El síndrome nefrítico es una categoría amplia de enfermedades glomerulares caracterizadas por hematuria Hematuria Presence of blood in the urine. Renal Cell Carcinoma glomerular, pérdida variable Variable Variables represent information about something that can change. The design of the measurement scales, or of the methods for obtaining information, will determine the data gathered and the characteristics of that data. As a result, a variable can be qualitative or quantitative, and may be further classified into subgroups. Types of Variables de la función renal e hipertensión. Estas características contrastan con las del síndrome nefrótico, que incluye enfermedades glomerulares caracterizadas por proteinuria Proteinuria The presence of proteins in the urine, an indicator of kidney diseases. Nephrotic Syndrome in Children grave, aunque a veces hay superposición de > 1 enfermedad glomerular en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el mismo individuo. Las presentaciones clínicas del síndrome nefrítico son muy variadas, desde asintomáticas con anomalías urinarias hasta enfermedades críticas potencialmente mortales. El diagnóstico se sugiere por hematuria Hematuria Presence of blood in the urine. Renal Cell Carcinoma, proteinuria Proteinuria The presence of proteins in the urine, an indicator of kidney diseases. Nephrotic Syndrome in Children leve a moderada y ciertas serologías (e.g., ANCA ANCA Group of systemic vasculitis with a strong association with anca. The disorders