Adult Health Maintenance (Clinical)
General Assessment Screening tests are used for public health problems that are asymptomatic at early stages. There must be a suitable screening test and accepted treatment available, as well as evidence that early treatment during the asymptomatic stage improves the long-term outcome.[21] History[5,10] Physical exam[5,10] Screening for Metabolic Disorders Hypertension[13,14,47] Table: Hypertension classification system by […]
Sepsis and Septic Shock (Clinical)

Overview Definitions Epidemiology[2,5] Risk factors[2,5,14] Etiology and Pathophysiology Etiology[2,5] Pathophysiology[2,5] Pathogen load and virulence + host genetic composition and comorbidities result in a complex, exaggerated, and prolonged host response to infection that evolves over time. Clinical Presentation Diagnosis General approach[2,3,6,9,13,14,16] Diagnostic criteria Criteria for sepsis:[9] Criteria for septic shock:[9] SOFA score:[6,9] Table: SOFA score[1,6,9] Organ/system […]
Diabetes Mellitus (Clinical)
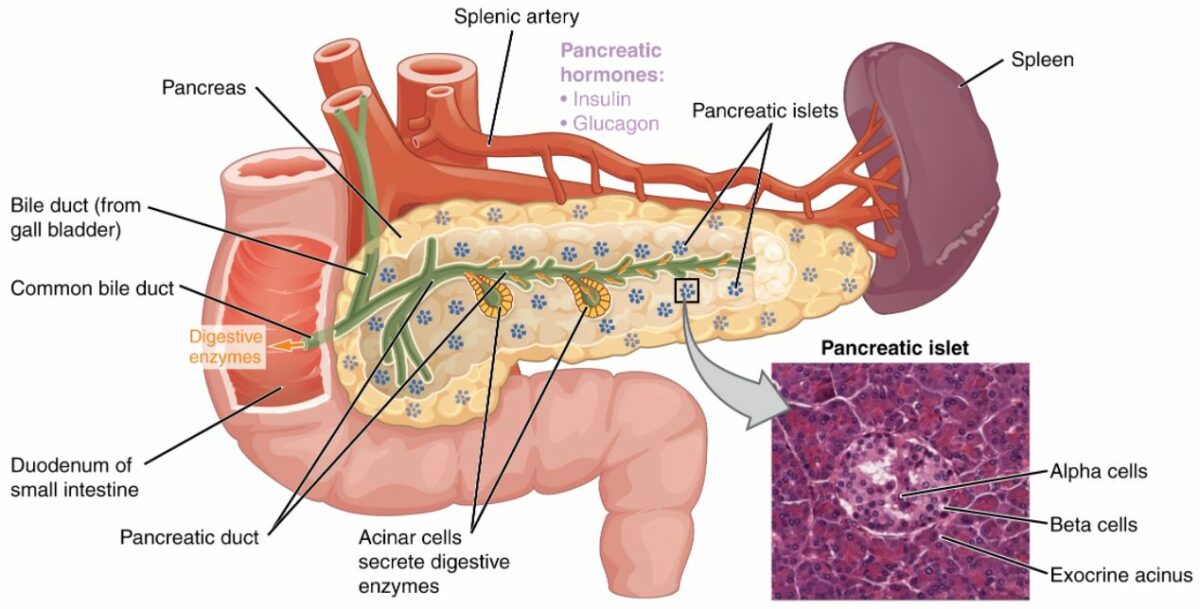
Definition Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a disorder of carbohydrate metabolism. Diabetes mellitus usually occurs in genetically predisposed individuals and is characterized by inadequate production of insulin