La toxoplasmosis Toxoplasmosis Toxoplasmosis is an infectious disease caused by Toxoplasma gondii, an obligate intracellular protozoan parasite. Felines are the definitive host, but transmission to humans can occur through contact with cat feces or the consumption of contaminated foods. The clinical presentation and complications depend on the host's immune status. Toxoplasma/Toxoplasmosis es una enfermedad infecciosa causada por Toxoplasma Toxoplasma Toxoplasmosis is an infectious disease caused by Toxoplasma gondii, an obligate intracellular protozoan parasite. Felines are the definitive host, but transmission to humans can occur through contact with cat feces or the consumption of contaminated foods. The clinical presentation and complications depend on the host's immune status. Toxoplasma/Toxoplasmosis gondii, un parásito protozoario intracelular obligado. Los LOS Neisseria felinos son el huésped definitivo, pero la transmisión a los LOS Neisseria humanos puede producirse por el contacto con las heces de los LOS Neisseria gatos o el consumo de alimentos contaminados. La presentación clínica y las complicaciones dependen del estado inmunitario del huésped. Generalmente, los LOS Neisseria pacientes inmunocompetentes no presentan síntomas, mientras que los LOS Neisseria inmunocomprometidos pueden desarrollar toxoplasmosis Toxoplasmosis Toxoplasmosis is an infectious disease caused by Toxoplasma gondii, an obligate intracellular protozoan parasite. Felines are the definitive host, but transmission to humans can occur through contact with cat feces or the consumption of contaminated foods. The clinical presentation and complications depend on the host's immune status. Toxoplasma/Toxoplasmosis en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el SNC o coriorretinitis. El diagnóstico suele realizarse mediante pruebas de serología o PCR PCR Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a technique that amplifies DNA fragments exponentially for analysis. The process is highly specific, allowing for the targeting of specific genomic sequences, even with minuscule sample amounts. The PCR cycles multiple times through 3 phases: denaturation of the template DNA, annealing of a specific primer to the individual DNA strands, and synthesis/elongation of new DNA molecules. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR). Los LOS Neisseria pacientes inmunocompetentes pueden no necesitar tratamiento. Los LOS Neisseria pacientes inmunocomprometidos o los LOS Neisseria que padecen una enfermedad grave pueden requerir un tratamiento combinado con pirimetamina, sulfadiazina y leucovorina.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Características generales:
Formas morfológicas:
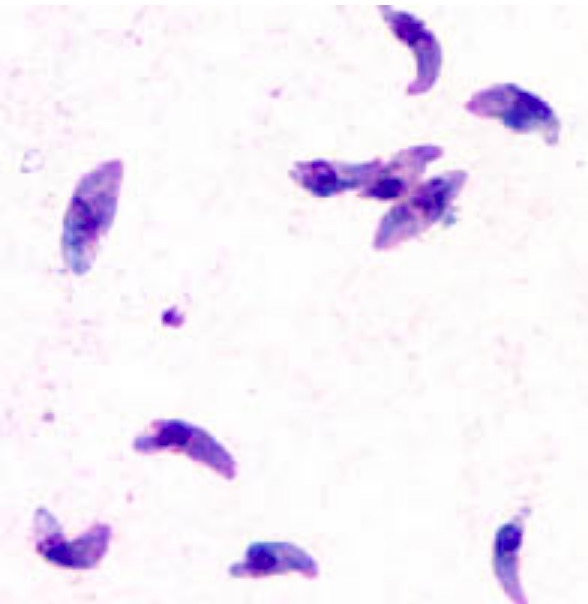
Taquizoítos deToxoplasma gondii teñidos con Giemsa:
Los taquizoítos suelen tener forma de media luna con un núcleo prominente situado en el centro.