are characterized by necrotizing inflammation of small and medium size vessels, with little or no immune-complex deposits in vessel walls. Rapidly Progressive Glomerulonephritis); la biopsia de riñón es necesaria en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la mayoría de los LOS Neisseria casos. El tratamiento varía tanto como las presentaciones clínicas, desde la vigilancia en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum casos leves hasta la inmunosupresión y plasmaféresis en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la enfermedad agresiva.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
El síndrome nefrítico se define por algunos o todos los LOS Neisseria siguientes hallazgos:

Microscopía de orina del síndrome nefrítico:
Izquierda: glóbulos rojos normales con aspecto circular
Derecha (3 imágenes): glóbulos rojos dismórficos con manchas en las membranas y células “Mickey Mouse
Los LOS Neisseria 2 mecanismos principales de lesión glomerular en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria síndromes nefríticos son la desregulación del complemento y la mediada por inmunocomplejos. Las formas hereditarias de glomerulonefritis (e.g., síndrome de Alport) tienen diferentes fisiopatologías.
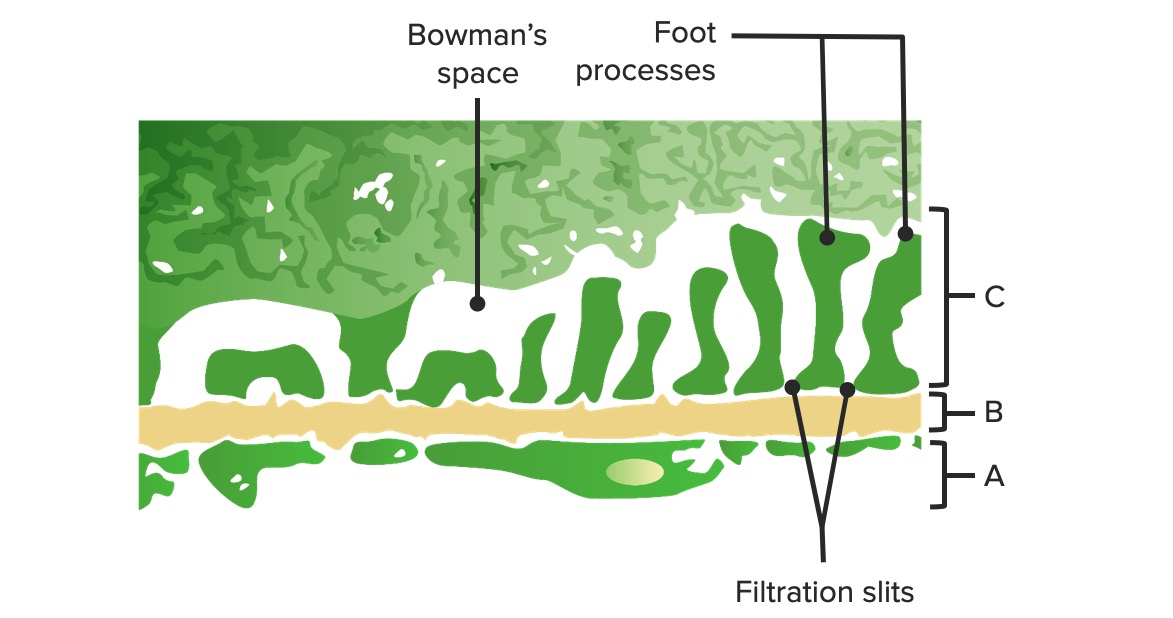
Diagrama de la barrera glomerular:
A: Endotelio fenestrado de los capilares glomerulares
B: Membrana basal
C: Capa epitelial que muestra los procesos podocitarios de los podocitos y las proteínas estructurales que crean el diafragma de hendidura
