Cannabinoids
Chemistry and Pharmacodynamics Chemistry Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is the psychoactive component of cannabis: Mechanism of action Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) Physiologic effects Cannabinoids bind to peripheral and central receptors: Pharmacokinetics Absorption Metabolism Excretion Drug interactions Additional potential drug interactions with cannabinoids include: Classification Table: Prescription cannabinoid formulations and indications Drug Notes on formulations Indications Dronabinol: Oral capsule Marinol® […]
Antivirals for Hepatitis B
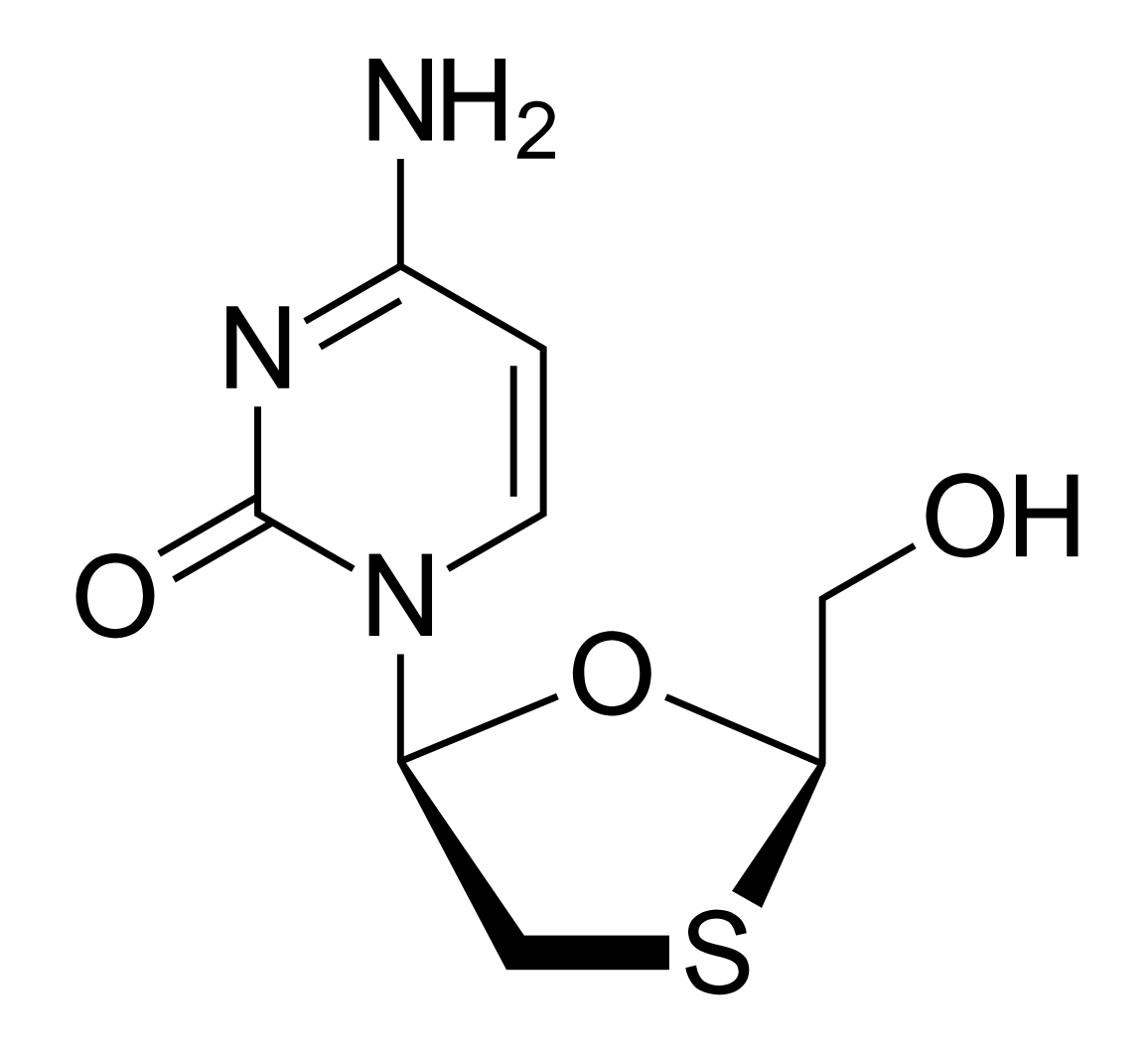
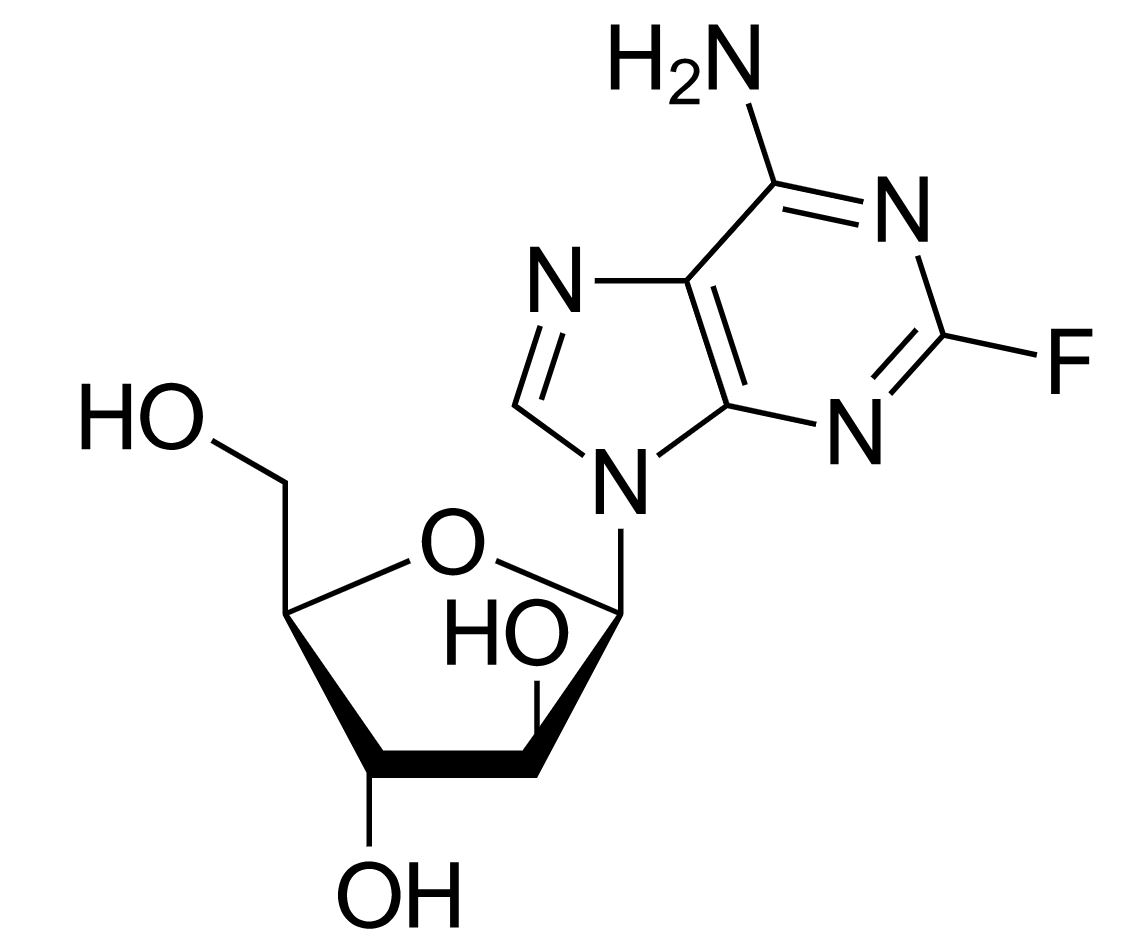
Chemistry and Pharmacodynamics Chemical structure Antivirals for hepatitis B have structures similar to those of nucleotides and nucleosides, thus they are classified as nucleoside/nucleotide analogs (also known as nucleoside/nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs)). Mechanism of action Pharmacokinetics Absorption Distribution and metabolism Excretion All of these medications are excreted by the kidneys. Indications Chronic hepatitis B […]
