Donovanosis
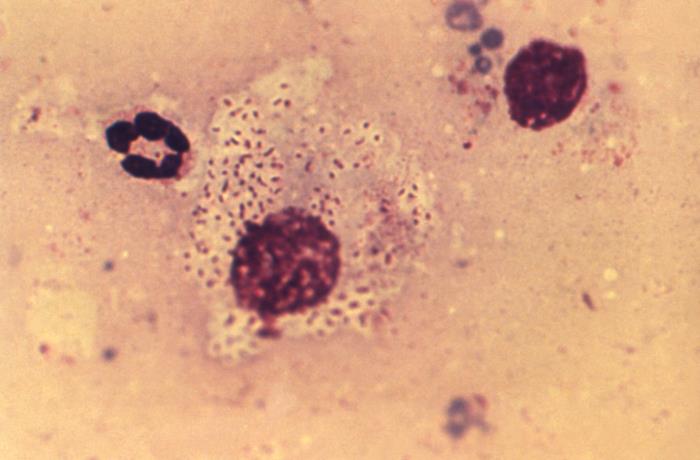
Overview Definition Donovanosis, or granuloma inguinale, is an STD characterized by chronic progressive ulcers affecting the genital region. Epidemiology Etiology Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation Signs and symptoms Complications Diagnosis and Management Diagnosis Management Differential Diagnosis References
Gonorrhea
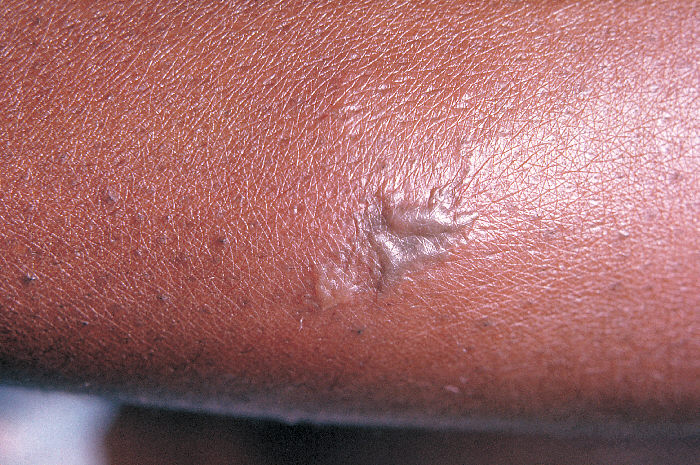
Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology Etiology Gonorrhea is caused by the pathogen Neisseria gonorrhoeae (N. gonorrhoeae): Risk factors: Pathophysiology Transmission Virulence factors Pathogenesis Antimicrobial resistance Clinical Presentation Urogenital infection in men Urogenital infection in women Extragenital infections Disseminated gonococcal infection Clinical presentation in children Newborn infections: After the neonatal period: Diagnosis Laboratory evaluation Disseminated gonococcal infection […]
Syphilis
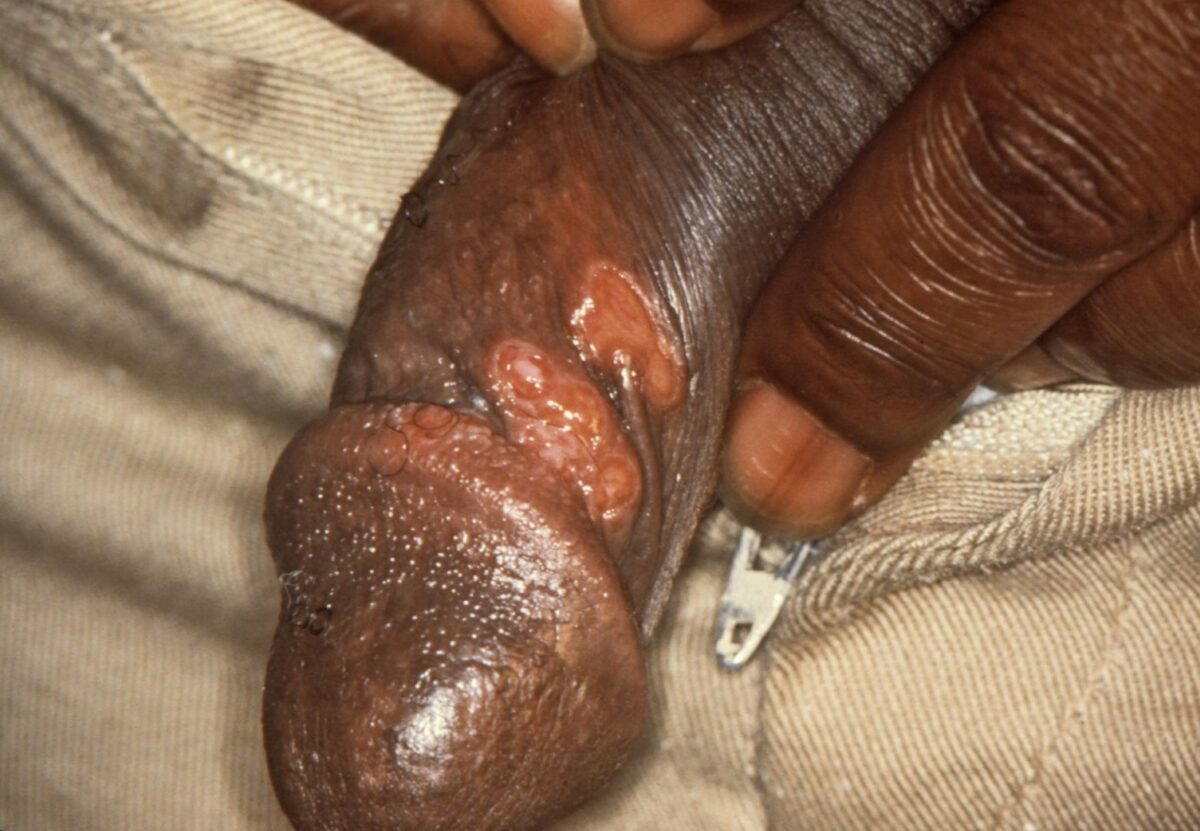