Las causas primarias y secundarias de glomerulonefritis varían según la etiología, pero tienen en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum común hematuria Hematuria Presence of blood in the urine. Renal Cell Carcinoma y grados variables de proteinuria Proteinuria The presence of proteins in the urine, an indicator of kidney diseases. Nephrotic Syndrome in Children. Los LOS Neisseria resultados de la biopsia difieren y es importante conocerlos.
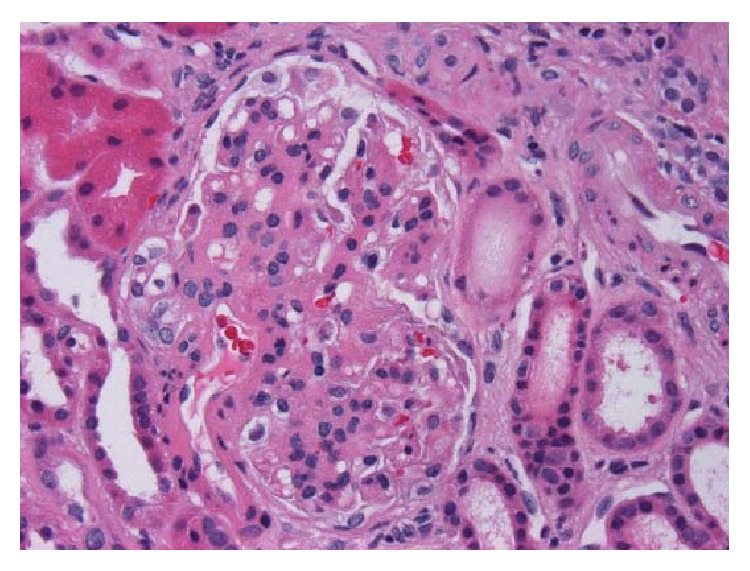
Biopsia de riñón con nefropatía por IgA:
Hematoxilina y eosina, x400. Glomérulo con mesangio engrosado e hipercelularidad mesangial segmentaria
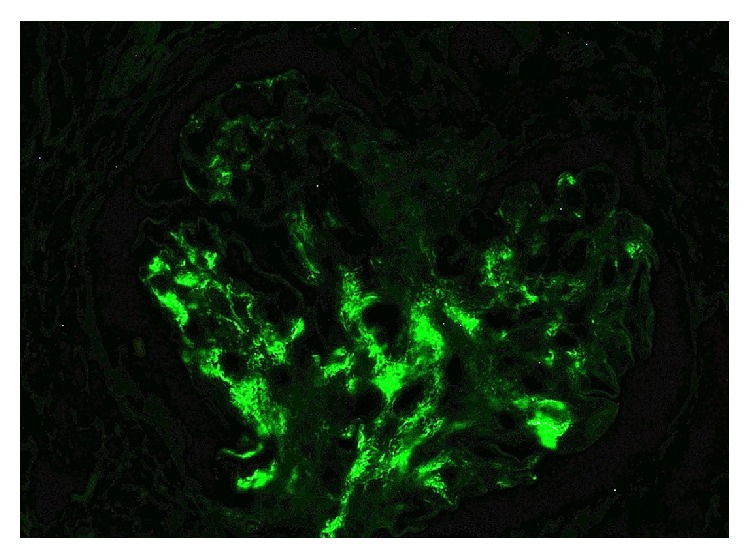
Nefropatía IgA:
Tinción de inmunofluorescencia que demuestra positividad para IgA
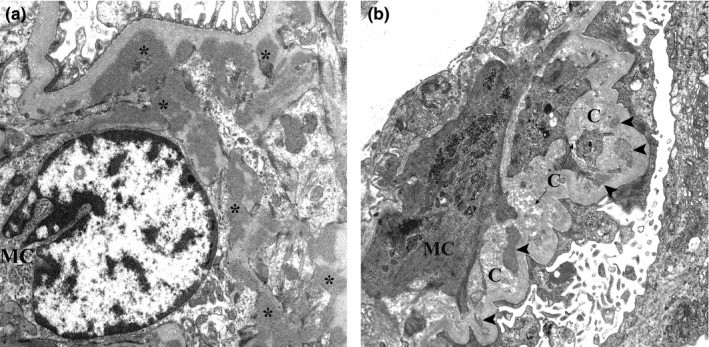
Micrografía electrónica de biopsia renal de nefropatía por IgA:
(a): Se muestran varios depósitos mesangiales electro-densos (asteriscos). Estos depósitos carecen del halo electro-lúcidos.
(b): Son evidentes los depósitos mesangiales con diversos grados de reabsorción (puntas de flecha) cerca de las fibras de colágeno.
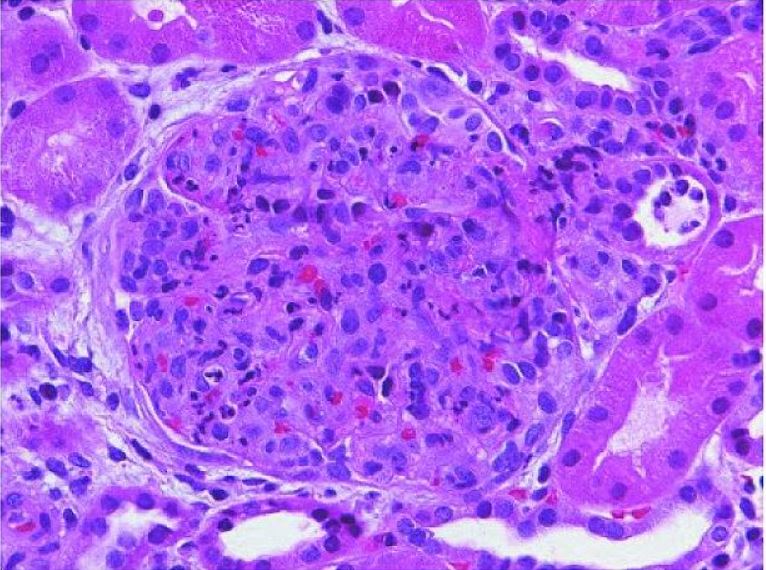
Glomerulonefritis postestreptocócica aguda:
Un glomérulo agrandado con cierre global de la luz capilar causado por la proliferación de células endógenas predominantemente mesangiales y la infiltración de monocitos transmitidos por la sangre y leucocitos polimorfonucleares (tinción hematoxilina y eosina).
