Electrocardiogram (ECG)
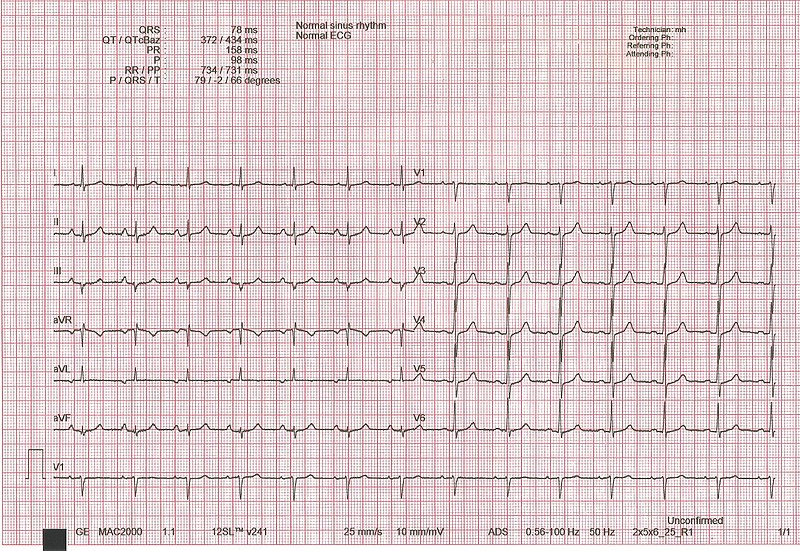
Overview In 1902 the electrocardiogram (ECG) was invented by Willem Einthoven, a Dutch physician. Einthoven received the 1924 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for the invention. Terminology Electrocardiogram is abbreviated/referred to as: ECG electrodes and leads ECG tracing Components A normal ECG tracing will have several predictable and reproducible components corresponding to electromechanical events […]
Hypercalcemia
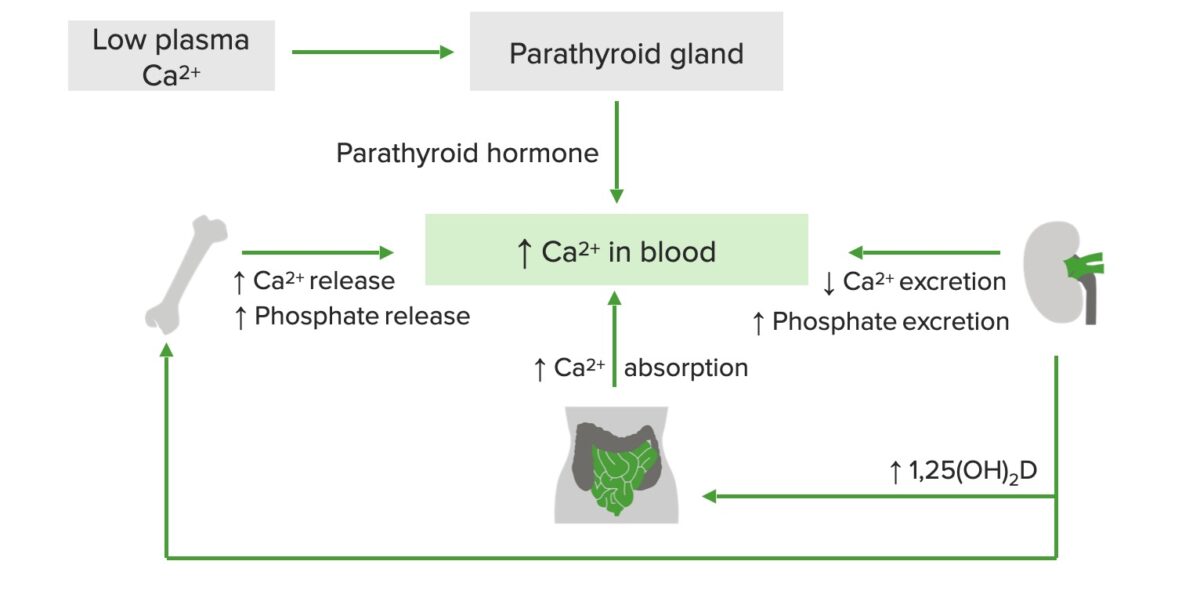
Calcium Homeostasis Calcium Calcium is the most abundant mineral in the human body, with 99% found in bone alone. Calcium in blood exists in 3 forms: Levels: Importance of calcium: Calcium regulation Bone, intestine, and kidneys are