Cryptosporidium Cryptosporidium A genus of coccidian parasites of the family cryptosporidiidae, found in the intestinal epithelium of many vertebrates including humans. Hyper-IgM Syndrome es un protozoo intracelular y una importante causa de diarrea infecciosa. La infección se transmite por vía fecal-oral y está causada por la ingestión de ooquistes de Cryptosporidium Cryptosporidium A genus of coccidian parasites of the family cryptosporidiidae, found in the intestinal epithelium of many vertebrates including humans. Hyper-IgM Syndrome; la fuente más común de brotes es el agua contaminada. Cryptosporidium Cryptosporidium A genus of coccidian parasites of the family cryptosporidiidae, found in the intestinal epithelium of many vertebrates including humans. Hyper-IgM Syndrome afecta a las células epiteliales intestinales; la infección se presenta como diarrea acuosa, náuseas, dolor Dolor Inflammation abdominal tipo cólico y, posiblemente, fiebre. La afección suele ser autolimitada (unos 10-14 días) en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum pacientes inmunocompetentes, pero puede ser crónica y más grave en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum pacientes inmunocomprometidos (con posible malabsorción, deshidratación y emaciación). La criptosporidiosis es una de las infecciones oportunistas que pueden aparecer en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum individuos con SIDA, dando lugar a la colangiopatía del SIDA. El diagnóstico se realiza mediante microscopía, inmunoanálisis o pruebas moleculares por PCR PCR Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a technique that amplifies DNA fragments exponentially for analysis. The process is highly specific, allowing for the targeting of specific genomic sequences, even with minuscule sample amounts. The PCR cycles multiple times through 3 phases: denaturation of the template DNA, annealing of a specific primer to the individual DNA strands, and synthesis/elongation of new DNA molecules. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) de muestras fecales. El tratamiento es principalmente de soporte, utilizando el agente antiprotozoario nitazoxanida en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum caso de enfermedad severa.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La transmisión se produce por vía fecal-oral. La ingestión de ooquistes de Cryptosporidium Cryptosporidium A genus of coccidian parasites of the family cryptosporidiidae, found in the intestinal epithelium of many vertebrates including humans. Hyper-IgM Syndrome inicia la infección. Las diferentes fuentes de transmisión son:
La infección se inicia por la ingesta de ooquistes completamente esporulados y resistentes al AL Amyloidosis ambiente.
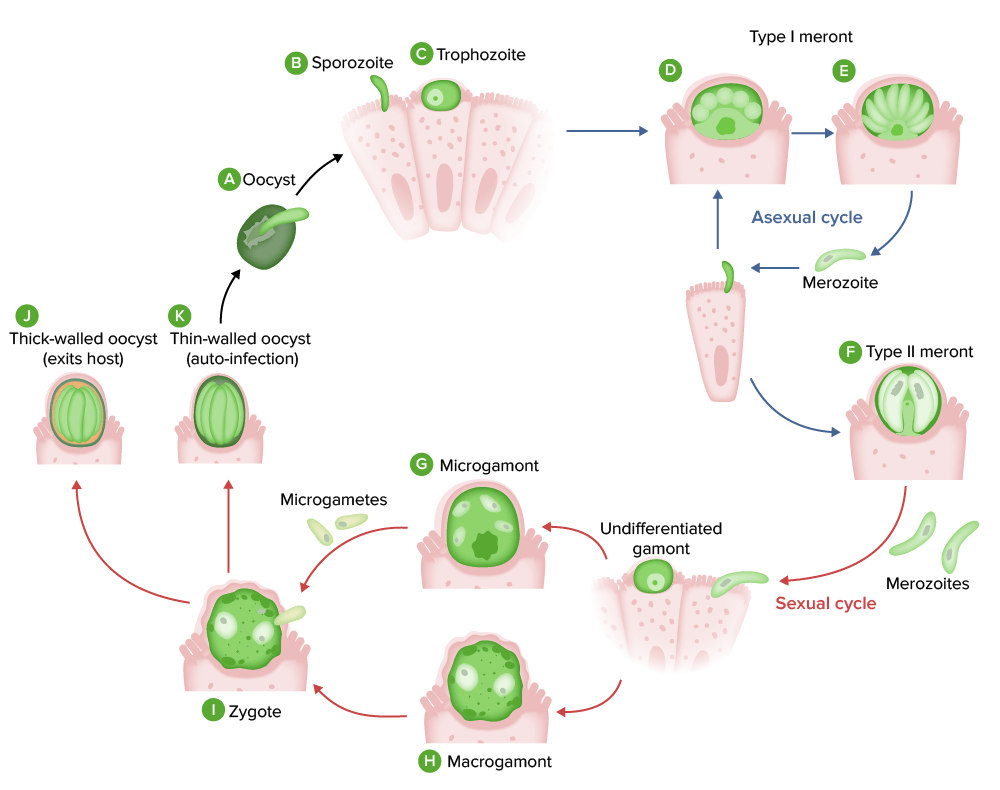
Ciclo de vida del Cryptosporidium: El ooquiste (A) se rompe, liberando esporozoítos (B) que se implantan en el borde en cepillo de los enterocitos. El esporozoíto se convierte en trofozoíto (C), que crece y madura en un meronte de tipo I (D) y (E). El meronte de tipo I libera merozoítos, que se implantan en los enterocitos cercanos y pueden volver a convertirse en merontes de tipo I (reproducción asexual) o en merontes de tipo II (que entran en el ciclo de reproducción sexual). Estos merontes de tipo II (F) liberan merozoítos que se implantan y maduran en gamontes indiferenciados. Después madurarán y se convertirán en un microgamonte (G, masculino) o en un macrogamonte (H, femenino). El microgamonte libera microgametos que fecundan al macrogamonte, creando un cigoto (I). A continuación, el cigoto madura en un ooquiste de pared gruesa (J, que sale del huésped en las heces) o en un ooquiste de pared fina (K, que permanece en el lumen gastrointestinal y libera esporozoítos que siguen infectando los enterocitos cercanos). Imagen por Lecturio.