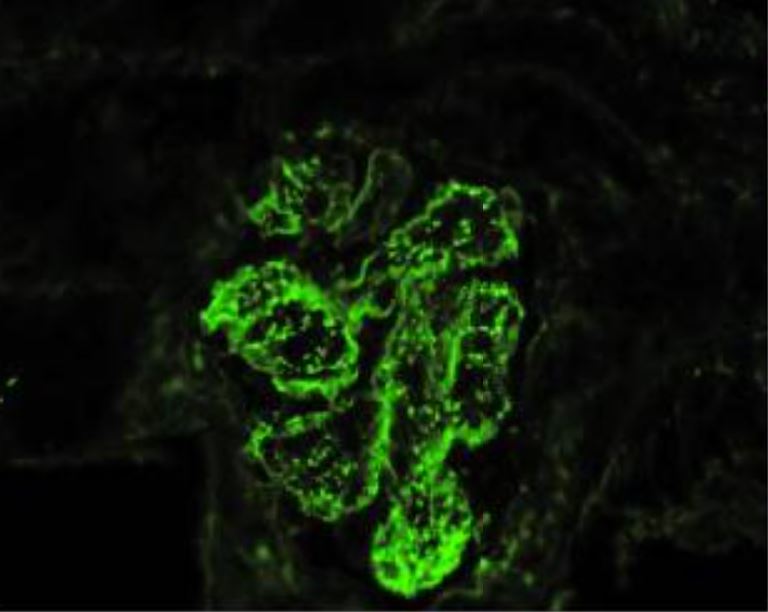
Glomerulonefritis postestreptocócica aguda con predominio de IgA y fiebre reumática concomitante (microscopía de inmunofluorescencia):
Muestra depósitos inmunes granulares mesangiales y glomerulares de la pared capilar con un patrón de “cielo estrellado” de dominancia de IgA
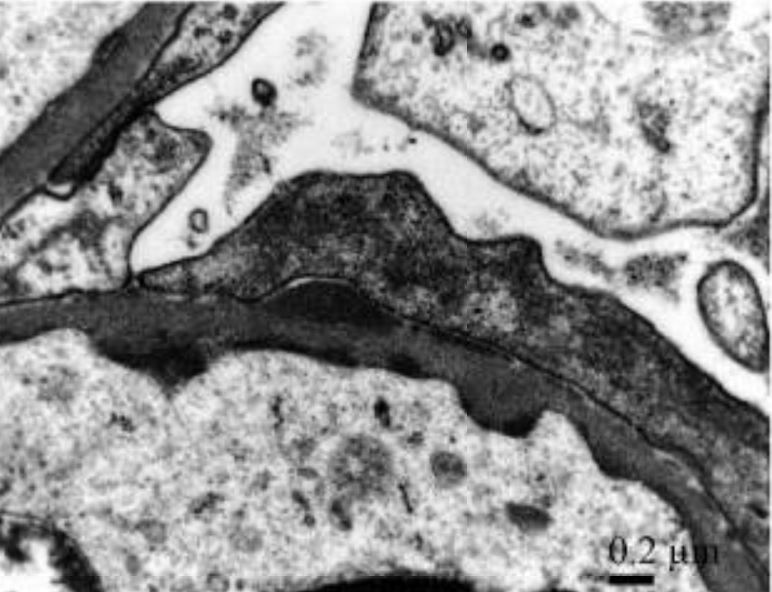
Glomerulonefritis postestreptocócica aguda con predominio de IgA y fiebre reumática concomitante:
Los depósitos subendoteliales y subepiteliales discretos electro-densos detectados en gran aumento muestran depósitos inmunes granulares mesangiales y de la pared capilar glomerular con un patrón de dominancia de IgA en “cielo estrellado”
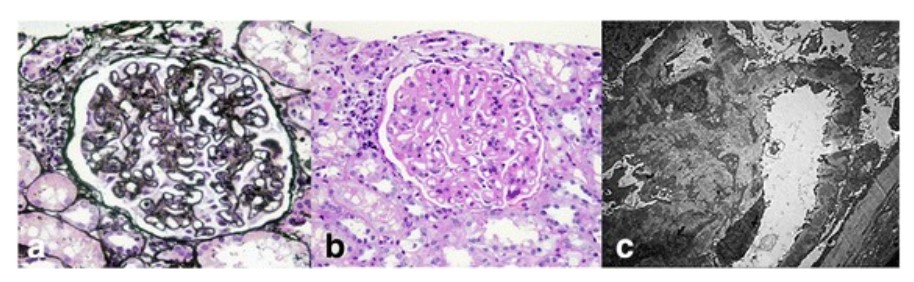
Hallazgos histopatológicos renales en el lupus eritematoso sistémico:
Las micrografías de luz de un glomérulo muestran un engrosamiento difuso de la membrana basal glomerular (tinción de ácido peryódico y metenamina de plata; 400x) (a) Con hipercelularidad mesangial y expansión de la matriz mesangial (tinción de ácido periódico-Schiff; 400x) (b). Los análisis de microscopía electrónica muestran numerosos depósitos subepiteliales y mesangiales electro-densos, así como depósitos dentro de la membrana basal glomerular con fusión extensa de los procesos podocitarios (5000x) (c).
