Equine Encephalitis Viruses
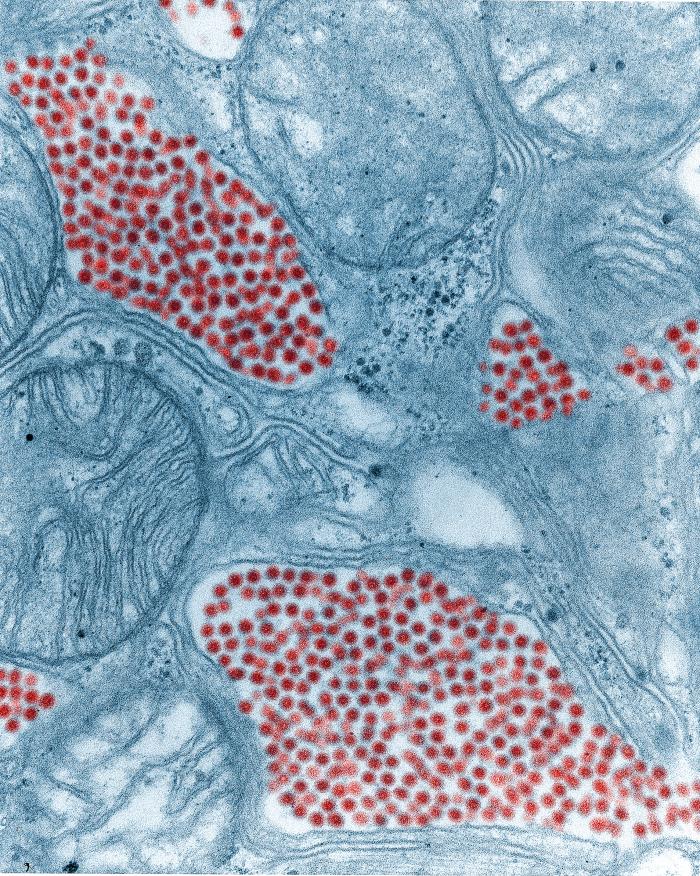
Classification General Characteristics and Epidemiology General features of equine encephalitis virus (EEV) Family: Togaviridae Genus: Alphavirus Genome: Positive-sense, ssRNA 11–12 kb in size Properties: Enveloped Lipid bilayer envelope has viral-encoded glycoproteins E1 and E2. Small icosahedral capsid Clinically relevant viruses and geographic distribution: Eastern equine encephalitis virus (EEEV) complex: Eastern equine encephalitis (EEE) virus: North […]
Meningitis
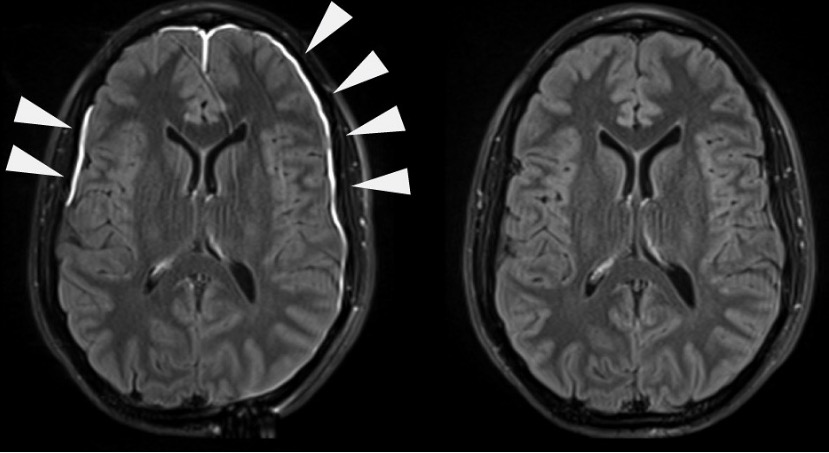
Overview Definition Meningitis is inflammation of the protective membranes of the brain and the spinal cord, collectively called the meninges, that is commonly caused by an acute infection. Epidemiology Etiology Meningitis can be of infectious (most common) or noninfectious origin. Infectious meningitis can be community- or hospital-acquired. Infectious meningitis Bacterial meningitis: Viral meningitis: Fungal meningitis: Parasitic […]
Encephalitis
Overview Definition Encephalitis is an inflammation of the brain parenchyma caused by an infection that is usually viral and presents as diffuse or focal neuropsychologic dysfunction. Epidemiology