Dermatologic Examination
Terminology Primary and secondary skin lesions Primary skin lesions occur as a direct result of a pathologic process, while secondary skin lesions are those that result from manipulation of the skin. Table: Primary skin lesions Primary skin lesion Description Macule Flat, nonpalpable skin lesion ≤ 1 cm in size Differs in color from the surrounding […]
Hidradenitis Suppurativa
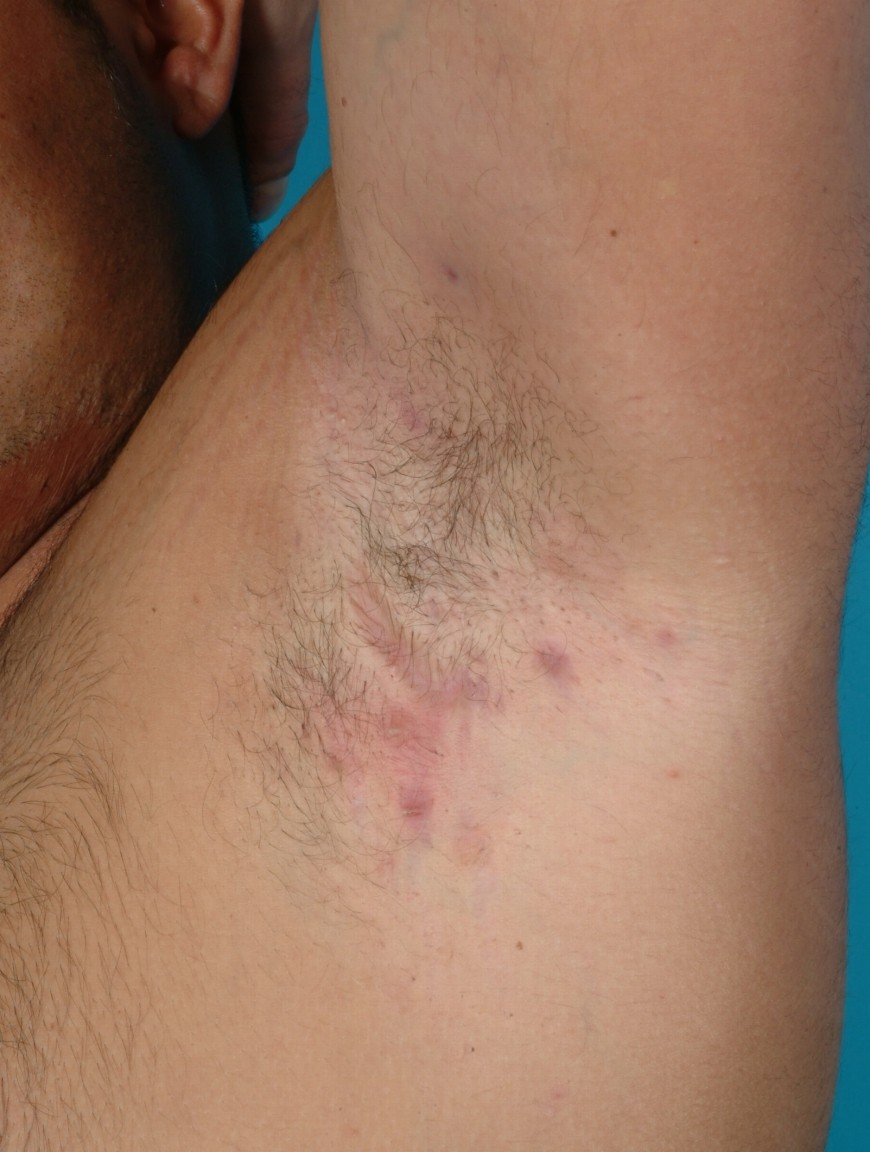
Overview Definition Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), also referred to as acne inversa, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition due to occlusion and rupture of hair follicles. Epidemiology Etiology Hidradenitis suppurativa develops due to blockage of hair follicles in the skin. Risk factors include: Pathophysiology Normal physiology The skin is mainly composed of 3 layers: Pathophysiology of […]
Dermatophytes/Tinea Infections
Overview General characteristics of dermatophytes Classification of tinea infections Tinea infections are classified and named by the body region affected. Pathogenesis Reservoir Transmission Host risk factors Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation Signs and symptoms are similar between the tinea infections, with some minor differences depending on the body region affected. Lesions tend to be well-demarcated, annular, peripheral […]
