La peste es una infección bacteriana causada por Yersinia pestis Yersinia pestis The plague is a bacterial infection caused by Yersinia pestis (Y. pestis), which primarily infects rodents. The disease is transmitted to humans via a flea bite. Inhalation of infectious droplets and handling infected animals or laboratory specimens are other means of transmission. The plague has 3 forms: bubonic (most common form), septicemic, and pneumonic. Yersinia pestis/Plague (Y. pestis), que infecta principalmente a los LOS Neisseria roedores. La enfermedad se transmite a los LOS Neisseria humanos a través de una picadura de pulga. La inhalación de gotas infecciosas y la manipulación de animales infectados o de muestras de laboratorio son otros medios de transmisión. La peste tiene 3 formas: bubónica (la más común), septicémica y neumónica. La peste bubónica da lugar a unos ganglios linfáticos inflamados y sensibles llamados bubones en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la zona inguinal. La peste neumónica y septicémica puede surgir como presentación primaria, pero también puede ser el resultado de la propagación hematógena de la enfermedad bubónica. El diagnóstico incluye los LOS Neisseria antecedentes y hallazgos clínicos, el cultivo, la reacción en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum cadena de la polimerasa ( PCR PCR Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a technique that amplifies DNA fragments exponentially for analysis. The process is highly specific, allowing for the targeting of specific genomic sequences, even with minuscule sample amounts. The PCR cycles multiple times through 3 phases: denaturation of the template DNA, annealing of a specific primer to the individual DNA strands, and synthesis/elongation of new DNA molecules. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)) y la serología. La tasa de mortalidad es elevada, por lo que es necesario un diagnóstico y un tratamiento rápido con antibióticos.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Casos de peste a nivel mundial:
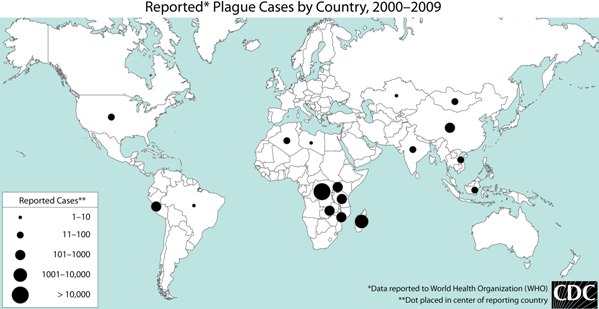
Mapa mundial de los casos de peste notificados a la World Health Organization (WHO), 2000–2009
Imagen: “World Plague Map – 2000 to 2009 – CDC” por CDC. Licencia: Dominio público.La peste en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum Estados Unidos:

Una pulga infectada con Y. pestis, mostrada como una masa oscura
El intestino anterior de esta pulga está bloqueado por una biopelícula de Y. pestis, que es un requisito previo para una transmisión eficaz.
Un pulgón infectado con la bacteria Y. pestis
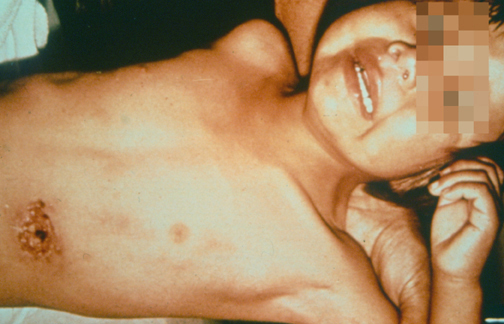
La imagen muestra a un niño con una picadura de pulga en el abdomen. El lugar de la inoculación se ha ulcerado. También se observa un ganglio linfático axilar prominente (bubo).