Overview Epidemiology Etiology Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation Syphilis is a multistage disease. Patients can present at any stage and infected individuals may not exhibit symptoms for years. Primary syphilis Secondary syphilis Latent syphilis Tertiary syphilis Diagnosis General approach It is difficult to diagnose syphilis. However, specific labs and the correlation of history and examination results can […]
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
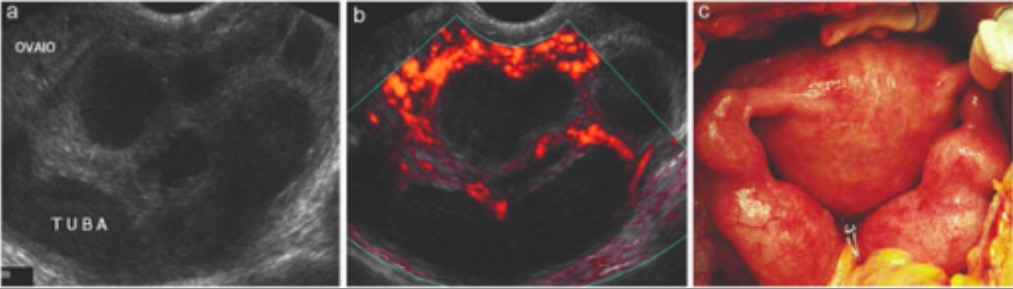
Overview Definition Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is an acute upper genital tract infection in women that affects the uterus, oviducts, ovaries, and possibly the adjacent pelvic organs. Epidemiology Etiology Pathophysiology Normal pelvic protection Pelvic infection Clinical Presentation Signs and symptoms Physical exam Complications Diagnosis and Management Diagnosis Diagnosis is primarily clinical with a high index […]
Diarrhea
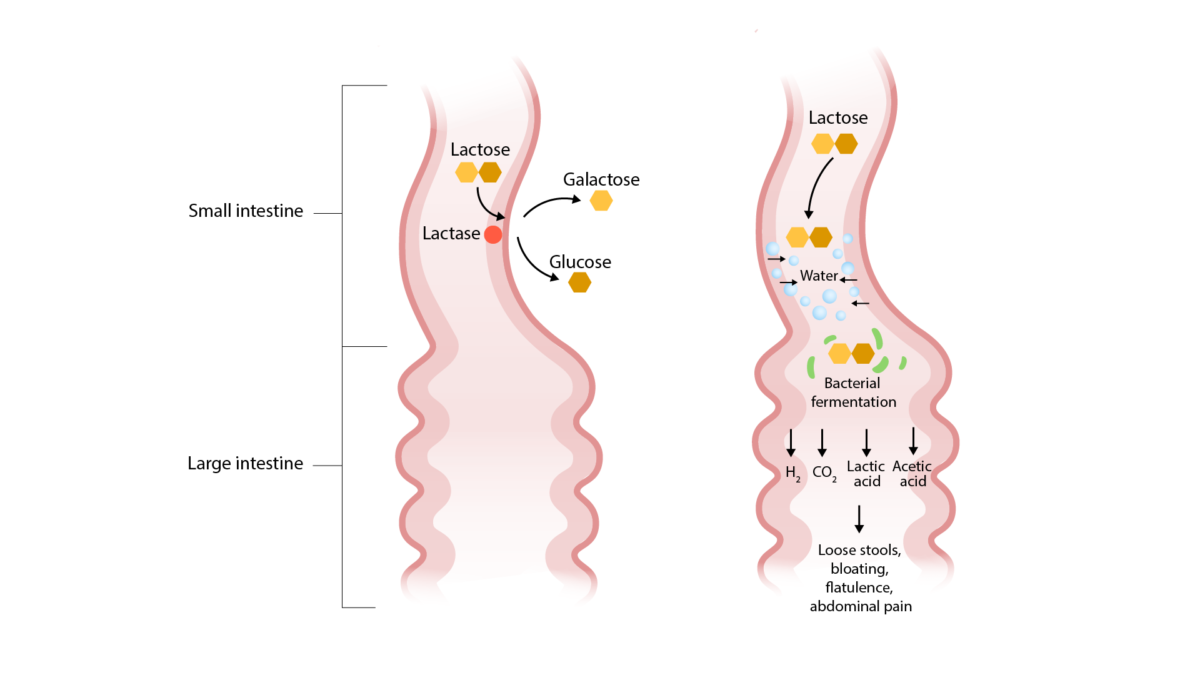