involved in homeostasis. Key elements of calcium regulation: Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology Mechanisms Hypercalcemia is characterized by elevated […]
Hypocalcemia

Calcium Homeostasis Calcium Calcium is the most abundant mineral in the human body; 99% is found in bone. Calcium in the blood exists in 3 forms: Levels: Importance of calcium: Calcium regulation Bone, intestine, and kidneys are involved in homeostasis. Key elements of calcium regulation: Etiology Associated with ↑ PTH: Hypoparathyroidism (↓ PTH): Drug induced: […]
Coronary Heart Disease
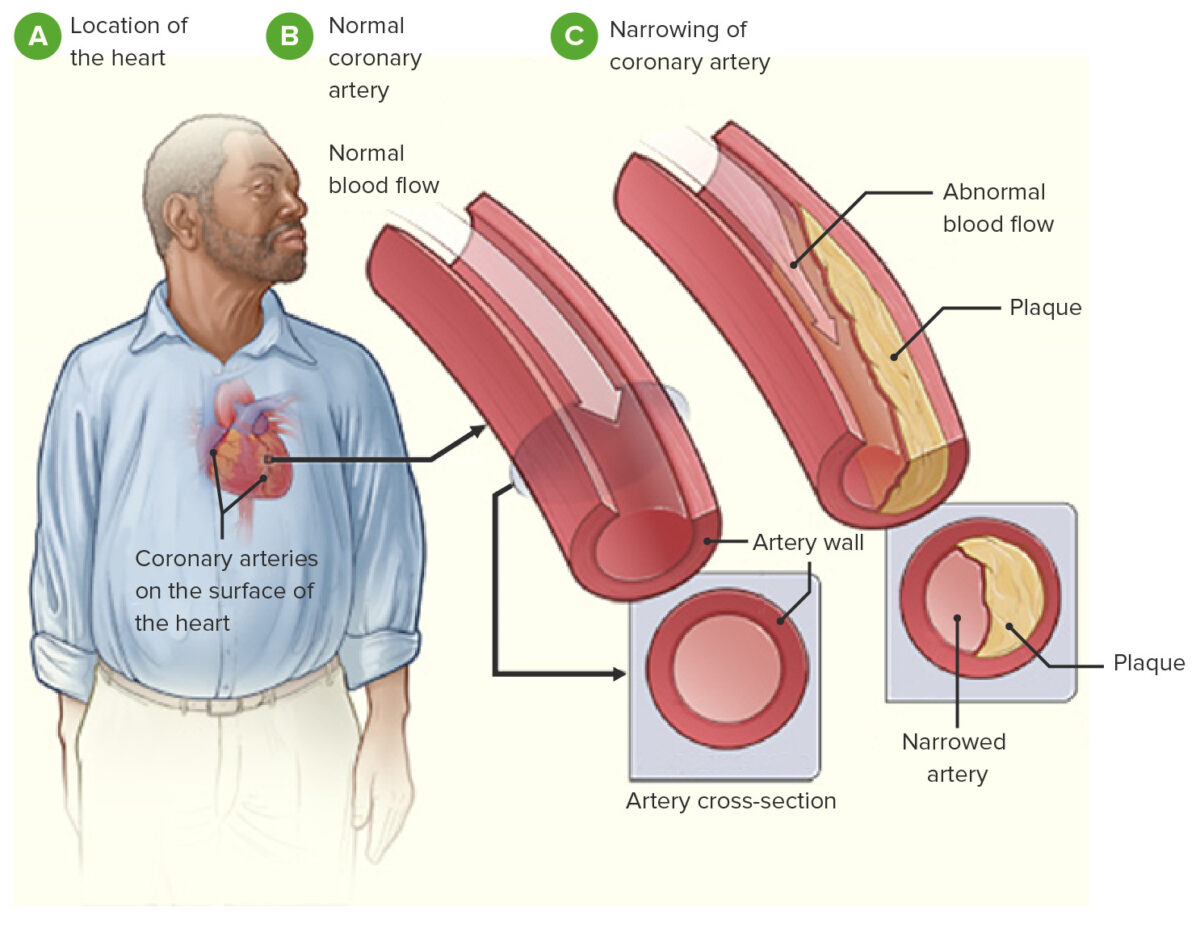
Overview Definition Coronary heart disease (CHD) is the manifestation of atherosclerosis in the coronary arteries such that there is an imbalance between oxygen supply and