La peste bubónica:
Peste neumónica:
Peste septicémica:
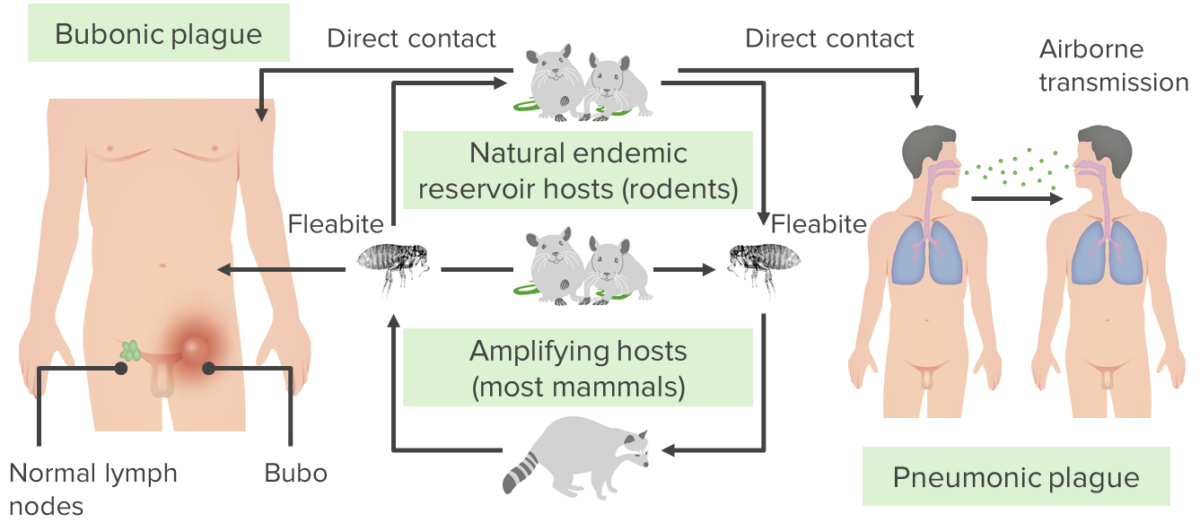
La transmisión de Yersinia pestis
El contacto directo con roedores o las picaduras de pulgas dan lugar a la peste bubónica, mientras que la transmisión por vía aérea (de persona a persona), ya sea por tos o estornudos, da lugar a la peste neumónica.
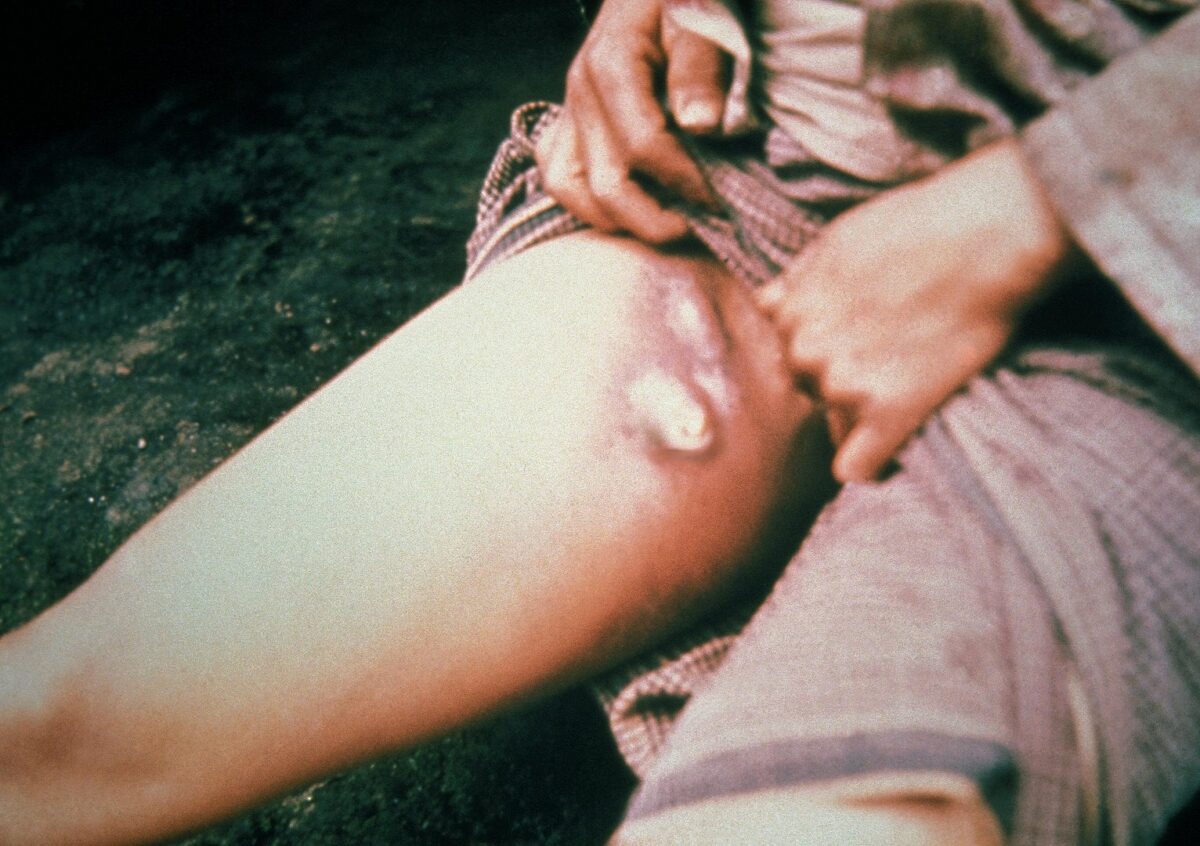
Peste bubónica: ganglios linfáticos inguinales inflamados en una persona infectada por la peste bubónica
