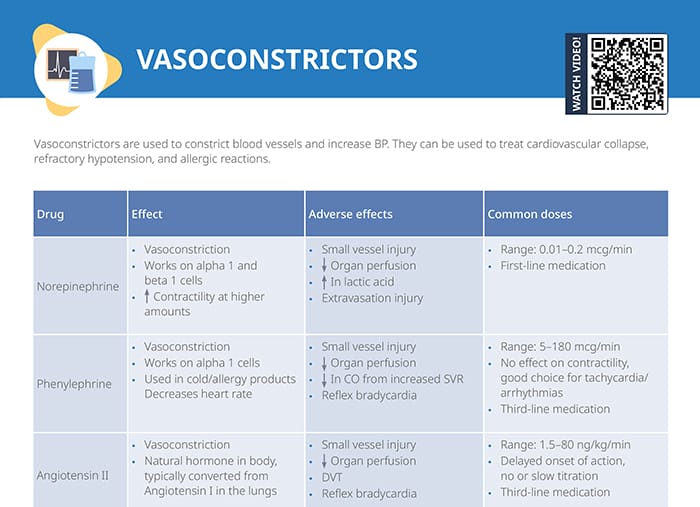
What are vasoconstrictors?
Definition
Vasoconstrictors are medications used to narrow (constrict) blood vessels, which leads to an increase in blood pressure.
How do vasoconstrictors work?
Vasoconstrictors often work by stimulating receptors on the smooth muscle cells of blood vessels. As the blood vessels constrict, the resistance to blood flow (systemic vascular resistance, SVR) increases. According to the formula for blood pressure (BP = CO [cardiac output] x SVR [systemic vascular resistance]), an increase in SVR directly increases blood pressure if cardiac output remains constant.
Indications
Vasoconstrictors can be used to treat cardiovascular collapse, refractory hypotension, and allergic reactions.
What is peripheral vasoconstriction?
Peripheral vasoconstriction is the narrowing of blood vessels specifically located outside the heart and brain, particularly those in the extremities (arms and legs).
How does peripheral vasoconstriction maintain homeostasis?
Increasing the resistance to blood flow in the peripheral arteries and therefore raising blood pressure helps maintain adequate perfusion of vital organs. Focusing perfusion and conserving heat to the vital organs instead of the extremities is helpful in emergency situations. In cases of severe blood loss, peripheral vasoconstriction helps maintain blood pressure.
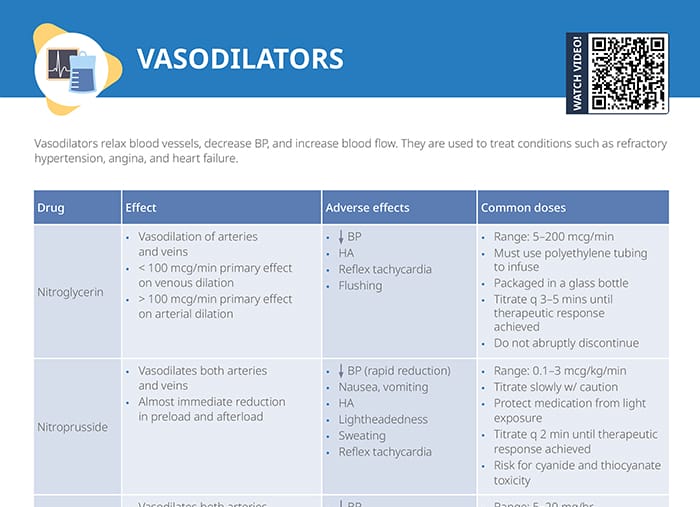
Overview of vasoconstrictors
Norepinephrine
Effects:
- Peripheral vasoconstriction
- Works on alpha 1 and beta 1 cells
- Increase in contractility at higher amounts
Adverse effects:
- Small vessel injury
- Decrease in organ perfusion
- Increase in lactic acid
- Extravasation injury
Common doses:
- Range: 0.01–0.2 mcg/min
- First-line medication
Phenylephrine
Effects:
- Vasoconstriction
- Works on alpha 1 cells
- Only works on arteries, not venous
Adverse effects:
- Small vessel injury
- Decrease in organ perfusion
- Decrease in CO from increased SVR
- Reflex bradycardia
Common doses:
- Range: 5–180 mcg/min
- No effect on contractility, good choice for tachycardia/arrhythmias
- Third-line medication
Angiotensin II
Effects:
- Vasoconstriction
- Natural hormone in body, typically converted from angiotensin I in the lungs
Adverse effects:
- Small vessel injury
- Decrease in organ perfusion
- DVT
- Reflex bradycardia
Common doses:
- Range: 1.5–80 ng/kg/min
- Delayed onset of action, no or slow titration
- Third-line medication
Vasopressin (ADH)
Effects:
- Vasoconstriction
- Natural hormone in the body
- Antidiuretic
Adverse effects:
- Small vessel injury
- Decrease in organ perfusion
- Increase in lactic acid
- Decrease in CO from increased SVR
- Decrease in urine output
Common doses:
- Range: 0.01–0.04 mcg/min
- Delayed onset of action, no or slow titration
Natural vasoconstrictors
In some cases, natural vasoconstrictors can be of interest for example for clients with migraines looking for alternative options. Well-known natural vasoconstrictors that could help reduce pain in clients looking for natural remedies include:
- Caffeine in moderation
- Peppermint
- Cold compresses
Nursing considerations for vasoconstriction medications
- Screen for drug interactions: beta adrenergic blockers, antidepressants, anti-HTN, cardiac glycosides
- Common goal is achieving a mean arterial pressure of (MAP) 60–65 mm Hg.
- Should be used at the lowest effective dose to avoid adverse effects
- May require invasive methods to closely monitor hemodynamic effects: arterial line, central venous cath, or pulmonary artery cath