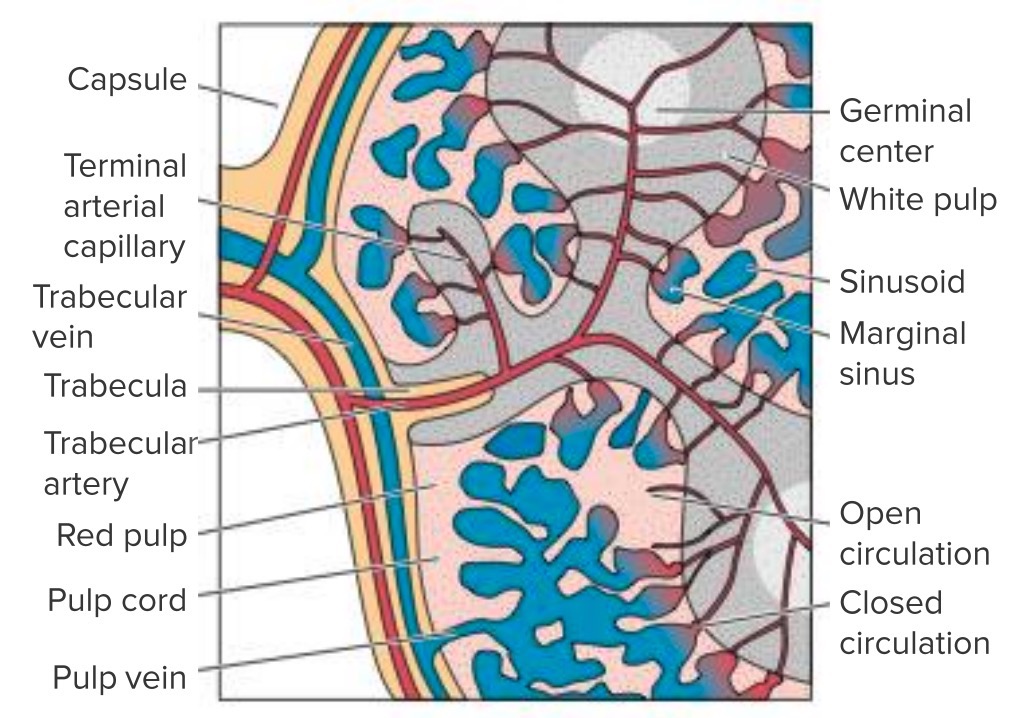
Splenomegaly
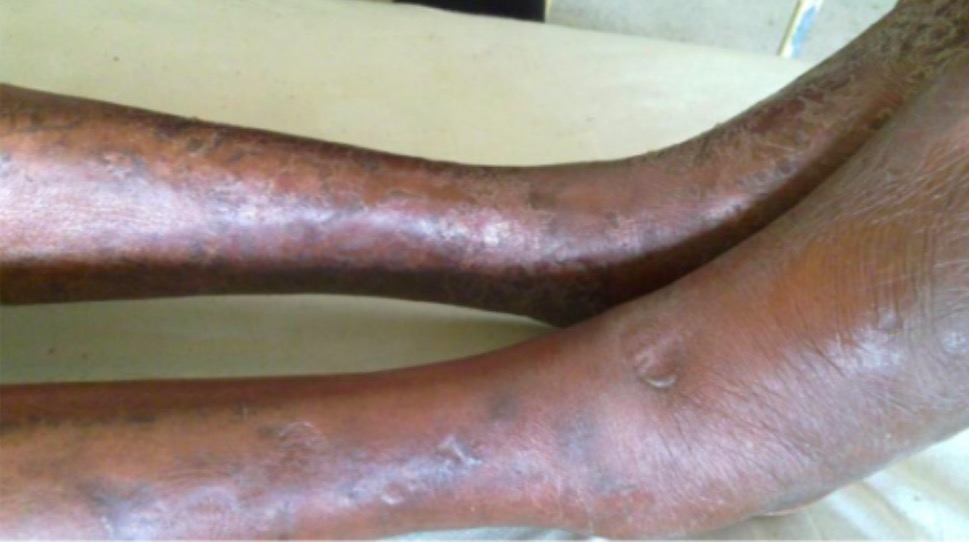
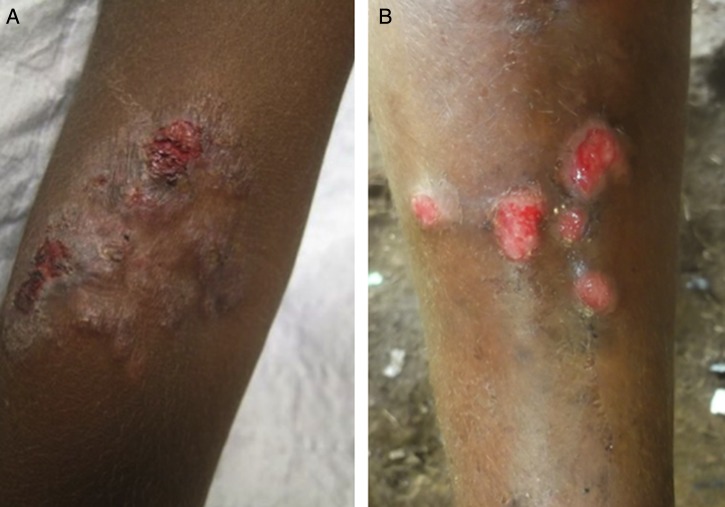
Yaws, Bejel, and Pinta
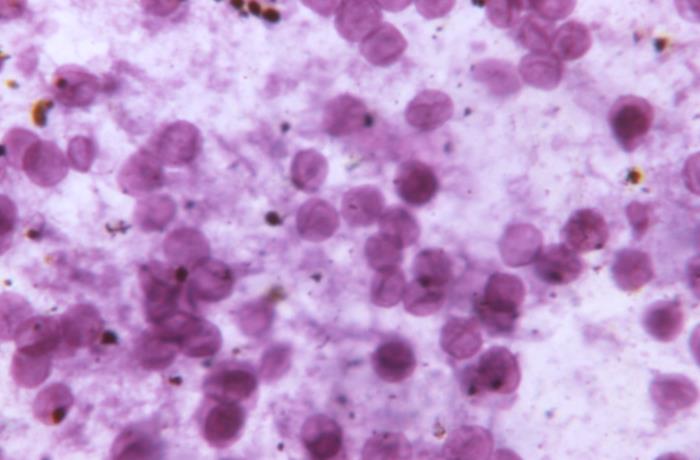