Classification There are 2 main types of encephalitis: Etiology Viral encephalitis is the most common form of encephalitis. Bacterial, fungal, and parasitic encephalitides are extremely rare. Viral causes: […]
Brain Abscess
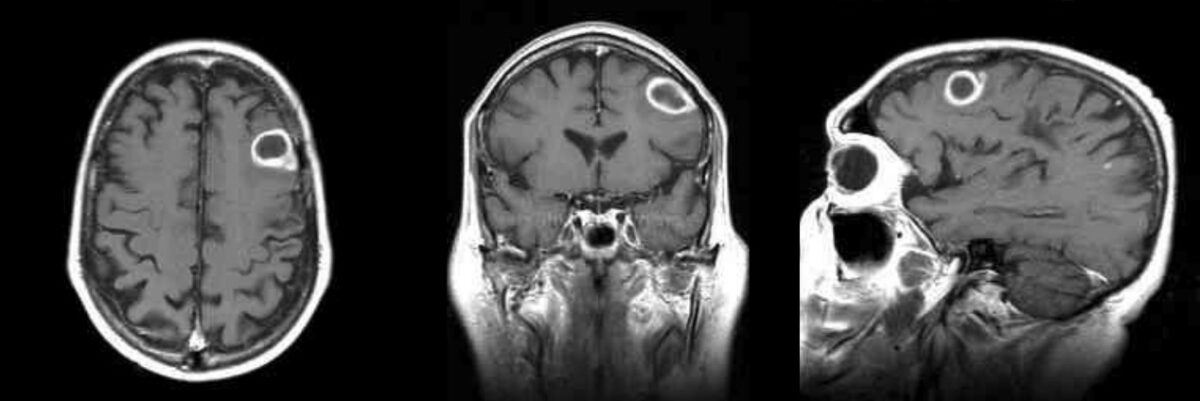
Overview Definition Brain abscess is an uncommon but life-threatening infectious collection of pus in the brain parenchyma. Epidemiology Etiology There are 2 routes of the spread of infection to the brain: Organisms causing brain abscess: Risk factors: Pathophysiology and Clinical Presentation Pathogenesis Stages of development of brain abscess after infection Early cerebritis (days 1–3): Late […]
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)

Overview Definition Urinary tract infection (UTI) is a pathogenic process that develops when a microorganism (usually bacteria) enters the body through the urethra and travels to the bladder and/or kidneys. Epidemiology Prevalence: Risk factors Etiology and Pathophysiology Escherichia coli Other bacteria Non-E. coli bacteria are associated with risk factors for drug resistance or in specific […]
Myocarditis
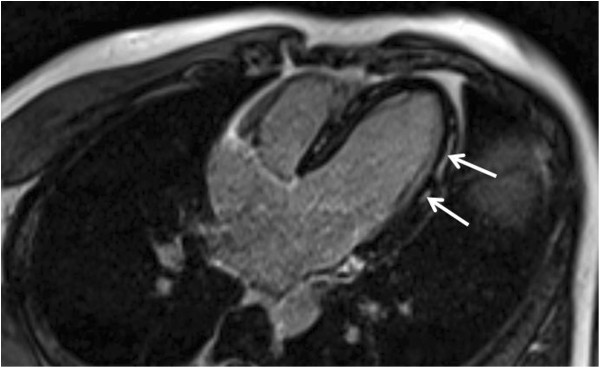
