La bronquitis aguda es una infección común de las vías respiratorias inferiores de los LOS Neisseria bronquios que provoca muchas consultas sanitarias al AL Amyloidosis año. Suele deberse a causas víricas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum pacientes sin enfermedad pulmonar crónica. Los LOS Neisseria síntomas son tos TOS Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) is a broad term used for a spectrum of syndromes related to the general region of the thoracic outlet, which involves the compression or irritation of elements of the brachial plexus, subclavian artery, or subclavian vein. Thoracic Outlet Syndrome, con o sin expectoración, que suele desaparecer en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum 1-3 semanas. La bronquitis aguda se diagnostica clínicamente, aunque una radiografía de tórax ayuda a aclarar el diagnóstico si se sospecha neumonía. El tratamiento es de soporte, y los LOS Neisseria antibióticos no están indicados en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum adultos por lo demás sanos.
Last updated: Jan 23, 2023
La bronquitis aguda es la inflamación aguda de las grandes vías aéreas del tracto respiratorio inferior en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la que el parénquima pulmonar no se ve VE Ventilation: Mechanics of Breathing afectado.
La bronquitis aguda es una enfermedad muy común.
La bronquitis aguda suele ser causada por una infección viral, aunque también pueden existir causas bacterianas.
La bronquitis aguda se caracteriza por la infección e inflamación de las células del tejido que recubre los LOS Neisseria bronquios.
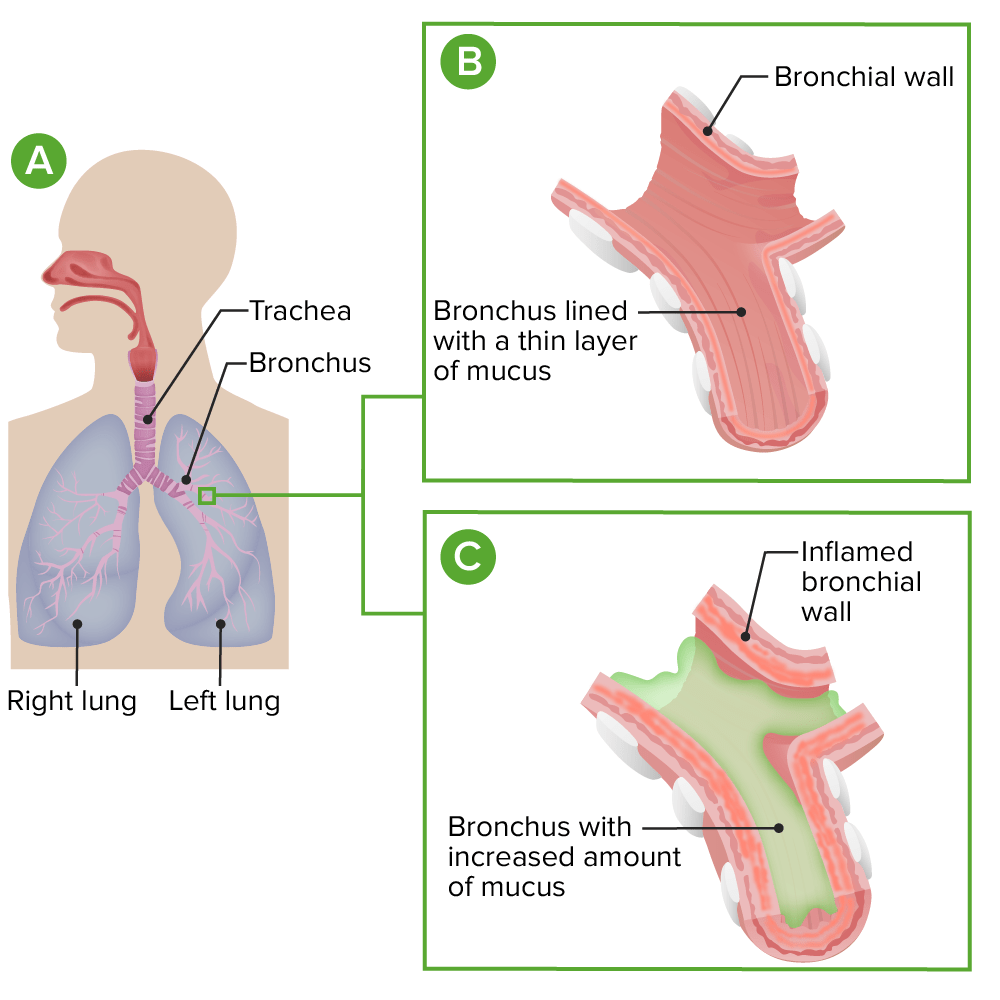
Fisiopatología de la bronquitis aguda
A: anatomía normal
B: vista detallada de un bronquio normal
C: bronquios inflamados con exceso de mucosidad en la bronquitis aguda
La bronquitis aguda suele ser una afección autolimitada con una tos TOS Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) is a broad term used for a spectrum of syndromes related to the general region of the thoracic outlet, which involves the compression or irritation of elements of the brachial plexus, subclavian artery, or subclavian vein. Thoracic Outlet Syndrome prominente que dura 1–3 semanas.
La bronquitis aguda suele ser un diagnóstico clínico que se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria antecedentes y el examen físico, y debe sospecharse en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum pacientes con un inicio agudo de tos TOS Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) is a broad term used for a spectrum of syndromes related to the general region of the thoracic outlet, which involves the compression or irritation of elements of the brachial plexus, subclavian artery, or subclavian vein. Thoracic Outlet Syndrome, que a menudo sigue a una infección de vías respiratorias superiores sin hallazgos de neumonía. Las pruebas adicionales pueden incluir:
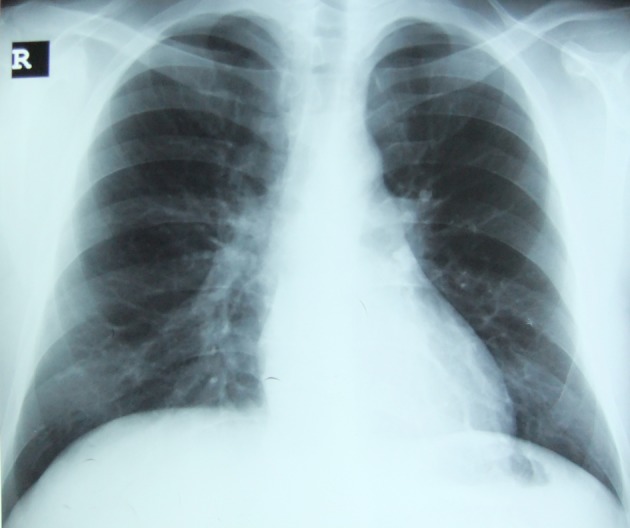
Radiografía de tórax que muestra prominencia broncovascular.
Imagen: “Chest radiography shows bronchovascular prominance on admission” por Sertogullarindan, B. et al. Licencia: CC BY 2.0La bronquitis aguda suele ser una enfermedad autolimitada que normalmente solo requiere cuidados de soporte.
Los LOS Neisseria antibióticos NO se recomiendan específicamente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la bronquitis aguda en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum adultos sin ningún otro problema de salud. Hay pruebas sólidas que apoyan la necesidad de evitar los LOS Neisseria antibióticos, aunque la prescripción excesiva e inadecuada sigue siendo frecuente.