Imagen: “Plague buboes” por CDC. Licencia: Dominio Público.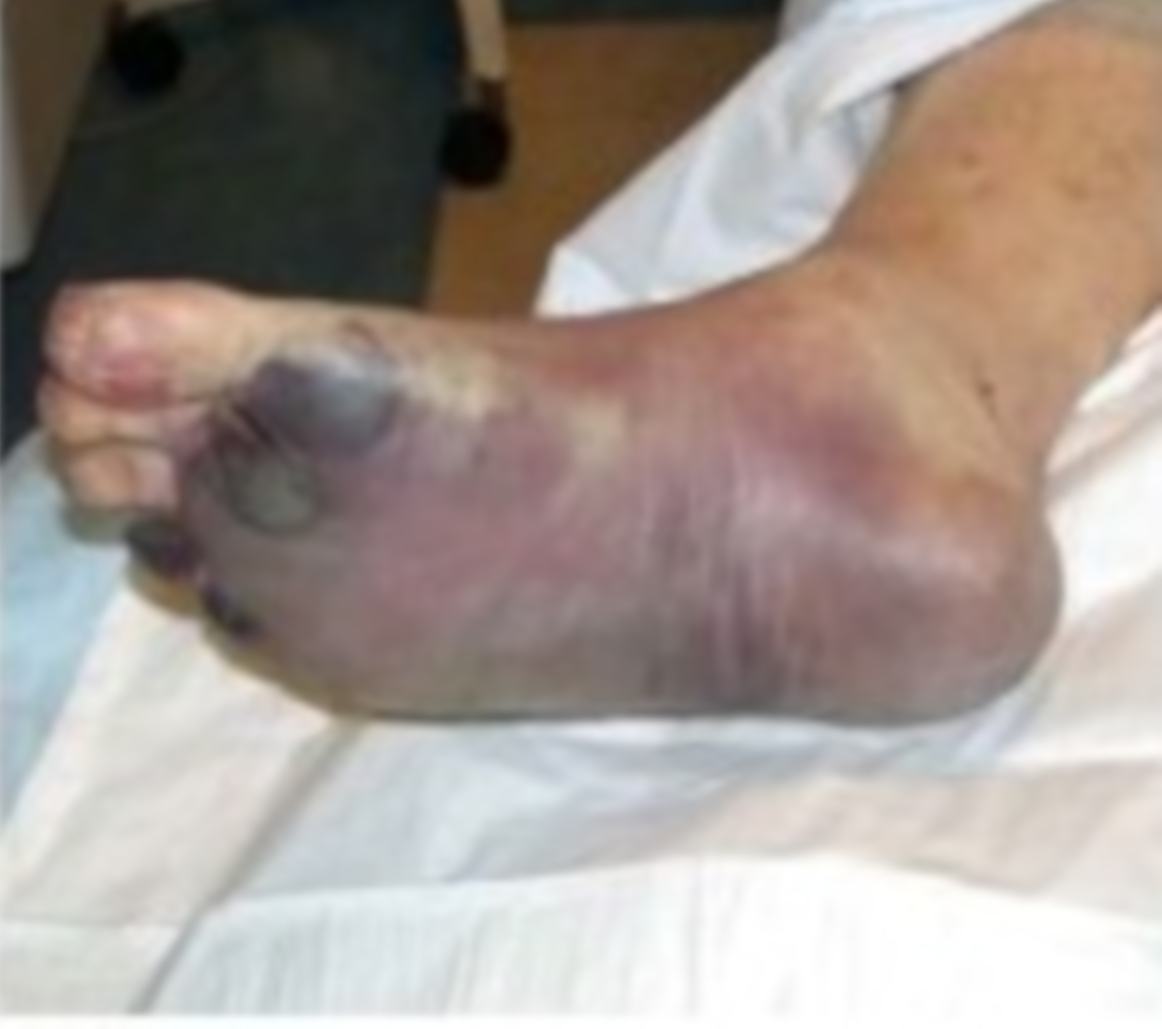
Peste septicémica: Infección por Y. pestis que provoca cambios necróticos en el pie derecho
Imagen: “PlagueTypes” por CDC. Licencia: Dominio Público.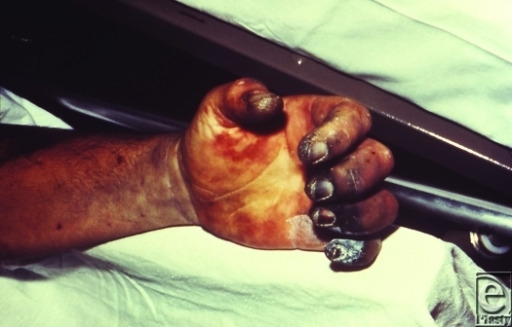
Paciente con la peste
La imagen muestra la gangrena de los dedos, efecto de la infección por Y. pestis a través del bioterrorismo.
