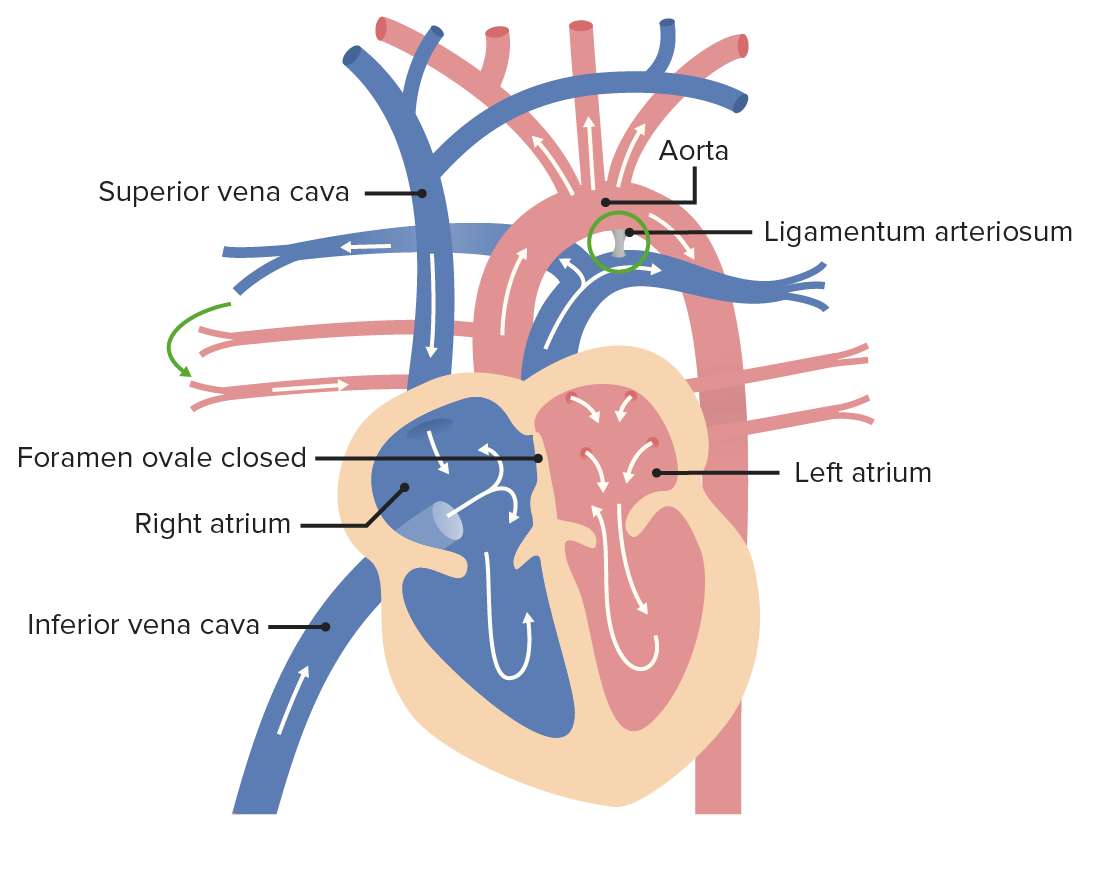
Prenatal and Postnatal Physiology of the Neonate
Overview Table: Overview of embryologic milestones during the prenatal period Gestational age in weeks Characteristics Weeks 3–4 Amniotic sac develops Placenta develops Weeks 5–8 Formation of the neural tube GI tract begins to develop. Weeks 9–12 1st breathing movements occur Hematopoiesis shifts from liver to spleen Head remains disproportionately large Extremities are fully formed All […]
Development of the Limbs
