Class 2 Antiarrhythmic Drugs (Beta Blockers)
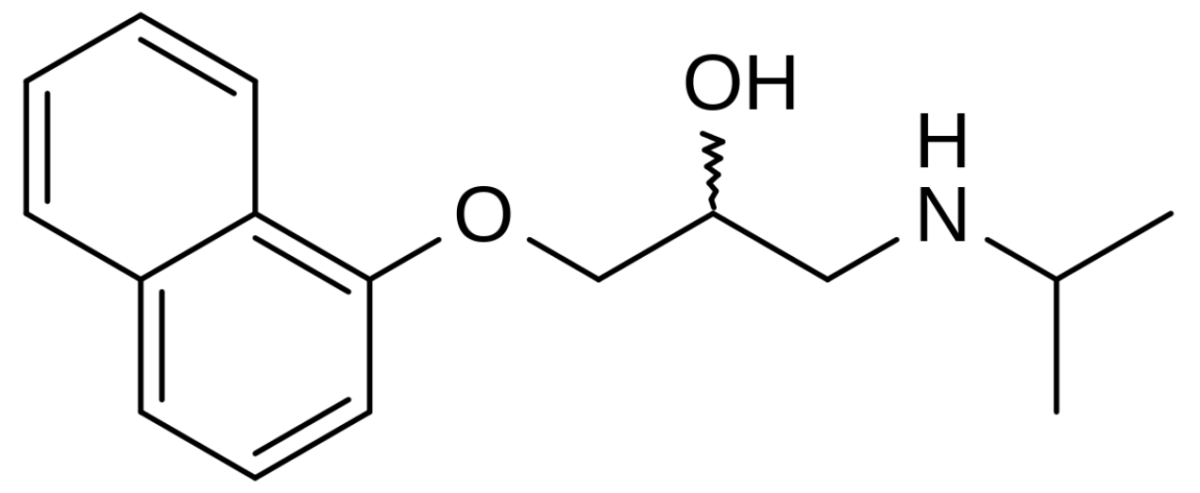
Chemistry and Pharmacodynamics Definition Class 2 antiarrhythmics include beta-blockers, which competitively inhibit epinephrine and norepinephrine from binding to the beta-adrenergic receptors on vascular and cardiac cells. Chemical structure Mechanism of action Physiologic effects Adrenergic receptor types and their properties Table: Adrenergic receptor types and their properties Receptor location Response to stimulus Response to blockade B1 […]
Movement Disorder Drugs

Overview Definition Movement disorders are a group of neurologic conditions that cause excessive voluntary or involuntary movements; these disorders can also cause reduced or slow movements. Classification Essential Tremor Definition Essential tremor, also called familial tremor, causes a benign postural tremor of the hands that can cause significant distress for individuals who are affected by […]
