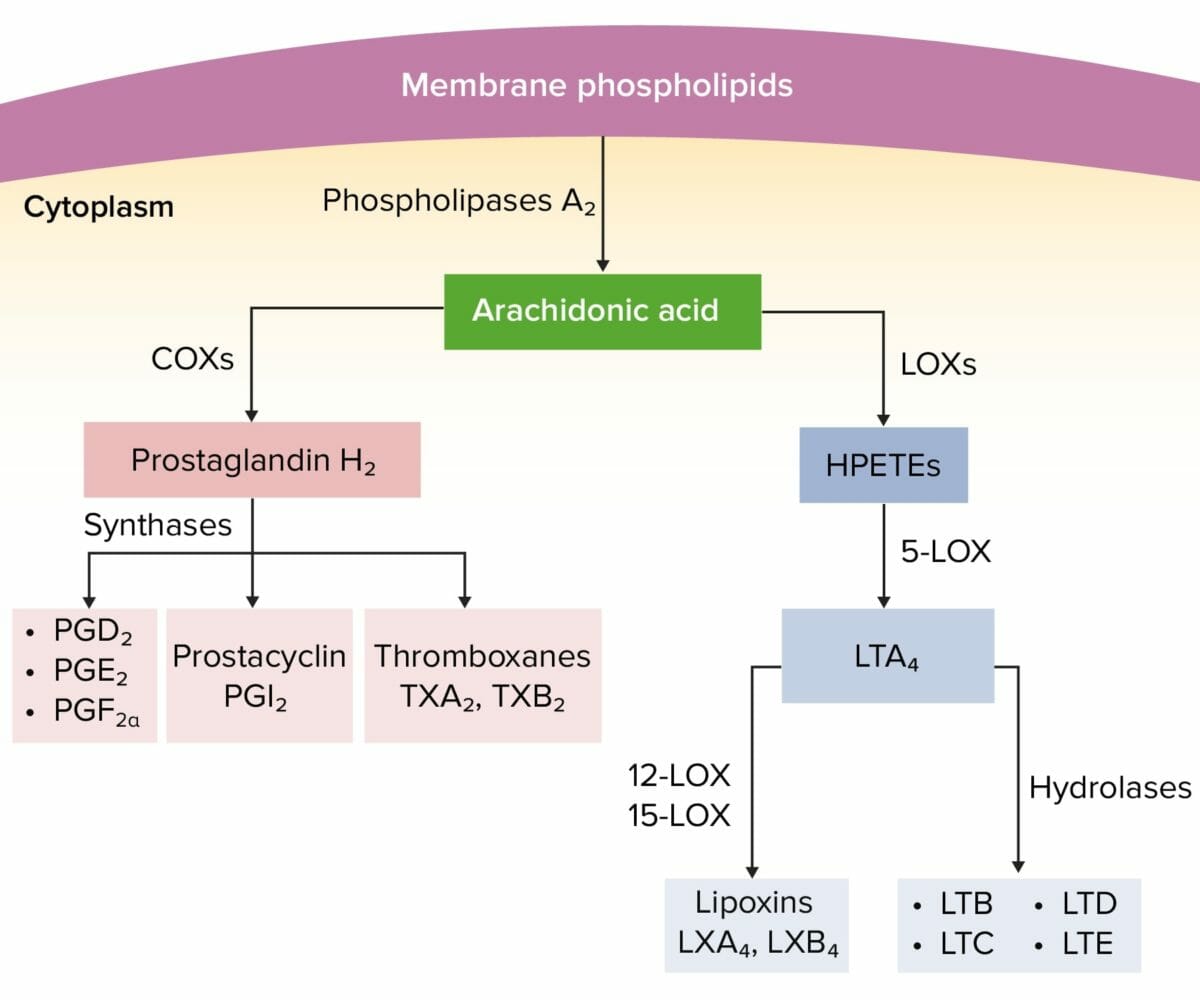
Pharmacodynamics Mechanism of action Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) exert their therapeutic effects by interrupting fatty acid metabolism, primarily the action of cyclooxygenase (COX) on arachidonic acid (AA). Pharmacokinetics NSAIDs are generally very similar: Classification NSAIDs can be divided into groups based on their ability to inhibit the isoforms of cyclooxygenase (COX-1 and COX-2). Indications Adverse […]
Chloramphenicol
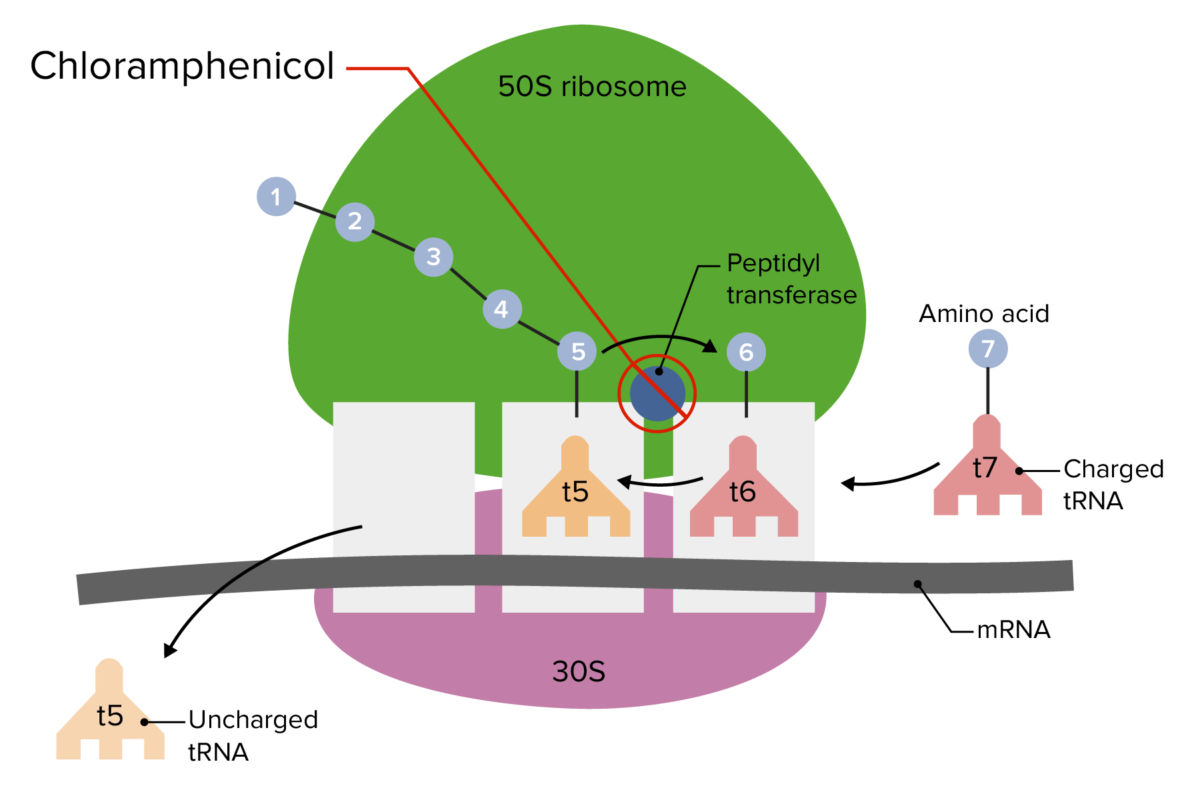
Pharmacodynamics and Pharmacokinetics Chemical structure Mechanism of action Pharmacokinetics Indications Antimicrobial coverage Types of infections Because of chloramphenicol’s side effects, use is generally limited to severe infections where resistance has developed against alternative agents: Adverse Effects and Contraindications Adverse effects Contraindications Drug interactions Mechanisms of Resistance Resistance mechanisms to chloramphenicol in bacteria include: Comparison of […]
Lincosamides