or resistance to insulin’s action on the pancreas. These features result in hyperglycemia and the long-term pathologic sequelae of DM. Epidemiology The prevalence of diabetes has significantly increased since […]
Asthma (Clinical)
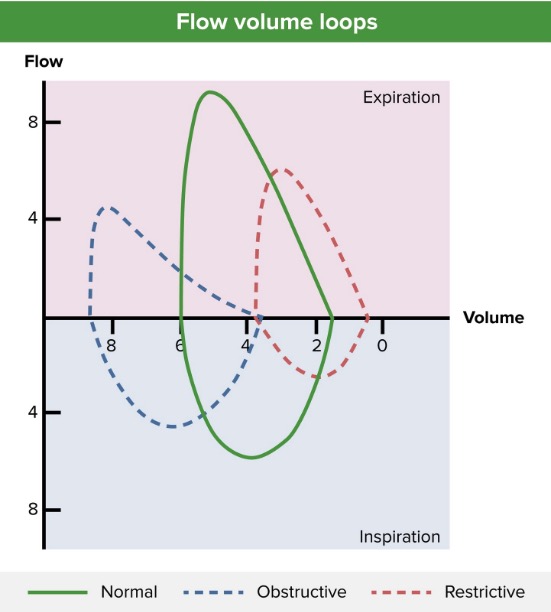
Definition and Epidemiology Definition Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways: Epidemiology[1,8] Etiology and Classification Predisposing factors for asthma[1,2,8,9] Asthma triggers[1,2,8,9] In established asthma, different triggers (precipitants) may exacerbate the symptoms. These include the following: Classification[1,6] Asthma can be classified based on its severity, level of control, and clinical phenotypes. Severity: Status of […]
Sarcoidosis (Clinical)
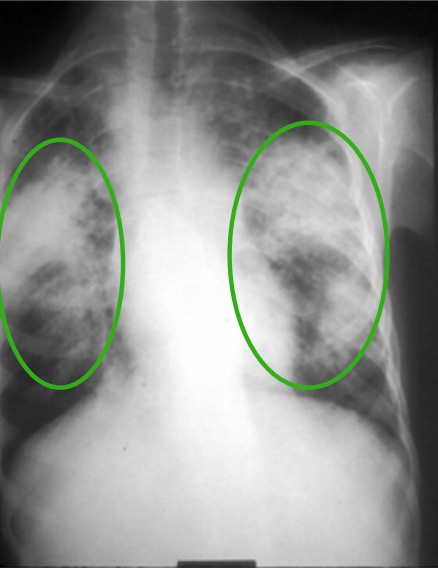
Overview Definition[1,3,7,18] Sarcoidosis is a multisystem inflammatory disease characterized by the formation of noncaseating granulomas that are most likely caused by a cell-mediated immune reaction of unknown etiology. Pulmonary sarcoidosis is a restrictive interstitial lung disease with granuloma formation in the: Extrapulmonary sarcoidosis is characterized by granuloma formation in: Sarcoidosis may be acute or chronic: […]
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) (Clinical)