Antivirals for Hepatitis C
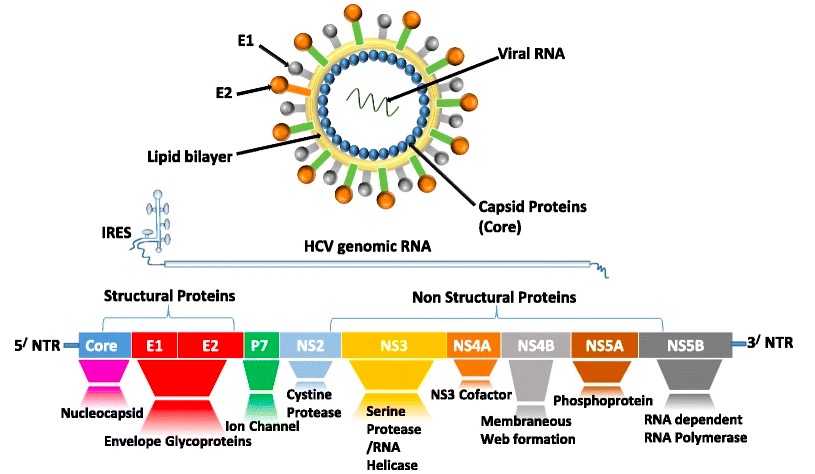
Overview Hepatitis C virus (HCV) Viral proteins Hepatitis C virus RNA encodes: Treatment regimens IFN-α Chemistry Interferons are a type of signaling protein belonging to the cytokines family. Mechanism of action IFN-α works through several mechanisms: Pharmacokinetics Indications Adverse effects Contraindications Drug interactions Ribavirin Chemistry Mechanism of action Pharmacokinetics Indications Adverse effects Contraindications Drug interactions […]
Local Anesthetics
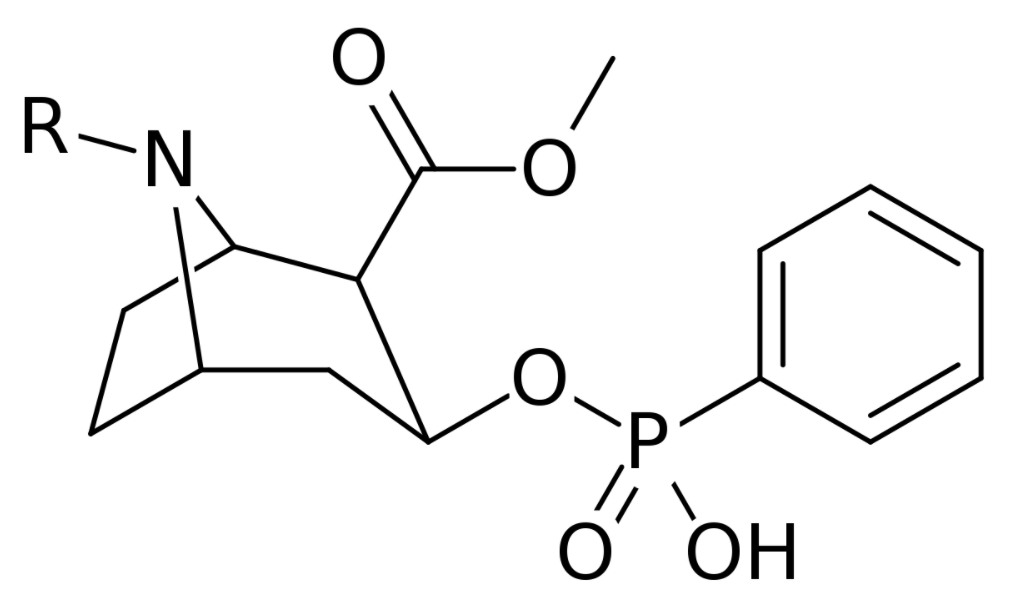
Chemistry and Pharmacodynamics Chemical structure Mechanism of action Physiologic effects Pharmacokinetics Absorption Distribution Metabolism Excretion Pharmacokinetics of commonly used local anesthetics Table: Pharmacokinetics of commonly used local anesthetics Agent Half-life (adults) Onset of action Metabolism Excretion Cocaine 30 minutes to 1.5 hours 15–30 seconds Hydrolysis: spontaneous and by plasma pseudocholinesterase; hepatic Renal Benzocaine Short (exact […]