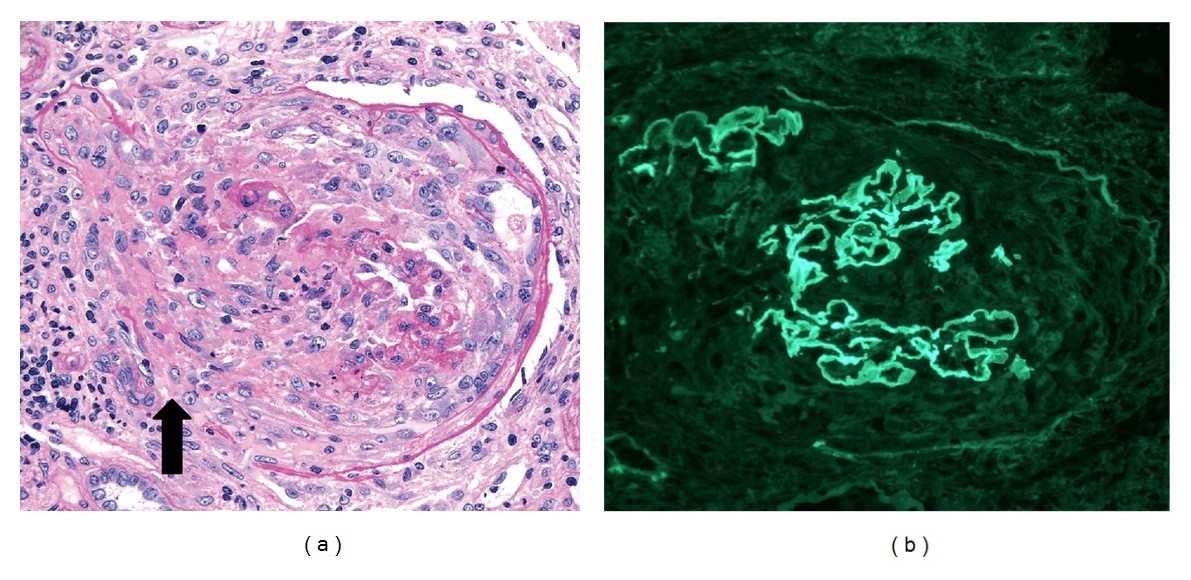
Glomérulos de una biopsia renal de glomerulonefritis semilunar, con anti-membrana basal glomerular y anticuerpos p-ANCA:
(a): El microscopio óptico muestra una semiluna destructiva celular con discontinuidades en la cápsula de Bowman (flecha; tinción de ácido periódico-Schiff, 250x). El intersticio adyacente tiene un infiltrado leucocítico mononuclear.
(b) Tinción de inmunofluorescencia (250x) que muestra una tinción de IgG lineal fuerte (3–4+) a lo largo de las paredes capilares. Las paredes capilares se rompen focalmente debido a la formación de semilunas.