Limb Formation Mnemonic: To quickly recall what happens during the 4th week, remember: 4 weeks → 4 limbs, 4 heart chambers Rotation of the Limbs Formation of Musculature Overview Muscle comes from myotome: ventrolateral cells originating from somites located on either side of neural tube that migrate to form muscles. As myotomes migrate, they form: […]
Development of the Abdominal Organs
Review of Early Embryologic Development Blastocyst and bilaminar disc The morula (ball of cells) undergoes a process called blastulation, in which a cavity begins to form. The cells then begin differentiating into outer and inner cell masses. Trilaminar disc The bilaminar disk undergoes a process called gastrulation to form the trilaminar disc. There are 3 […]
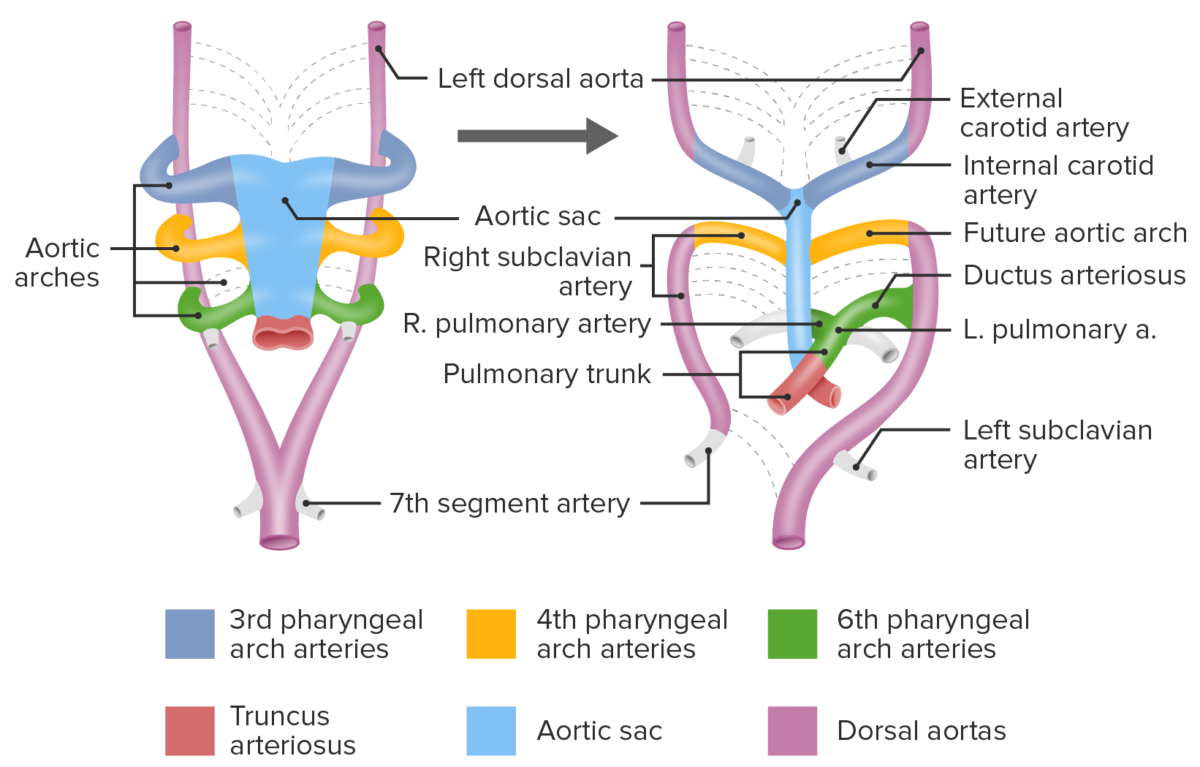
Branchial Apparatus and Aortic Arches
Review of Early Embryologic Development Blastocyst and bilaminar disc The morula (ball of cells) undergoes a process called blastulation, in which a cavity begins to form. The cells then begin differentiating into outer and inner cell masses. Trilaminar disc The bilaminar disk undergoes a process called gastrulation to form the trilaminar disc. Cells from the […]
Gastrulation and Neurulation