Pneumocystis jirovecii/Pneumocystis Pneumonia (PCP)
Dermatophytes/Tinea Infections
Minimal Change Disease
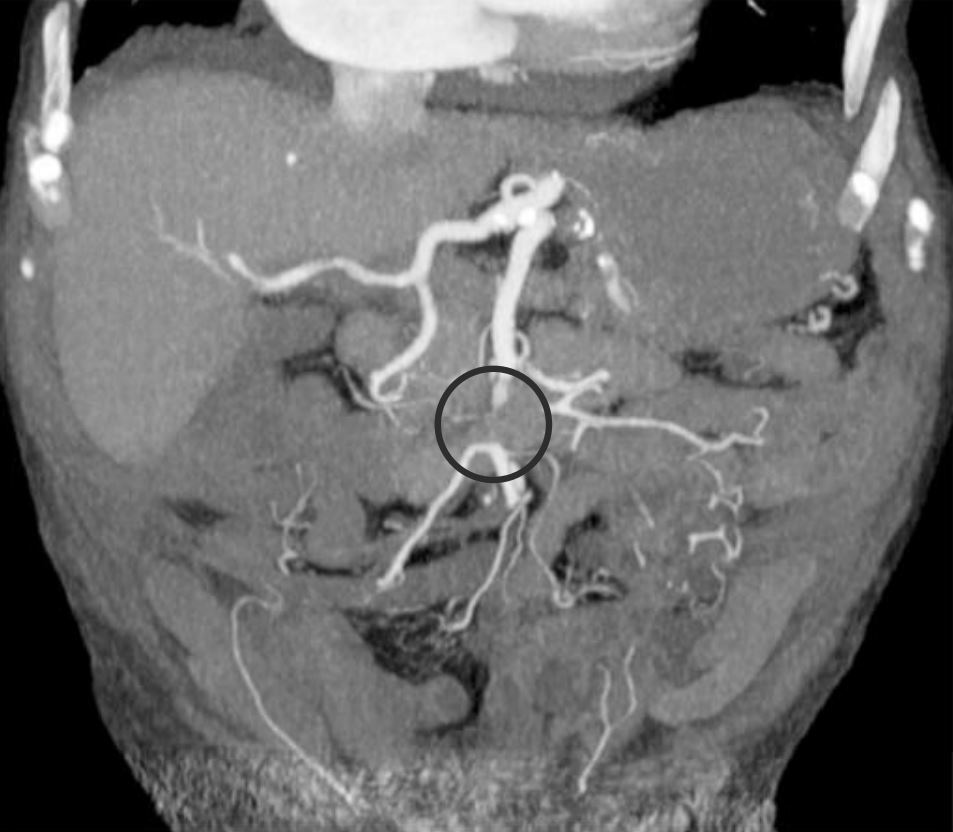
Intestinal Ischemia