Malassezia Fungi
General Characteristics and Epidemiology General features of Malassezia Clinically relevant species There are a number of recognized species: Associated diseases Epidemiology Tinea versicolor: Malassezia folliculitis: Pathogenesis Reservoir Malassezia are part of the normal skin flora in humans and animals. Host risk factors Predisposing risk factors for disease include: Pathophysiology Tinea versicolor: Seborrheic dermatitis: Malassezia folliculitis: […]
Seborrheic Keratosis
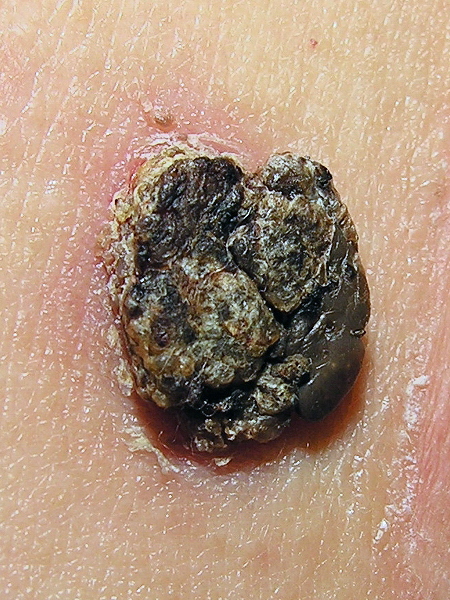
Overview Definition Seborrheic keratosis (SK) is a benign skin tumor consisting of proliferating immature keratinocytes. Epidemiology Etiology Pathophysiology and Clinical Presentation Pathogenesis Morphology Histology Clinical presentation Diagnosis and Management Diagnosis Physical exam: Dermoscopy: Biopsy: Management Differential Diagnosis References
Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema)
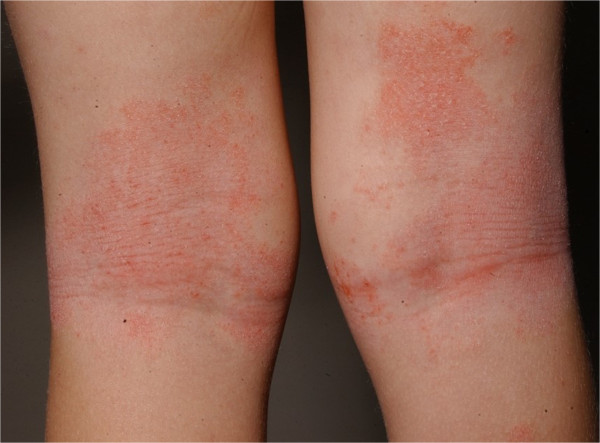