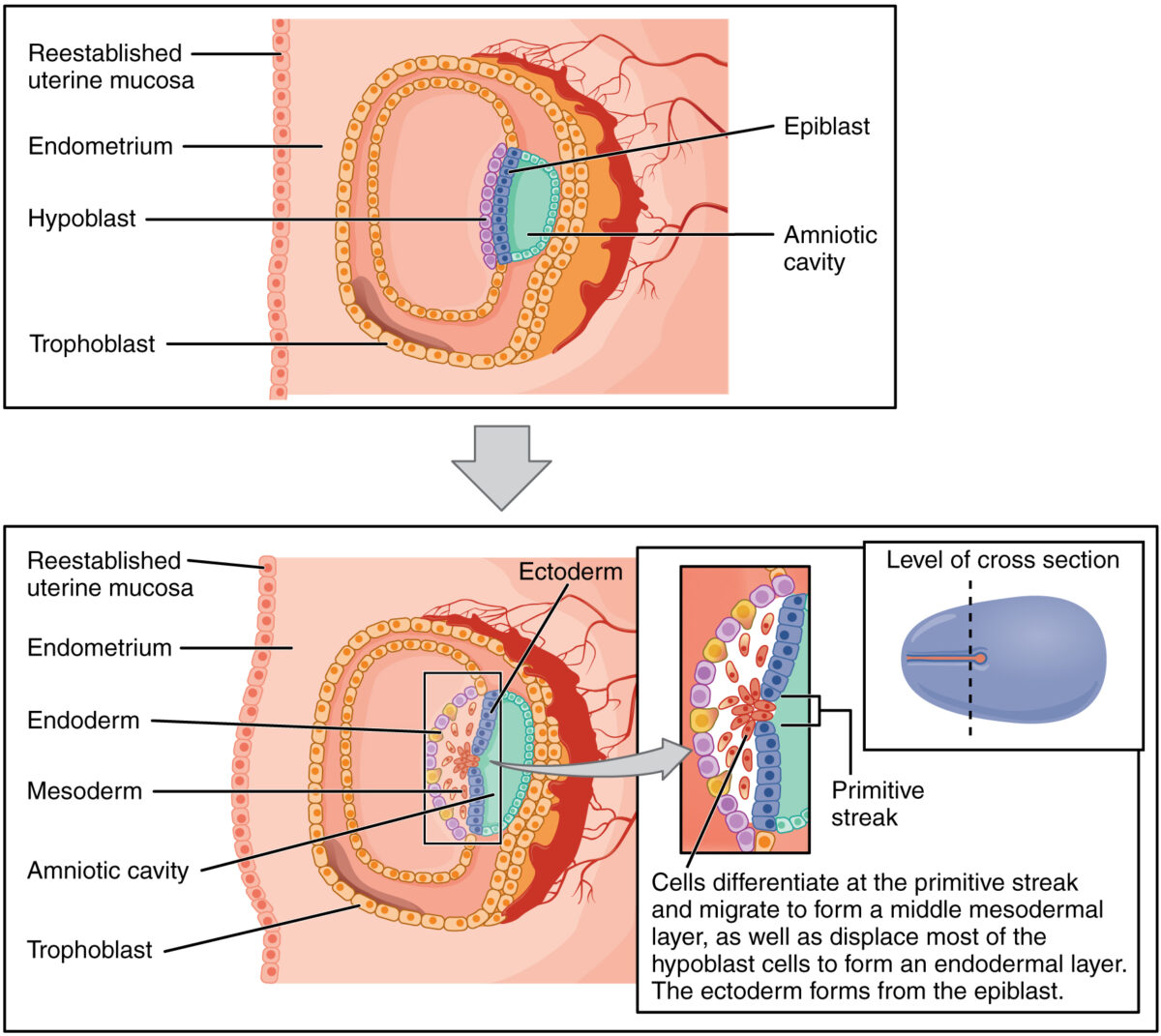
Review of Early Development Morula, blastocyst, and bilaminar disc Implantation Gastrulation Overview of gastrulation Gastrulation is the process by which the bilaminar disk develops into the trilaminar disc. Primitive streak and the primitive groove Epiblast migration The trilaminar disc Formation of the chorionic cavity Formation of the notochord Neurulation Neurulation is the process by which […]
Teratogenic Birth Defects
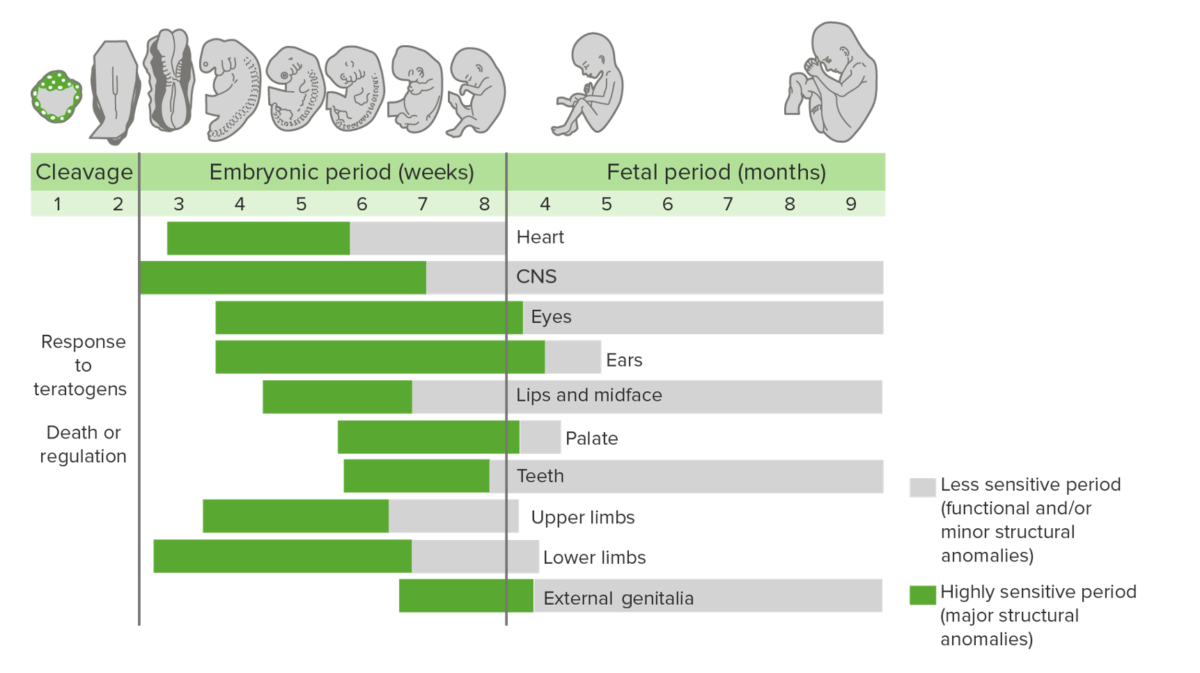
