Bisphosphonates
Chemistry and Pharmacodynamics Chemical structure Mechanism of action Pharmacokinetics Absorption Distribution Metabolism Excretion Classification Bisphosphonates are classified by structure. Bisphosphonate compounds are either nitrogenous or nonnitrogenous. The nitrogenous subtype contains nitrogen in the long chain (R2). Indications Bisphosphonates treat a number of conditions associated with bones: Adverse Effects and Contraindications Adverse effects Warnings Contraindications Drug […]
Osmotic Diuretics
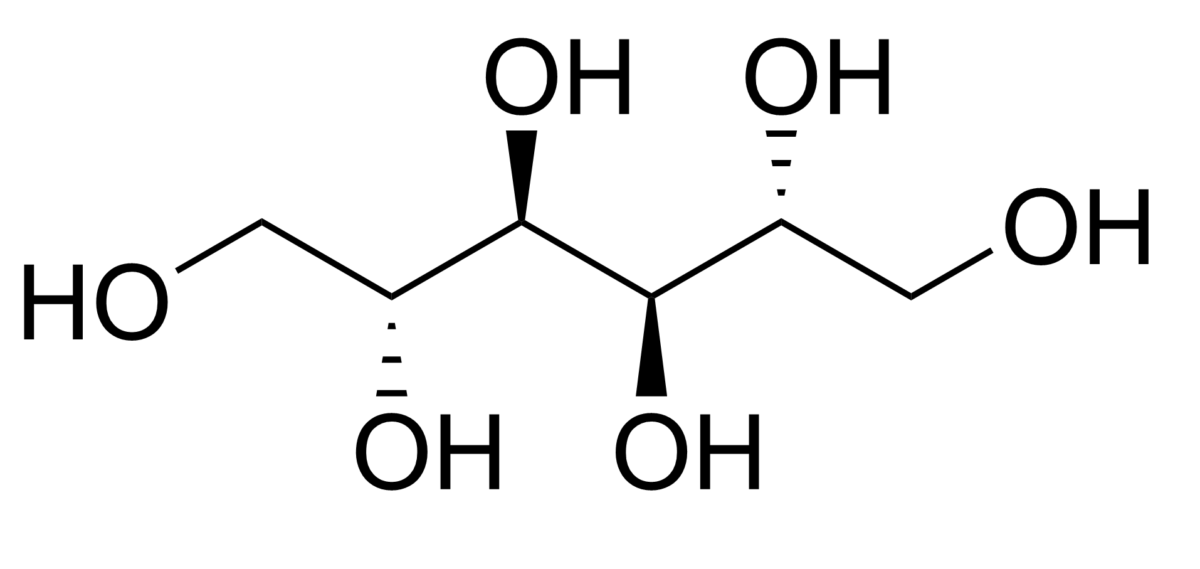
Chemistry and Pharmacodynamics Definition An osmotic diuretic is an osmotically active agent that is filtered into the renal tubules but not reabsorbed. The presence of this substance in the renal tubules keeps water in the tubules, resulting in diuresis. Chemical structure Mannitol is a nonabsorbable 6-carbon simple sugar alcohol. Mechanism of action Physiologic effects Pharmacokinetics […]
Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors
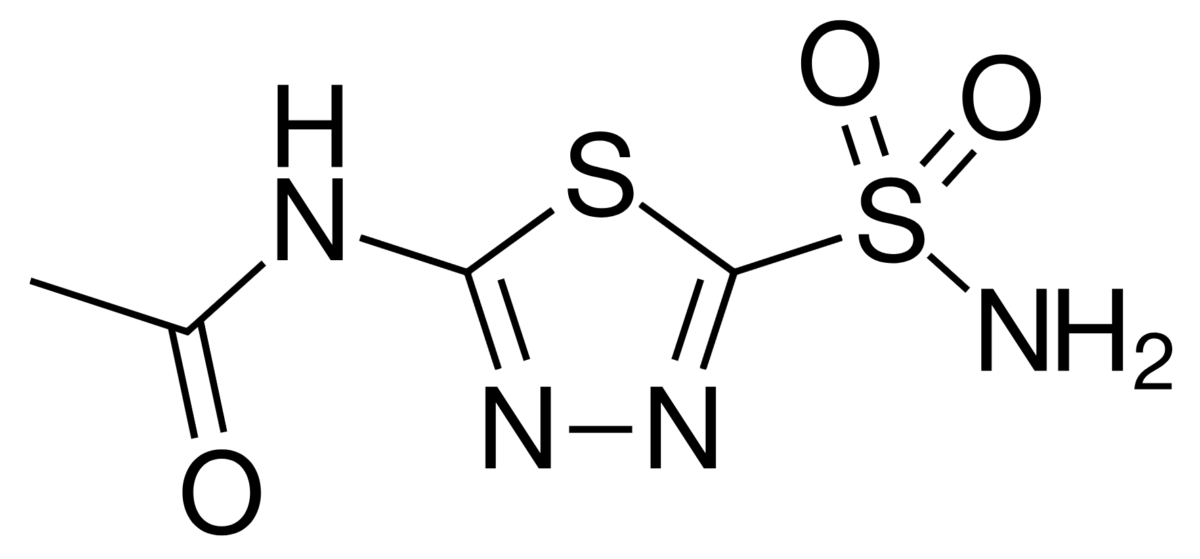