Antidiarrheal Drugs
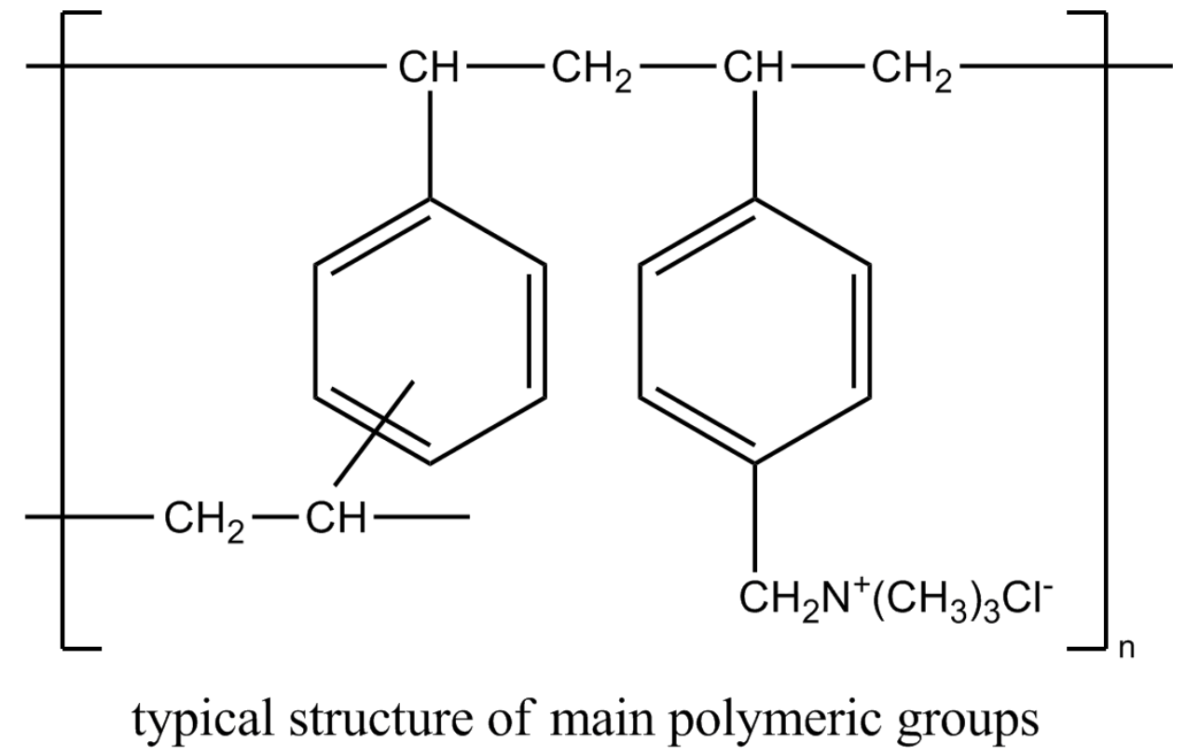
Overview Diarrhea Diarrhea is the passage of ≥ 3 loose or liquid stools within 24 hours. Classification: General management: Drug classes Antidiarrheal properties These drug classes may improve symptoms of diarrhea via: Opioid Agonists Medications within this class The opioid agonists utilized for their antidiarrheal activity are: Mechanism of action Pharmacokinetics Loperamide: Diphenoxylate: Indications Adverse […]
Thyroid Replacement Therapy

Overview Pathophysiology of hypothyroidism Medical condition defined by deficiency of thyroid hormones: Thyroxine (T4) Triiodothyronine (T3) These hormones play an integral role in various functions: Metabolism Growth and development Catecholamine function Pituitary hormone synthesis regulation (feedback loop) Clinically, a deficiency in these hormones can lead to abnormal changes in: Energy levels Weight Thermoregulation HR Bowel […]