myocardial demands resulting in ischemia to a portion of the myocardium. Epidemiology Most common cause of death in the world Most common cardiovascular disease in the world Incidence rate: 0.6% […]
Pericardial Effusion and Cardiac Tamponade
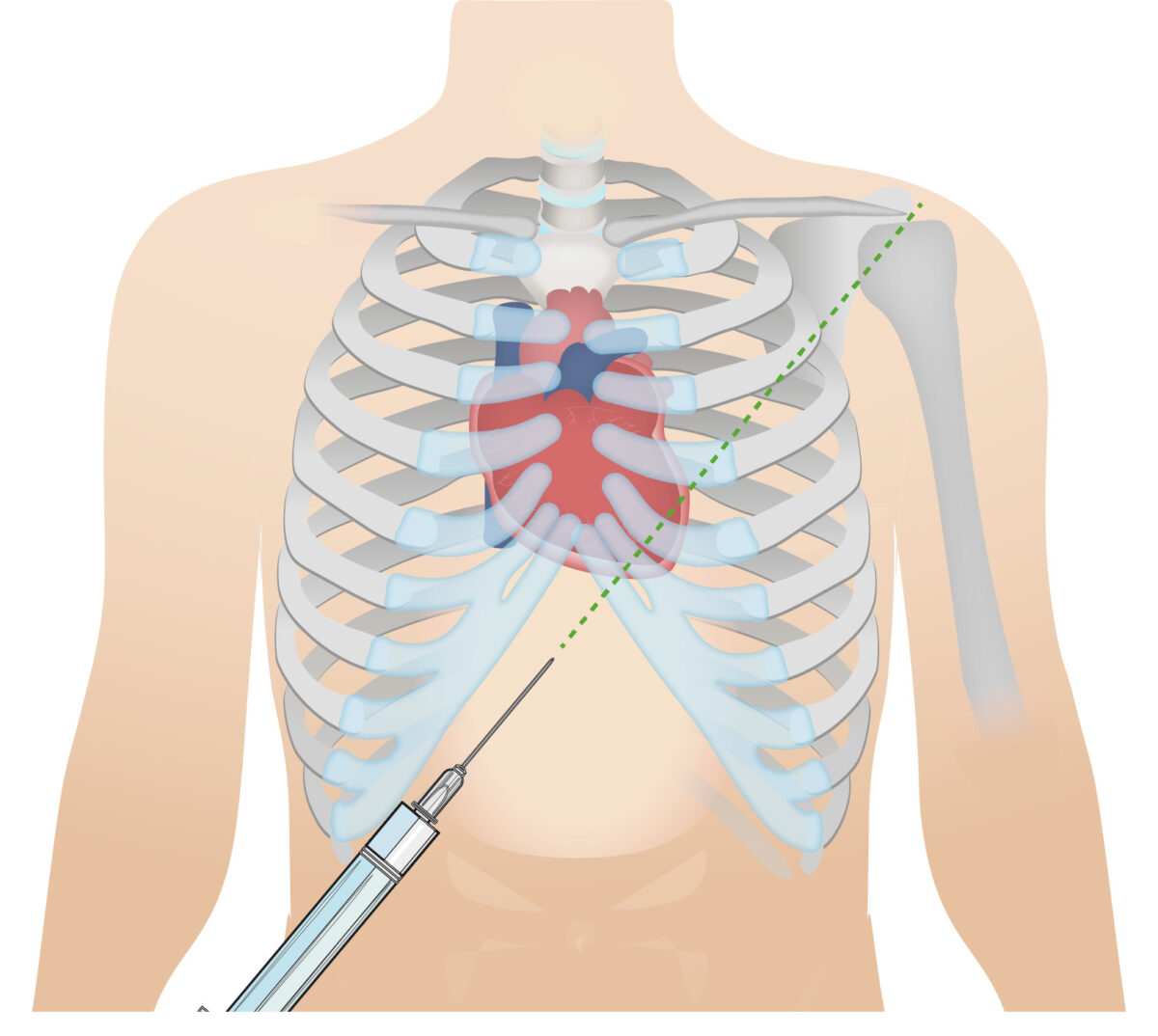
Epidemiology and Etiology Definition Pericardial effusion is the accumulation of fluid in the pericardial space. Cardiac tamponade is the accumulation of pericardial fluid sufficient to impair cardiac filling and cause hemodynamic compromise. The rate of fluid accumulation, and not necessarily the amount, is most important. Epidemiology Pericardial effusion: Cardiac tamponade: Etiology Many conditions are associated […]
Hyperkalemia
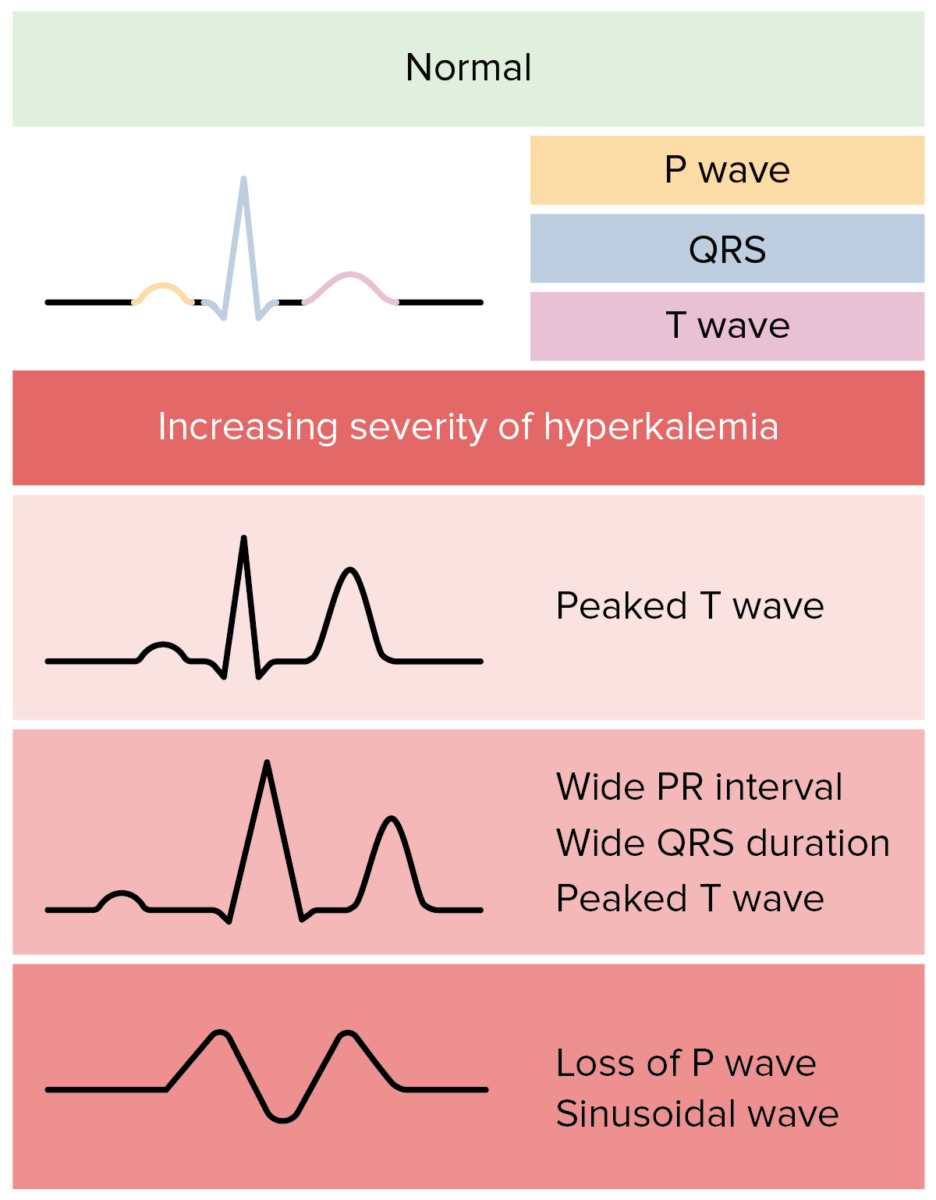
