Syndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone Secretion (SIADH) (Clinical)
Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) Source[3,4,10] Secreted in response to[1,10,13] Function[3,4,10,13] Etiology and Pathophysiology ADH levels normally rise when plasma osmolality exceeds 280 mOsm/kg; this mechanism is impaired with SIADH. Pathophysiology[1,4,13] Etiology[1,4,10] The major causes of SIADH are medications, malignancies, or infections affecting the CNS or lungs. Table: Causes of acquired SIADH Major causes Examples Central nervous […]
Hepatorenal Syndrome (Clinical)
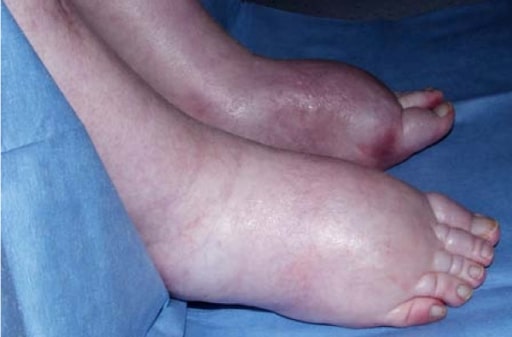
Etiology Hepatorenal syndrome (HRS) is associated with portal hypertension due to:[1] Pathophysiology Trigger factors are any interventions or conditions that cause arterial hypovolemia: Clinical Presentation and Diagnosis Diagnostic criteria may vary depending on practice location. The following information is based on US, UK, and European recommendations. Clinical presentation[3,7] Classification and diagnostic criteria HRS is a […]