Antithyroid Drugs

Overview Pathophysiology of hyperthyroidism Antithyroid medications Thionamides Pharmacodynamics Pharmacokinetics Methimazole: Propylthiouracil: Indications Adverse effects Thionamides are associated with a low incidence of severe side effects, but these may include: Precautions Considerations for thionamide management in pregnant individuals: Drug interactions Iodides Pharmacodynamics Indications Iodine can be used for: Adverse effects Contraindications Drug interactions Radioactive Iodine Pharmacodynamics […]
Gastric Acid Drugs
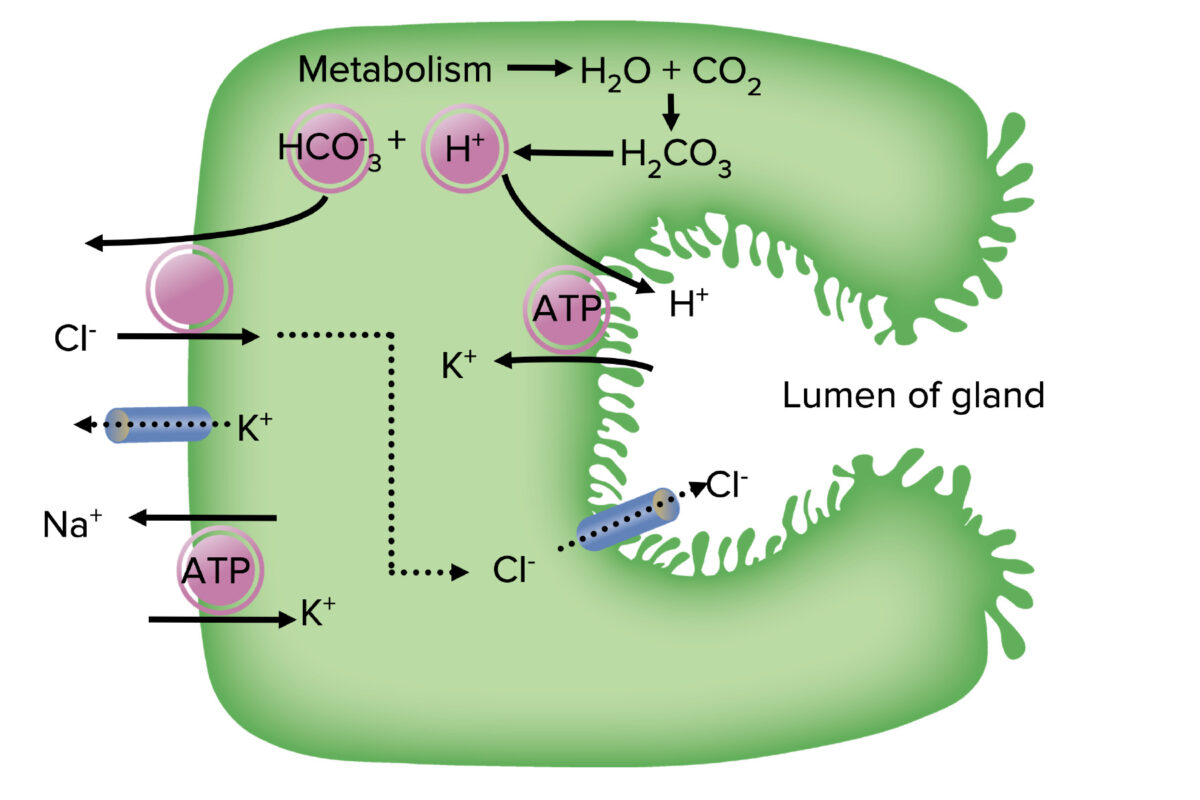
Overview Physiology of acid secretion Parietal cells are located in the body of the stomach and secrete hydrochloric acid (HCl) into the lumen. Receptors and regulation Acid production is stimulated by: Drug classes Common medication classes used to control gastric acid secretion include: PPIs Definition Proton pump inhibitors are a group of drugs irreversibly inhibiting […]
