Bunyaviridae Bunyaviridae A family of viruses, mainly arboviruses, consisting of a single strand of RNA. Virions are enveloped particles 90-120 nm diameter. The complete family contains over 300 members arranged in five genera: orthobunyavirus; hantavirus; nairovirus; phlebovirus; and tospovirus. Bunyavirales es una familia de virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de ARN que se clasifica en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum 5 géneros: Orthobunyavirus Orthobunyavirus A genus of the family bunyaviridae containing over 150 viruses, most of which are transmitted by mosquitoes or flies. They are arranged in groups defined by serological criteria, each now named for the original reference species (previously called serogroups). Many species have multiple serotypes or strains. Bunyavirales ( virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology La Crosse), Hantavirus Hantavirus A genus of the family bunyaviridae causing hantavirus infections, first identified during the korean war. Infection is found primarily in rodents and humans. Transmission does not appear to involve arthropods. Hantaan virus is the type species. Bunyavirales, Nairovirus Nairovirus A genus of the family bunyaviridae named after nairobi sheep disease, an acute, hemorrhagic, tick-borne, gastroenteritis affecting sheep and goats. The type species is dugbe virus. Some viruses in this genus are capable of causing severe and fatal disease in humans. Bunyavirales ( virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de la fiebre hemorrágica de Crimea-Congo), Phlebovirus Phlebovirus A genus of the family bunyaviridae comprising many viruses, most of which are transmitted by phlebotomus flies and cause phlebotomus fever. The type species is rift valley fever virus. Bunyavirales ( virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de la fiebre del Valle del Rift) y Tospovirus Tospovirus A genus of plant viruses in the family bunyaviridae. Tomato spotted wilt virus is the type species. Transmission occurs by at least nine species of thrips. Bunyavirales. Las características comunes de la familia de virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology con un genoma tipo ácido ribonucleico (ARN) de sentido negativo monocatenario, incluyen que tiene tres segmentos, y que se encuentra en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum una estructura esférica envuelta. Las infecciones generalmente son transmitidas por artrópodos o roedores. Hay múltiples manifestaciones clínicas, en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum general se presentan como fiebres hemorrágicas y/o encefalitis. Los LOS Neisseria procedimientos de diagnóstico incluyen serología y RT-PCR RT-PCR A variation of the pcr technique in which cDNA is made from RNA via reverse transcription. The resultant cDNA is then amplified using standard pcr protocols. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR). El tratamiento es principalmente de soporte.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025

Identificación de los virus ARN:
Los virus pueden clasificarse de muchas maneras. Sin embargo, la mayoría de los virus tienen un genoma formado por ADN o ARN. Los virus del genoma de ARN se pueden caracterizar adicionalmente basándose en la presencia de ARN monocatenario o bicatenario. Los virus “envueltos” están cubiertos por una fina capa de membrana celular (normalmente tomada de la célula huésped). Si no poseen envoltura, los virus se denominan “desnudos”. Los virus con genomas monocatenarios se denominan virus de “sentido positivo” si el genoma se utiliza directamente como ARN mensajero (ARNm), el cual se traduce en proteínas. Los virus monocatenarios de “sentido negativo” emplean la ARN polimerasa dependiente de ARN, una enzima viral, para transcribir su genoma en ARN mensajero.
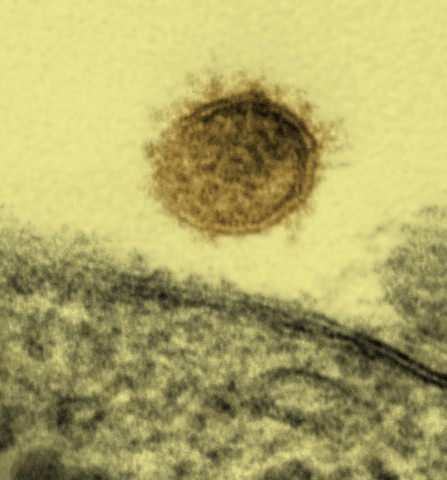
Una partícula del virus Sin Nombre que se muestra gemando de una célula Vero:
El virus Sin Nombre causa el síndrome pulmonar por hantavirus en América del Norte.