Enteric Fever (Typhoid Fever) (Clinical)
Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology[2,3] Etiology[2,4] Pathophysiology Transmission[1,2,4,5] Pathogenesis[4] After ingestion of Salmonella Typhi: Clinical Presentation Infection with S. Typhi results in typhoid (or enteric) fever. Typhoid fever is a severe systemic illness associated with fever (cardinal symptom) and abdominal pain.[1,2,4,9,13] Table: Three-phase or -week progression (if untreated) Clinical course Findings Week 1 Bacteremia Gradually rising fever […]
Transfusion Products (Clinical)
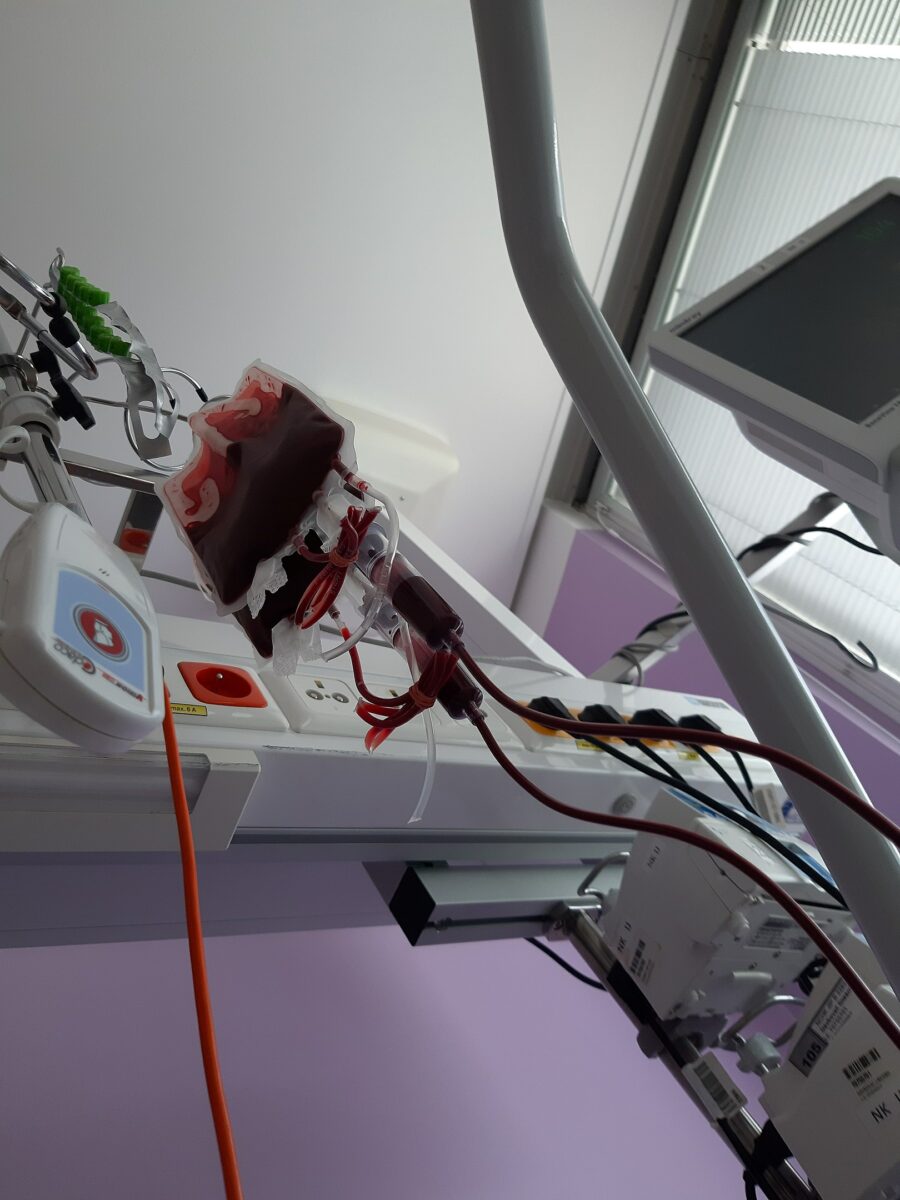
Introduction Blood transfusions are a very common medical procedure.[1,2,9] Table: Blood group compatibility for giving and receiving blood Blood type Can give to individuals with blood type Can receive from donors with blood type A+ A+, AB+ A+, A–, O+, O A– A+, A-, AB+, AB– A-, O– B+ B+, AB+ B+, B–, O+, O– […]