Cryptosporidium Cryptosporidium A genus of coccidian parasites of the family cryptosporidiidae, found in the intestinal epithelium of many vertebrates including humans. Hyper-IgM Syndrome causa diarrea secretora asociada a malabsorción.
La criptosporidiosis sintomática se presenta con:
La criptosporidiosis se asocia a las siguientes complicaciones (más frecuentes en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum pacientes inmunocomprometidos):
Los LOS Neisseria exámenes parasitológicos de heces no incluyen regularmente el descarte de criptosporidiosis, a menos que haya un brote de diarrea. Si se sospecha la presencia de Cryptosporidium Cryptosporidium A genus of coccidian parasites of the family cryptosporidiidae, found in the intestinal epithelium of many vertebrates including humans. Hyper-IgM Syndrome, debe solicitarse una prueba específica cuando se envíen las muestras al AL Amyloidosis laboratorio.
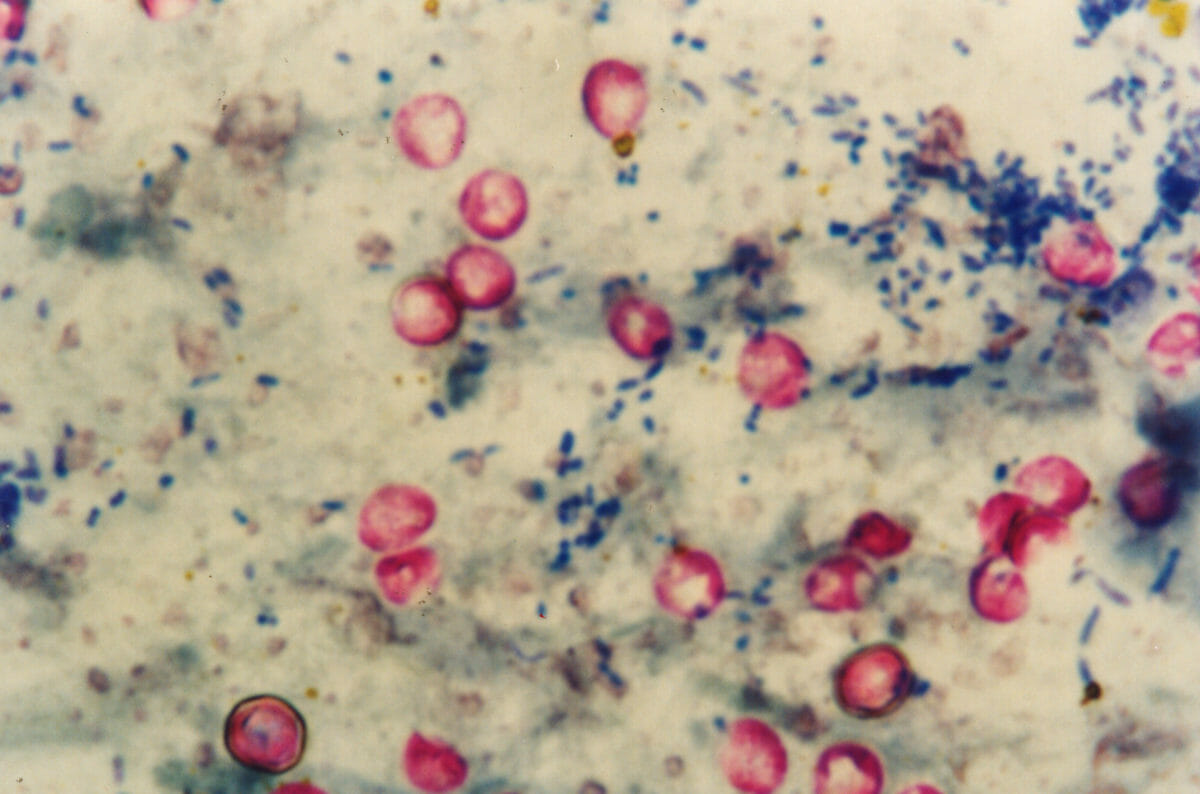

En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum casos con diarrea importante:
La mayoría de los LOS Neisseria pacientes son asintomáticos o presentan una enfermedad leve. El tratamiento de soporte es el enfoque principal.
La criptosporidiosis es una de las infecciones oportunistas que pueden aparecer en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum pacientes con infección por VIH.