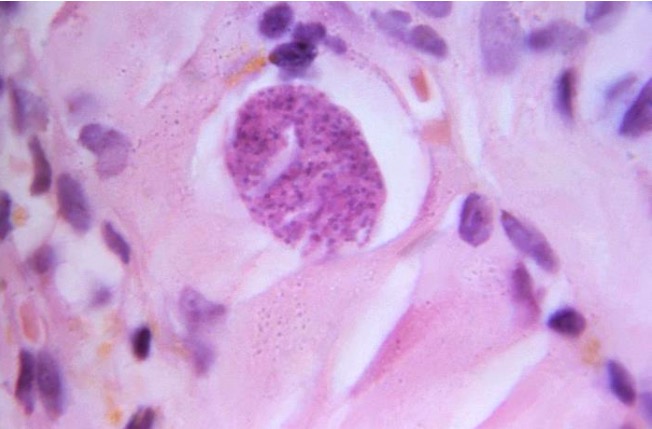
Microfotografía teñida con hematoxilina y eosina de un quiste tisular de Toxoplasma gondii que contiene bradizoítos en desarrollo en el tejido muscular humano
Imagen: “16547” por CDC/Dr. Martin Hicklin. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoLa toxoplasmosis Toxoplasmosis Toxoplasmosis is an infectious disease caused by Toxoplasma gondii, an obligate intracellular protozoan parasite. Felines are the definitive host, but transmission to humans can occur through contact with cat feces or the consumption of contaminated foods. The clinical presentation and complications depend on the host’s immune status. Toxoplasma/Toxoplasmosis es causada por el Toxoplasma Toxoplasma Toxoplasmosis is an infectious disease caused by Toxoplasma gondii, an obligate intracellular protozoan parasite. Felines are the definitive host, but transmission to humans can occur through contact with cat feces or the consumption of contaminated foods. The clinical presentation and complications depend on the host’s immune status. Toxoplasma/Toxoplasmosis gondii.
Ciclo de vida:
Ciclo de vida y fisiopatología en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum humanos:
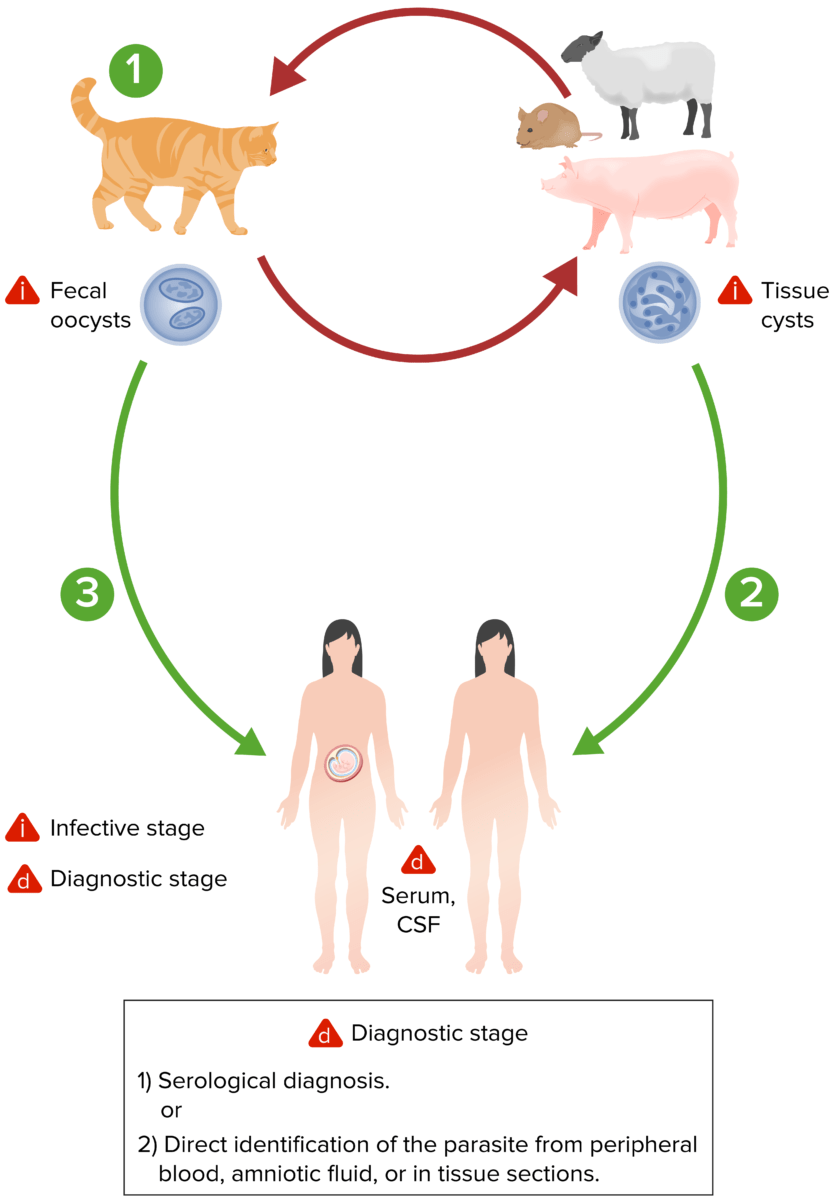
El ciclo de vida de Toxosplasma gondii. Tanto los ooquistes como los quistes tisulares se transforman en taquizoítos poco después de la ingestión. Los taquizoítos se localizan en el tejido neural y muscular y se transforman en bradizoítos tisulares. Si una mujer embarazada se infecta, los taquizoítos pueden infectar al feto a través del torrente sanguíneo.