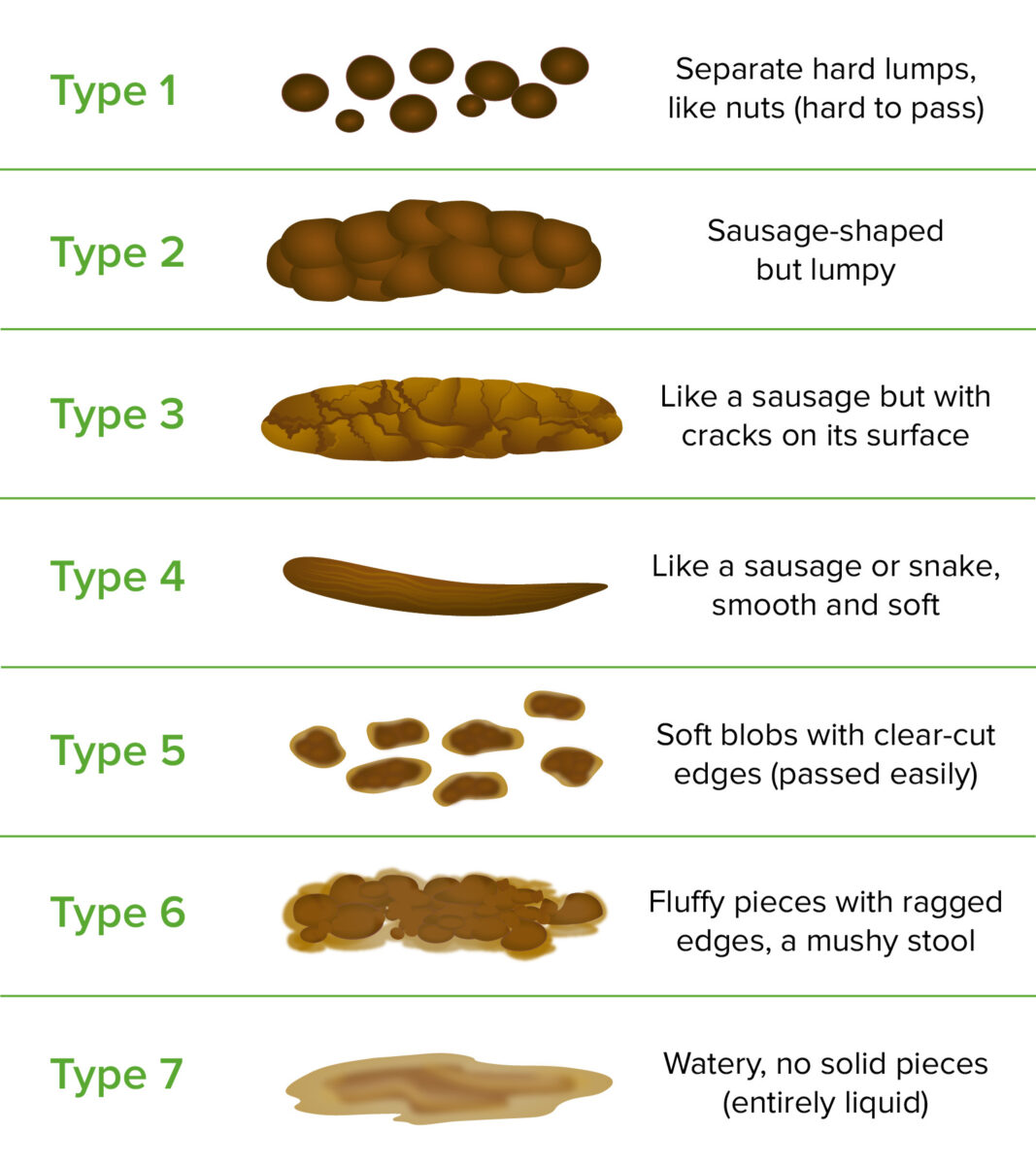
Constipation

Hypocalcemia

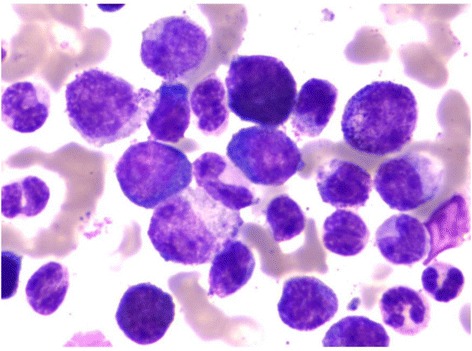
Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
Hypercoagulable States