Antimetabolite Chemotherapy
Overview Cell-cycle kinetics Chemotherapy Antimetabolite classification The subtypes of antimetabolite chemotherapy agents are: Drug resistance Antifolates Antifolate agents Methotrexate (MTX) Pemetrexed Pralatrexate Comparison of antifolate agents Table: Comparison of antifolate agents Agent Mechanism of action Labeled indications Adverse effects Additional considerations Methotrexate Inhibit DHFR ALL Breast cancer Gestational trophoblastic neoplasia Head and neck cancer Non-Hodgkin […]
Hematopoietic Growth Factors
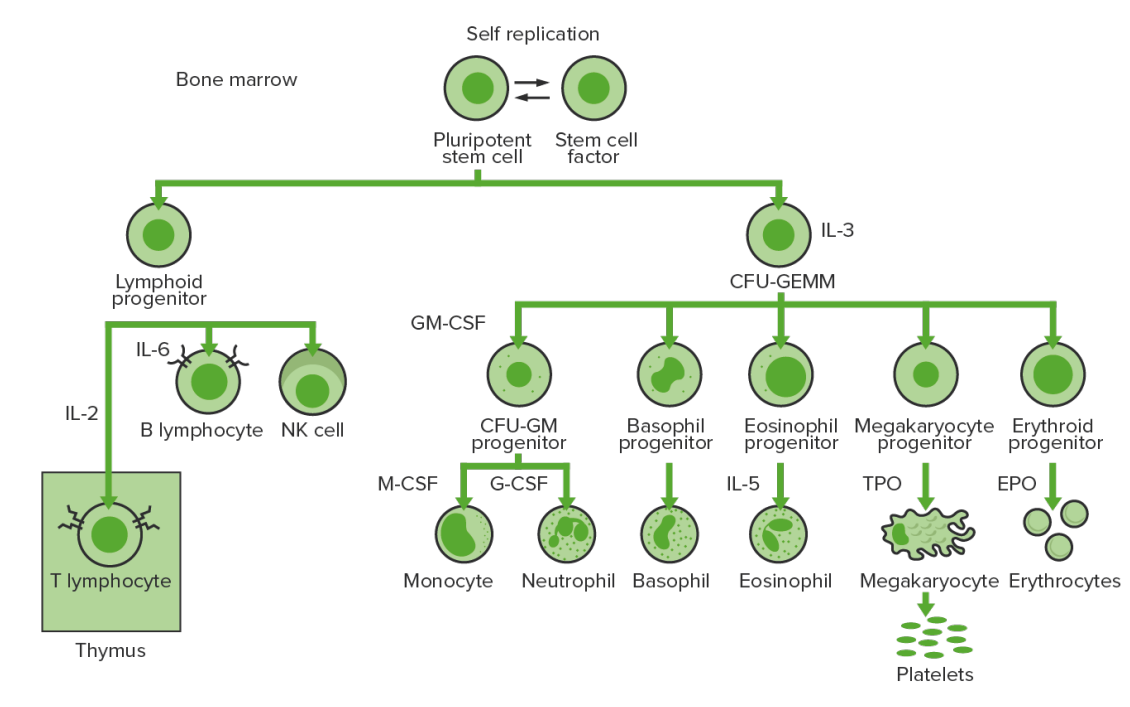
Overview Definition Hematopoietic growth factors are glycoproteins that regulate the proliferation, differentiation, and maturation of progenitor cells, as well as the function of the mature cells. Hematopoiesis Major hematopoietic growth factors and pharmacologic agents Table: Major hematopoietic growth factors and pharmacologic agents Cytokines/growth factors Activities Pharmacologic agent(s) Erythropoietin (EPO) Stimulates erythropoiesis, including differentiation Epoetin alfa […]