Overview General considerations K+ is the main intracellular cation in all cells and is distributed unevenly between the intracellular fluid (98%) and extracellular fluid (2%). Sites of action in the kidney Normal response to ingested K+ A normal Western diet contains approximately 70–150 mmol of K+ per day. This diet is unlikely to lead to […]
Cardiomyopathy: Overview and Types
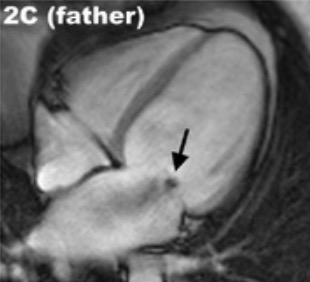
Overview Definition Cardiomyopathies are diseases that affect the structure and function of the heart muscle (myocardium) in the absence of secondary causes (e.g., coronary artery disease, hypertension, valvular disease, and congenital heart disease). Epidemiology Etiology Causes vary: Approximately ⅓ of cases have a genetic cause. Classification By morphology: By etiology: Pathophysiology Diagnosis Diagnostic approach varies […]
Restrictive Cardiomyopathy
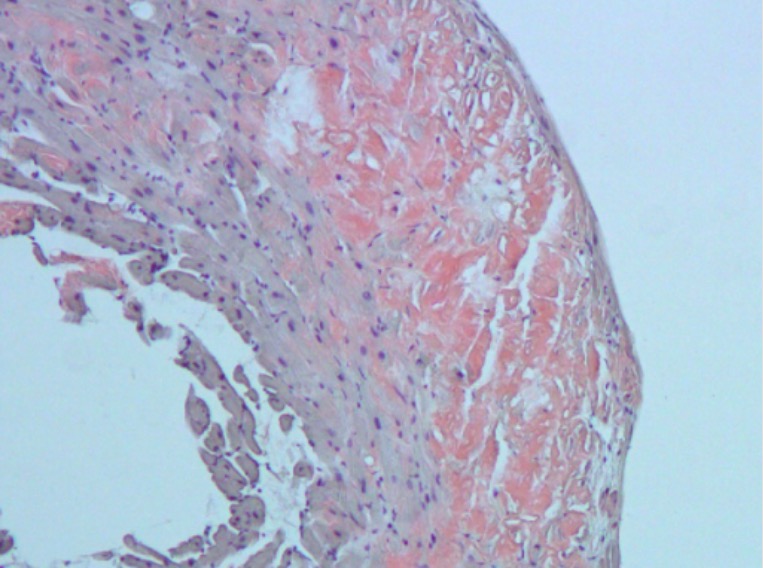
Overview Definition Restrictive cardiomyopathy (RCM) is a disease of the heart muscle characterized by decreased compliance of the ventricles, nondilated heart muscle, and diastolic dysfunction (impaired filling of the ventricles). Epidemiology Rarest cardiomyopathy 5% of all cases Incidence and prevalence are etiology-dependent: Amyloidosis Most common RCM in the United States Men = women Common in […]
Endocarditis
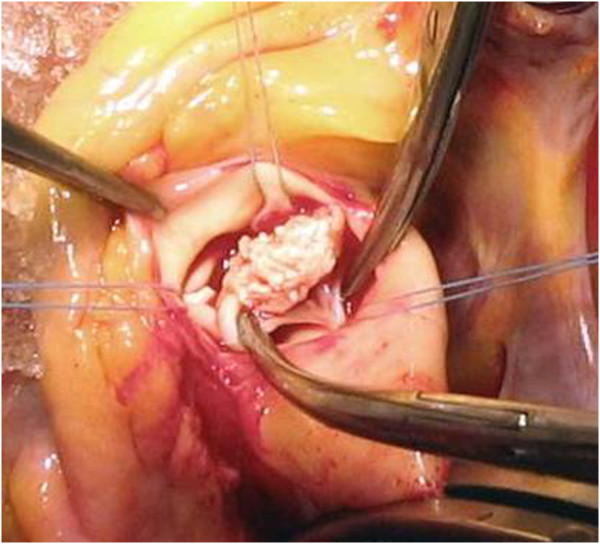
Overview Definition Epidemiology Infective endocarditis: Noninfective endocarditis: Infective endocarditis etiologies Infective endocarditis may be caused by numerous organisms; the list below is not exhaustive. Noninfective endocarditis etiologies Risk Factors and Pathophysiology Risk factors The following are risk factors for IE: Infective endocarditis Noninfective endocarditis Classification Infective endocarditis can be further classified based on the clinical […]
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
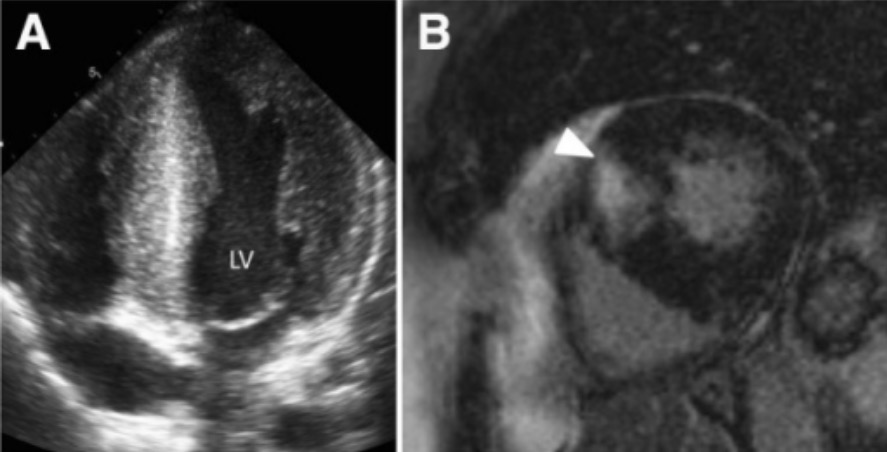
Overview Epidemiology Etiology Approximately 60%–70% of cases are caused by mutations affecting the thick or thin myofilament proteins of the sarcomeres (contractile components of the heart). Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation Many individuals affected by HCM are asymptomatic throughout their lives. For some, typically during adolescence, sudden cardiac death is the 1st symptom. History Symptoms: Family history: […]