Postpartum Endometritis (Clinical)
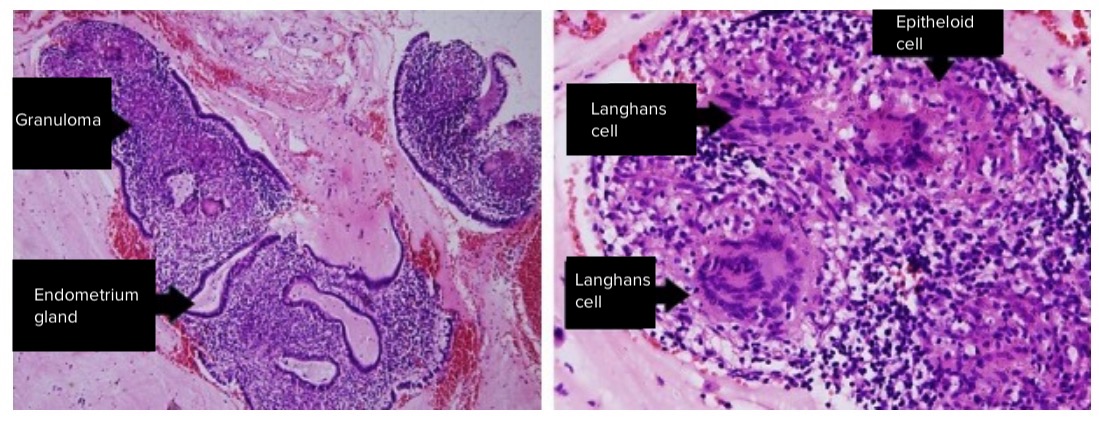
Overview Definition Endometritis is an inflammation of the inner lining of the uterus, the endometrium. Epidemiology[2,6–8] Risk factors[3,6] Pathophysiology Pathophysiologic mechanism[3,6,7] PP endometritis is caused by movement of normal vaginal flora to the uterus → colonization of the damaged uterine lining → infection and inflammation. Microbiology[2,3,6–8] PP endometritis is a polymicrobial infection involving both aerobic […]
Ovarian Cysts (Clinical)
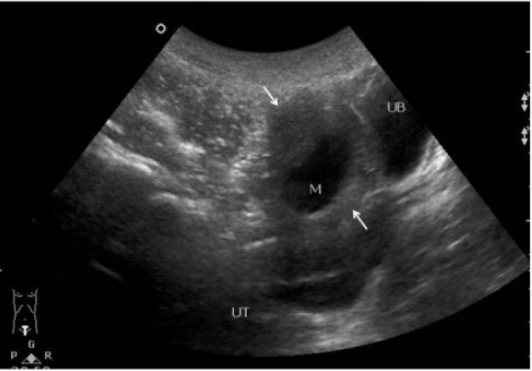
Nonneoplastic (Benign) Cysts Functional cysts (follicular cysts, corpus luteal cysts, theca lutein cysts)[1] Hemorrhagic cysts and endometriomas[1,6] Neoplastic Cysts Classification[1,6] Table: Classification of neoplastic cysts Cell of origin Benign tumors Malignant tumors Epidemiology and notes Epithelial cell tumors Cystadenomas: Serous Mucinous Carcinomas: High-grade serous Low-grade serous Mucinous Clear cell Endometroid 90% of primary malignant ovarian […]