Imagen por Lecturio.La presentación clínica de la toxoplasmosis Toxoplasmosis Toxoplasmosis is an infectious disease caused by Toxoplasma gondii, an obligate intracellular protozoan parasite. Felines are the definitive host, but transmission to humans can occur through contact with cat feces or the consumption of contaminated foods. The clinical presentation and complications depend on the host’s immune status. Toxoplasma/Toxoplasmosis puede variar dependiendo la función inmunitaria del huésped y los LOS Neisseria órganos implicados. La siguiente tabla resume las distintas enfermedades:
| Huésped | Enfermedad | Presentación |
|---|---|---|
| Huésped inmunocompetente | Infección subclínica (aproximadamente el 90% de los LOS Neisseria casos) | Asintomática |
| Enfermedad sistémica aguda | Signos y síntomas comunes:
|
|
| Huéspedes inmunocomprometidos (e.g., SIDA) | Toxoplasmosis Toxoplasmosis Toxoplasmosis is an infectious disease caused by Toxoplasma gondii, an obligate intracellular protozoan parasite. Felines are the definitive host, but transmission to humans can occur through contact with cat feces or the consumption of contaminated foods. The clinical presentation and complications depend on the host’s immune status. Toxoplasma/Toxoplasmosis del SNC (enfermedad definitoria de SIDA, recuento de CD4 < 100 células/µl) |
|
| Coriorretinitis | Síntomas:
|
|
| Neumonitis |
|
|
| Feto, recién nacido o lactante | Toxoplasmosis Toxoplasmosis Toxoplasmosis is an infectious disease caused by Toxoplasma gondii, an obligate intracellular protozoan parasite. Felines are the definitive host, but transmission to humans can occur through contact with cat feces or the consumption of contaminated foods. The clinical presentation and complications depend on the host’s immune status. Toxoplasma/Toxoplasmosis congénita | Tríada clásica:
|
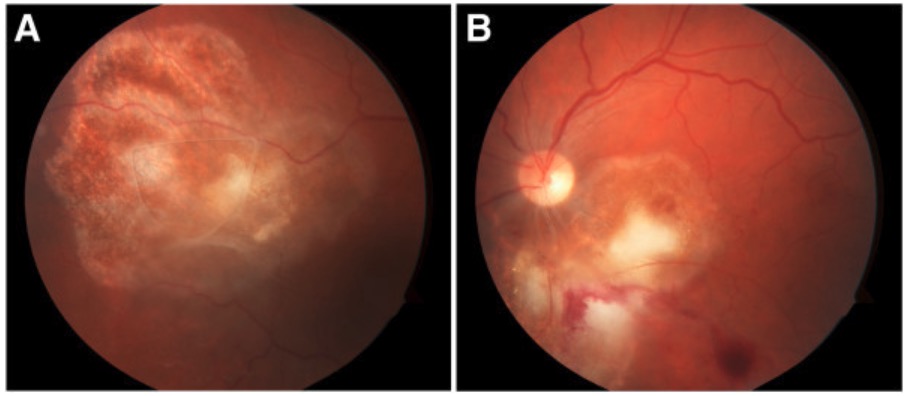
Examen del fondo de ojo de la coriorretinitis por Toxoplasma:
Se observan las lesiones algodonosas blanco-amarillentas en el ojo derecho (A) e izquierdo (B).
La evaluación diagnóstica se guiará por la presentación clínica del paciente.
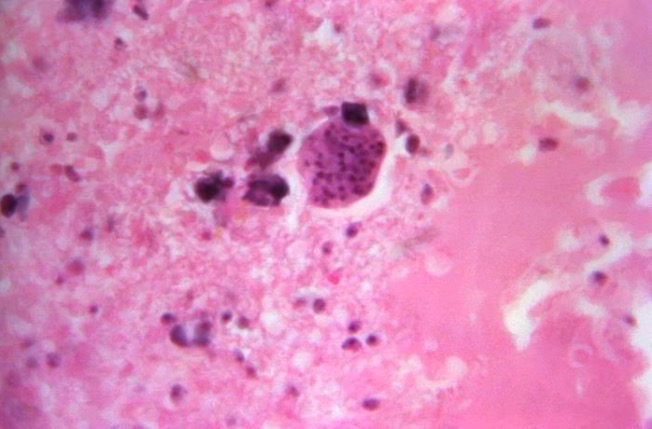
Microfotografía de un quiste tisular de Toxoplasma gondii en una muestra de tejido cerebral
Imagen: “16543” por CDC/Dr. Martin Hicklin. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoSi se sospecha de toxoplasmosis Toxoplasmosis Toxoplasmosis is an infectious disease caused by Toxoplasma gondii, an obligate intracellular protozoan parasite. Felines are the definitive host, but transmission to humans can occur through contact with cat feces or the consumption of contaminated foods. The clinical presentation and complications depend on the host’s immune status. Toxoplasma/Toxoplasmosis congénita o del sistema nervioso central, se puede solicitar imagenología cerebral.
