El virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology del Nilo Occidental es un virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de ácido ribonucleico (ARN) monocatenario, de sentido positivo y envuelto, del género Flavivirus Flavivirus A genus of flaviviridae containing several subgroups and many species. Most are arboviruses transmitted by mosquitoes or ticks. The type species is yellow fever virus. Tick-borne Encephalitis Virus. Las aves son los LOS Neisseria principales huéspedes y la enfermedad es transmitida con mayor frecuencia por los LOS Neisseria mosquitos Culex. La mayoría de las personas infectadas por el virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology del Nilo Occidental son asintomáticas. Algunos pacientes desarrollan la fiebre del Nilo Occidental (una enfermedad febril autolimitada) y una proporción muy pequeña de pacientes desarrollan la enfermedad neuroinvasiva del Nilo Occidental. La enfermedad neuroinvasiva del Nilo Occidental incluye meningitis Meningitis Meningitis is inflammation of the meninges, the protective membranes of the brain, and spinal cord. The causes of meningitis are varied, with the most common being bacterial or viral infection. The classic presentation of meningitis is a triad of fever, altered mental status, and nuchal rigidity. Meningitis, encefalitis y parálisis flácida aguda. El diagnóstico se confirma con serología de suero, serología del líquido cefalorraquídeo (LCR) o reacción en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum cadena de polimerasa ( PCR PCR Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a technique that amplifies DNA fragments exponentially for analysis. The process is highly specific, allowing for the targeting of specific genomic sequences, even with minuscule sample amounts. The PCR cycles multiple times through 3 phases: denaturation of the template DNA, annealing of a specific primer to the individual DNA strands, and synthesis/elongation of new DNA molecules. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR), por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés). No se dispone de terapia antiviral Antiviral Antivirals for Hepatitis B, por lo que el tratamiento es de soporte. La prevención se centra en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el control local de los LOS Neisseria mosquitos y el tamizaje de la sangre y órganos donados.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025

Identificación de los virus ARN:
Los virus pueden clasificarse de muchas maneras. Sin embargo, la mayoría de los virus tienen un genoma formado por ácido desoxirribonucleico (ADN) o ARN. Los virus con genoma ARN pueden caracterizarse además por tener ARN monocatenario o bicatenario. Los virus “envueltos” están cubiertos por una fina capa de membrana celular (normalmente tomada de la célula huésped). Si la capa está ausente, los virus se denominan “desnudos”. Los virus con genomas monocatenarios son de “sentido positivo” si el genoma se emplea directamente como ARN mensajero (ARNm), que se traduce en proteínas. Los virus monocatenarios de “sentido negativo” emplean la ARN polimerasa dependiente de ARN, una enzima viral, para transcribir su genoma en ARN mensajero.