Overview Definition Diarrhea is the passage of ≥ 3 watery or loose stools in 24 hours. Classification Diarrhea can be classified by the duration of symptoms: Additionally, diarrhea may be classified based on the underlying etiology and pathophysiology: Etiology Infectious diarrhea Inflammatory/invasive: Noninflammatory/noninvasive: Risk factors: Noninfectious diarrhea Secretory: Osmotic: Malabsorption: Inflammatory/exudative: Altered motility: Pathophysiology Infectious […]
Chlamydial Infections
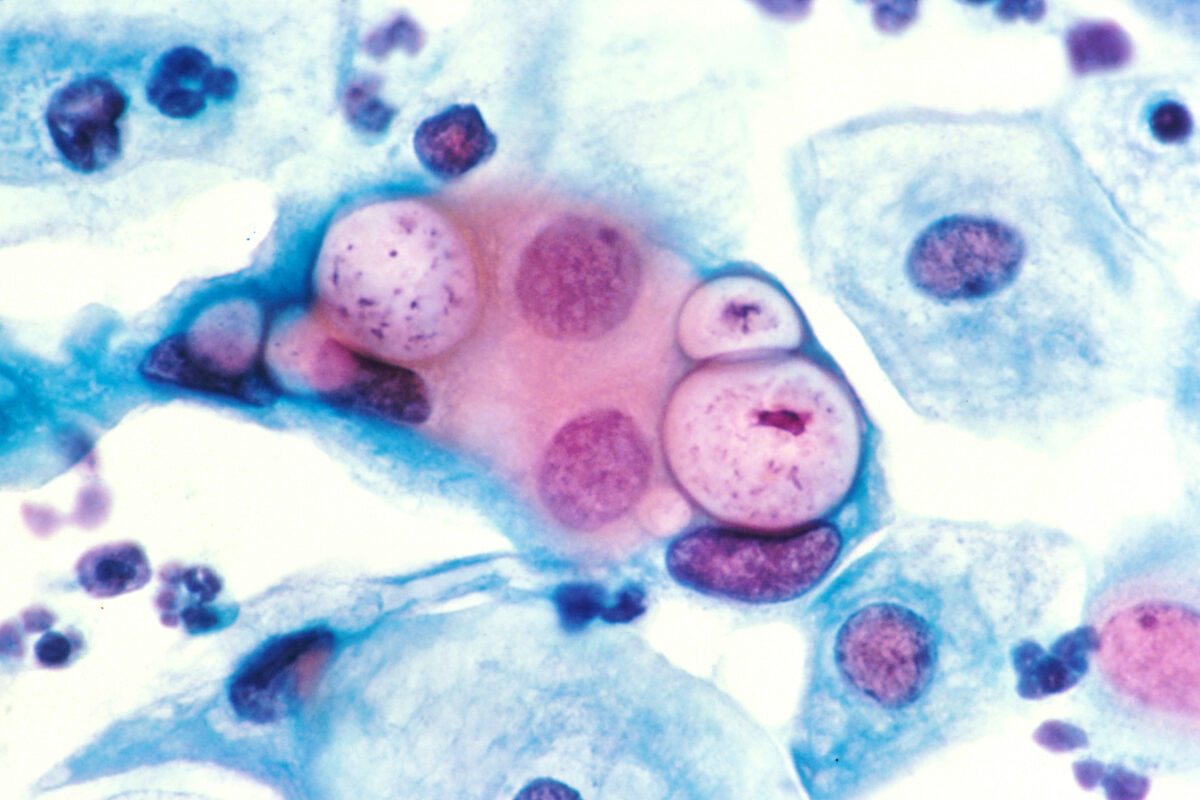
Overview Definition Chlamydial infections are infectious diseases caused by bacteria belonging to the Chlamydiaceae family. Epidemiology Transmission Pathophysiology and Clinical Presentation Pathophysiology C. trachomatis infections Genital disease (serovars d–k): Infant disease: Eye disease (serovars a–c): Lymphogranuloma venereum (serovars l1–l3): Respiratory diseases caused by C. pneumoniae and C. psittaci Diagnosis History: Physical exam: Laboratory studies: Management […]