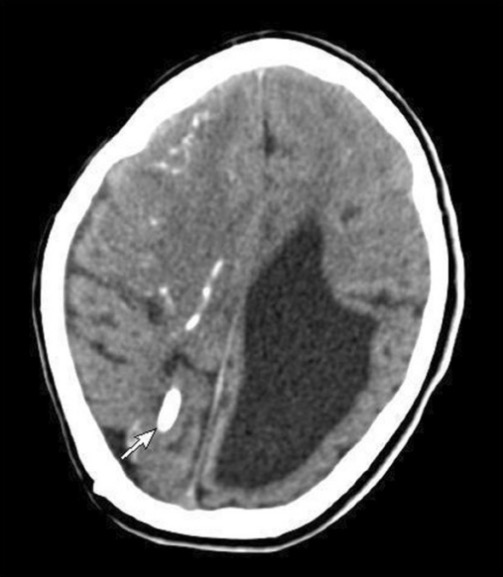
Una imagen de TC que muestra calcificación del parénquima (flecha), múltiples calcificaciones subependimarias y ventrículos dilatados debido a la toxoplasmosis congénita
Imagen:“Computerized tomography of brain” por Department of Pediatrics (39), College of Medicine, King Saud University, PO Box 2925, 11461 Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Licencia: CC BY 2.0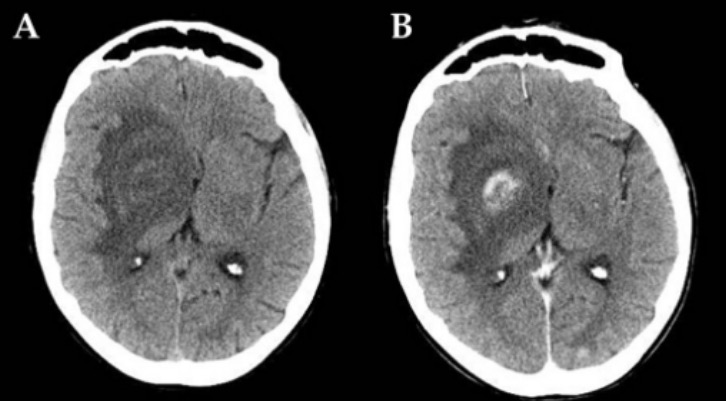
Caso de toxoplasmosis del SNC relacionada con SIDA:
Una TC de una localización toxoplásmica en la región capsulonuclear derecha con amplio edema perilesional antes (A) y después (B) de la inyección de contraste
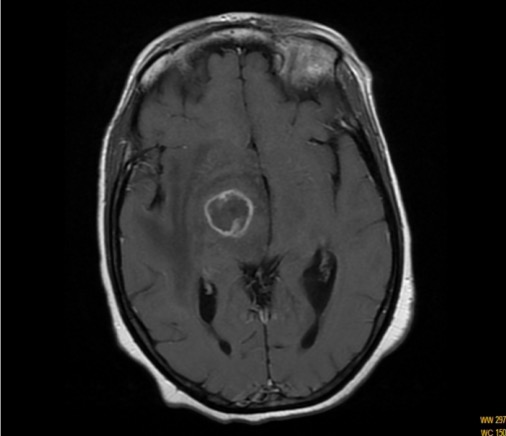
Imagen de una RM de toxoplasmosis del SNC en un paciente con SIDA: RM ponderada en T1 que muestra una lesión con realce en forma de anillo
Imagen:“T1-weighted magnetic resonance imaging scan” por Department of Internal Medicine, Hassan II University Hospital, Faculty of Medicine and Pharmacy, University Sidi Mohammed Ben Abdellah, Morocco. Licencia: CC BY 2.0Los LOS Neisseria pacientes inmunocompetentes no suelen requerir tratamiento. Sin embargo, el tratamiento es necesario para los LOS Neisseria pacientes inmunocomprometidos, embarazadas o con síntomas graves o prolongados.