Epidemiology Classification Primary malformations: Secondary malformations: Double malformations or “Siamese twins:” Two fetuses that have grown together due to incomplete intertwining of the embryoblast in the blastocyst stage (13th day): Terminology Pathophysiology The development of malformations varies throughout different stages of embryological/fetal development and is referred to as phase-dependent vulnerability. Maternal Systemic Illnesses Substance Use […]
Development of the Urogenital System
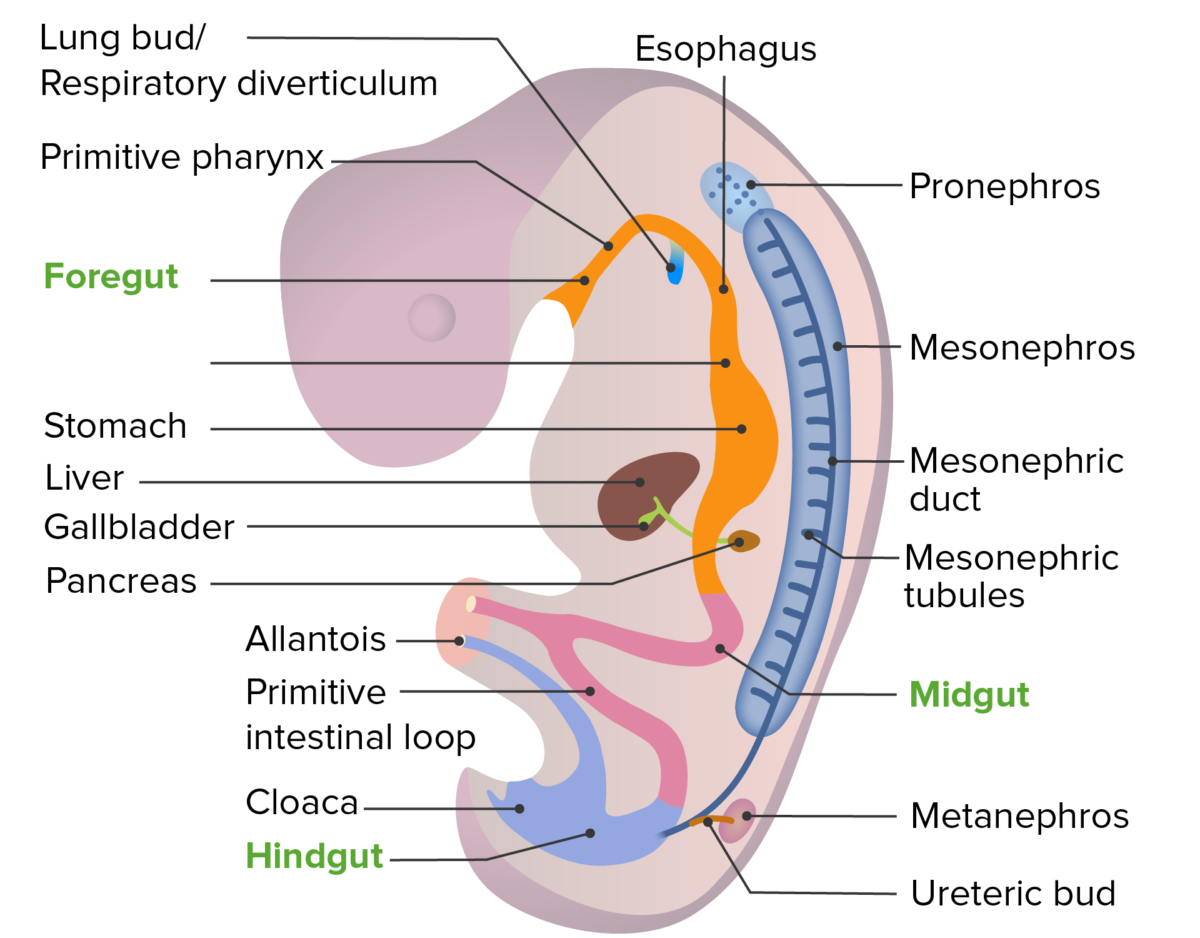
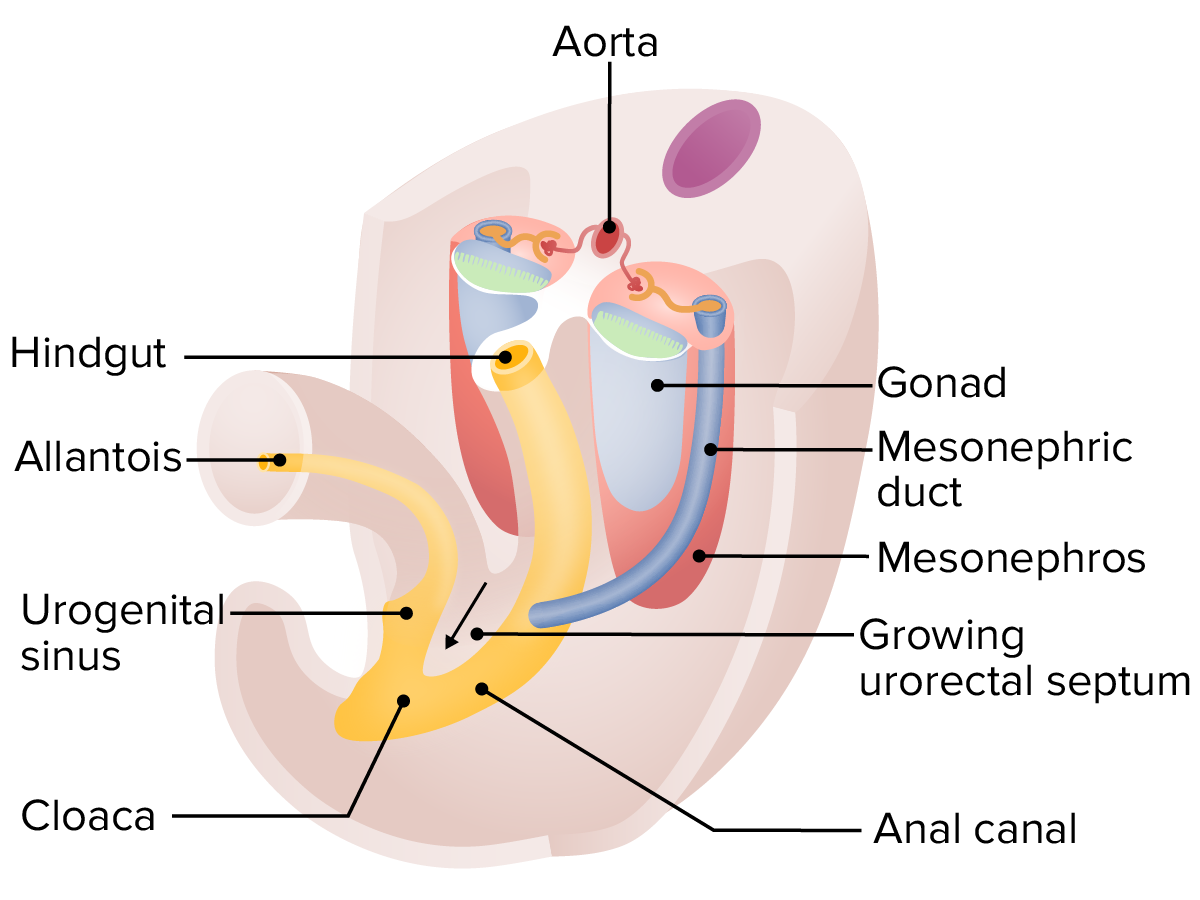