Chemistry and Pharmacodynamics Definition Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors (CAIs) are diuretics that block the carbonic anhydrase enzymes. Chemical structure Acetazolamide is a sulfonamide. Background: HCO3– reabsorption in the proximal tubule Bicarbonate cannot be directly reabsorbed by the kidneys; it must be converted into CO2 in the lumen and then reconverted to HCO3– once inside the cell. […]
Thiazide Diuretics
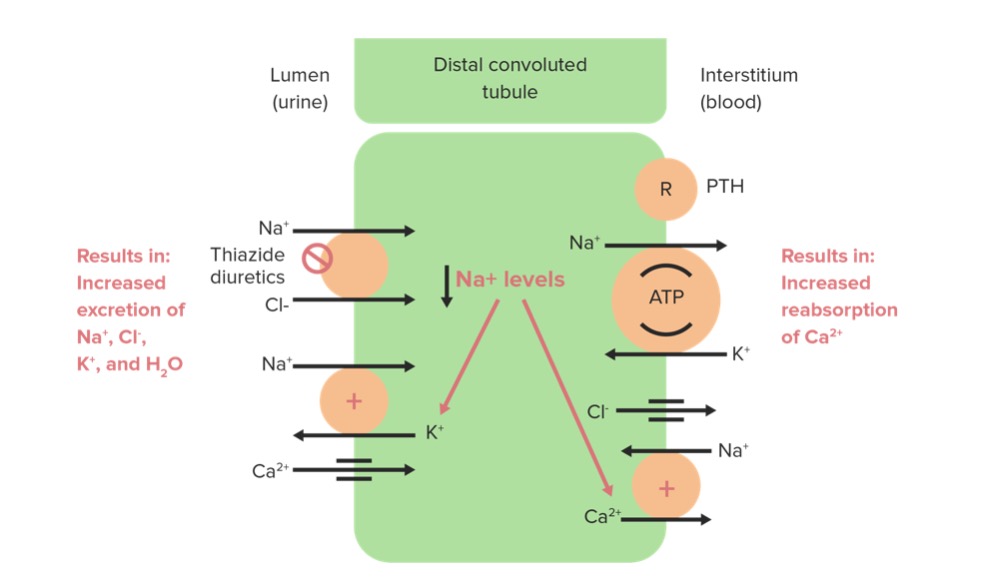
Overview Overview of antihypertensive agents Table: Drugs used to treat hypertension Location of action Class Subclasses Renal drugs Drugs affecting the RAAS ACEis ARBs Direct renin inhibitors Diuretics Thiazide diuretics Loop diuretics Potassium-sparing diuretics Extrarenal drugs Direct vasodilators Calcium channel blockers Potassium channel openers Nitrodilators Endothelin antagonists Agents acting via the sympathetic nervous system Drugs […]
Laxatives
Overview Definition Laxatives are medications that increase the frequency of bowel movements. Classification General indications General side effects Bulk-forming Laxatives Chemistry Bulk-forming laxatives tend to be either: Agents Mechanism of action Pharmacokinetics Indications Contraindications Adverse effects Adverse effects tend to be minimal with these agents but may include: Stimulant Laxatives Agents Mechanism of action Pharmacokinetics […]
Statins
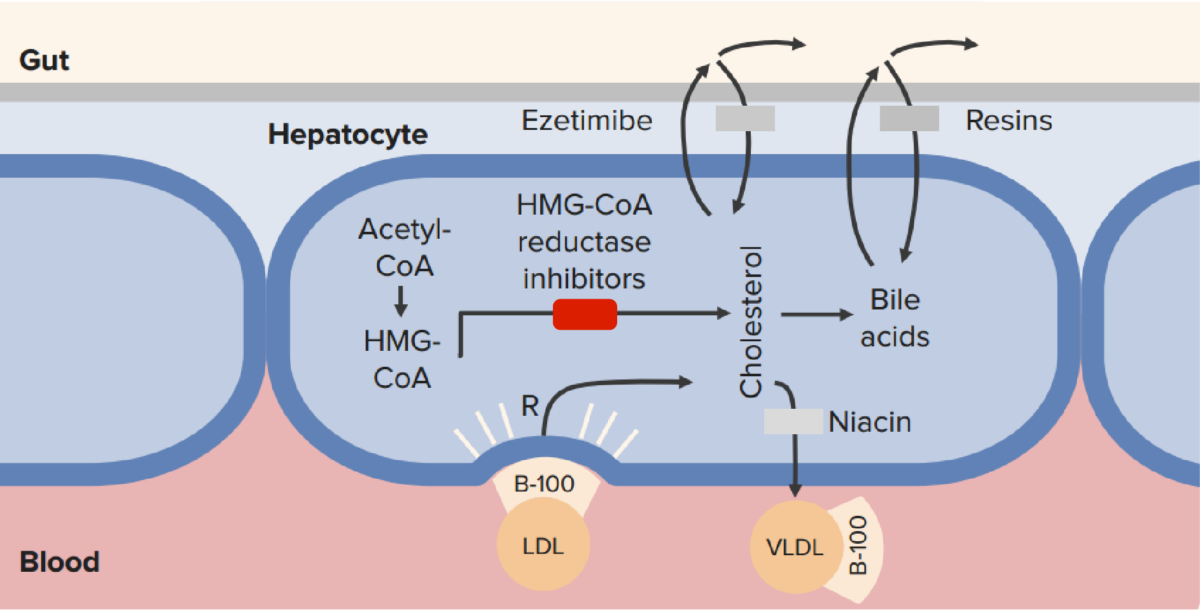