Overview Definition Myocarditis is an inflammatory disease of the myocardium. Epidemiology Etiology Causes of infectious myocarditis The following table summarizes the infectious causes of myocarditis. Keep in mind that this list is not exhaustive. Table: Causes of infectious myocarditis Viral Bacterial Parasitic Fungal Coxsackie B virus Adenovirus Parvovirus B19 Human herpesvirus 6 Epstein-Barr virus Cytomegalovirus […]
Endocarditis
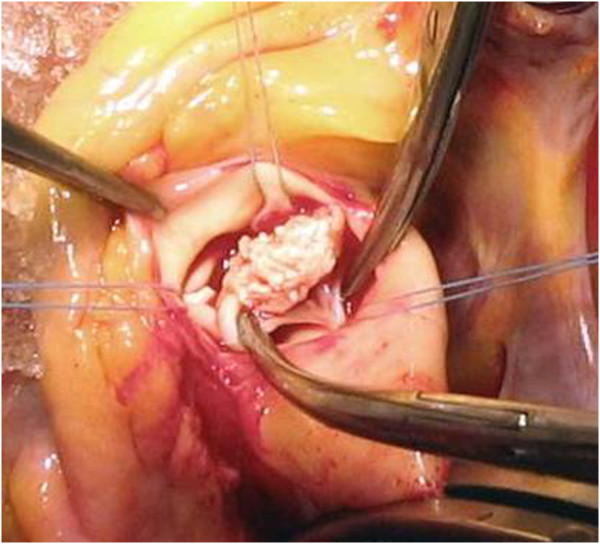
Overview Definition Epidemiology Infective endocarditis: Noninfective endocarditis: Infective endocarditis etiologies Infective endocarditis may be caused by numerous organisms; the list below is not exhaustive. Noninfective endocarditis etiologies Risk Factors and Pathophysiology Risk factors The following are risk factors for IE: Infective endocarditis Noninfective endocarditis Classification Infective endocarditis can be further classified based on the clinical […]
Condylomata Acuminata (Genital Warts)
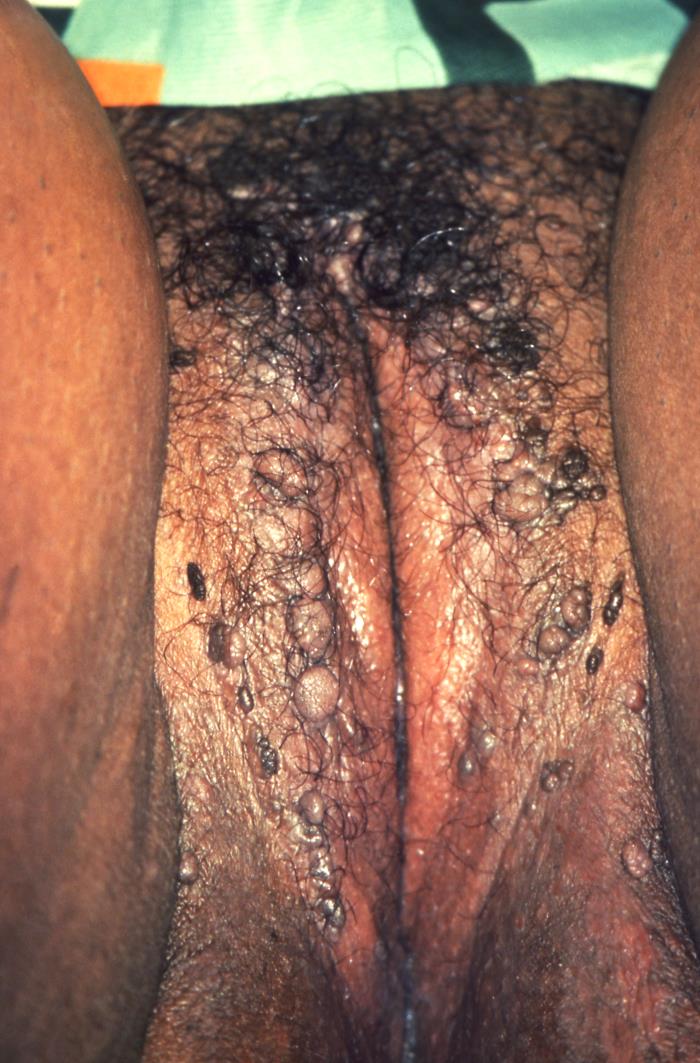
Overview Epidemiology Etiology Condylomata acuminata are specifically lesions created by HPV. Pathophysiology Infection to resolution: Histopathology Clinical Presentation and Diagnosis Clinical manifestation Patients are often