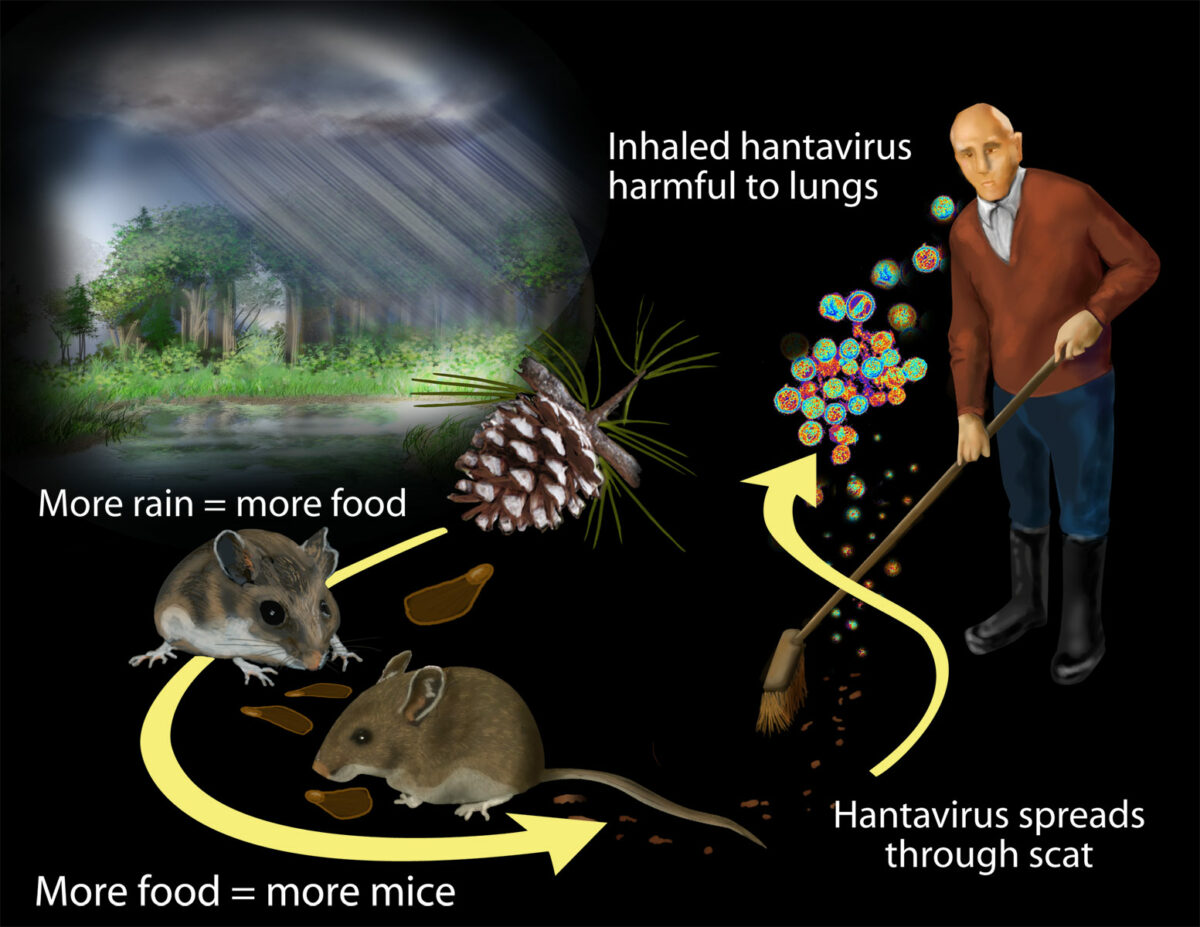
Transmisión de hantavirus:
Los investigadores encontraron que el contacto con roedores y sus desechos pone a los humanos en riesgo de exposición al hantavirus. Las lluvias masivas asociadas con fenomeno del Niño de 1991-1992 impulsaron la productividad de las plantas.
La población de roedores creció al alimentarse con la materia vegetal más abundante. El mayor contacto con roedores y sus desechos pone a más humanos en riesgo de exposición al hantavirus.