Early Embryonic Development Bilaminar disc Develops around week 2 of embryonic life: Trilaminar disc Layers: Folding Development of the Urinary System The kidney develops from embryonic mesoderm in 3 successive forms from the nephrogenic cords as the cords elongate in a cranial-to-caudal direction. Pronephros Mesonephros Metanephros The permanent kidney is formed from the metanephros. Position […]
Embryoblast and Trophoblast Development
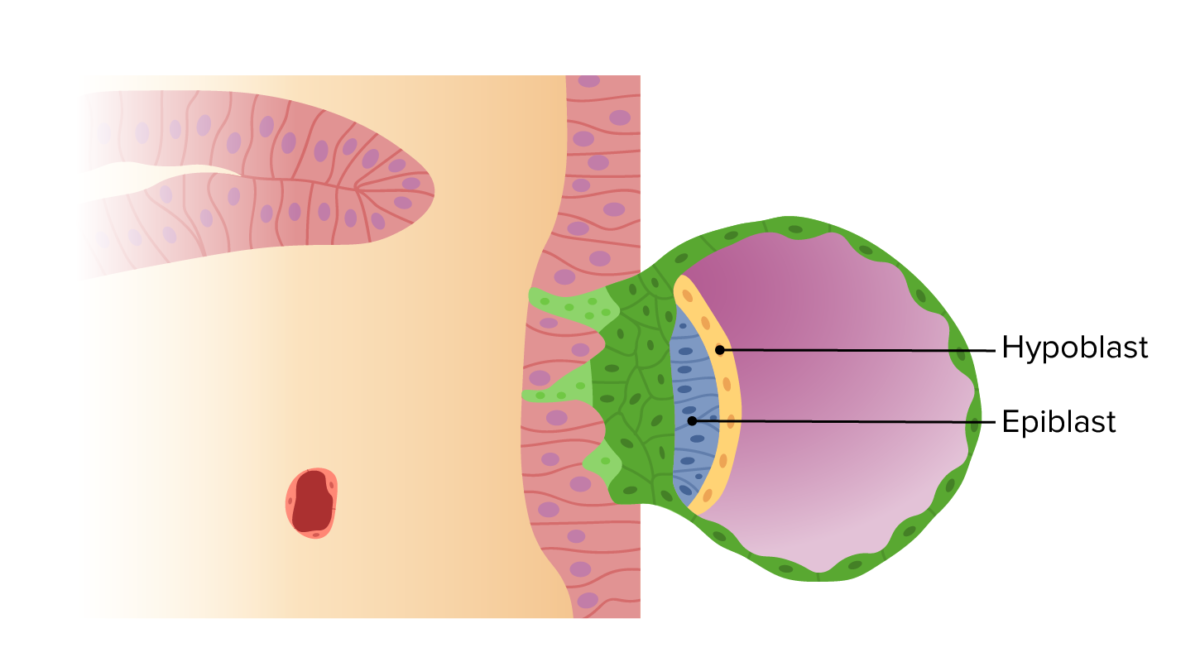
Formation of the Blastocyst Implantation of the Blastocyst The trophoblast is primarily responsible for implantation of the blastocyst. Formation