Non-insulinotropic Diabetes Drugs
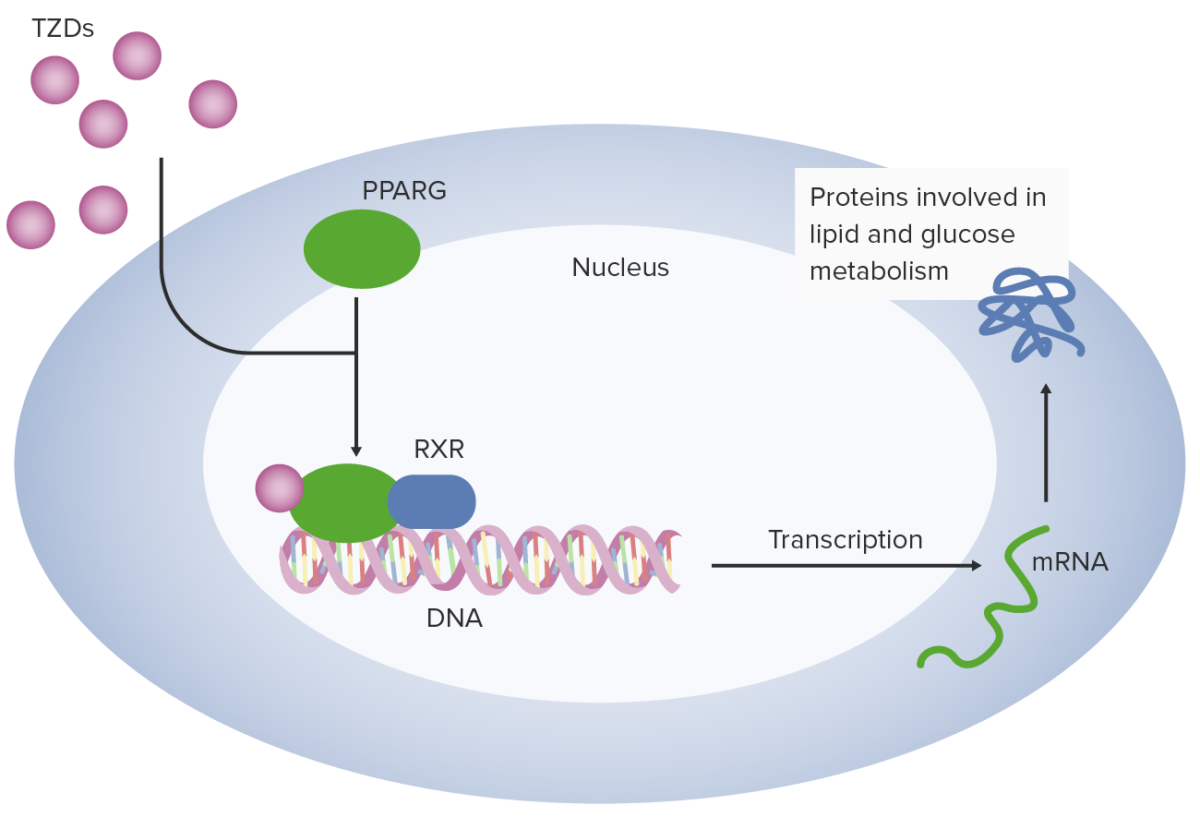
Overview Diabetes mellitus, type 2 Classification Hyperglycemic medications can be classified on the basis of their mechanism of action: Insulinotropic drugs: ↑ insulin secretion Non-insulinotropic drugs: do not affect insulin release Biguanides Metformin is the only available medication in the biguanide drug class. Pharmacodynamics Pharmacokinetics Indications Adverse effects Contraindications Drug interactions Drugs associated with increased […]
Insulinotropic Diabetes Drugs
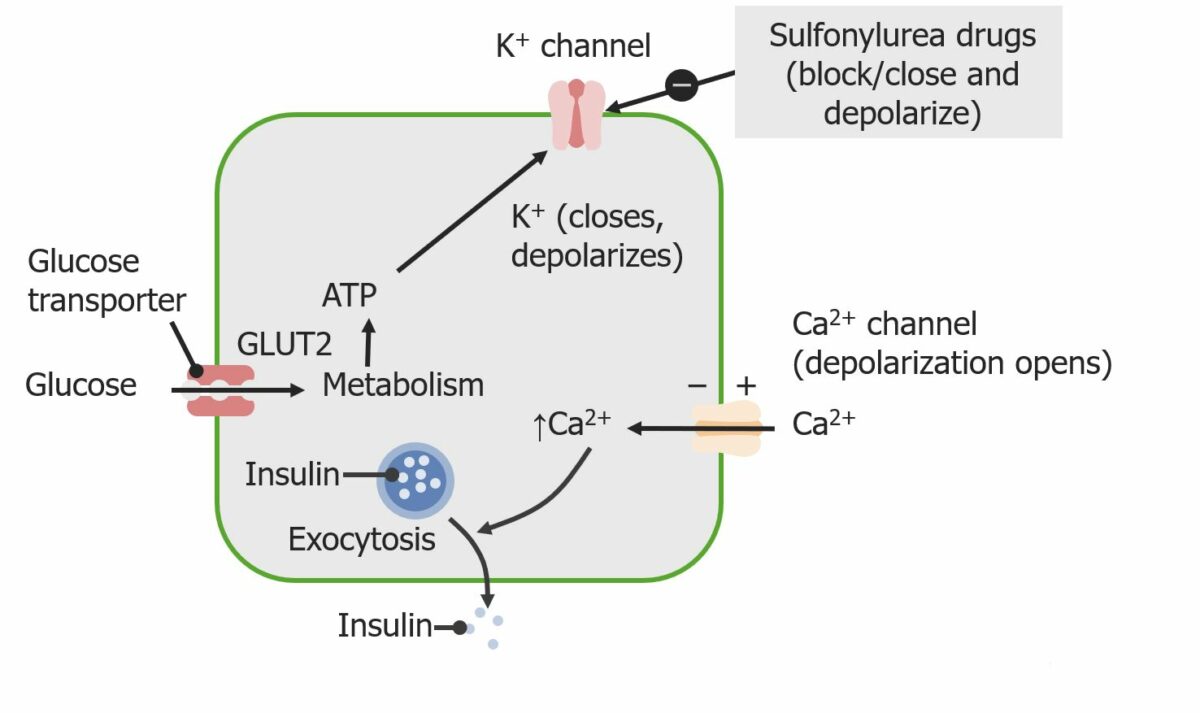
Overview Type 2 diabetes mellitus Caused by: Peripheral insulin resistance: Cellular insulin receptors do not appropriately respond to insulin. Beta-cell dysfunction: long term ↑ in insulin demand → defective insulin secretion Results in hyperglycemia Pharmacologic management can target: Insulin release Insulin resistance Glucagon release Gluconeogenesis Glucose uptake Classification Hypoglycemic (or antihyperglycemic) medications can be classified […]
