El eritema multiforme es una reacción de hipersensibilidad aguda caracterizada por lesiones cutáneas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum diana con múltiples anillos y centros oscuros. Las lesiones pueden ir acompañadas de síntomas sistémicos (e.g., fiebre) y lesiones mucosas (e.g., bullas). La mayoría de los LOS Neisseria pacientes con eritema multiforme tienen un antecedente de infección viral reciente (especialmente el virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology herpes simple) o bacteriana (generalmente Mycoplasma pneumoniae Mycoplasma pneumoniae Short filamentous organism of the genus mycoplasma, which binds firmly to the cells of the respiratory epithelium. It is one of the etiologic agents of non-viral primary atypical pneumonia in man. Mycoplasma). El eritema multiforme se diagnostica clínicamente y el tratamiento se dirige a remover el agente causal y al AL Amyloidosis alivio de los LOS Neisseria síntomas.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
El eritema multiforme es una reacción inmunitaria mediada por células (reacción de tipo IV) dirigida contra los LOS Neisseria antígenos del agente causante, los LOS Neisseria cuales se depositan en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la piel.
| Clasificación | Etiologías | Ejemplos |
|---|---|---|
| Causas infecciosas (más comunes, 90% de los LOS Neisseria casos) | Bacteriana |
|
| Viral |
|
|
| Fúngica | Histoplasmosis Histoplasmosis Histoplasmosis is an infection caused by Histoplasma capsulatum, a dimorphic fungus. Transmission is through inhalation, and exposure to soils containing bird or bat droppings increases the risk of infection. Most infections are asymptomatic; however, immunocompromised individuals generally develop acute pulmonary infection, chronic infection, or even disseminated disease. Histoplasma/Histoplasmosis, dermatofitos | |
| Causas no infecciosas | Medicamentos |
|
| Malignidad |
|
|
| Misceláneas |
|
El eritema multiforme se clasifica en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum función de la presencia de lesiones en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las mucosas y de los LOS Neisseria síntomas sistémicos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum eritema multiforme menor y mayor.
| Lesiones cutáneas | Afectación de la mucosa | Síntomas sistémicos | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Eritema multiforme menor | ✔ | ||
| Eritema multiforme mayor | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
El eritema multiforme generalmente se resuelve espontáneamente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el plazo de 1 mes, sin secuelas a largo plazo. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum raras ocasiones, el eritema multiforme puede reaparecer, hasta 6 veces/año durante 10 años (generalmente asociada a una infección por HSV HSV Herpes simplex virus (HSV) is a double-stranded DNA virus belonging to the family Herpesviridae. Herpes simplex virus commonly causes recurrent infections involving the skin and mucosal surfaces, including the mouth, lips, eyes, and genitals. Herpes Simplex Virus 1 and 2).
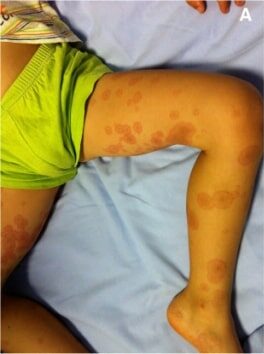
Lesiones en diana con una forma regular y redonda y 3 zonas concéntricas: una zona central de color rojo más oscuro, una zona rosa más pálida y un anillo rojo periférico
Imagen: “Erythema multiforme” por Pediatric Unit, Maternal & Infant Department, S. Chiara University-Hospital, Via Roma 67, Pisa 56126, Italy. Licencia: CC BY 2.0, editada por Lecturio.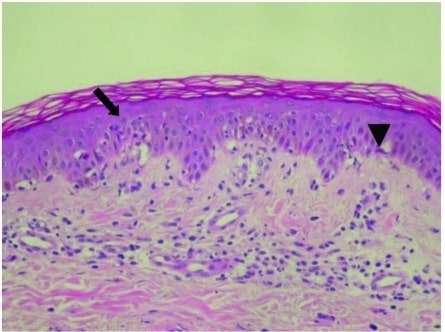
Cambios epidérmicos en el eritema multiforme con degeneración vacuolada de las células basales (flecha) y necrosis de queratinocitos individuales dispersos (cabeza de flecha)
Imagen: “Epidermal Changes in Erythema Multiforme” por Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Taipei Medical University Hospital, Taipei, Taiwan. Licencia: CC BY 2.5