El derrame pericárdico es la acumulación de líquido en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el espacio pericárdico que rodea del corazón. El pericardio no se expande fácilmente, por lo que la acumulación rápida de líquido provoca un aumento de la presión alrededor del corazón. El aumento de la presión restringe el llenado cardíaco, lo que provoca una disminución del gasto cardíaco y taponamiento cardíaco. Los LOS Neisseria signos y síntomas suelen aparecer en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el contexto del taponamiento cardíaco e incluyen disnea, hipotensión, ruidos cardíacos disminuidos, ingurgitación yugular y pulso paradójico. El diagnóstico de derrame pericárdico se confirma con ultrasonido cardíaco. Los LOS Neisseria derrames pequeños en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum pacientes hemodinámicamente estables se tratan médicamente. Los LOS Neisseria derrames más grandes y el taponamiento cardíaco pueden requerir una pericardiocentesis Pericardiocentesis Puncture and aspiration of fluid from the pericardium. Cardiac Surgery o una pericardiotomía.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
El derrame pericárdico es la acumulación de líquido en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el espacio pericárdico.
El taponamiento cardíaco es la acumulación de líquido pericárdico suficiente para impedir el llenado cardíaco y causar compromiso hemodinámico. Lo más importante es la velocidad de acumulación de líquido, y no necesariamente la cantidad.
Derrame pericárdico:
Taponamiento cardíaco:
Múltiples trastornos están asociados al AL Amyloidosis derrame pericárdico, incluyendo:
Sin taponamiento cardíaco:
Taponamiento cardíaco:
En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria derrames pericárdicos de gran tamaño y en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el taponamiento cardíaco pueden observarse lo siguiente:
Signos vitales:
Hallazgos cardiovasculares:
Hallazgos respiratorios:
Hallazgos periféricos:
La tríada describe los LOS Neisseria hallazgos clásicos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el taponamiento cardíaco:
ECG ECG An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a graphic representation of the electrical activity of the heart plotted against time. Adhesive electrodes are affixed to the skin surface allowing measurement of cardiac impulses from many angles. The ECG provides 3-dimensional information about the conduction system of the heart, the myocardium, and other cardiac structures. Electrocardiogram (ECG):
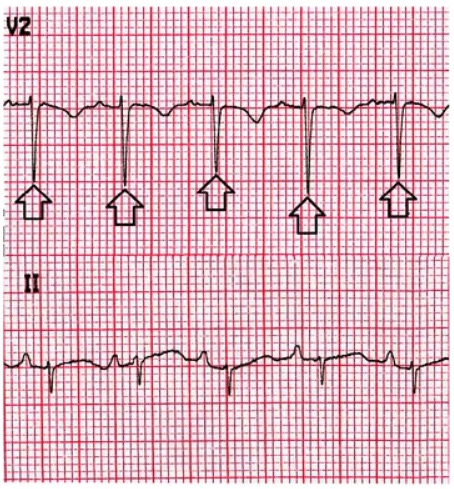
Alternancias eléctricas en un ECG en un paciente con un gran derrame pericárdico:
Las flechas señalan la amplitud alternante del complejo QRS.
Radiografía de tórax:

Cardiomegalia por derrame pericárdico antes y después del drenaje:
(a) Radiografía de tórax que muestra una cardiomegalia debido a la acumulación de un derrame pericárdico
(b) Resolución de la cardiomegalia tras el drenaje del líquido.
Ultrasonido cardíaco:
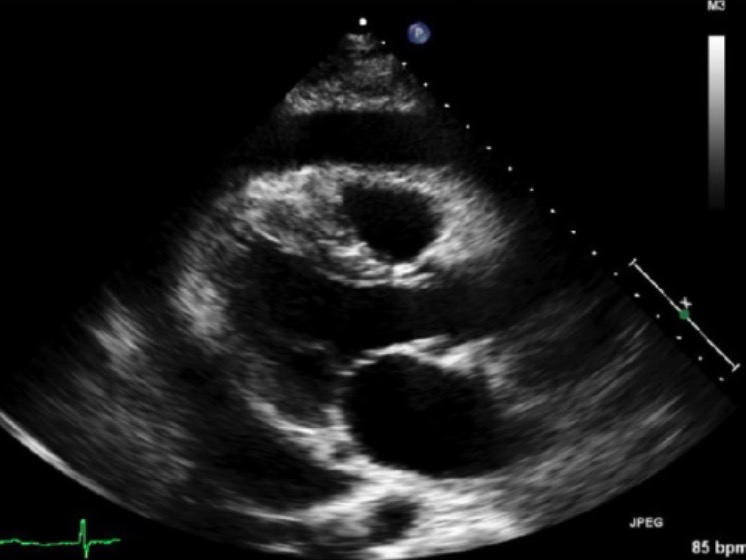
Ultrasonido cardíaco transtorácico que muestra un derrame pericárdico (región ecolúcida alrededor del corazón)
Imagen: “Transthoracic echocardiography” por Department of Internal Medicine, The University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, NM 87106, USA. Licencia: CC BY 4.0TC y RM:
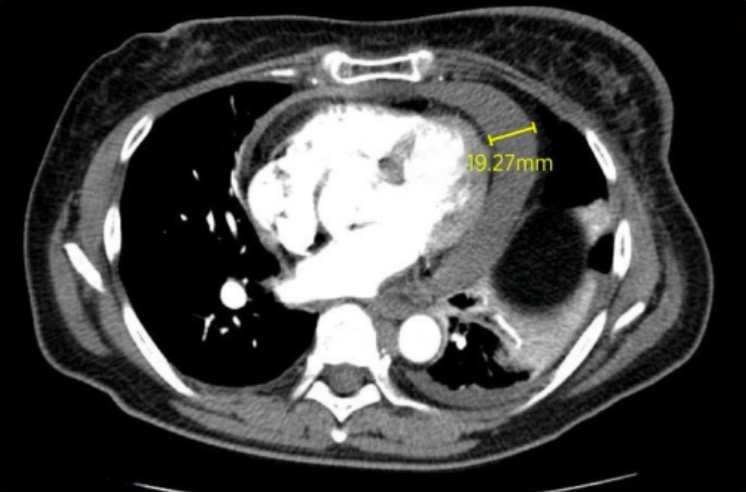
Una TC que muestra un derrame pericárdico de 19,27 mm.