Pelvic Organ Prolapse (Clinical)
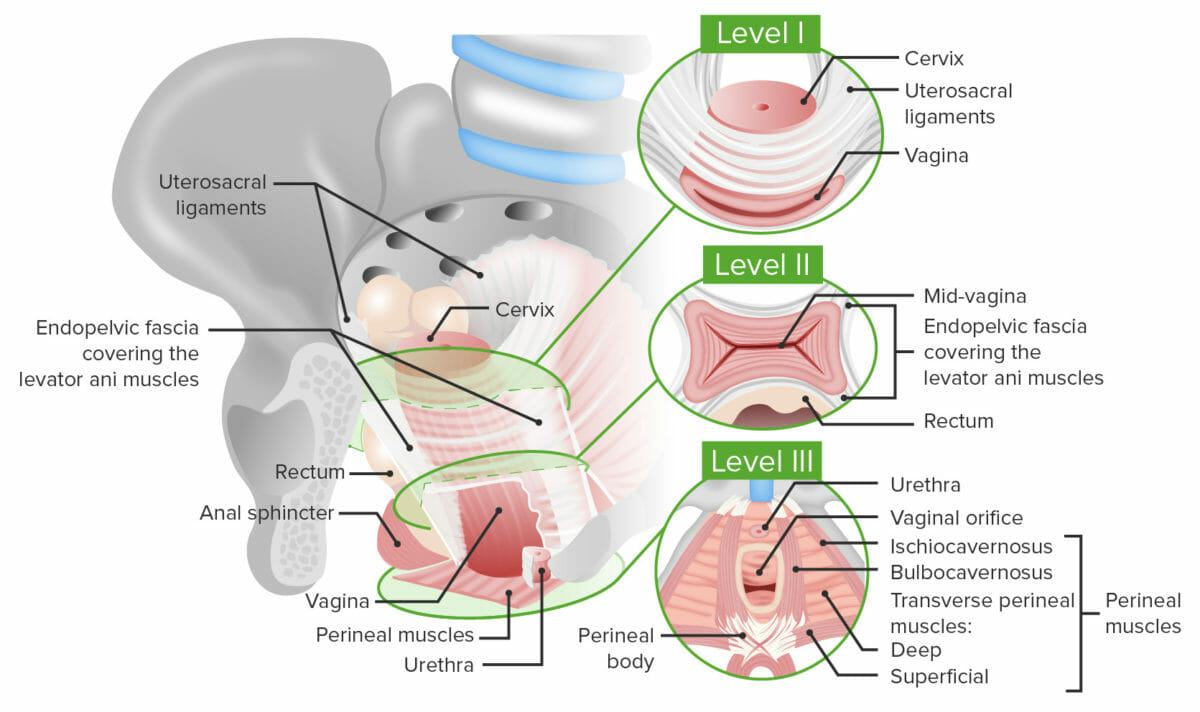
Overview Definitions[1,4] Pelvic organ prolapse (POP): a general term referring to prolapse of 1 or more of the pelvic organs (e.g., bladder, uterus, rectum) into the vaginal canal Visualizing POP Visualizing POP, especially apical POP, can be difficult. Etiology[1,4] Prolapse is due to weakness and insufficiency of the pelvic floor, which normally keeps organs in […]
Ovarian Torsion (Clinical)
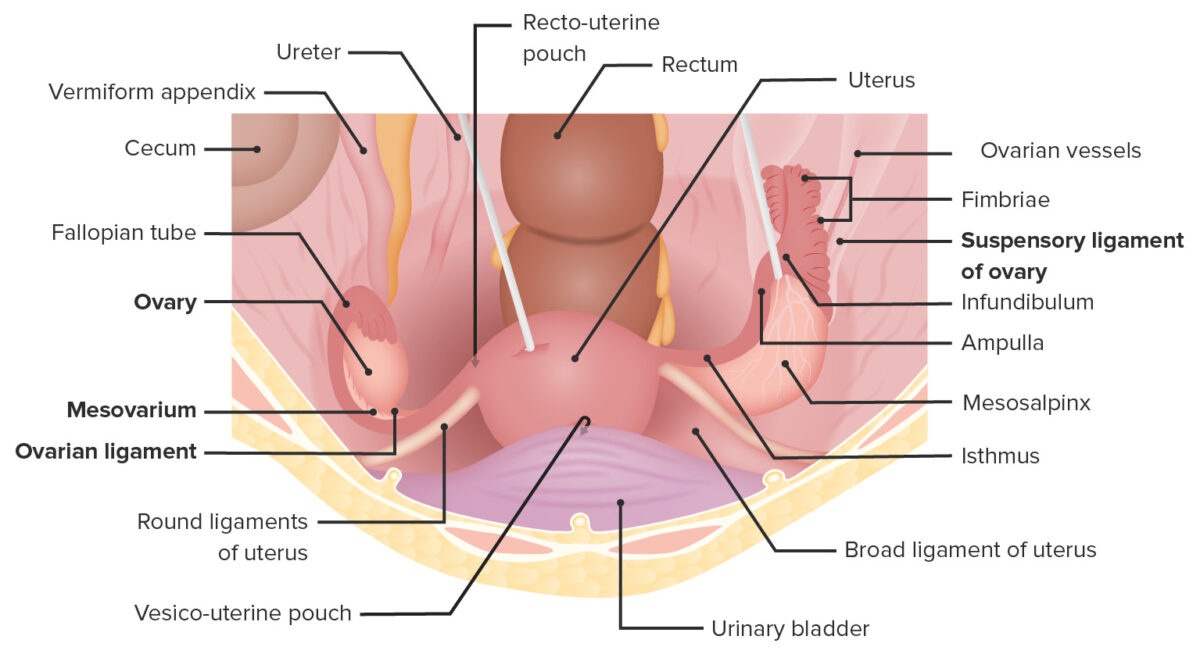
Overview Definition Ovarian torsion is the twisting of the ovaries along their axis. Ovarian torsion may or may not include the fallopian tubes and if it does, it is termed adnexal torsion. Anatomy[2] Epidemiology[1–5,7,8] Pathogenesis Ovarian or adnexal torsion involves the following sequence of events:[1–3] Clinical Presentation Diagnosis and Management Adnexal torsion is suspected based […]
Chorioamnionitis (Clinical)