| Síndrome pulmonar por hantavirus Hantavirus A genus of the family bunyaviridae causing hantavirus infections, first identified during the korean war. Infection is found primarily in rodents and humans. Transmission does not appear to involve arthropods. Hantaan virus is the type species. Bunyavirales | Fiebre hemorrágica por hantavirus Hantavirus A genus of the family bunyaviridae causing hantavirus infections, first identified during the korean war. Infection is found primarily in rodents and humans. Transmission does not appear to involve arthropods. Hantaan virus is the type species. Bunyavirales | |
|---|---|---|
| Incubación | 1–3 semanas | 1–3 semanas (hasta 6 semanas) |
| Diagnóstico |
|
|
| Manifestaciones clínicas | Pródromo: síntomas similares a los LOS Neisseria de la gripe, aparición repentina de dificultad para respirar con edema Edema Edema is a condition in which excess serous fluid accumulates in the body cavity or interstitial space of connective tissues. Edema is a symptom observed in several medical conditions. It can be categorized into 2 types, namely, peripheral (in the extremities) and internal (in an organ or body cavity). Edema pulmonar de rápida evolución | Fiebre, presión arterial baja/ shock Shock Shock is a life-threatening condition associated with impaired circulation that results in tissue hypoxia. The different types of shock are based on the underlying cause: distributive (↑ cardiac output (CO), ↓ systemic vascular resistance (SVR)), cardiogenic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), hypovolemic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), obstructive (↓ CO), and mixed. Types of Shock, IRA |
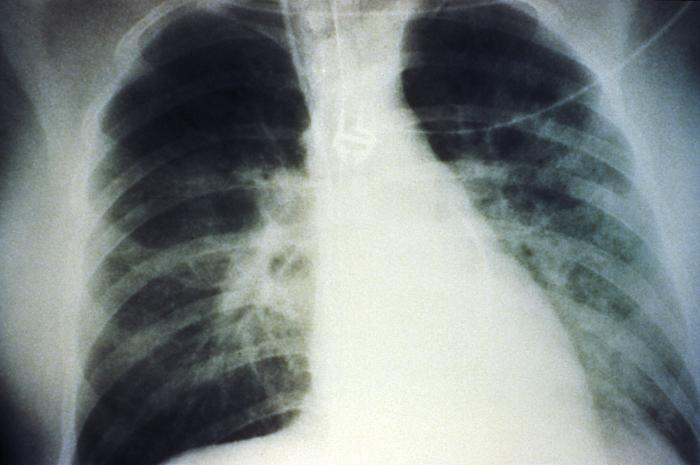
Una radiografía de tórax anteroposterior muestra un derrame pulmonar bilateral en estadio medio debido al síndrome pulmonar por hantavirus:
La evolución radiológica del síndrome pulmonar por hantavirus comienza con cambios mínimos por edema pulmonar intersticial que progresa a edema alveolar con afectación bilateral severa. Los derrames pleurales son frecuentes y, a menudo, lo suficientemente grandes como para ser evidentes radiográficamente.
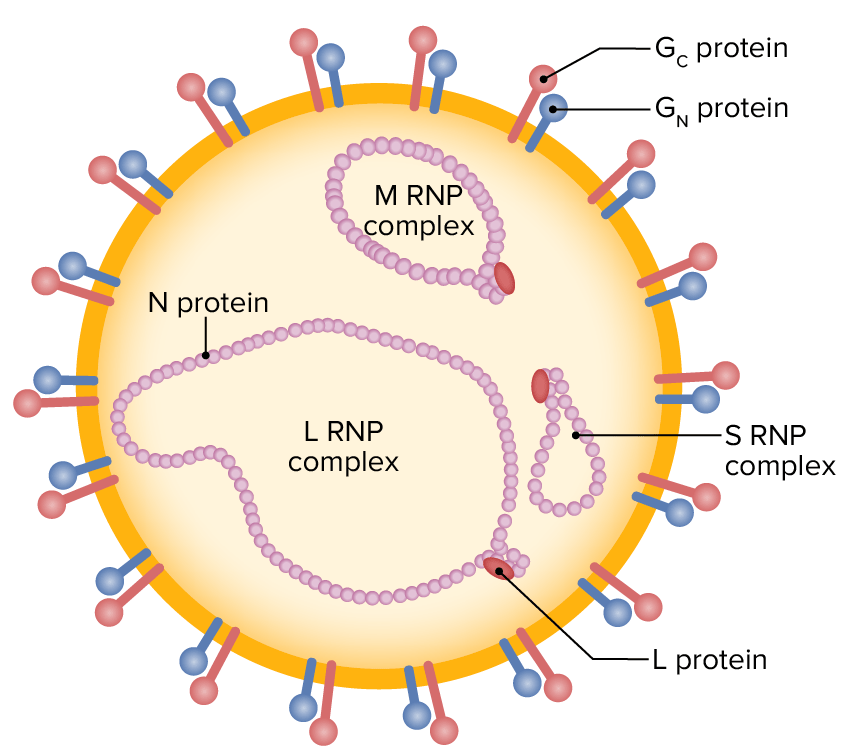
Ilustración esquemática de una partícula de nairovirus (ARN monocatenario envuelto que contiene segmentos L, M y S, rodeado de glicoproteínas externas)
RNP: ribonucleoproteína
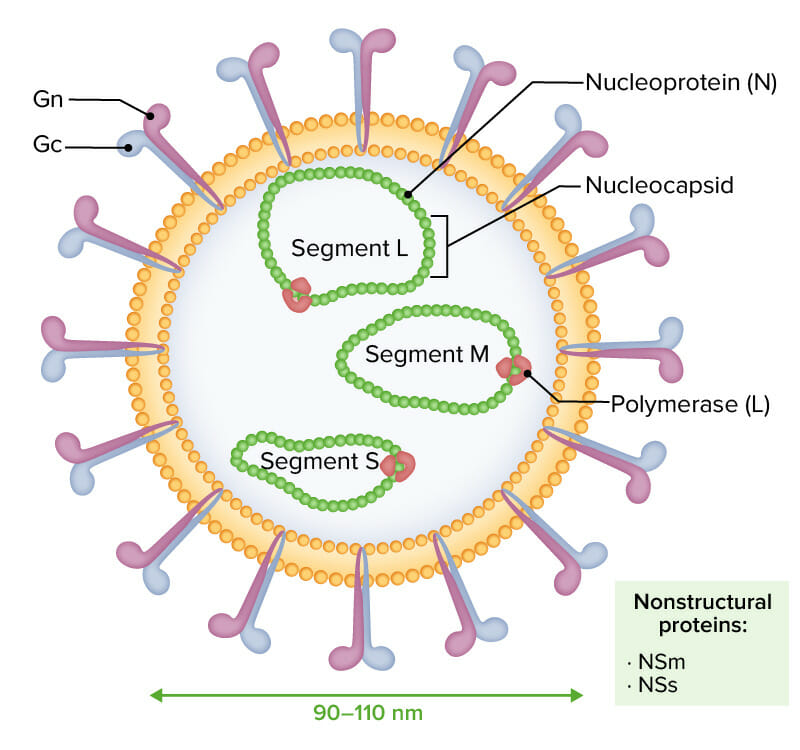
Los viriones envueltos del virus de la fiebre del Valle del Rift se caracterizan por un genoma de ARN negativo o ambisentido compuesto por 3 segmentos monocatenarios (designados L, M y S):