Chemistry and Pharmacodynamics Definition Statins are competitive inhibitors of the enzyme HMG-CoA reductase, which is the rate-limiting step in cholesterol biosynthesis in the liver. Chemical structure Statins are structural analogs of HMG-CoA. Mechanism of action Normal physiology: Statins: Physiologic effects Pharmacokinetics Absorption Distribution Metabolism Excretion Classification Statins are classified on the basis of their percent […]
Antiplatelet Drugs
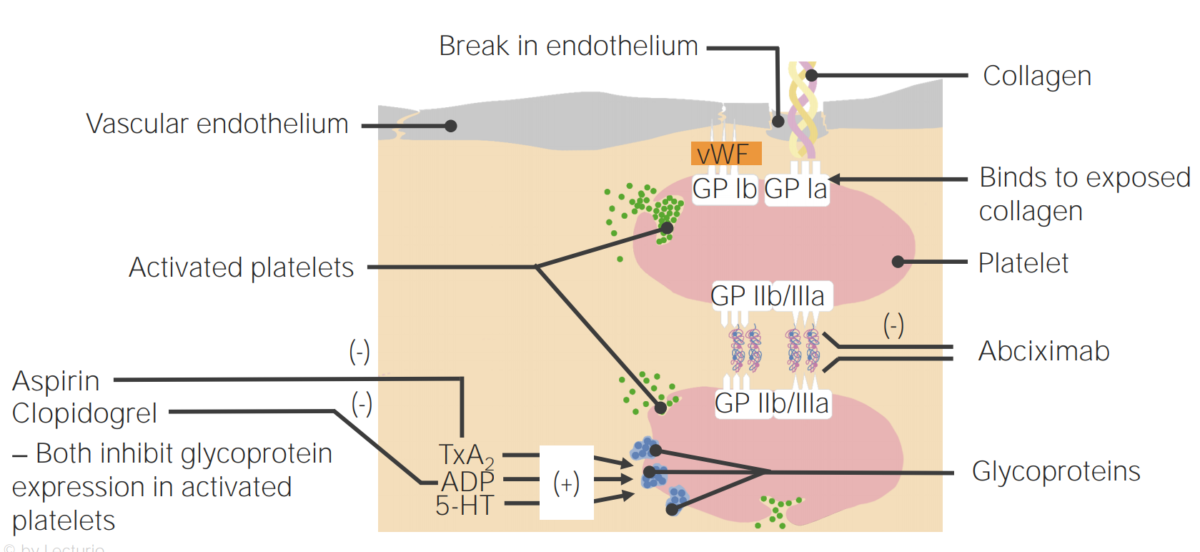
Overview Definition Antiplatelet agents are medications that inhibit platelet aggregation, a critical step in the formation of the initial platelet plug. General indications Antiplatelets are used in the treatment and/or prevention of arterial thrombosis. Common indications include: Classification There are several primary classes of antiplatelet agents: Platelets and Formation of the Platelet Plug After endothelial […]
Anticoagulants
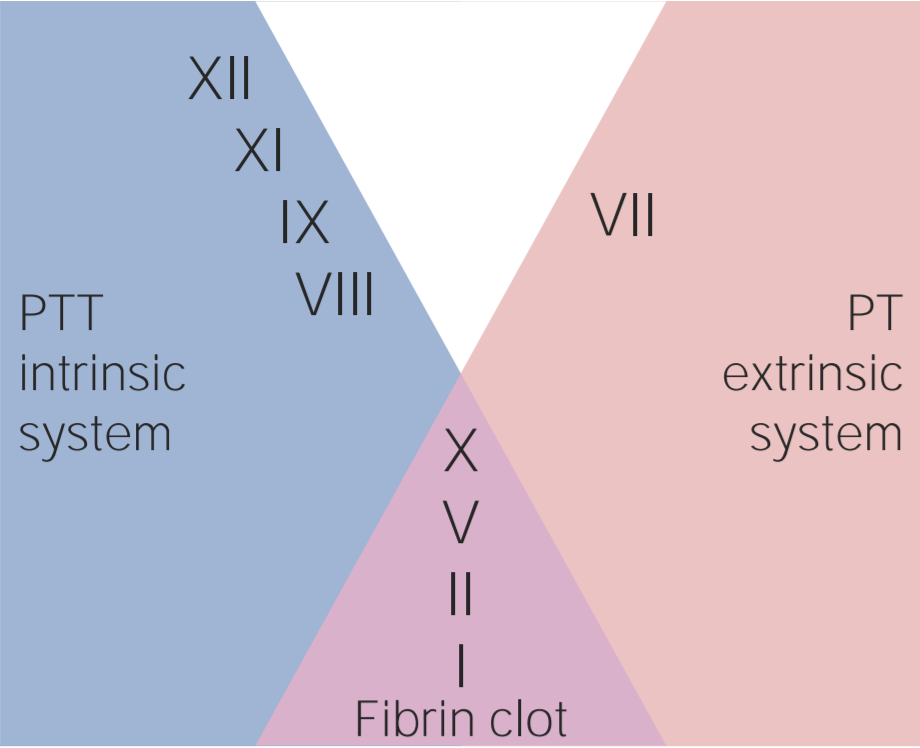
Overview Definition Anticoagulants are a category of drugs that inhibit the coagulation cascade. General indications Anticoagulants are indicated in the treatment and prophylaxis of thrombotic events including: Classification There are several primary classes of anticoagulants: Physiology: Overview of the coagulation cascade The coagulation cascade is a series of reactions that ultimately generates a strong, cross-linked […]
Anti-HIV Drugs

Overview Antiretroviral drugs Virion structure of HIV Replication cycle of HIV Major classes of antiretroviral drugs Table: Major classes of antiretroviral drugs Type of drug Mechanism of action Reverse transcriptase inhibitors NRTIs: nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors NtRTIs: nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors NNRTIs: non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors Interfere with the translation of viral RNA into DNA […]
Asthma Drugs

Overview Table: Classification of drugs used in asthma Function Class Examples Bronchodilators β-agonists Short-acting β-agonists (SABAs): albuterol, terbutaline, levalbuterol Long-acting β-agonists (LABAs): salmeterol, formoterol Methylxanthines Theophylline Muscarinic antagonists Short-acting muscarinic antagonist (SAMA): ipratropium Long-acting muscarinic antagonist (LAMA): tiotropium Anti-inflammatory agents Mast cell degranulation inhibitors (chromones) Cromolyn, nedocromil Antibodies Against IgE: omalizumab Against interleukin (IL)-5: mepolizumab […]