of Bilaminar Disk and Amniotic Cavity Embryoblast differentiation The embryoblast gives rise to the bilaminar disk and amniotic cavity. The embryoblast differentiates into the epiblast and hypoblast. Together, they are referred to as the bilaminar disc. […]
Fertilization and First Week
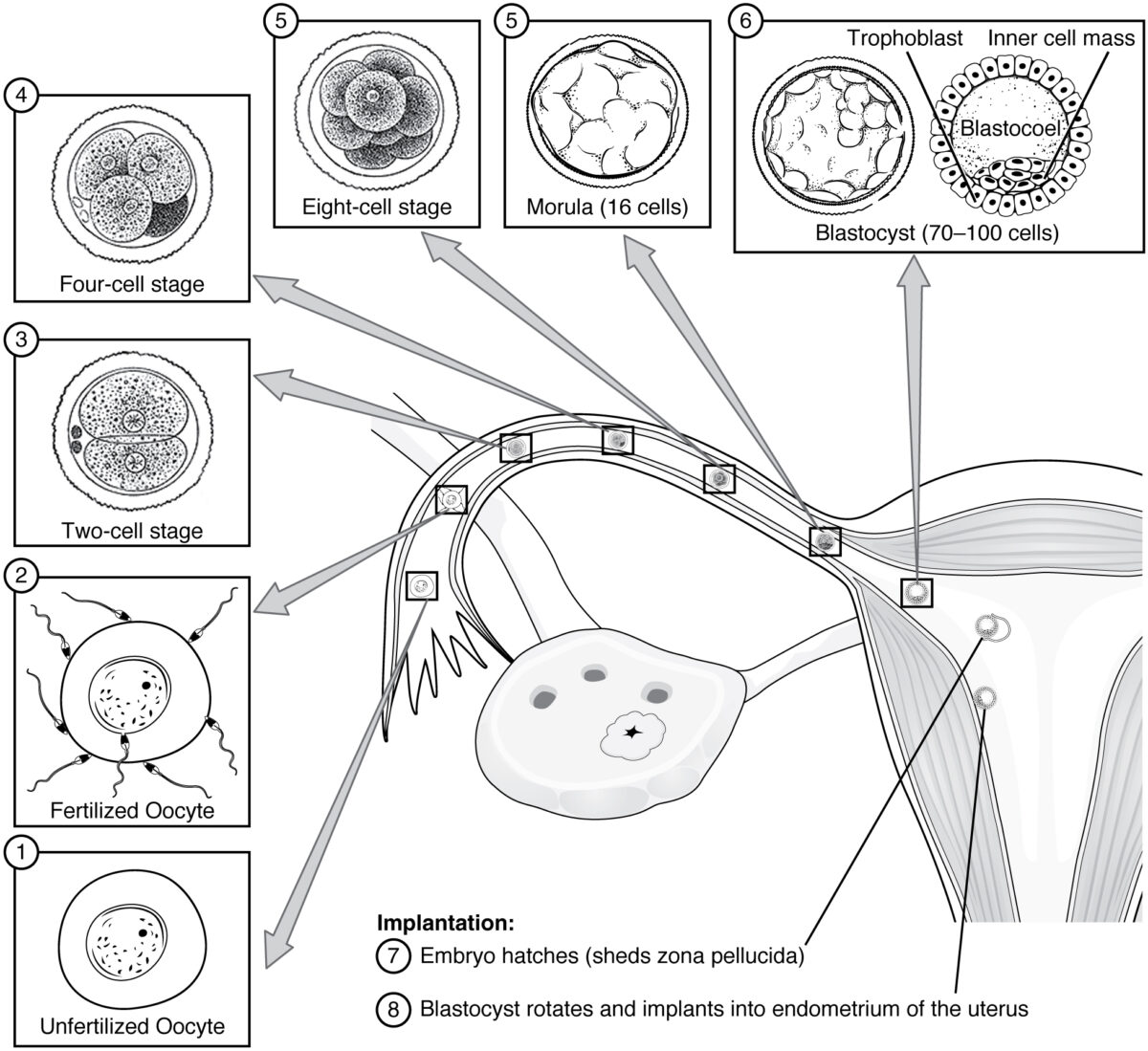
Fertilization Sperm enter the uterus with sexual intercourse, subsequently entering the fallopian tubes and traveling upstream to the ampulla of the fallopian tube. The ampulla is the location of fertilization, which is a multistep