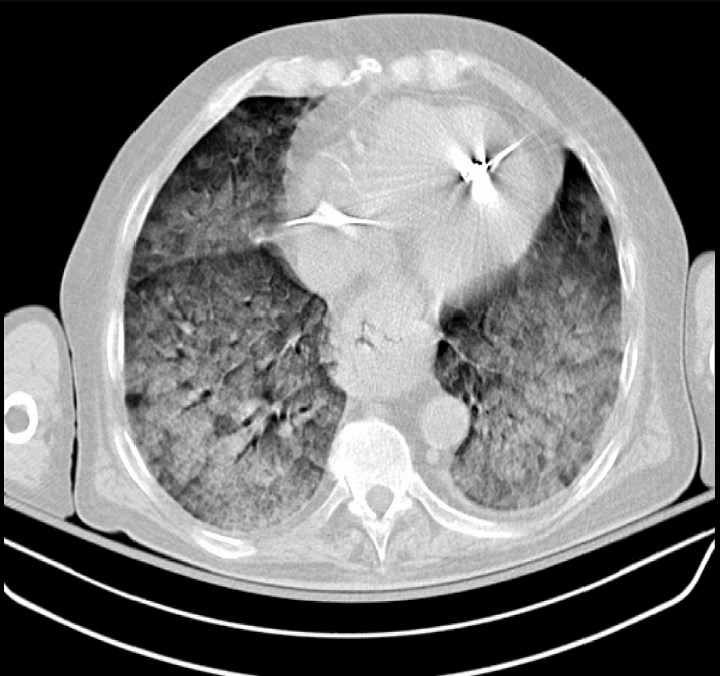
Overview Definition[1–3,5] Acute respiratory distress syndrome is a clinical syndrome (not a pathologic diagnosis) characterized by a sudden onset of hypoxemia and bilateral pulmonary edema without cardiac failure. The underlying mechanism of ARDS is diffuse alveolar damage (DAD): Epidemiology[1–3,5] Etiology[1–3,5] Acute respiratory distress syndrome results from clinical disorders that affect the lungs either directly or […]
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) (Clinical)
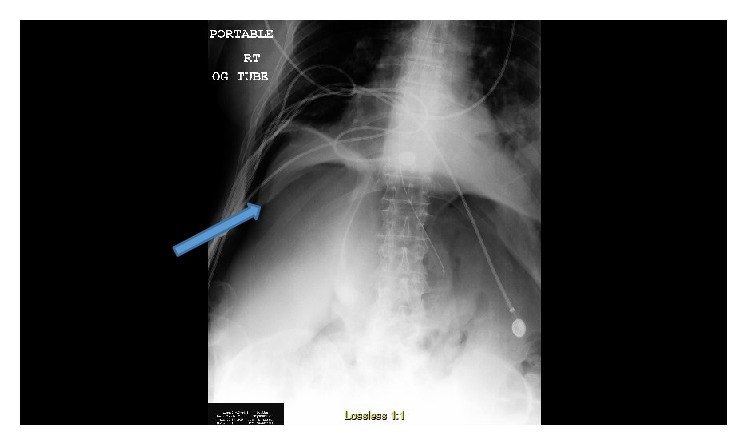
Overview Definition Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a heterogeneous lung disease characterized by chronic respiratory symptoms due to airflow limitation resulting from airway disease and/or parenchymal destruction. Types[1,5,7] The subtypes may have differing presentations and response to therapy. Patients may have any combination of both. Epidemiology[1,5,7] Etiology[1,5,7,21] Risk factors[2] Pathophysiology The pattern of pathologic […]
Hyponatremia (Clinical)
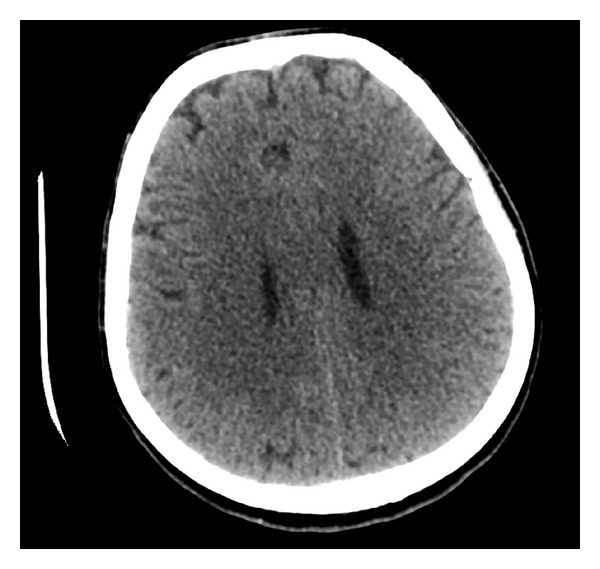
Overview Physiology and classification[6–8] Epidemiology[10,15] Etiology[1,4] The etiology of hyponatremia is determined by knowing the volume status, as well as the serum and urine osmolality. Hypovolemic: Euvolemic: Hypervolemic: Pathophysiology Hyponatremia usually reflects an excess of total body water and not a deficiency in total body sodium.