Social structure refers to the organization of individuals in a society or group. It is determined by certain theories of coexistence that allow society to be a stable and functional institution. These theories explain the interactions between groups (macrosociology and microsociology). They also explain the activities that allow for balance within society (functionalism) and the differences that could generate conflicts (conflict theory). Other theories include social constructionism, symbolic interactionism, rational choice theory, and social exchange theory.
Last updated: Aug 13, 2022
Microsociology refers to everyday face-to-face interactions among people on a small scale Scale Dermatologic Examination. Interpretive analysis, which differs from statistical or empirical observations, forms the basis of microsociology.
“The Cabdriver and his Fare,” published in 1959 by Fred Davis, is one of the most famous studies on microsociology. Davis spent six months working as a cabdriver and noted the interactions between himself and his passengers. He observed that the interactions were not only random and fleeting; they also tended to be unique, and repetition was rare. He suggested that most of the interaction time was spent developing trust Trust Confidence in or reliance on a person or thing. Conflict of Interest between the driver and the passenger—whether the driver will take the passenger to their exact destination and whether the passenger will pay and tip appropriately.
Macrosociology refers to interactions on a large scale Scale Dermatologic Examination and at the level of the social structure. It also focuses on smaller groups, such as families, but in relation to the whole society or population in which they are living.
Social equilibrium Equilibrium Occurs when tumor cells survive the initial elimination attempt These cells are not able to progress, being maintained in a state of dormancy by the adaptive immune system. In this phase, tumor immunogenicity is edited, where T cells keep selectively attacking highly immunogenic tumor cells.This attack leaves other cells with less immunogenicity to potentially develop resistance to the immune response. Cancer Immunotherapy is necessary to have a strong society. All aspects of society are related to one another. Different social institutions perform different functions and every institution is interrelated. Slow social change is acceptable, but large changes can destroy social stability. According to this perspective, the more a person fulfills a social role that has more importance to society, the more that role qualifies for a greater reward.
This, in turn, fosters social stratification through the unequal valuation of the various roles within a community (i.e., the notion that certain tasks or roles in society are of more value than others). Individuals that take up higher-value roles or positions tend to be better rewarded than others.
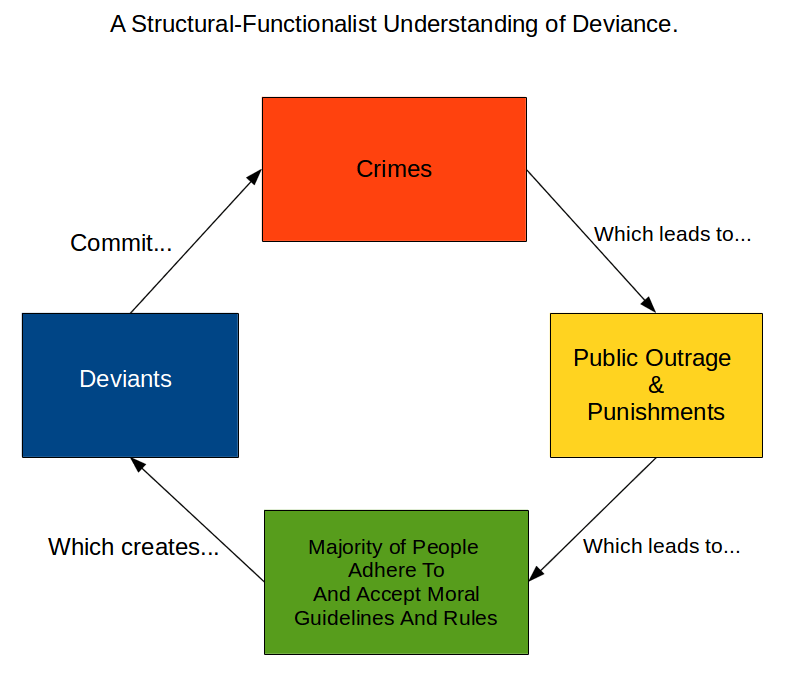
Functionalism emphasizes the importance of deviance in the creation of social stability.
The recognition and punishment of deviance by society creates norms that instruct that society on acceptable and unacceptable behavior. This creates boundaries between populations (“deviant” and “non-deviant”). However, as a stigmatized trait or behavior becomes more mainstream, society may gradually adjust to incorporate said trait.
The conflict theory, proposed by Karl Marx, argues that society, individuals, and groups within social confines interact with one another on the basis not of consensus but of conflict. Marx proposed that society is based on differences in status and power, and conflict arises because of the unequal distribution of resources.
Conflict theorists raise awareness of inequalities through arguments such as asking how a rich society can consist of so many poor members. According to Marx, social division is based on people’s relationship Relationship A connection, association, or involvement between 2 or more parties. Clinician–Patient Relationship to production activities: either an individual owns the factories or works in them. Modern conflict theorists believe that stratification creates class conflict.
Major criticism of conflict theory includes:
Recent advancements in this theory state that:
Furthermore, the theory posits that a society with an unequal distribution of labor oppresses and exploits disadvantaged groups, which in turn suppresses both their creativity and their abilities.
Symbolic interactionism is a theoretical approach in sociology that describes how societies are created and maintained through the repeated actions of individuals. The theory was developed in 1969 by Herbert Blumer, who believed that we must look at society through an individual’s eyes rather than expect them to conform to our understanding of it. He also noted that language shapes what each person thinks and does because it employs symbols (words).
According to Blumer, social interaction comprises four main principles:
Other modifications of this theory have been developed, but most sociologists follow the work of Blumer.
Symbolic interactionism is a microsocial approach that focuses on individual interactions and how people interpret those interactions. It states that people do not merely rely on the roles that society has set for them; rather, they change their roles according to the situation.
For example, shaking hands is considered a symbol of friendship and greeting. This simple act indicates that a person is polite and well-mannered. Now, suppose someone refuses to shake hands; that would be considered rude. However, if that person has a broken right arm Arm The arm, or “upper arm” in common usage, is the region of the upper limb that extends from the shoulder to the elbow joint and connects inferiorly to the forearm through the cubital fossa. It is divided into 2 fascial compartments (anterior and posterior). Arm: Anatomy and cannot shake hands in the normal manner, then one would naturally understand the situation and not consider that person to be rude. Hence, an individual shapes their world according to realities rather than the rules applied to them by society.
Social standing influences how one interacts with others. Individuals are likely to interact with those who share a similar social standing. This can explain how a society becomes divided, as people tend to associate with groups of similar educational backgrounds, interests, and desires for a common lifestyle.
Social constructionism mainly centers on how societies construct their own social rules and norms based on both subjective and objective reality, focusing on the social rather than the biological process. It can be defined as ideas that are (a) created by a society based on interactions and (b) believed by that society as normal, or something natural that may or may not be based on reality. Similarly, the ideas that one society espouses may not be prevalent in other societies; rather, others may reject them.
The rational choice theory states that individuals use their self-interests to make choices that will provide them with the greatest benefit. However, there are many critics of rational choice theory who point out that we do not live in an ideal world people where everyone will make optimal decisions that provide them with the greatest benefit. In reality, people are often moved by emotions and external factors.
Transitivity can be explained by the logical conclusion that if an individual prefers A over B and B over C, then they prefer A over C. This preference can be a strict preference, a weak preference, or an indifference.
The social exchange theory has roots in both economics and psychology. It describes the social change that occurs between individuals due to social negotiations. This can be summarized in four points:
The feminist theory covers aspects of gender Gender Gender Dysphoria inequality and gender Gender Gender Dysphoria differences. This theory highlights problems and social aspects according to the female point of view, which is otherwise overlooked by the dominant male point of view. In the past, women were identified as bodies and as passive individuals, while men were identified as minds and active individuals. As a result, women were not considered equal to men, and in routine work, men were considered superior to women.
Gender Gender Gender Dysphoria differences:
In society, gender Gender Gender Dysphoria roles have already been defined and passed down as such. Therefore, women are assigned different duties than men, and this gender Gender Gender Dysphoria inequality has led to an unequal distribution of labor. Dominant themes explored in this theory include discrimination, sexual objectification, and aesthetics, as well as contemporary art.