Cardiac Glycosides
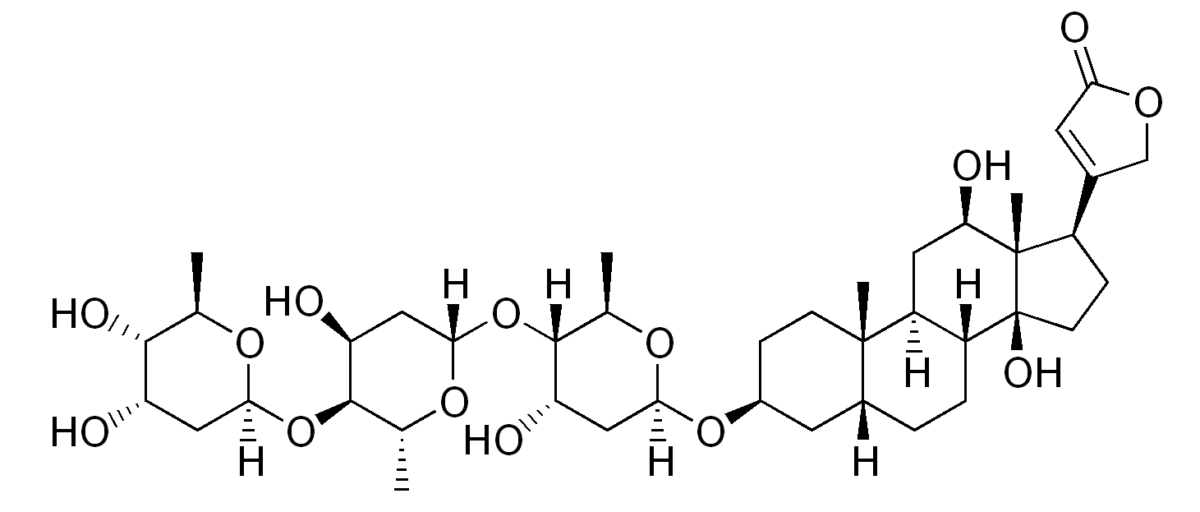
Chemistry and Pharmacodynamics Chemical structure Digoxin is the prototype drug of the cardiac glycoside class and the only drug in the class used for medicinal purposes. Mechanism of action Physiologic effects Pharmacokinetics Absorption Distribution Metabolism and excretion Indications Heart failure Arrhythmia Digoxin is indicated for rate control when other therapies are ineffective or contraindicated: Adverse […]
Opioid Analgesics
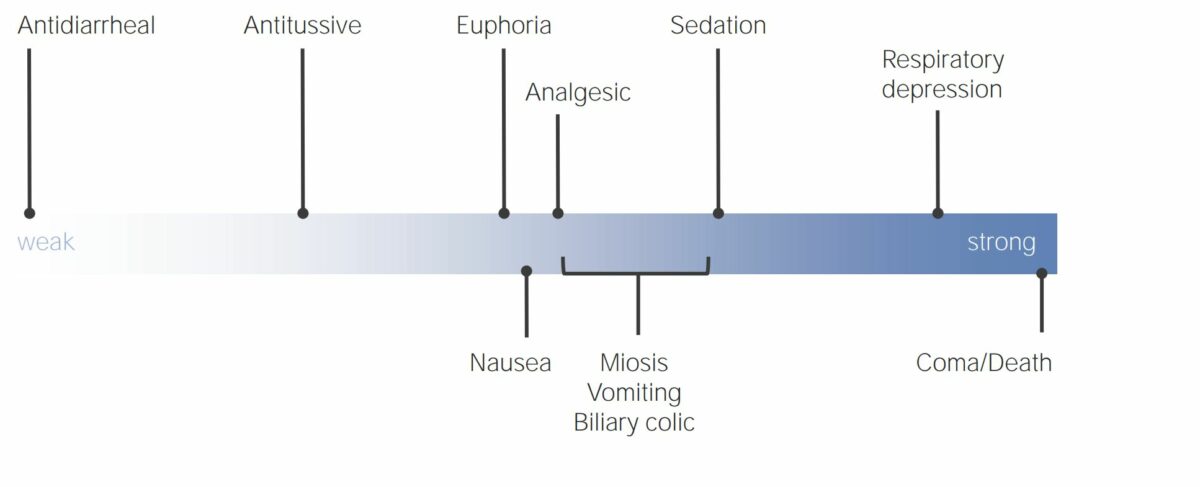
Pharmacodynamics Definitions Opioids are a class of natural or synthetic drugs that act on opioid receptors to provide analgesia and CNS effects. Mechanism of action Opioid receptors The following table summarizes and compares the effects of opioid receptors: Table: Opioid receptor subtypes Mu (μ) receptor Kappa (κ) receptor Delta (δ) receptor Effect on analgesia Spinal […]