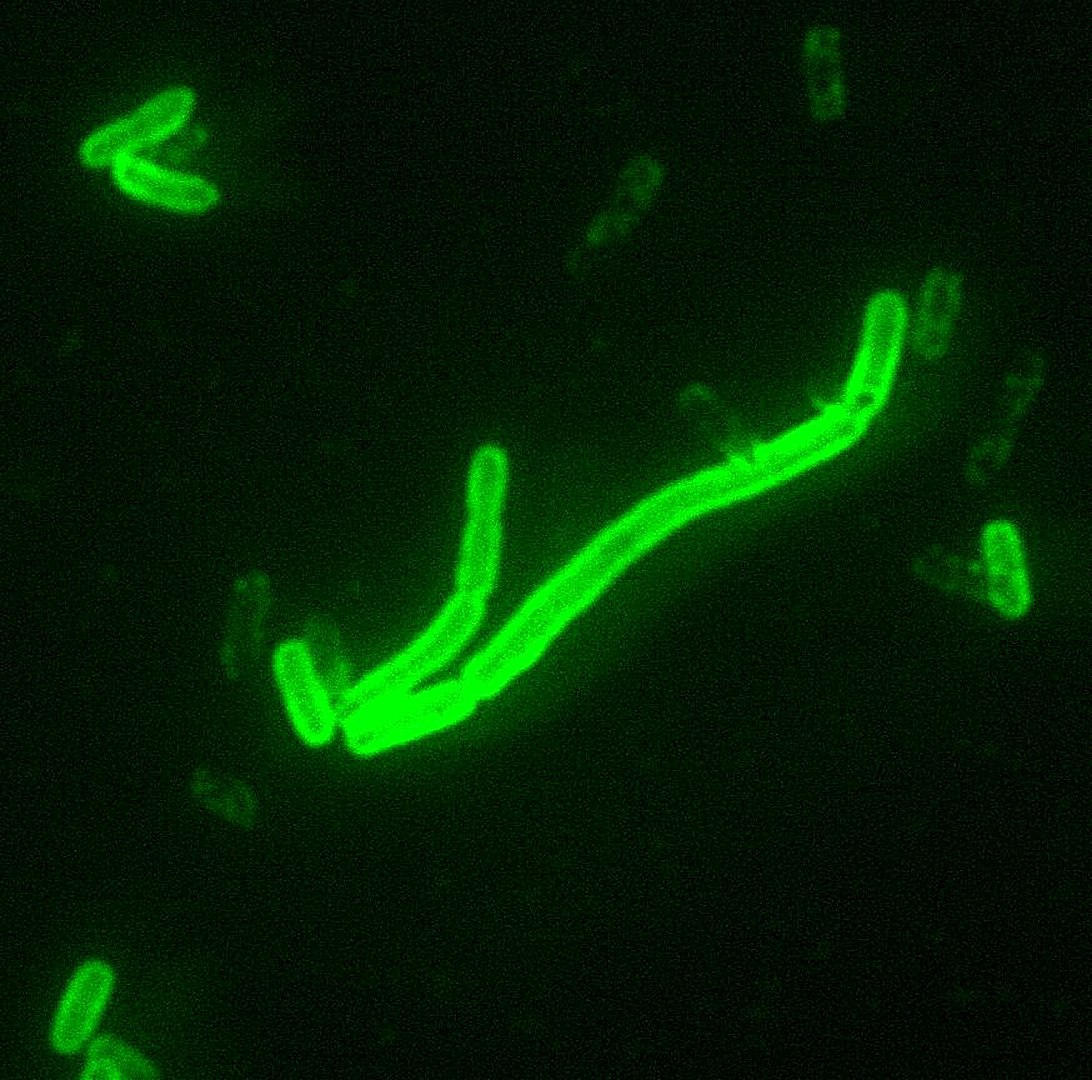
Yersinia pestis: bajo microscopio, teñido con tinción fluorescente
Imagen: “Yersinia pestis fluorescent” por CDC/Courtesy of Larry Stauffer, Oregon State Public Health Laboratory. Licencia: Dominio Público.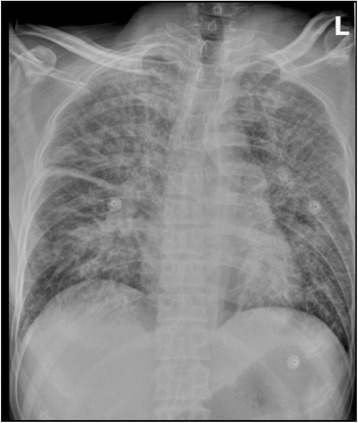
Un paciente con peste neumónica
Una radiografía de tórax muestra un aumento de las marcas pulmonares, con una pleura interlobar gruesa en un paciente que presentó fiebre, tos y disnea tras la exposición a un perro pastor.