First-Generation Anticonvulsant Drugs
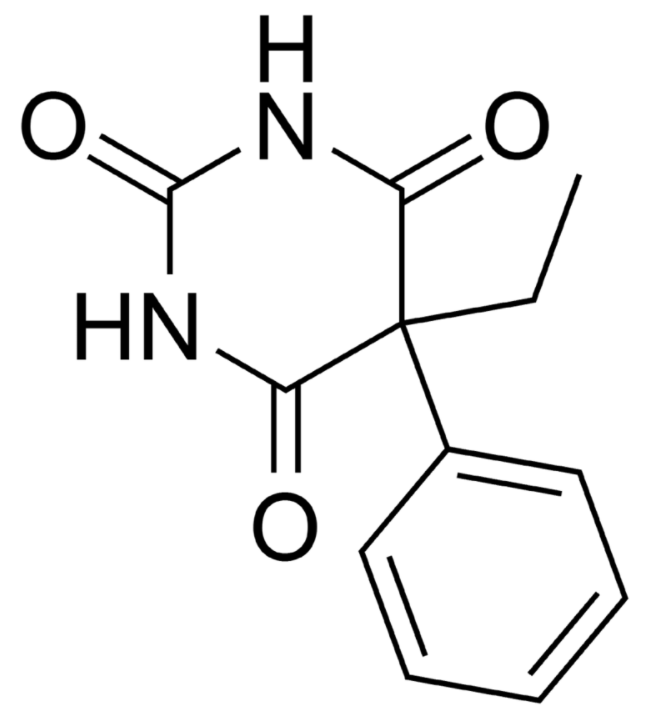
Overview Definitions Anticonvulsant drugs are used to suppress abnormal electrical activity in the brain through various mechanisms. Pathophysiology of seizures The hyperexcitable state of neurons results via the following 3 steps: General mechanisms of first-generation antiseizure drugs Phenobarbital Chemistry and pharmacodynamics Pharmacokinetics Indications Drug-drug interactions Adverse effects and contraindications Phenytoin Chemistry and pharmacodynamics Pharmacokinetics Indications […]
Antiadrenergic Drugs
Overview Overview of the ANS The ANS is subdivided into the sympathetic and parasympathetic pathways. Both pathways contain 2 efferent neurons in series known as the preganglionic and postganglionic neurons. Preganglionic neuron: Postganglionic neuron: Chemistry and Pharmacodynamics Chemistry Mechanisms of action Antiadrenergic drugs work by inhibiting the postganglionic adrenergic receptors. These are G-protein-coupled receptors. Alpha […]
Anthelmintic Drugs

Overview Classification of helminths The different classes of helminths are: Classification of anthelmintic drugs The most commonly used anthelmintic drugs are: Benzimidazoles Medications in this class Mechanism of action Pharmacokinetics Indications Albendazole and mebendazole have activity against a broad spectrum of: Adverse effects Diethylcarbamazine Mechanism of action Pharmacokinetics Indications Diethylcarbamazine is indicated for the following […]
Amebicides
Overview Amebiasis Classification of amebicides A combination of tissue and luminal amebicides are prescribed to treat amebiasis. Luminal amebicides: Tissue amebicides: Iodoquinol Mechanism of action Pharmacokinetics Indications Iodoquinol was used to treat intestinal amebiasis. It’s no longer available in the United States as of 2025 due to FDA enforcement against unapproved products. Adverse effects Contraindications […]