HIV Infection and AIDS
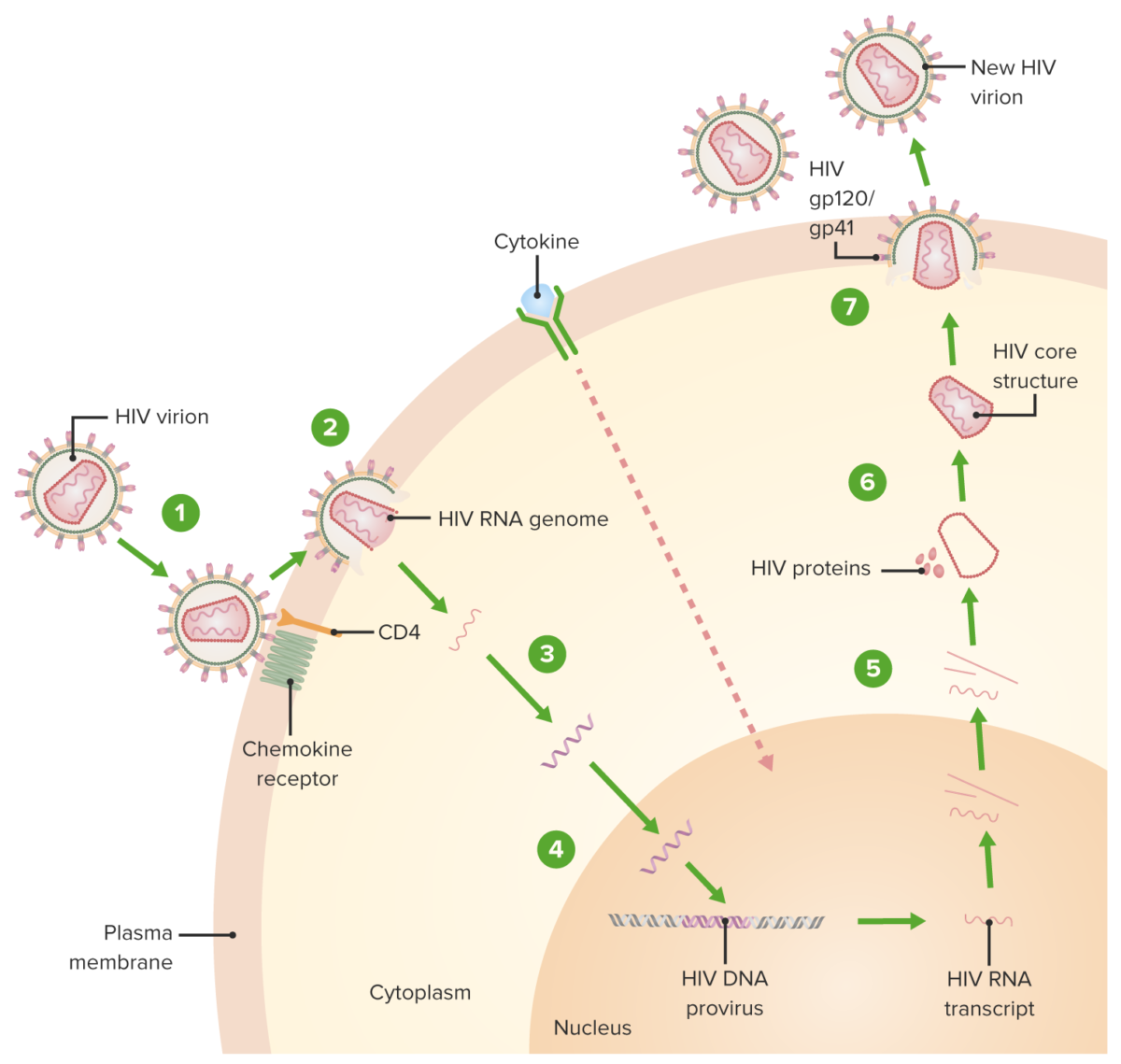
Epidemiology Worldwide United States Etiology and Transmission HIV Modes of HIV transmission Sexual: Parenteral: Vertical: Factors affecting transmission Pathophysiology HIV replication cycle Natural history Acute phase (infection, dissemination, retroviral syndrome): Chronic phase/clinical latency: AIDS: Clinical Presentation Categories of HIV infection The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) classification notes that CD4+ T lymphocyte count […]
Gastroenteritis
Overview Epidemiology Etiology Pathogenesis Mechanism of diarrhea Non-inflammatory (adhesion, enterotoxin) Inflammatory (invasion, cytotoxin) Penetrating (invades lymphatics) Presentation Watery diarrhea Dysentery (blood or mucus) or inflammatory diarrhea Enteric fever Stool findings No fecal white blood cells (WBCs) Mild or no increase in fecal lactoferrin Fecal polymorphonuclear leukocytes Increased fecal lactoferrin Fecal mononuclear leukocytes Pathogen involved Vibrio […]
Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome
Overview Definition Hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS) is a disease of the capillaries (microangiopathy) that causes the formation of blood clots, anemia caused by the destruction of RBC in these clotted capillaries (hemolytic anemia), acute kidney injury, and low platelets (thrombocytopenia). Epidemiology Etiology Etiology is classified as acquired (infectious versus noninfectious) or hereditary. Pathophysiology The pathophysiology […]
Vaccination
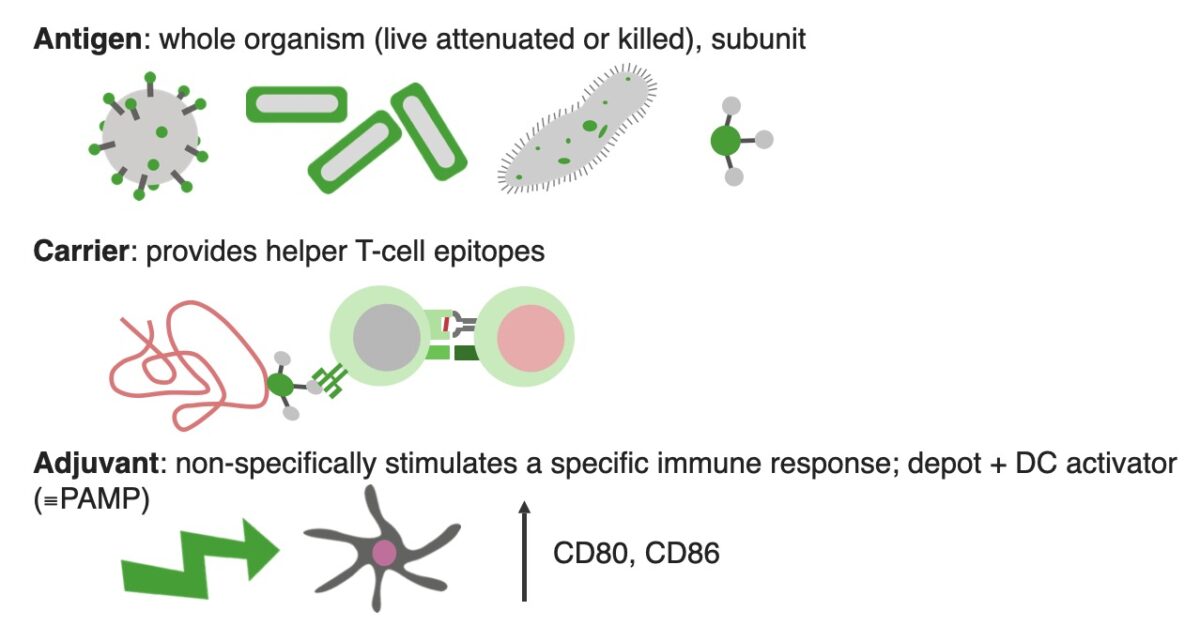
Overview Active and Passive Immunization Active immunization Passive immunization Types of Active Vaccines Table: Types of active vaccines Vaccine type Description Pros Cons Examples Live attenuated Microorganism loses its pathogenicity but retains capacity for transient growth within inoculated hosts. Induces cellular and humoral responses Induces strong, often lifelong immunity May revert to virulent form Often […]