asymptomatic, presenting only for the appearance of lesions. The diagnosis of HPV may cause significant psychosocial distress, given the associated stigma. Diagnosis Management and Complications Management Spontaneous and complete resolution […]
Influenza Viruses/Influenza
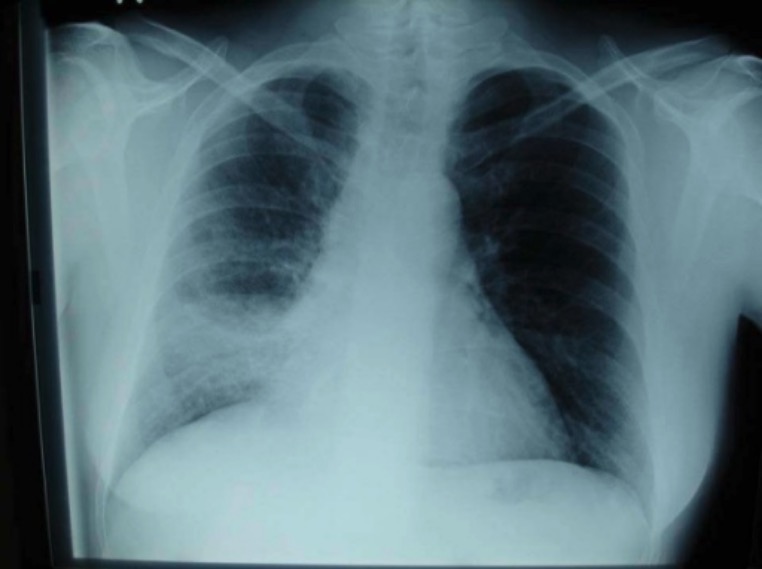
Classification General Characteristics Structure and basic features The influenza virus is a member of the Orthomyxoviridae family. Clinically relevant species and diseases Influenza viruses cause a febrile respiratory disease known as influenza. There are 3 distinct clinically relevant species of the virus: Table: Characteristics and clinical manifestations of influenza viruses Characteristics Influenza A Influenza B […]
Chancroid
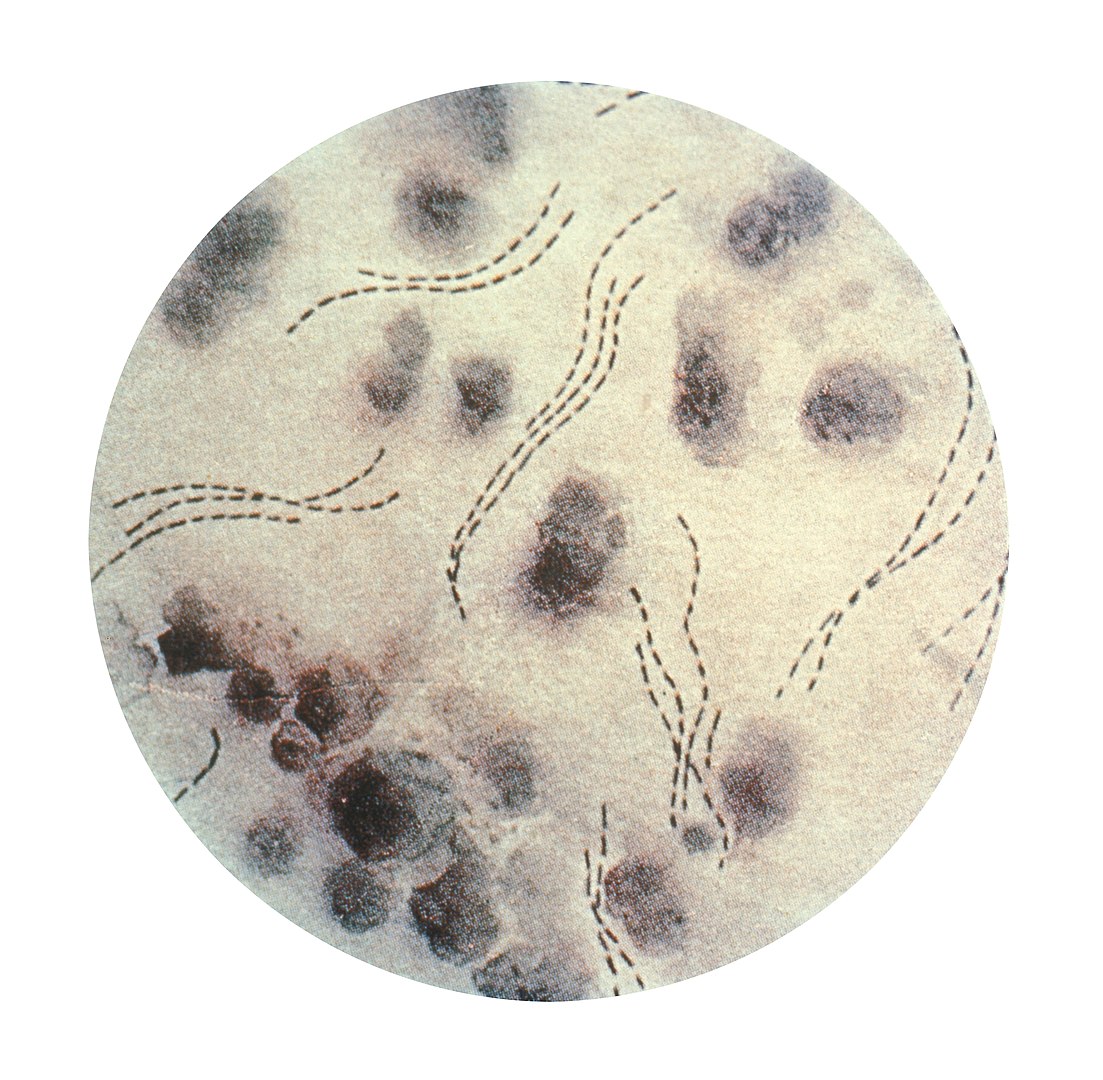
Overview Definition Chancroid (soft chancre) is a sexually transmitted disease caused by a bacterium, Haemophilus ducreyi, characterized by painful genital ulcers and suppurative inguinal adenopathy. Etiology Epidemiology Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation Diagnosis Diagnosis is made by clinical judgment and tests to rule out the 2 most common causes of genital ulcers, herpes simplex virus (HSV) and […]