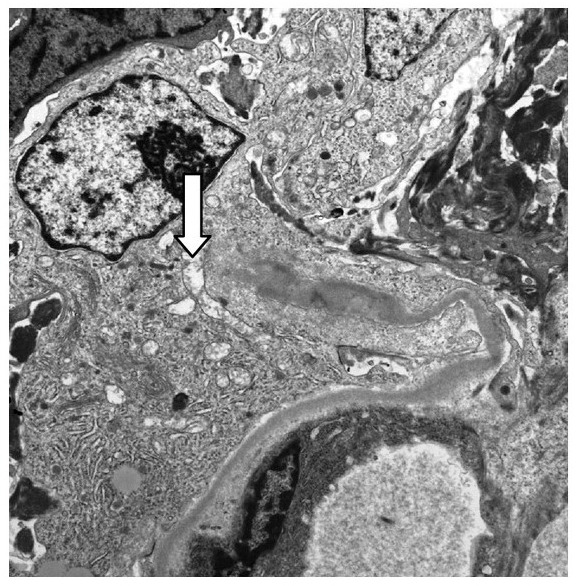
Micrografía electrónica 10 000x que muestra una pared capilar glomerular rota (flecha) asociada con una semiluna celular en la enfermedad de Goodpasture
Imagen: “Glomeruli from the renal biopsy” por Tariq Javed and Parag Vohra. Licencia: CC BY 3.0, recortada por Lecturio.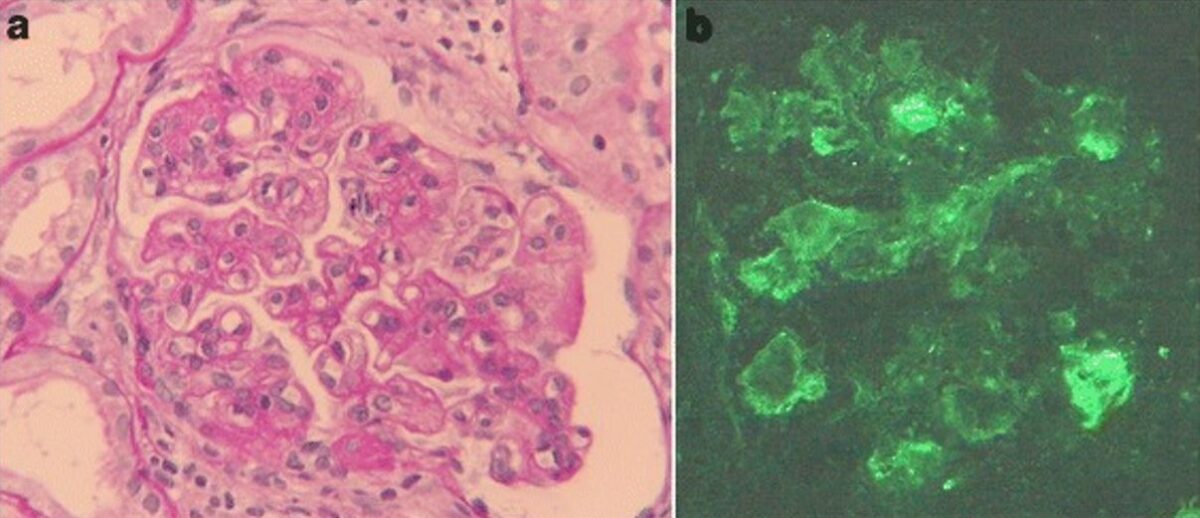
Glomerulonefritis membranoproliferativa asociada a hepatitis C
a) Hallazgos de microscopía óptica de biopsia renal: la tinción de ácido periódico-Schiff revela hipercelularidad mesangial, acentuación lobulillar y doble contorno de la membrana basal (aumento original, 400x).
b) La tinción por inmunofluorescencia de IgM es positiva a lo largo del asa capilar (aumento original, 400x).
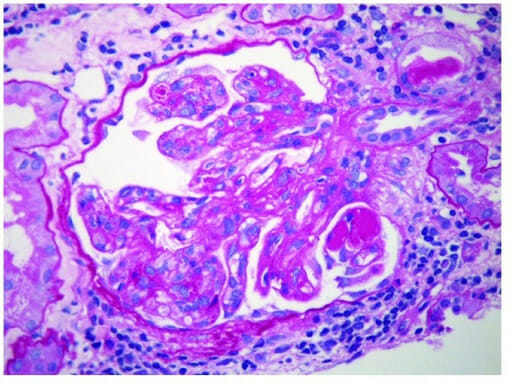
Glomerulonefritis membranoproliferativa:
Micrografía electrónica de glomerulonefritis membranoproliferativa que muestra depósitos inmunes subendoteliales