process. Step 1: 1st contact Step 2: binding of sperm and oocyte Step 3: release of sperm contents 1st Week of […]
Gametogenesis
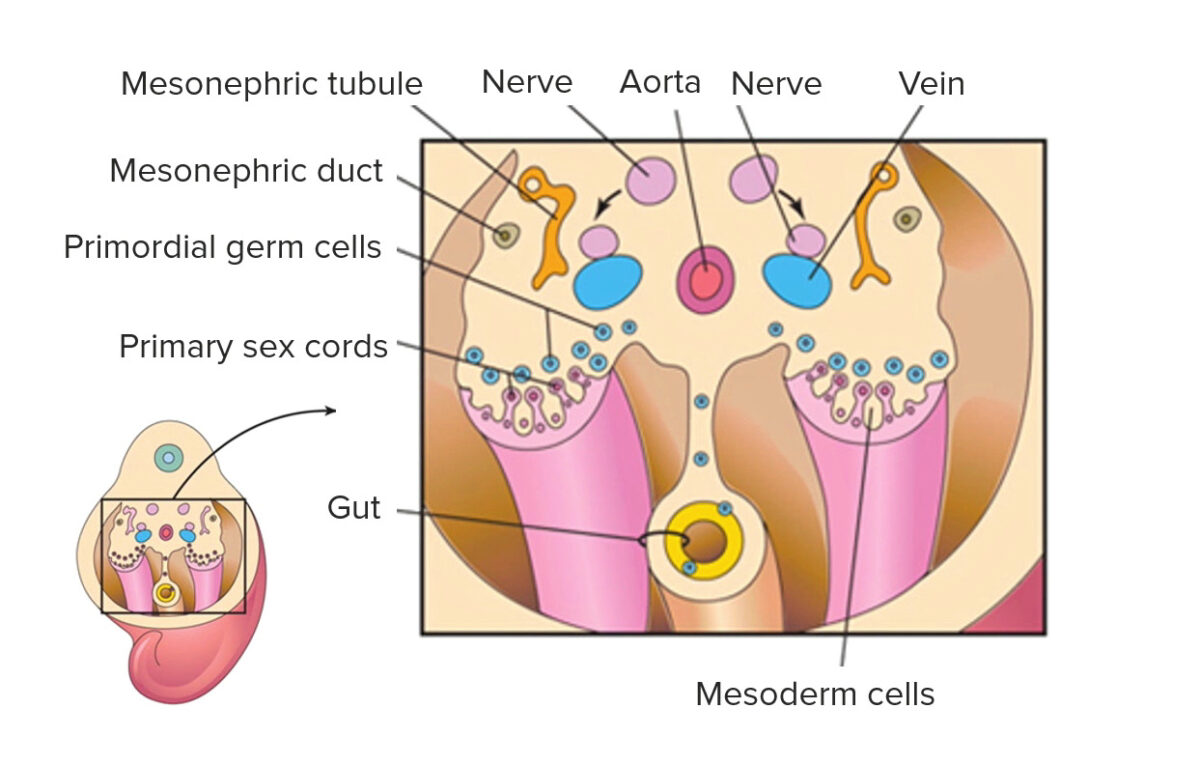
Overview Emigration of germ cells Gametogenesis Oogenesis Oogenesis is the process of ovum production from PGCs. Formation of ovum Follicle development Folliculogenesis is a complex process in which an ovarian follicle, containing an oocyte, matures through several stages. Ovulation Spermatogenesis Spermatogenesis is the process of sperm production from PGCs. Location Overview: Sertoli cells: Formation of […]