Overview Definition Atopic dermatitis (also known as eczema) is a disorder of altered skin barrier integrity and immune dysregulation that presents as a chronic relapsing inflammatory skin disease. Epidemiology Etiology Pathophysiology and Clinical Presentation Pathophysiology Clinical presentation Diagnosis History Physical exam (skin) Laboratory studies Management Supportive/prophylactic measures Patient education: Elimination of exacerbating factors: Skin hydration […]
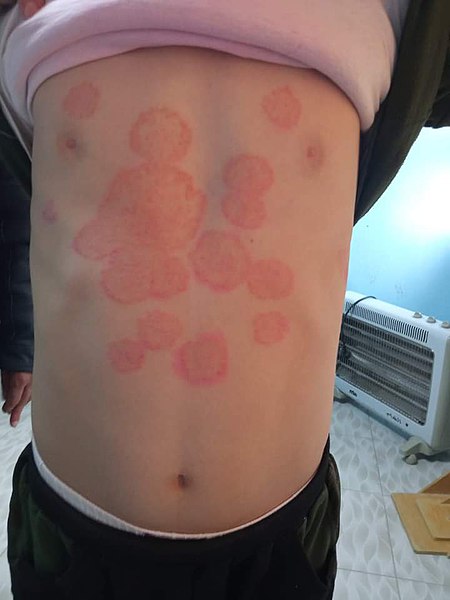
Urticaria (Hives)
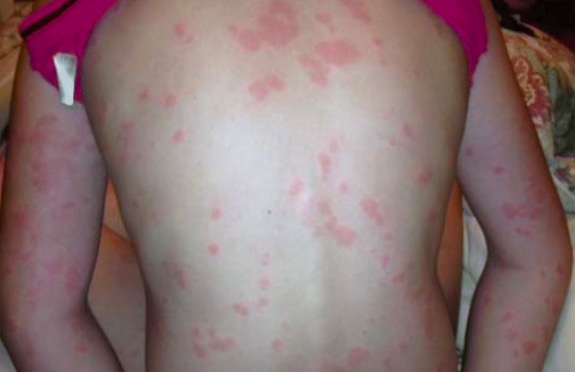
Overview Definition Urticaria is a vascular reaction of the skin noted as a transient appearance of slightly elevated plaques (wheals) that are redder or paler than adjacent skin and often accompanied by significant itching. Epidemiology Etiology IgE-mediated urticarias (type I hypersensitivity, release of histamine from mast cells) are often due to exposure to certain allergens: […]
Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome (SSSS)
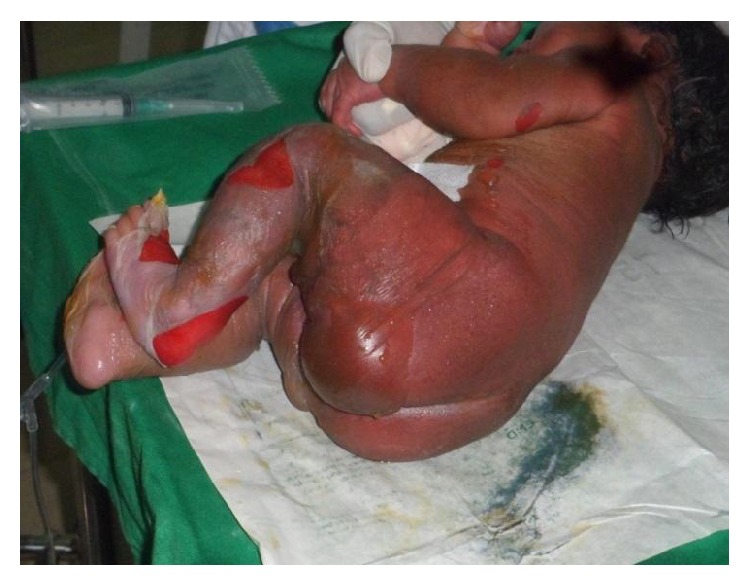
Overview Epidemiology Etiology Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation Diagnosis and Management Diagnosis Management Management of SSSS includes aggressive treatment of primary infection and supportive care. Differential Diagnosis Comparison of common childhood rashes Number Other names for the disease Etiology Description 1st disease Measles Rubeola 14-day measles Morbilli Measles morbillivirus Cough, coryza, conjunctivitis Koplik’s spots (blue-white spots with […]
Acne Vulgaris
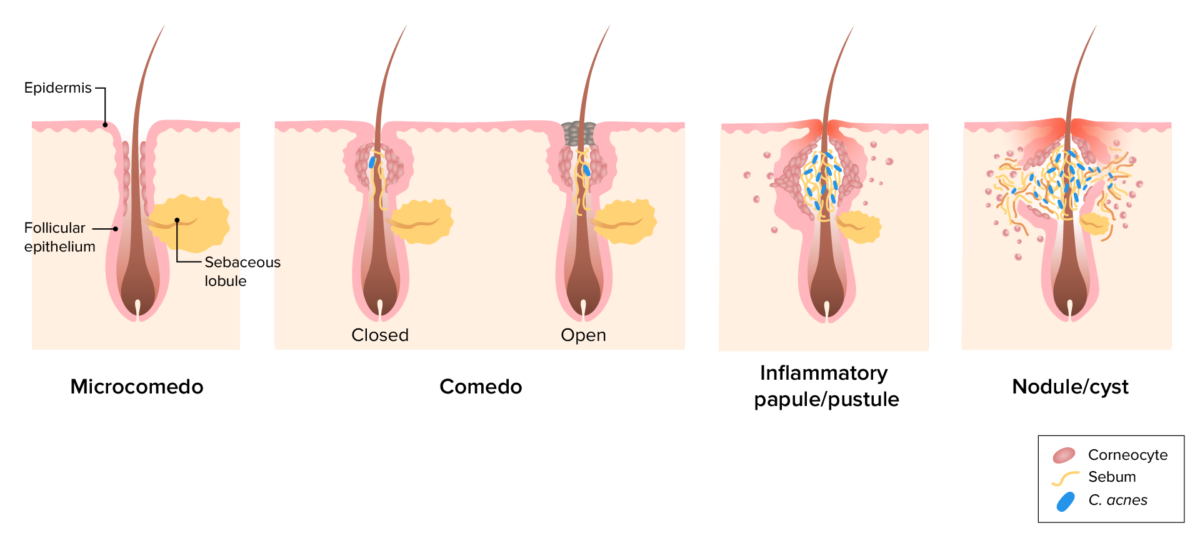
Overview Epidemiology Etiology Pathophysiology Acne vulgaris is a disorder of the pilosebaceous unit (which includes the hair follicle and sebaceous gland) and is characterized by 4 pathogenic factors: Clinical Presentation Classification and presentation of acne lesions Noninflammatory acne (comedones): Inflammatory acne: Common locations Sequelae Severe variants The following variants are rare forms of acne that […]
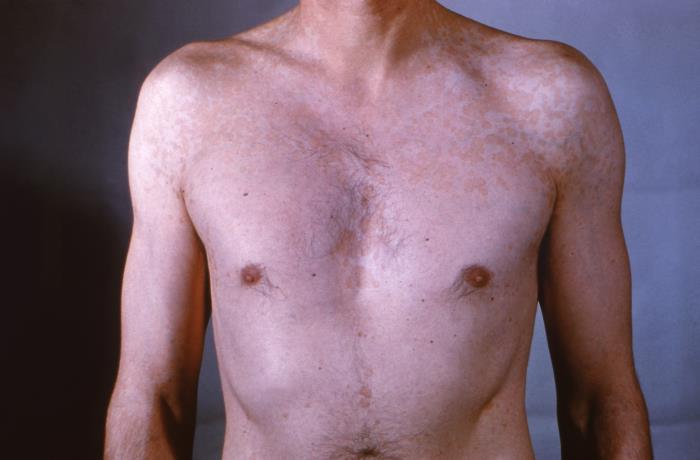
Vitiligo
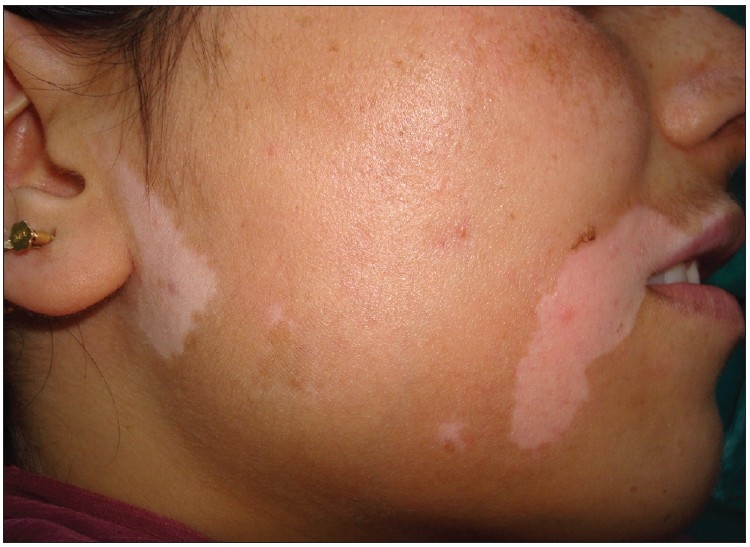
Definition and Epidemiology Definition Vitiligo is a progressive skin condition in which there is destruction of melanocytes resulting in the loss of skin pigmentation. Epidemiology Etiology and Pathophysiology Etiology The cause of vitiligo is unknown, but is postulated to be a result of multiple factors. Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation and Diagnosis Clinical presentation Vitiligo results in […]