[2,4,7,8] Clinical Presentation Acute (< 48 hours)[6–9,12] Chronic (> 48 […]
Hospital-Acquired and Ventilator-Associated Pneumonias (Clinical)
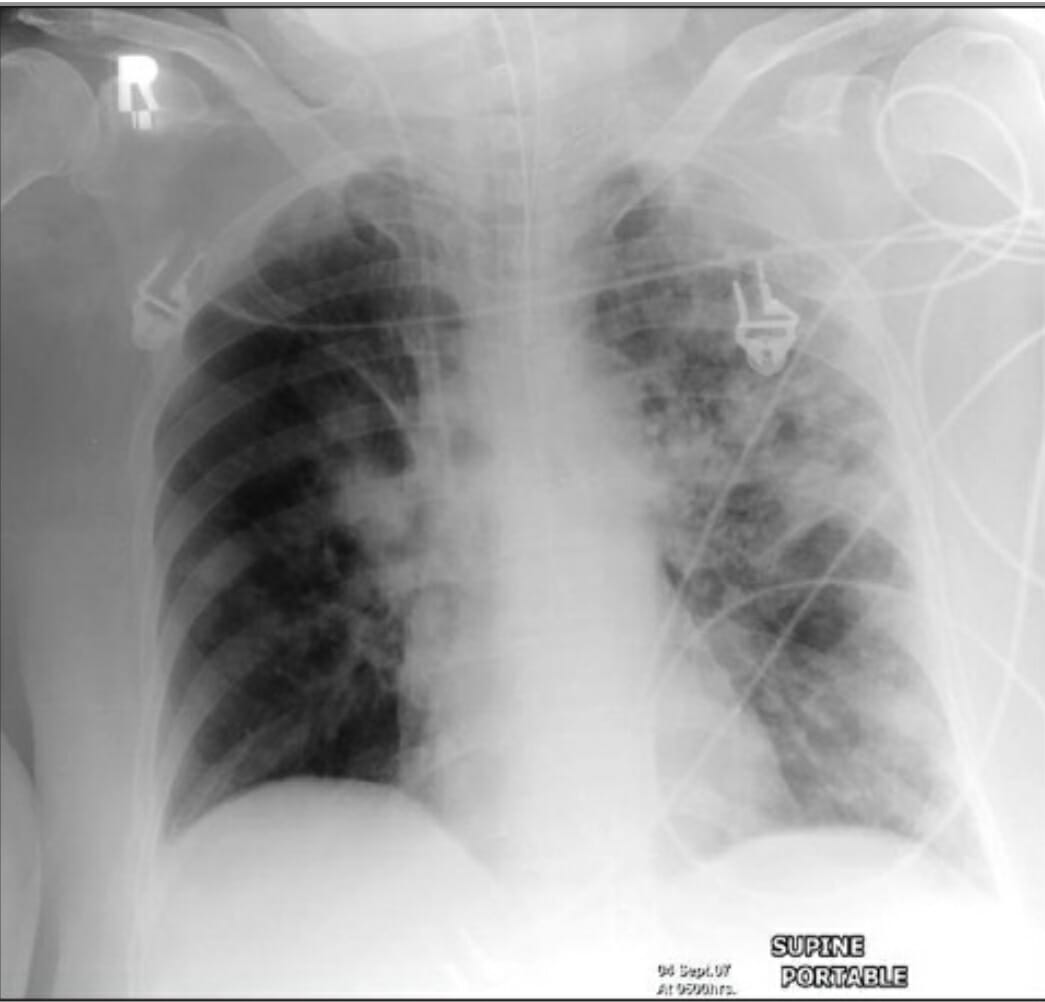
Overview Definition Pneumonia is the infection of the lung parenchyma. Types of pneumonia Classification based on the site where infection was acquired:[1,8] Classification by etiology:[12,13] Epidemiology[1,2,9] General: HAP: VAP: Etiology and Pathophysiology Etiology[1,3,9,15] Pathophysiology of VAP and HAP[1] Clinical Presentation and Diagnosis Clinical presentation Signs and symptoms may include:[1] With mechanical ventilation, suggestive findings may […]
Seizures (Clinical)
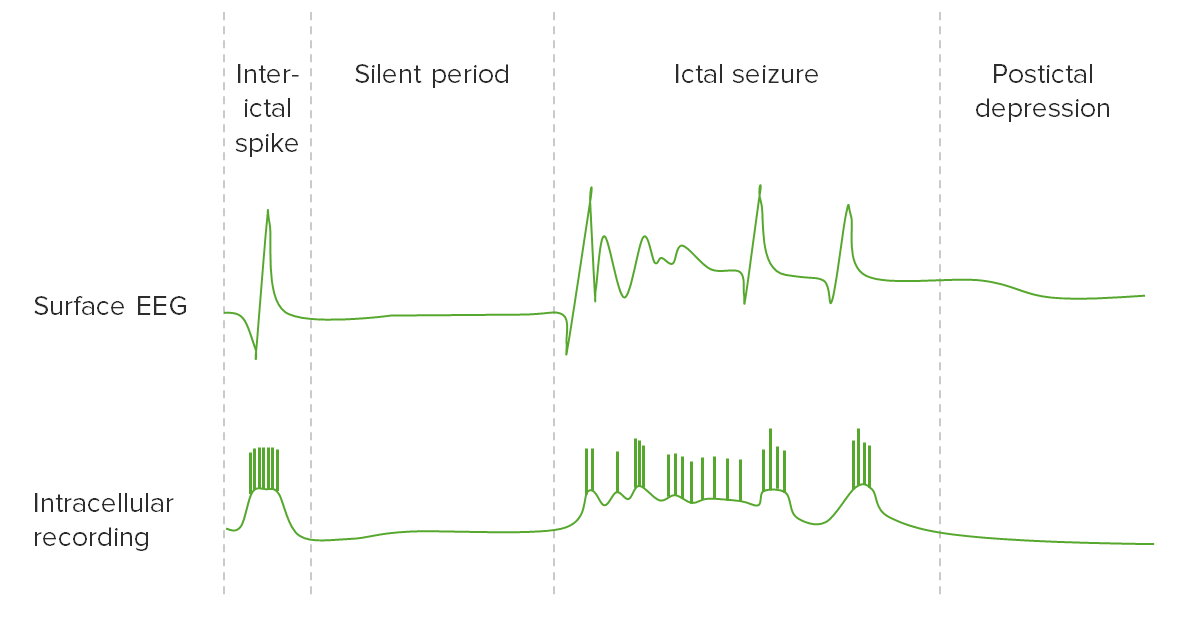
Overview Definition[1] Seizures are episodes of neurologic dysfunction caused by abnormal excitatory activities of neurons characterized by a sudden change in senses, perception, motor activity, or behavior. Epidemiology[1,3] Seizure phases[1,6] Pathophysiology Step 1: short in the circuit[12,13] Step 2: driving of normal neighbors[13] Step 3: failure of inhibition[13] Clinical Presentation Focal seizures[1,3,4] Table: Types of […]