What is brain herniation?
Definition
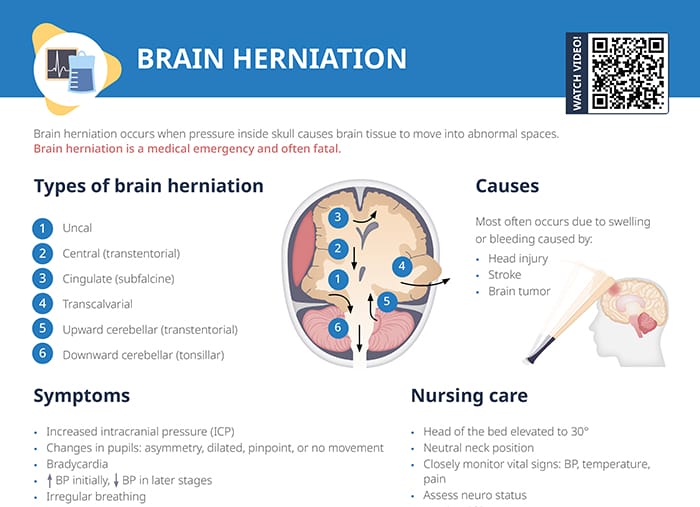
Brain herniation occurs when pressure inside the skull pushes brain tissue into abnormal spaces.
Brain herniation is a medical emergency and often fatal, with a low survival rate if not treated immediately.
Causes
Brain herniation is most often caused by swelling or bleeding due to:
- Head injury
- Stroke
- Brain tumor
Types of brain herniation
The types of brain herniation can be differentiated by the location of the herniation:
- Uncal: uncus (innermost part of the temporal lobe) pushed down over the tentorium
- Central (transtentorial): brain’s central structures pushed downward through the tentorial notch
- Cingulate (subfalcine): cingulate gyrus displaced under the falx cerebri
- Transcalvarial: brain tissue getting pushed through a defect in the skull
- Upward cerebellar (transtentorial)
- Downward cerebellar (tonsillar)
Stages of brain herniation
The progression of brain herniation can be classified as follows:
- Initial stage: increased intracranial pressure without significant brain tissue shift
- Early herniation: beginning of tissue displacement, with altered consciousness and mild neurological deficits
- Late herniation: severe tissue shift, significant neurological impairment, and potential brainstem compression
- Terminal stage: irreversible brain damage and failure of brainstem functions
Brain herniation symptoms and signs
- Increased intracranial pressure (ICP)
- Changes in pupils: asymmetry, dilated, pinpoint, or no movement
- Bradycardia
- ↑ BP initially, ↓ BP in later stages
- Irregular breathing
- Severe headache
- Weakness
- Cardiac and respiratory arrest
- Coma
- Loss of brainstem activity
Herniation can cause brain death due to irreversible brain stem dysfunction or damage to the brain’s respiratory and cardiovascular centers, causing respiratory or cardiac arrest.
Affected persons may exhibit the symptoms of the Cushing’s triad indicating increased intracranial pressure: hypertension, bradycardia, and irregular breathing.
Brain herniation treatment and nursing care tasks
Management
The goal when treating brain herniation is to reduce swelling and pressure.
Measures:
- Endotracheal intubation
- Hyperventilation with ICP and CO2 monitoring
- Fluid management
- Drain for CSF based on elevation and parameters of order
- Surgery to remove clot, tumor
- Craniectomy
- Diuretics
- BP control
- Therapeutic hypothermia
- Induced coma
Nursing care tasks
- Elevate head of the bed to 30°, keep a neutral neck position
- Monitoring:
- Vital signs: BP, temperature, pain
- Intracranial pressure
- I&O assessment
- Neuro status assessment
- Follow orders for sedation and pain medication
- DVT and ulcer prophylaxis
Family education
Inform the family that the client’s prognosis is affected by multiple factors, including
- Client age
- Location, type and duration of herniation
- Concurrent trauma
Provide emotional support and resources for families during the acute and rehabilitation phases.