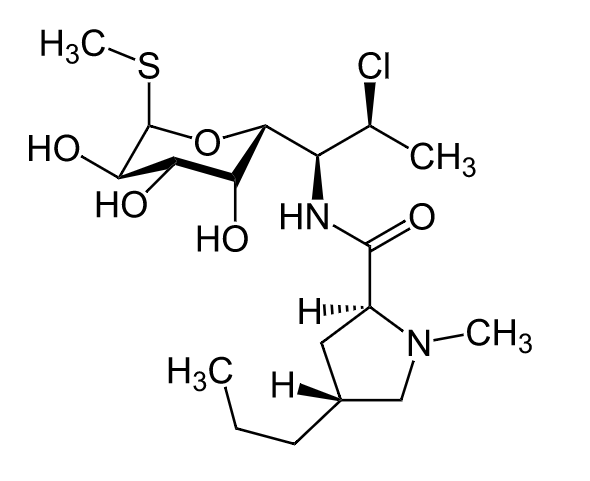
Chemistry and Pharmacodynamics Chemical structure Mechanism of action Pharmacokinetics Since lincomycin is rarely used, the pharmacokinetics of clindamycin are have been listed: Absorption and distribution Metabolism and excretion Indications Antimicrobial coverage Type of infections Adverse Effects and Contraindications Adverse effects Contraindications Drug interactions Mechanisms of Resistance There are 3 main routes of resistance: Comparison of […]
Aminoglycosides
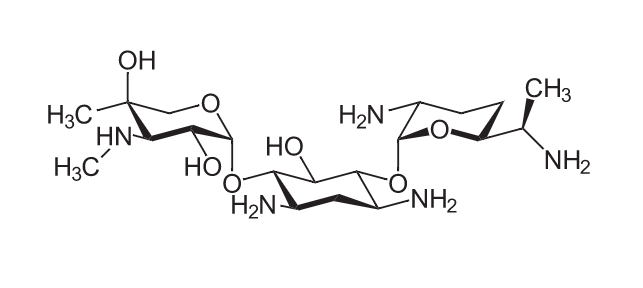
Chemistry and Pharmacodynamics Chemical structure Mechanism of action Pharmacokinetics Absorption Distribution Excretion Indications Antimicrobial coverage Types of infections Adverse Effects and Contraindications Adverse effects Contraindications Drug interactions Monitoring Mechanism of Resistance Several mechanisms of aminoglycoside resistance: Comparison of Antibiotics The following table compares antibiotics, which inhibit bacterial protein synthesis: Table: Comparison of several classes of […]
