El shock Shock Shock is a life-threatening condition associated with impaired circulation that results in tissue hypoxia. The different types of shock are based on the underlying cause: distributive (↑ cardiac output (CO), ↓ systemic vascular resistance (SVR)), cardiogenic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), hypovolemic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), obstructive (↓ CO), and mixed. Types of Shock es una afección potencialmente mortal que se asocia a una alteración de la circulación que provoca hipoxia tisular. Los LOS Neisseria diferentes tipos de shock Shock Shock is a life-threatening condition associated with impaired circulation that results in tissue hypoxia. The different types of shock are based on the underlying cause: distributive (↑ cardiac output (CO), ↓ systemic vascular resistance (SVR)), cardiogenic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), hypovolemic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), obstructive (↓ CO), and mixed. Types of Shock se basan en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la causa subyacente: distributivo (↑ gasto cardíaco, ↓ resistencia vascular sistémica), cardiogénico (↓ gasto cardíaco, ↑ resistencia vascular sistémica), hipovolémico (↓ gasto cardíaco, ↑ resistencia vascular sistémica), obstructivo (↓ gasto cardíaco) y mixto. Los LOS Neisseria síntomas más comunes son taquicardia, taquipnea, hipotensión, alteraciones mentales y oliguria Oliguria Decreased urine output that is below the normal range. Oliguria can be defined as urine output of less than or equal to 0. 5 or 1 ml/kg/hr depending on the age. Renal Potassium Regulation. Las medidas de tratamiento varían en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum función de la causa sospechada del shock Shock Shock is a life-threatening condition associated with impaired circulation that results in tissue hypoxia. The different types of shock are based on the underlying cause: distributive (↑ cardiac output (CO), ↓ systemic vascular resistance (SVR)), cardiogenic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), hypovolemic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), obstructive (↓ CO), and mixed. Types of Shock y pueden incluir ventilación mecánica, líquidos intravenosos para reanimación de volumen, vasopresores, transfusión de sangre/productos sanguíneos.
Last updated: Dec 28, 2025
El shock Shock Shock is a life-threatening condition associated with impaired circulation that results in tissue hypoxia. The different types of shock are based on the underlying cause: distributive (↑ cardiac output (CO), ↓ systemic vascular resistance (SVR)), cardiogenic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), hypovolemic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), obstructive (↓ CO), and mixed. Types of Shock es un estado de disfunción orgánica potencialmente mortal y que es consecuencia de la hipoxia tisular debida a la disminución del suministro de oxígeno, el aumento del consumo de oxígeno y/o la utilización defectuosa del mismo.
| Tipo de shock Shock Shock is a life-threatening condition associated with impaired circulation that results in tissue hypoxia. The different types of shock are based on the underlying cause: distributive (↑ cardiac output (CO), ↓ systemic vascular resistance (SVR)), cardiogenic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), hypovolemic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), obstructive (↓ CO), and mixed. Types of Shock | Presión venosa central (PVC) | Presión capilar pulmonar | Gasto cardíaco | Resistencia vascular sistémica |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Distributivo | ↓ | ↓ | ↑ | ↓ |
| Cardiogénico | ↑ | ↑ | ↓ | ↑ |
| Obstructivo | ↑ | ↓↑ | ↓ | ↑ |
| Hipovolémico | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ | ↑ |
Siempre se debe mantener una alta sospecha clínica de shock Shock Shock is a life-threatening condition associated with impaired circulation that results in tissue hypoxia. The different types of shock are based on the underlying cause: distributive (↑ cardiac output (CO), ↓ systemic vascular resistance (SVR)), cardiogenic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), hypovolemic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), obstructive (↓ CO), and mixed. Types of Shock. Las características sugestivas incluyen taquicardia, hipotensión, alteración mental, oliguria Oliguria Decreased urine output that is below the normal range. Oliguria can be defined as urine output of less than or equal to 0. 5 or 1 ml/kg/hr depending on the age. Renal Potassium Regulation, pulsos periféricos débiles y piel fría y húmeda.
¡El
shock
Shock
Shock is a life-threatening condition associated with impaired circulation that results in tissue hypoxia. The different types of shock are based on the underlying cause: distributive (↑ cardiac output (CO), ↓ systemic vascular resistance (SVR)), cardiogenic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), hypovolemic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), obstructive (↓ CO), and mixed.
Types of Shock es una emergencia médica!
Iniciar el tratamiento y la evaluación simultánea
en
EN
Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins.
Erythema Nodosum busca de la etiología, utilizando
los
LOS
Neisseria hallazgos de
los
LOS
Neisseria antecedentes, la exploración física, el monitoreo hemodinámico y
los
LOS
Neisseria estudios de laboratorio. La mejor manera de lograrlo es con un equipo multidisciplinario
en
EN
Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins.
Erythema Nodosum un entorno equipado con recursos como la unidad de cuidados intensivos (UCI).
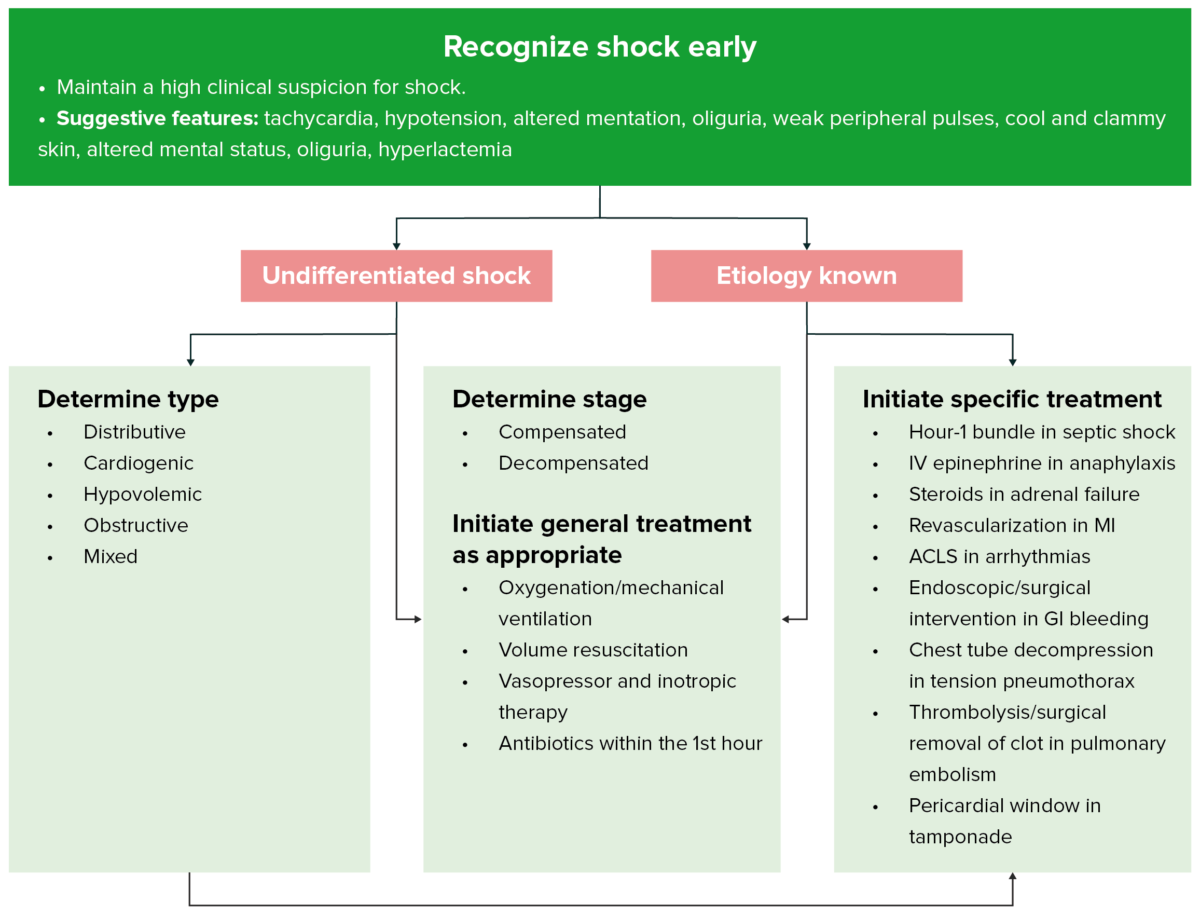
Abordaje al shock
Imagen por Lecturio.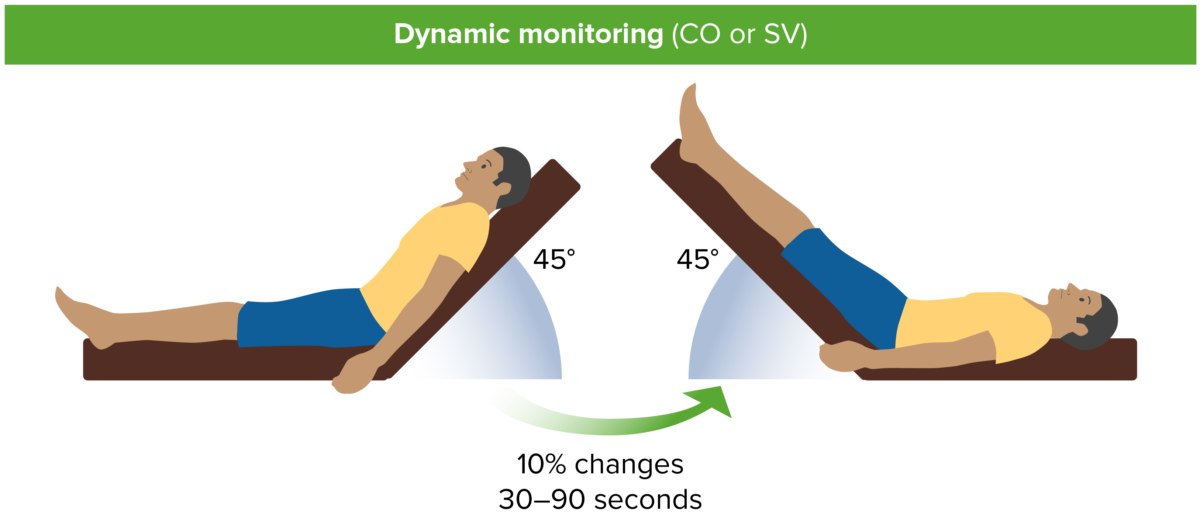
Elevación pasiva de piernas. CO: gasto cardíaco (por sus siglas en inglés); SV: volumen sistólico (por sus siglas en inglés).
Imagen por Lecturio.