Las 3 moléculas de ARN están encapsuladas por la nucleoproteína (N), dando forma a la nucleocápside e interactuando con la polimerasa viral (L). Las glicoproteínas Gn y Gc se observan externamente. Las proteínas no estructurales NSm y NSs se expresan durante la infección.
Imagen que muestra la morfología ultraestructural exhibida por numerosas partículas del virus La Crosse (LCV)
Imagen: “Image showing the ultrastructural morphology exhibited by numerous La Crosse virus (LCV) particles” por Dr. Erskine Palmer, USCDCP.Licencia: Dominio Público| Organismo | Hantavirus Hantavirus A genus of the family bunyaviridae causing hantavirus infections, first identified during the korean war. Infection is found primarily in rodents and humans. Transmission does not appear to involve arthropods. Hantaan virus is the type species. Bunyavirales | Virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de la fiebre hemorrágica de Crimea-Congo | Virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de la fiebre del valle del Rift | Virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de La Crosse | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Características | Virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de ARN monocatenario, envuelto y de sentido negativo | ||||
| Género | Hantavirus Hantavirus A genus of the family bunyaviridae causing hantavirus infections, first identified during the korean war. Infection is found primarily in rodents and humans. Transmission does not appear to involve arthropods. Hantaan virus is the type species. Bunyavirales u Orthohantavirus | Nairovirus Nairovirus A genus of the family bunyaviridae named after nairobi sheep disease, an acute, hemorrhagic, tick-borne, gastroenteritis affecting sheep and goats. The type species is dugbe virus. Some viruses in this genus are capable of causing severe and fatal disease in humans. Bunyavirales | Phlebovirus Phlebovirus A genus of the family bunyaviridae comprising many viruses, most of which are transmitted by phlebotomus flies and cause phlebotomus fever. The type species is rift valley fever virus. Bunyavirales | Orthobunyvirus | |
| Transmisión | Inhalación y contacto directo con la orina y las heces de ratones infectados | Contacto con garrapatas infectadas (especialmente Hyalomma spp.) |
|
Picadura de mosquito | |
| Presentación Clínica |
|
Fiebre hemorrágica |
|
Encefalitis | |
| Diagnóstico |
|
|
|
|
|
| Tratamiento | De soporte |
|
De soporte | De soporte | |