Imagen: “CT pulmonary embolus” por Stanford Hospital and Clinics, Stanford, California. Licencia: CC BY 2.0Se puede realizar un análisis del líquido pericárdico y una biopsia pericárdica para determinar la causa del derrame. Se pueden realizar las siguientes pruebas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el líquido pericárdico:
Para determinar la etiología de un derrame pericárdico se pueden realizar las siguientes pruebas:
Consideraciones generales:
Pericardiocentesis Pericardiocentesis Puncture and aspiration of fluid from the pericardium. Cardiac Surgery:
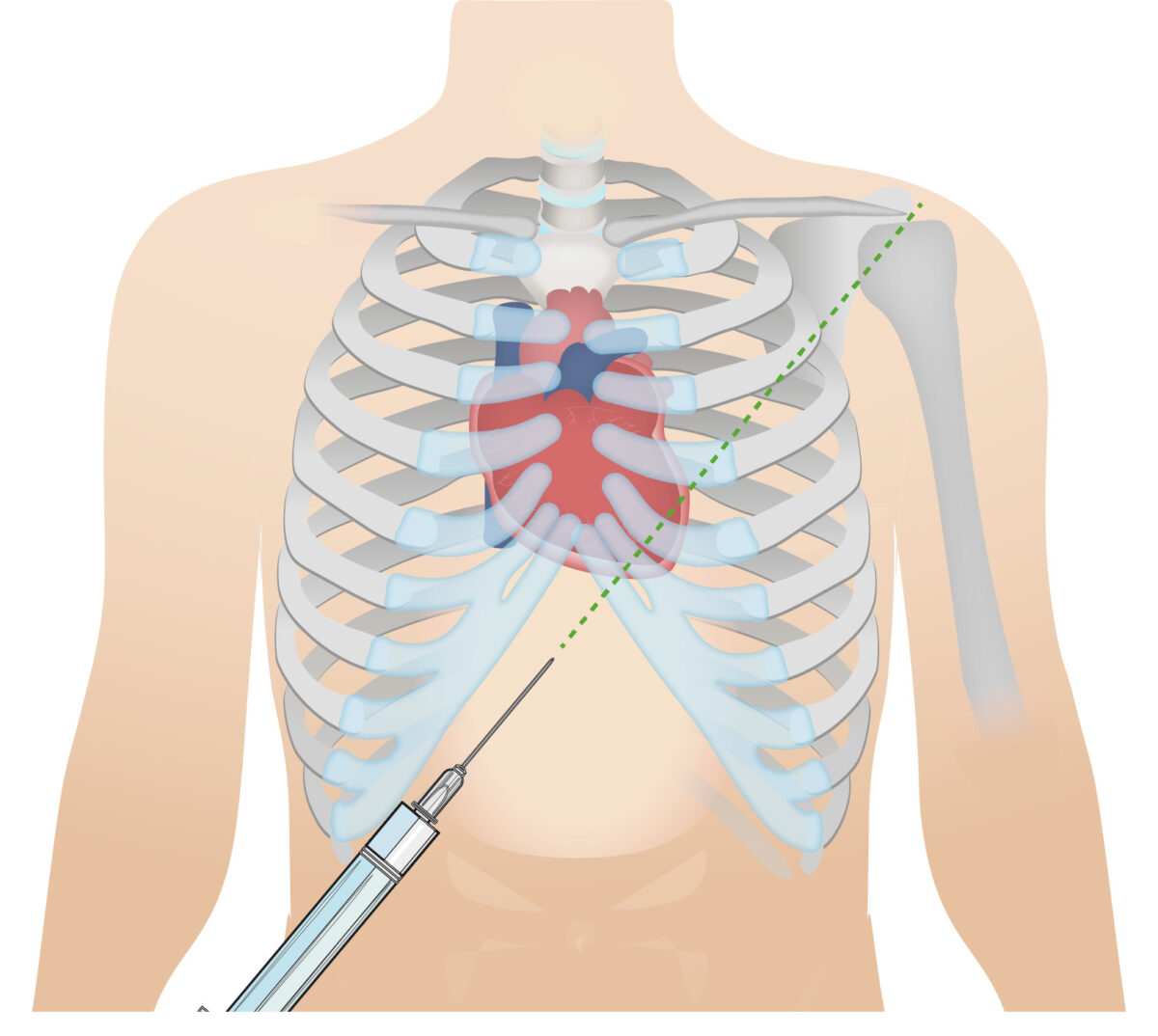
Abordaje subxifoideo para la pericardiocentesis:
Este abordaje permite el drenaje del líquido pericárdico.
Tratamiento quirúrgico: