Stevens-Johnson Syndrome
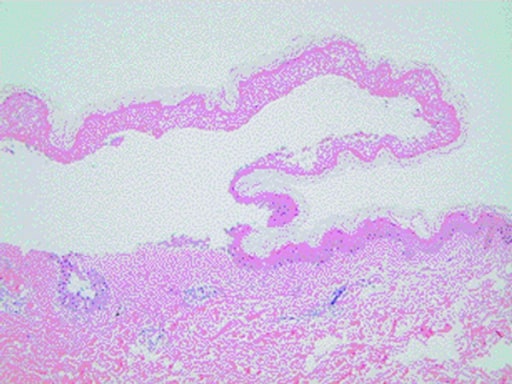
Overview Classification Subtype Involved BSA Stevens-Johnson syndrome 30% of BSA BSA: body surface area SJS: Stevens-Johnson syndrome TEN: toxic epidermal necrolysis Epidemiology Etiology The following table lists the major common medications and infectious causes of SJS/TEN: Types Examples Medications Antiepileptics Lamotrigine, phenobarbital, carbamazepine, phenytoin Sulfa Cotrimoxazole, sulfasalazine Other antibiotics Aminopenicillins, fluoroquinolones, cephalosporins NSAIDs Meloxicam, piroxicam […]
Psoriasis
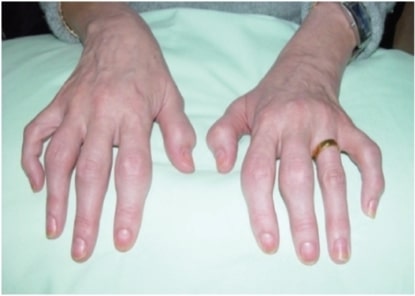
Overview Epidemiology Relatively common in children and adults 0.5%–11% of people worldwide 1%–3% of people in the United States Can be seen at any age, but incidence peaks at the ages of 20–30 and 50–60 (median age is 28 years) ⅓ of patients have a first-degree relative with the disease. Seasonal variation: worse in winter than […]
Erythema Multiforme
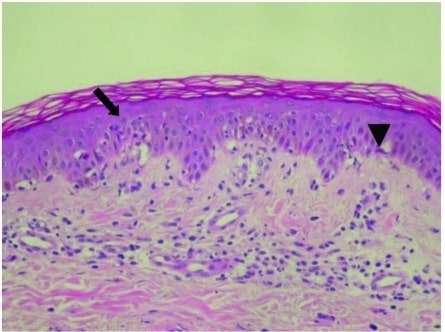
Overview Epidemiology Etiology Erythema multiforme (EM) is a cell-mediated immune reaction (type IV reaction) directed against the antigens of the offending agent, which deposit in the skin. Classification Etiologies Examples Infectious causes (most common, 90% of cases) Bacterial Mycoplasma pneumonia Rickettsia Chlamydophila psittaci Salmonella typhi Mycobacterium tuberculosis Histoplasma capsulatum Viral Herpes simplex virus (HSV) types […]
Seborrheic Dermatitis
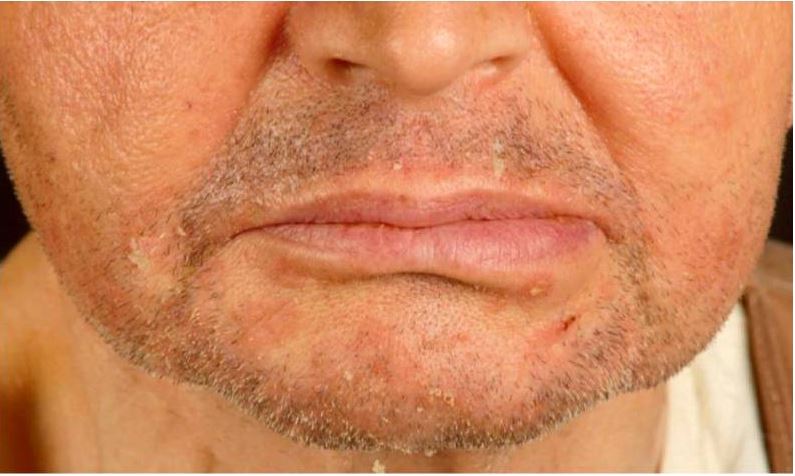
Epidemiology and Etiology Seborrheic dermatitis is a common chronic skin disorder that is characterized by erythematous patches with greasy, yellowish scales that most often appear in areas with prominent sebaceous glands (scalp, face, upper trunk, and anogenital area). Epidemiology Etiology Unclear, but may be affected by the following: Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation General features Seborrheic dermatitis […]
Labial and Genital Herpes
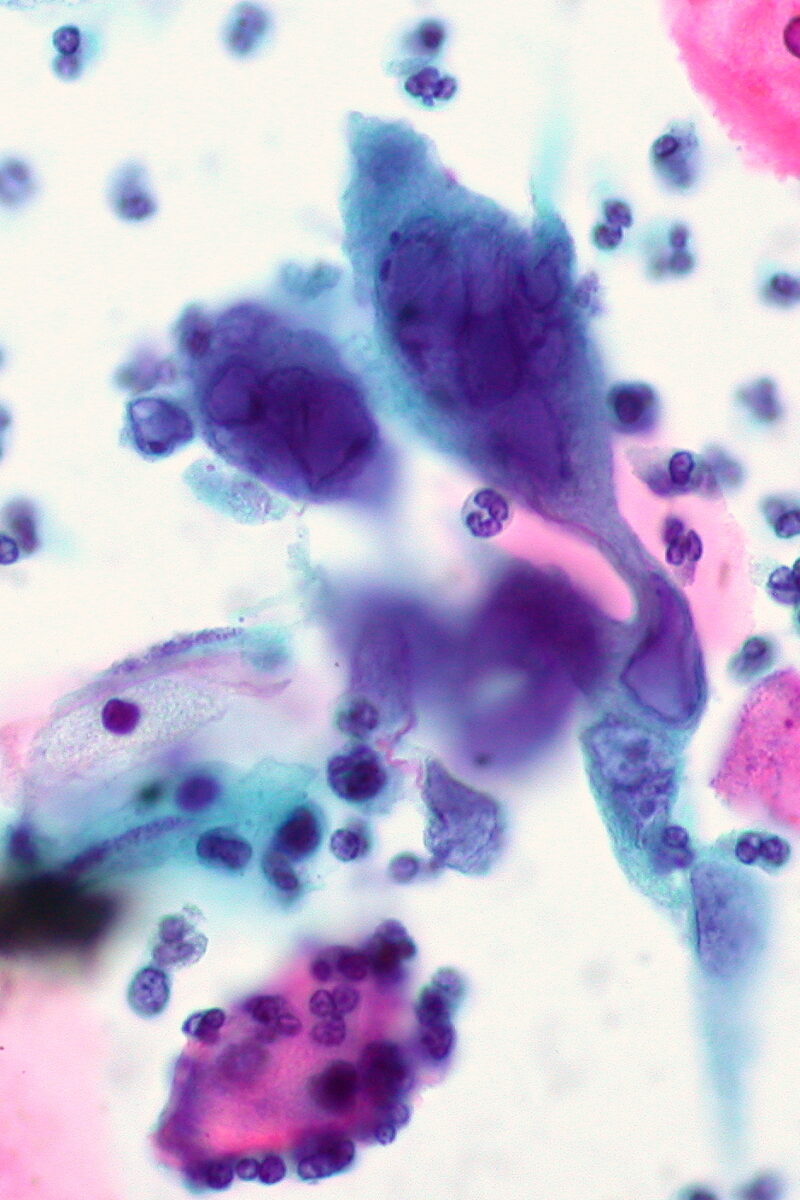
Definition Genital herpes is a mucocutaneous ulcerative disease caused by either herpes simplex virus (HSV) type 1 or 2. HSV-1: HSV-2: Epidemiology Etiology Causative agent: herpes simplex virus Transmission Risk factors Pathophysiology Primary infection Primary infection occurs when the virus travels through tiny breaks or even microscopic abrasions in the skin or mucous membranes in […]
Impetigo
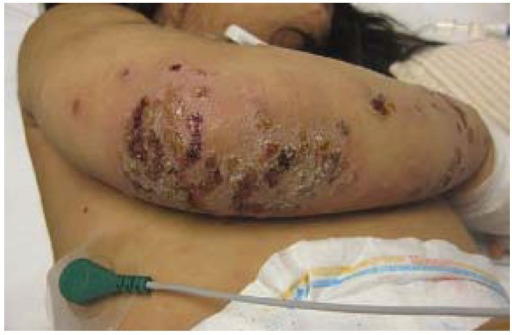
Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology Etiology Clinical Presentation There are 3 variants of impetigo: Non-bullous impetigo Bullous impetigo Ecthyma Diagnosis Diagnosis is usually clinical, based on the natural sequence of the lesions and the presence of honey-colored crusts on pediatric patients aged 2–5 years. Management and Complications Management Management depends on the type and severity of […]
Erythema Nodosum
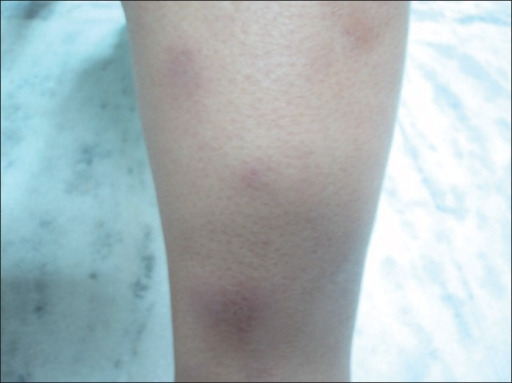
Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology: Etiology: Classification Etiologies Examples Infectious causes Bacterial Streptococcal infections (most common), especially pharyngitis Tuberculosis Mycoplasma pneumonia Viral Infectious mononucleosis Hepatitis B virus Fungal Coccidiomycosis Histoplasmosis Blastomycosis Noninfectious causes Drugs Penicillins Sulfonamide Oral contraceptive pills Malignancy Leukemia Lymphoma Solid malignancies Inflammatory bowel disease Ulcerative colitis Crohn’s disease Miscellaneous Sarcoidosis: Lofgren’s syndrome Pregnancy […]