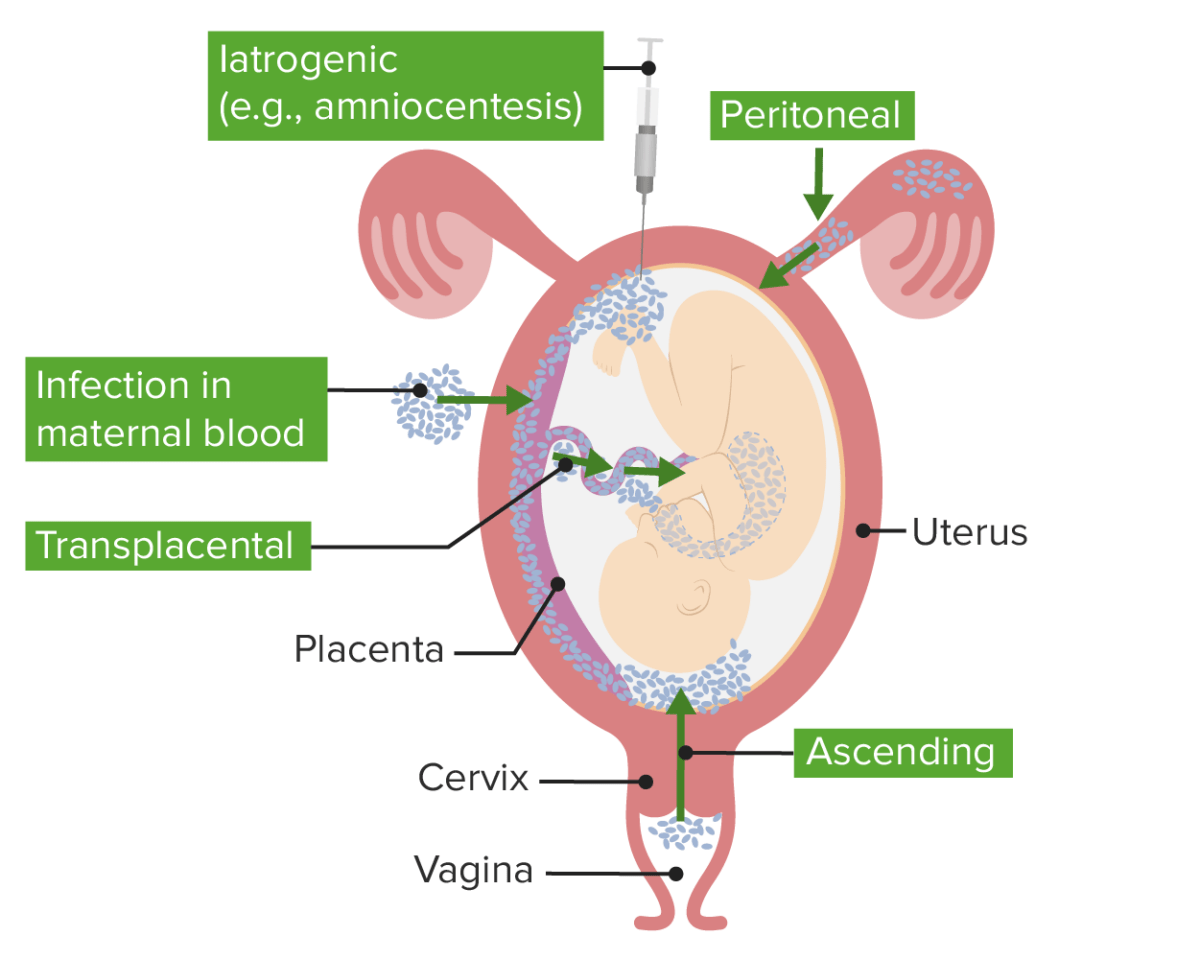
Definition and Epidemiology Definition Also known as intraamniotic infection (IAI), chorioamnionitis is an infection, and resulting inflammation, of any combination of the fetal membranes (chorion and amnion), amniotic fluid, placenta, umbilical cord (funisitis), and/or the fetus. Epidemiology[1,4–7] Chorioamnionitis is the most common cause of peripartum infection, with the following incidence rates: Etiology Intraamniotic infection and […]
Polyhydramnios (Clinical)
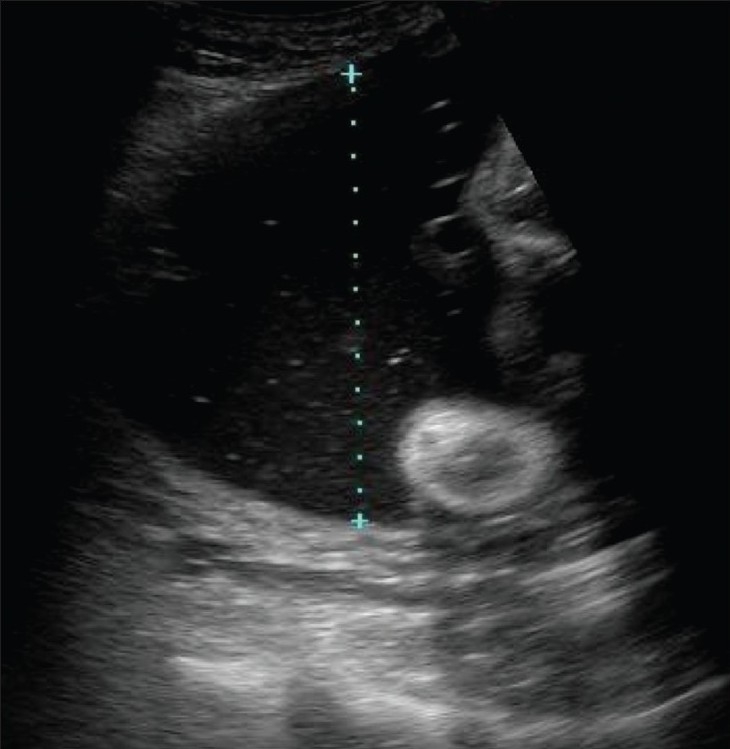
Overview Definition Polyhydramnios is an abnormally high level of amniotic fluid in the amniotic sac. Epidemiology[1,2,6] Etiology[1,2,5] Pathophysiology Two major causes of polyhydramnios: Clinical Presentation Diagnosis Diagnostic criteria can vary based on location. The following information is based on US medical society recommendations. History[1,2] Physical exam[1,2,6,9] Amniotic fluid assessment[3,4,8,9] Table: Classification of mild, moderate, and […]