Oxazolidinones
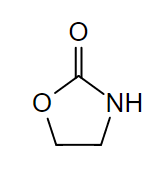
Chemistry and Pharmacodynamics Chemical structure Mechanism of action Pharmacokinetics Absorption and distribution Metabolism Excretion Indications Antimicrobial coverage Types of infections These medications are FDA-approved for: Adverse Effects Adverse effects Warnings Linezolid may cause a hypertensive crisis in the following conditions: Drug interactions Comparison of Antibiotics Table: Comparison of several classes of bacterial protein synthesis inhibitor […]
Macrolides and Ketolides
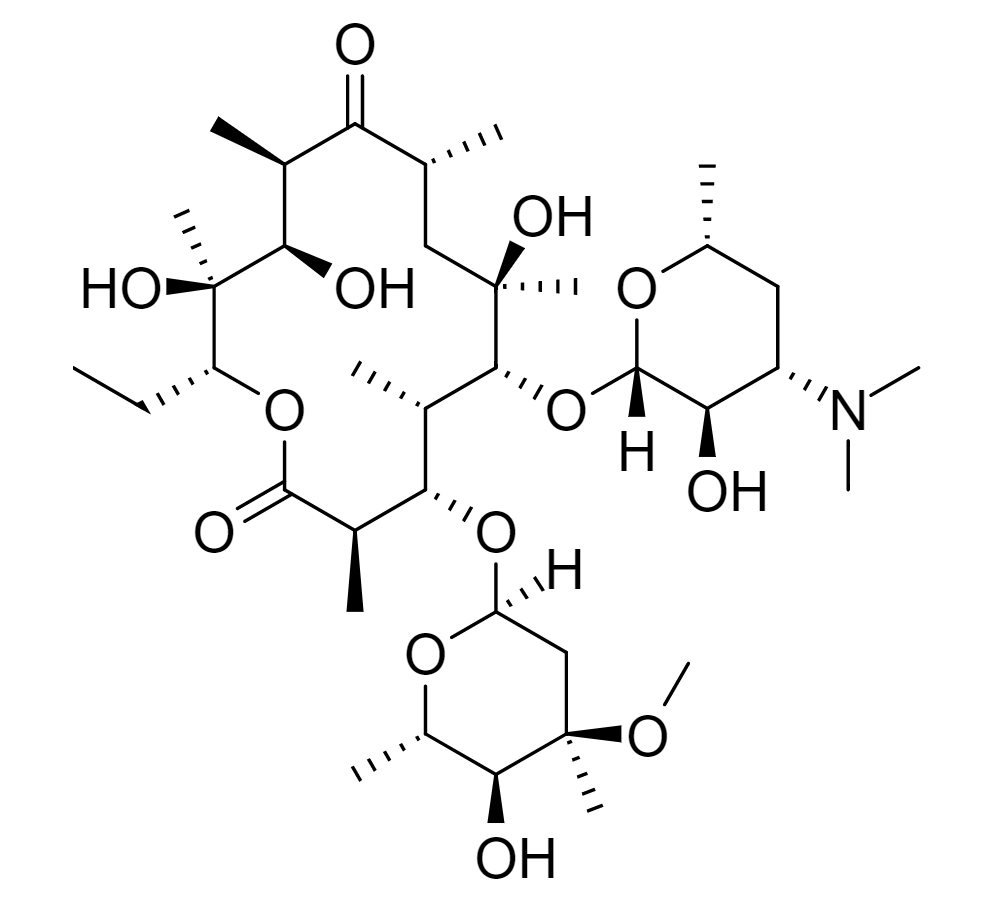
Chemistry and Pharmacodynamics Chemical structure Mechanism of action General: Fidaxomicin is an exception: Pharmacokinetics Table: Pharmacokinetics of macrolides and ketolides Macrolides Ketolides Absorption Erythromycin: Destroyed by stomach acid → requires enteric coating Relatively poor absorption Food interferes with absorption Azithromycin and clarithromycin: Stable in the stomach Better absorption Fidaxomicin: Minimal systemic absorption Reaches high fecal […]