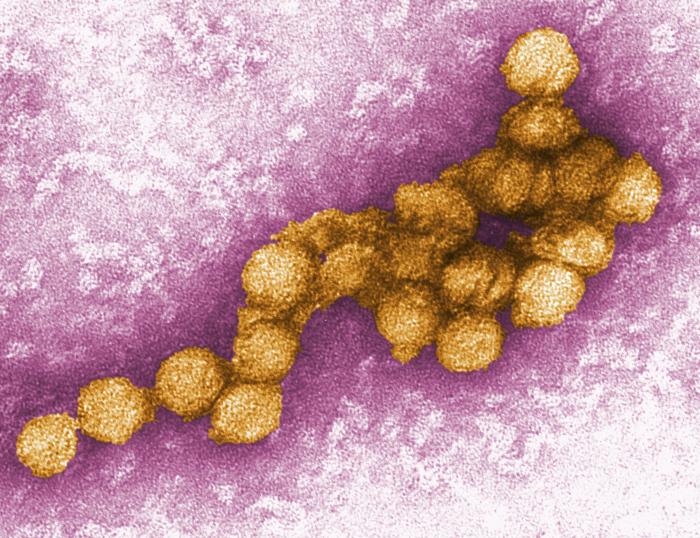
Una imagen coloreada de microscopio electrónico de transmisión de los viriones del Nilo Occidental
Imagen: “West Nile virus” por CDC/P.E. Rollin. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoDos linajes filogénicos del virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology del Nilo Occidental causan las siguientes enfermedades:
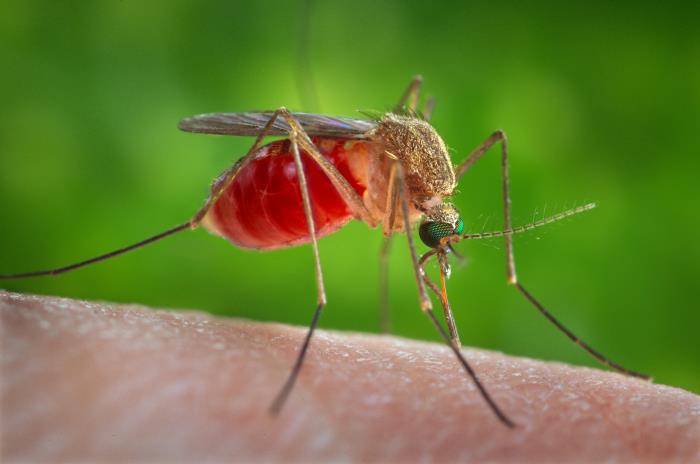
Una hembra mosquito Culex responsable de la transmisión del virus del Nilo Occidental
Imagen: “Culex mosquito” por CDC/James Gathany. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoMayor riesgo de infección:
Mayor riesgo de enfermedad neuroinvasiva:
La mayoría de los LOS Neisseria pacientes son asintomáticos. La enfermedad sintomática puede variar en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum gravedad y presentación.
Aproximadamente el 20% de los LOS Neisseria pacientes infectados desarrollarán una enfermedad leve y autolimitada.
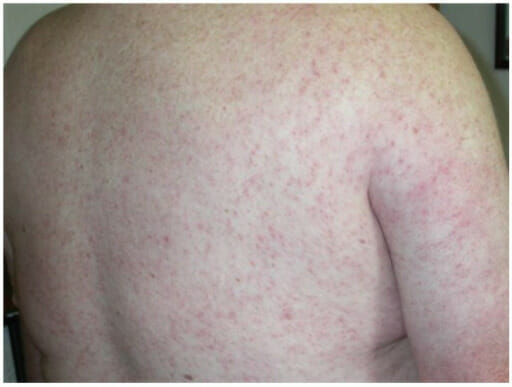
Erupción maculopapular debida al virus del Nilo Occidental
Imagen: “Diffuse maculopapular rash associated with West Nile virus infection” por James J Sevjar. Licencia: CC BY 3.0Aproximadamente el 1% de los LOS Neisseria pacientes infectados pueden experimentar:
Estudios definitivos:
Evaluación de soporte:
Actualmente, no se dispone de terapia antiviral Antiviral Antivirals for Hepatitis B; el tratamiento es de soporte. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum pacientes con enfermedad neuroinvasiva, puede ser necesario lo siguiente:
| Organismo | Virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de la encefalitis transmitida por garrapatas | Virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de la encefalitis japonesa | Virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de la encefalitis de San Louis | Virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology del Nilo Occidental |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Características | Las características estructurales son casi idénticas. | |||
| Región |
|
|
América del Norte |
|
| Transmisión | Garrapata | Mosquito | Mosquito | Mosquito |
| Cuadro Clínico |
|
|
|
|
| Diagnóstico |
|
Serología | Serología |
|
| Tratamiento | De soporte | De soporte | De soporte | De soporte |
| Prevención |
|
Medidas para evitar los LOS Neisseria mosquitos | Medidas para evitar los LOS Neisseria mosquitos | |